
Precautions
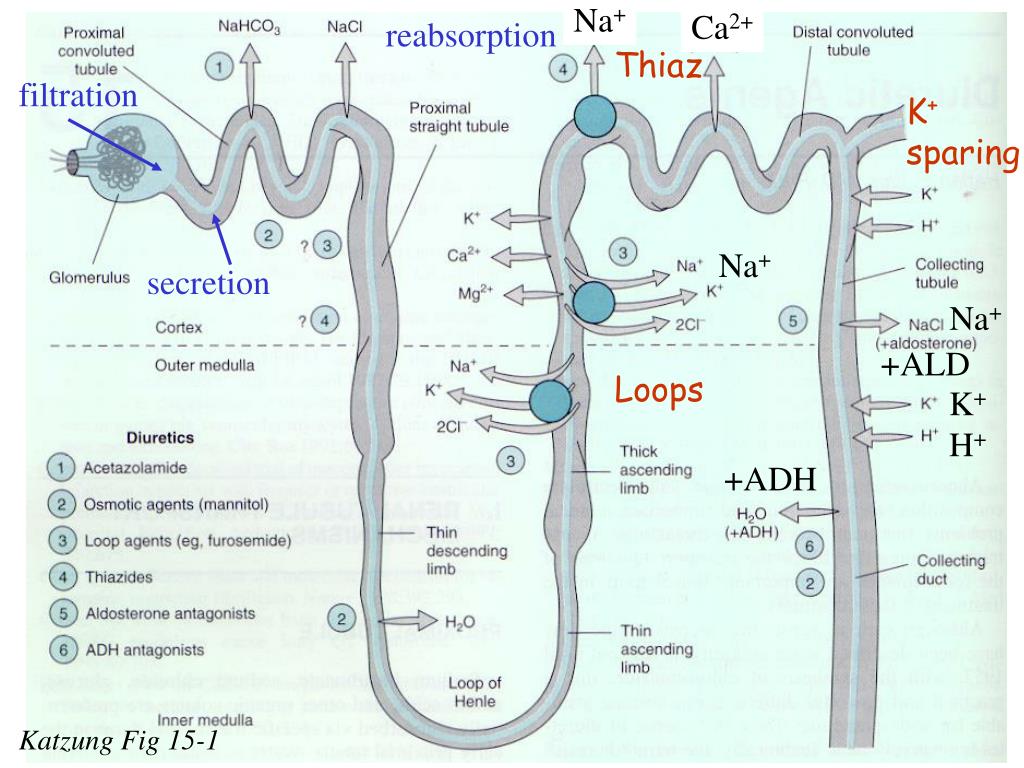
Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase (CA) inhibitor sometimes used as a respiratory stimulant for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) with the goal of improving oxygenation, reducing carbon dioxide retention, and aiding liberation from mechanical ventilation and/or attempting to correct a metabolic alkalosis.
What is the purpose of acetazolamide?
Oral acetazolamide may cause poor weight gain in a small subset of children on treatment. Metabolic acidosis may be a mediating factor for growth failure. Our data suggest that acetazolamide does not cause significant weight changes in cases of pediatric glaucoma. Growth parameters should be followe …
Does acetazolamide cause weight gain?
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) does not define Diamox 125 MG as a controlled substance. What Is Prescribed For Altitude Sickness? Diamox (Acetazolamide) can be given to you by your doctor. As a result, your body is used to the higher altitude faster.
Is acetazolamide a controlled substance?
What is Acetazolamide and how is it used? Acetazolamide is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of Epilepsy, seizures, drug-induced Edema, acute altitude sickness, and Glaucoma. Acetazolamide may be used alone or with other medications.
What is acetazolamide used for?
Who should not use acetazolamide?
Before taking this medicine You should not use acetazolamide if you are allergic to it, or if you have: severe liver disease, or cirrhosis; severe kidney disease; an electrolyte imbalance (such as acidosis or low levels of potassium or sodium in your blood);
When should you take acetazolamide?
To prevent altitude sickness, start taking acetazolamide 1 to 2 days before you start to climb. Continue taking it while you are climbing and for at least 48 hours after you have reached your final altitude. You may need to continue taking this medication while staying at the high altitude to control your symptoms.
How does acetazolamide work as a diuretic?
a potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. The diuretic effect of acetazolamide is due to its action in the kidney on the reversible reaction involving hydration of carbon dioxide and dehydration of carbonic acid. The result is renal loss of bicarbonate (HCO3 ion), which carries out sodium, water, and potassium.
What class of drug is acetazolamide?
Acetazolamide belongs to a class of drugs called Anticonvulsants, Other; Antiglaucoma, Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.
How fast does acetazolamide work?
It's often used along with other antiseizure medications. How long does acetazolamide take to work? The immediate-release pills can work within 1 to 2 hours. The extended-release pills are released more slowly in the body than the immediate-release pills.
What are the common side effects of acetazolamide?
Common side effects of acetazolamide include:dizziness,lightheadedness, and.an increased amount of urine, especially during the first few days as your body adjusts to the medication.Other side effects of acetazolamide include blurred vision,dry mouth,drowsiness,loss of appetite,changes in the sense of taste,More items...
Does acetazolamide lower blood pressure?
Acetazolamide showed a clear orthostatic effect by significantly decreasing the standing systolic blood pressure (BP), while propranolol, at the doses used, had no obvious reducing effect on BP.
Is acetazolamide a strong diuretic?
The diuretic action of acetazolamide is therefore weak and not clinically useful.
How long does acetazolamide stay in your system?
Acetazolamide is fairly rapidly absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract with peak plasma concentrations occurring about 2 hours after administration by mouth. It has been estimated to have a plasma half-life of about 4 hours.
What happens when you stop taking acetazolamide?
Stopping this medicine suddenly may make your epilepsy worse. Do not use this medicine to treat any other complaints unless your doctor says to. Do not give Diamox to anyone else, even if their symptoms seem similar to yours.
What are the long term effects of taking acetazolamide?
Tiredness. Blurred vision. Increased blood sugar. Increased sensitivity to the sun.
What is acetazolamide 250 mg tablet used for?
Acetazolamide 250mg Tablets are used to treat: glaucoma (a condition of the eye), by reducing the pressure within the eye. abnormal retention of fluids (Acetazolamide 250mg Tablets acts as a diuretic) epilepsy (fits or convulsions).
When should I take acetazolamide for altitude sickness?
To prevent altitude sickness, start taking acetazolamide 1 to 2 days before you start to climb. Continue taking it while you are climbing and for at least 48 hours after you have reached your final altitude. You may need to continue taking this medication while staying at the high altitude to control your symptoms.
What can you not take with acetazolamide?
InteractionsDrug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. ... Some products that may interact with this drug include: lithium, memantine, methenamine, orlistat, certain drugs used to treat seizures (topiramate, zonisamide).More items...
Does acetazolamide make you lose weight?
Several clinical studies have reported weight loss as an adverse effect of acetazolamide, and it has shown some beneficial effects in treating psychosis (hence no risk of increasing the primary illness).
What are the long term effects of taking acetazolamide?
Tiredness. Blurred vision. Increased blood sugar. Increased sensitivity to the sun.
What is altitude sickness?
Altitude sickness, also known as mountain sickness, can happen at high altitudes, especially higher than 8,000 feet, like places in Colorado. The a...
Can pregnant women take acetazolamide?
There haven't been enough studies about acetazolamide use in pregnant women, so it should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit is...
Can I drink alcohol while taking acetazolamide?
Drinking alcohol while taking acetazolamide can raise your risk of side effects, especially sleepiness and drowsiness. Don't drink a lot of alcohol...
Can acetazolamide be used to treat epilespy?
This medication has worked for people struggling with seizures. But, epilepsy guidelines don't mention acetazolamide as a first or second choice in...
How long does acetazolamide take to work?
The immediate-release pills can work within 1 to 2 hours. The extended-release pills are released more slowly in the body than the immediate-releas...
What is acetazolamide used for?
Acetazolamide is a diuretic and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor medication that is used to treat several illnesses. [1]
How does acetazolamide help with glaucoma?
Acetazolamide is a classic treatment option for glaucoma as it causes a reduction in the aqueous humor. As well, it is useful for the treatment of altitude sickness, because of its underlying mechanism of action. The medication works to excrete bicarbonate. By doing so, it alkalizes the urine as there is greater bicarbonate in the urine. As a result, the blood is more acidic, given that the bicarbonate has been excreted out. Some mechanisms equate the carbon dioxide concentrations in the body to the degree of acidity, resulting in an artificial compensatory mechanism to what the body believes to be excess carbon dioxide. This compensation results in faster and deeper breathing. The outcome of that is higher concentrations of oxygen in the body, which improves the ability of the body to adjust itself to the higher altitude levels. [3]
What is diamox used for?
III. Its use as a diuretic in patients with severe congestive heart failure due to cor pulmonale.
Where is carbonic anhydrase found?
Carbonic anhydrase is found in red blood cells and also the proximal tubule of the kidney. It works to reabsorb sodium, bicarbonate, and chloride. Once acetazolamide inhibits carbonic anhydrase, sodium, bicarbonate, and chloride get excreted rather than reabsorbed; this also leads to the excretion of excess water.
Is acetazolamide a diuretic?
Acetazolamide is a diuretic and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor medication that is used to treat several illnesses. FDA-approved indications include glaucoma, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, congestive heart failure, altitude sickness, periodic paralysis, and epilepsy. This activity outlines the indications, contraindications, interactions, monitoring, and other therapeutic information pertinent to members of an interprofessional team in the care of patients with conditions requiring the use of acetazolamide.
Can you take acetazolamide with food?
Patients take acetazolamide with or without food, and the patient should drink plenty of fluids with the medication. Available dosages are 125 mg, 250 mg, and 500 mg tablets.[5] These are also available in instant-release and extended-release drug dosage forms.
Can acetazolamide cause hypokalemia?
Acetazolamide can induce electrolyte abnormalities. As such, those with hypokalemia or hyponatremia should not use it. Similarly, it can decrease kidney function, and clinicians should avoid using it with anyone with kidney disease or decreased kidney function.
What is acetazolamide?
Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that affects your body's fluid balance. It helps remove water and electrolytes in your urine, lowers the amount of fluid in your eyes, calms your nervous system, and allows your body to use oxygen better at high altitudes.
What is the latest news about acetazolamide?
This month, GoodRx is excited to announce deeper discounts through GoodRx Gold, our membership program that can save you up to 90% on your medications.
How much does acetazolamide cost?
Unless there is a specific reason you need the brand, the generic medication will be a better value. For even more savings, use a GoodRx coupon and pay just a fraction of the retail price.
How long does it take for acetazolamide to work?
The immediate-release pills can work within 1 to 2 hours. The extended-release pills are released more slowly in the body than the immediate-release pills. With this in mind, the effects of the extended-release pills last a bit longer than the immediate-release pills. If you're receiving acetazolamide as in injection from your provider, it can work as quickly as a few minutes.
Can you take acetazolamide with a prescription?
It is also sometimes used to prevent or lessen some effects in mountain climbers who climb to high altitudes, and to treat other conditions as determined by your doctor. These medicines are available only with your doctor's prescription. Save up to 59% on Acetazolamide.
Can carbonic anhydrase inhibitors make kidney disease worse?
Kidney disease or stones—Higher blood levels of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may result, which may increase the chance of side effects Also, these medicines may make the condition worse.
Do older people take carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
Therefore, it may not be known whether they work exactly the same way they do in younger adults. Although there is no specific information comparing use of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in the elderly with use in other age groups, these medicines are not expected to cause different side effects or problems in older people than they do in younger adults.
What is acetazolamide used for?
Expand Section. Acetazolamide is used to treat glaucoma, a condition in which increased pressure in the eye can lead to gradual loss of vision. Acetazolamide decreases the pressure in the eye. Acetazolamide is also used to reduce the severity and duration of symptoms (upset stomach, headache, shortness of breath, dizziness, drowsiness, ...
What are the side effects of acetazolamide?
Acetazolamide may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away: 1 upset stomach 2 vomiting 3 loss of appetite
How should this medicine be used?
Acetazolamide comes as a tablet and capsule to take by mouth. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take acetazolamide exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
What should I know about storage and disposal of this medication?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom).
Can acetazolamide make you drowsy?
if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking acetazolamide. you should know that this drug may make you drowsy. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how this drug affects you. remember that alcohol can add to the drowsiness caused by this drug.
Can you crush acetazolamide?
Take acetazolamide exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor. If you are taking the extended-release ( long-acting) form of acetazolamide (Diamox Sequels), do not crush or chew the capsules.
Can you get pregnant while taking acetazolamide?
tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking acetazolamide, call your doctor immediately.
What is acetazolamide used for?
It has also been used in the treatment of altitude sickness, Ménière's disease, increased intracranial pressure and neuromuscular disorders. In epilepsy, the main use of acetazolamide is in menstrual-related epilepsy and as an add on to other treatments in refractory epilepsy.
What is the effect of acetazolamide on blood pH?
Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme found in red blood cells and many other tissues that catalyses the following reaction: hence lowering blood pH, by means of the following reaction that carbonic acid undergoes: which has a pK a of 6.3.
What enzyme is responsible for reabsorption of sodium and chloride?
The enzyme carbonic anhydrase is found here, allowing the reabsorption of bicarbonate, sodium, and chloride. By inhibiting this enzyme, these ions are excreted, along with excess water, lowering blood pressure, intracranial pressure, and intraocular pressure.
Is acetazolamide a diuretic?
Common side effects include numbness, ringing in the ears, loss of appetite, vomiting, and sleepiness. It is not recommended in those with significant kidney problems, liver problems, or who are allergic to sulfonamides. Acetazolamide is in the diuretic and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor families of medication.
Is acetazolamide safe for pregnancy?
Pregnancy and lactation. Acetazolamide is pregnancy category B3 in Australia, which means that studies in rats, mice and rabbits in which acetazola mide was given intravenously or orally caused an increased risk of fetal malformations, including defects of the limbs.
Can acetazolamide be used for dural ectasia?
Though various websites on the internet report that acetazolamide can be used to treat dural ectasia in individuals with Marfan Syndrome, the only supporting evidence for this assertion exists from a small study of 14 patients which was not peer-reviewed or submitted for publication.
Does acetazolamide cause liver disease?
Marked liver disease or impairment of liver function, including cirrhosis because of the risk of development of hepatic encep halopathy. Acetazolamide decreases ammonia clearance.
What is acetazolamide used for?
Uses of Acetazolamide Tablets: It is used to get rid of extra fluid. It is used to treat or prevent altitude sickness. It is used to help control certain kinds of seizures . It is used to treat glaucoma . It may be given to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
What are the side effects of acetazolamide?
Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away: Upset stomach or throwing up.
What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take Acetazolamide Tablets?
Tell your doctor about the allergy and what signs you had.
What are some things I need to know or do while I take Acetazolamide Tablets?
Tell all of your health care providers that you take this medicine (acetazolamide tablets). This includes your doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and dentists.
How is this medicine (Acetazolamide Tablets) best taken?
Use this medicine (acetazolamide tablets) as ordered by your doctor. Read all information given to you. Follow all instructions closely.
What to do if you have questions about acetazolamide?
If you have any questions about this medicine (acetazolamide tablets), please talk with your doctor, nurse, pharmacist, or other health care provider.
Can acetazolamide affect growth?
If you are 65 or older, use this medicine (acetazolamide tablets) with care. You could have more side effects. This medicine may affect growth in children and teens in some cases. They may need regular growth checks. Talk with the doctor.
What is acetazolamide used for?
Uses. Acetazolamide is used to prevent and reduce the symptoms of altitude sickness. This medication can decrease headache, tiredness, nausea, dizziness, and shortness of breath that can occur when you climb quickly to high altitudes (generally above 10,000 feet/3,048 meters). It is particularly useful in situations when you cannot make ...
Why is acetazolamide used for seizures?
It is also used to decrease a buildup of body fluids ( edema) caused by heart failure or certain medications. Acetazolamide can work less well over time, so it is usually used only for a short period.It has also been used with other medications to treat certain types of seizures (petit mal and unlocalized seizures ).
How to report acetazolamide side effects in Canada?
In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345. Precautions. Before taking acetazolamide, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies.
Can you take acetazolamide at high altitude?
You may need to continue taking this medication while staying at the high altitude to control your symptoms. If you develop severe altitude sickness, it is important that you climb down as quickly as possible. Acetazolamide will not protect you from the serious effects of severe altitude sickness.
Does acetazolamide help with altitude sickness?
Acetazolamide will not protect you from the serious effects of severe altitude sickness. (See also Precautions.) If you are taking this drug for another condition (such as glaucoma, seizures ), use this medication regularly as directed to get the most benefit from it.
Can you chew acetazolamide?
Do not open, break, or chew the capsules. Doing so can destroy the long action of the drug and may increase side effects. Acetazolamide may be taken with or without food. Drink plenty of fluids unless otherwise directed by your doctor. The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment.
Are you currently using Acetazolamide?
This survey is being conducted by the WebMD marketing sciences department.
What is the purpose of Diamox?
How to Take and Store. Side Effects. Warnings and Interactions. Diamox (acetazolamide), a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, is used most commonly to treat glaucoma , epilepsy, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, edema, and high-altitude sickness. Diamox is also sometimes used off-label to treat familial periodic paralysis, ...
What enzyme converts water and carbon dioxide to hydrogen ions?
Carbonic anhydrase is an Important enzyme In the body that converts water and carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. By inhibiting carbonic anhydrase activity, Diamox affects human physiology in several ways:
How does diamox affect the kidneys?
By inhibiting carbonic anhydrase activity, Diamox affects human physiology in several ways: Diamox reduces the amount of acid excreted by the kidneys, causing the kidneys to excrete more bicarbonate, sodium, potassium, and water, and the urine to become alkaline . Diamox reduces the production of aqueous humor (the clear fluid produced in the eye, ...
Why was the Diamox trial stopped?
The study was stopped prematurely because too many of the enrolled patients were unable to tolerate Diamox.
What is the name of the condition where the pressure inside the head increases?
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also known as pseudotumor cerebri: in this condition, patients have increased pressure inside their head due to accumulation of spinal fluid. This can occur because of an increase in spinal fluid production or a decrease of its absorption. Patients usually have headaches, visual loss, and papilledema (swelling of the optic nerves). IIH most frequently affects obese women of childbearing age. Diamox is commonly used to treat this condition and is believed to decrease the rate of spinal fluid production.
Does Diamox affect the central nervous system?
Diamox seems to inhibit neuronal function in the central nervous system.
Does Diamox help with migraines?
Migraines: Diamox has been reported to be of benefit in a few cases of familial hemiplegic migraine (a rare inherited disorder characterized by migraine attacks accompanied by weakness on one side of the body). 5 In addition, there are anecdotal reports that Diamox may be helpful in preventing other kinds of migraine headaches, in particular, migraines related to changes in the weather, or to the menstrual cycle. However, these anecdotal reports are not supported by anything resembling clinical studies.
What enzyme is acetazolamide?
Acetazolamide is an enzyme inhibitor that acts specifically on carbonic anhydrase, the enzyme that catalyzes the reversible reaction involving the hydration of carbon dioxide and the dehydration of carbonic acid.
What is the chemical name for acetazolamide?
The chemical name for Acetazolamide is N - (5-Sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2yl)-acetamide and has the following structural formula: Acetazolamide is available for intravenous use, and is supplied as a sterile powder requiring reconstitution. Each vial contains Acetazolamide sodium equivalent to 500 mg of Acetazolamide.
What is the effect of acetazolamide on the kidney?
The diuretic effect of Acetazolamide is due to its action in the kidney on the reversible reaction involving hydration of carbon dioxide and dehydration of carbonic acid. The result is renal loss of HCO 3 ion, which carries out sodium, water, and potassium. Alkalinization of the urine and promotion of diuresis are thus affected.
What test is used to monitor sulfonamide reactions?
Laboratory Tests. To monitor for hematologic reactions common to all sulfonamides, it is recommended that a baseline CBC and platelet count be obtained on patients prior to initiating Acetazolamide therapy and at regular intervals during therapy.
How long does acetazolamide stay in the fridge?
Reconstituted solutions retain their physical and chemical properties for 3 days under refrigeration at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F), or 12 hours at room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
Is acetazolamide a sulfonamide?
Since Acetazolamide is a sulfonamide derivative, cross sensitivity between Acetazolamide, sulfonamides and other sulfonamide derivatives is possible.
Is acetazolamide an adjuvant?
Evidence seems to indicate that Acetazolamide has utility as an adjuvant in treatment of certain dysfunctions of the central nervous system (e.g., epilepsy). Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in this area appears to retard abnormal, paroxysmal, excessive discharge from central nervous system neurons.
What is acetazolamide?
Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Acetazolamide reduces the formation of hydrogen and bicarbonate ions from carbon dioxide and water by noncompetitive, reversible inhibition of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, thereby reducing the availability of these ions for active transport into secretions.
How is acetazolamide excreted?
Acetazolamide is excreted unchanged by the kidneys via tubular secretion and passive reabsorption. There is no evidence of enterohepatic circulation although small amounts of unchanged drug are eliminated in the bile. Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
Where is acetazolamide absorbed?
Acetazolamide is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Acetazolamide is distributed throughout body tissues; it concentrates principally in erythrocytes, plasma and kidneys and to a lesser extent in liver, muscles, eyes and the central nervous system. Acetazolamide does not accumulate in tissues.
Can acetazolamide cause liver damage?
Idiosyncratic, clinically apparent liver injury from acetazolamide and methazolamide is rare, but several instances have been reported as isolated case reports. Acetazolamide is a sulfonamide and cross reactivity to sulfonamide reactions have been reported. The liver injury typically arises after a few days to weeks of therapy and the pattern of serum enzyme elevations is usually hepatocellular or mixed. Immunoallergic features (rash, fever, eosinophilia) are common, but autoantibody formation is not. Both acetazolamide and methazolamide have been linked to Stevens Johnson Syndrome and a genetic association has been made with HLA-B*5901. Hepatic involvement and jaundice can occur in some cases of Stevens Johnson Syndrome.
Is acetazolamide a dermal absorption?
Oral ingestion is the usual means of exposure. There is no appreciable dermal absorption. There is no significant absorption or local irritation. ANIMAL/PLANT STUDIES: Numerous animal studies have demonstrated that the toxicity of acetazolamide was very low in the species studied (mouse, dog, rat, monkey).
Does acetazolamide help with epilepsy?
The efficacy of acetazolamide in epilepsy is in part due to the production of metabolic acidosis ; however, direct actions of acetazolamide in the CNS also contribute to its anticonvulsant action. Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.).
Does acetazolamide increase oxygen?
The anticonvulsant activity of Acetazolamide may depend on a direct inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the CNS, which decreases carbon dioxide tension in the pulmonary alveoli, thus increasing arterial oxygen tension. The diuretic effect depends on the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase, causing a reduction in the availability of hydrogen ions for active transport in the renal tubule lumen. This leads to alkaline urine and an increase in the excretion of bicarbonate, sodium, potassium, and water.

Medical uses
Acetazolamide is used to prevent and reduce the symptoms of altitude sickness.
May Treat: Open angle glaucoma · Angle-closure glaucoma · Absence epilepsy · Anoxia due to high altitude · Edema and more
Brand Names: Diamox · Diamox Sequels · Ak-Zol · Storzolamide
Drug Class: Diuretic - Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
May Treat: Open angle glaucoma · Angle-closure glaucoma · Absence epilepsy · Anoxia due to high altitude · Edema and more
Brand Names: Diamox · Diamox Sequels · Ak-Zol · Storzolamide
Drug Class: Diuretic - Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Consult a doctor before using
Driving: May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Use caution
Administration
Risks
Treatment
Prevention
- Acetazolamide is used to treat glaucoma, a condition in which increased pressure in the eye can lead to gradual loss of vision. Acetazolamide decreases the pressure in the eye. Acetazolamide is also used to reduce the severity and duration of symptoms (upset stomach, headache, shortness of breath, dizziness, drowsiness, and fatigue) of altitude (mo...
Diagnosis
- Acetazolamide comes as a tablet and capsule to take by mouth. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take acetazolamide exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Preparation
- If you are taking the extended-release (long-acting) form of acetazolamide (Diamox Sequels), do not crush or chew the capsules.
Overview
- Take the missed dose as soon as you remember it. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for the missed one.
Mechanism of action
- Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). It is important to keep all medication out of sight and reach of children as many containers (such as weekly pill minders and those for eye drops, creams, patches, and inhalers) are not child-resista…
Medical uses
- Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory. Your doctor will order certain tests to check your response to acetazolamide.
Side effects
- It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription (over-the-counter) medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you visit a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important information to carry with you in case of emergencies.
Interactions
Acetazolamide, sold under the trade name Diamox among others, is a medication used to treat glaucoma, epilepsy, altitude sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension (raised brain pressure of unclear cause), urine alkalinization, and heart failure. It may be used long term for the treatment of open angle glaucoma and short term for acute angle closure glaucoma until s…
History
Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, hence causing the accumulation of carbonic acid. Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme found in red blood cells and many other tissues that catalyses the following reaction:
H2CO3 ⇌ H2O + CO2
hence lowering blood pH, by means of the following reaction that carbonic aci…
Research
It is used in the treatment of glaucoma, drug-induced edema, heart failure-induced edema, epilepsy and in reducing intraocular pressure after surgery. It has also been used in the treatment of altitude sickness, Ménière's disease, increased intracranial pressure and neuromuscular disorders.
In epilepsy, the main use of acetazolamide is in menstrual-related epilepsy and as an add on to other treatments in refractory epilepsy. Though various websites on the internet report that acet…
External links
Common adverse effects of acetazolamide include the following: paraesthesia, fatigue, drowsiness, depression, decreased libido, bitter or metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, black stool, polyuria, kidney stones, metabolic acidosis and electrolyte changes (hypokalemia, hyponatremia). Whereas less common adverse effects include Stevens–Johnson syndrome, anaphylaxis and blood dyscrasias.