
What is the function of sinus?
A Sinus or sinuses are…. hollow air cavities in the skull connecting the nasal passages. They are connected via a narrow passageway called the ostium. The sinuses purpose is to humidify the air to the lungs, as well as create mucus secretion to eliminate unwanted particles from the body.
What is a sinus cavity in the head?
Sinus Cavities. Sinuses also serve as sound-resonance chambers for speech. The paired and often asymmetrical (not perfectly mirrored) sinuses are small, or rudimentary, at birth but grow as the skull grows. They are fairly well developed by age seven or eight, but don’t reach their maximum size until after puberty.
Where is the maxillary sinus located in the skull?
Maxillary sinuses: These are the largest of the sinuses and are located behind the cheekbones near the maxillae, or upper jaws. Sphenoid sinuses: The sphenoid sinuses are located in the sphenoid bone near the optic nerve and the pituitary gland on the side of the skull.
What is the function of paranasal sinuses?
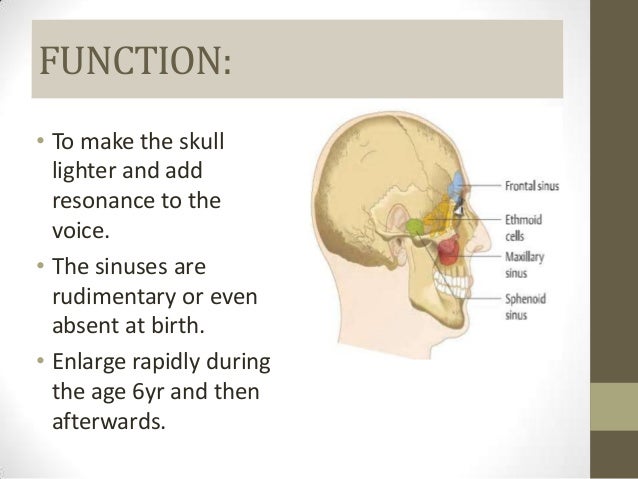
The paranasal sinuses have a wide variety of functions, including lightening the weight of the head, humidifying and heating inhaled air, increasing the resonance of speech, and serving as a crumple zone to protect vital structures in the case of facial trauma.
What are air sinuses?
One of many small hollow spaces in the bones around the nose. Paranasal sinuses are named after the bones that contain them: frontal (the lower forehead), maxillary (cheekbones), ethmoid (beside the upper nose), and sphenoid (behind the nose).
What is the function of maxillary air sinus?
The maxillary sinuses are lined with cells that make mucus to keep the nose from drying out. Anatomy of the paranasal sinuses (spaces between the bones around the nose).
What are the 4 sinuses in the skull?
The word “sinus” is most commonly understood to be the paranasal sinuses that are located near the nose and connect to the nasal cavity. There are four paranasal sinuses, each corresponding with the respective bone from which it takes its name: maxillary, ethmoid, sphenoid, and frontal.
How do you clear a blocked maxillary sinus?
Maxillary Sinus Massage Using your index and middle fingers, apply pressure near your nose between your cheekbones and jaw. Move your fingers in a circular motion toward your ears. You can use your thumbs instead of your fingers for a deeper massage. This should take 30 seconds to a minute.
Why do sinuses affect ears?
Your sinuses are located close to your ear canal, and when they become congested, swollen, and clogged, these issues can affect your ear's hearing function. Your Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle of your ear to your throat, will become clogged, preventing fluid from moving through.
What is sinus and its function?
The sinuses are four paired cavities (spaces) in the head. They are connected by narrow channels. The sinuses make thin mucus that drains out of the channels of the nose. This drainage helps keep the nose clean and free of bacteria. Normally filled with air, the sinuses can get blocked and filled with fluid.
Why do sinuses exist?
Normally these structures help humidify and filter air. A thin wall, called the septum, divides the nose. Most of the sinuses drain into the nose through a small channel or drainage pathway that doctors call the “middle meatus.”
How many sinuses are in the human head?
Most people have four pairs of sinus cavities in their heads ― or eight total. Two large frontal sinuses are located above your eyes and in your forehead. Two sphenoid and two ethmoid sinuses are set between your eyes and behind your nose.
What does maxillary sinus drain?
The maxillary sinus drains into the middle meatus, with the ostium of the sinus opening into the nose on the superior aspect of the medial wall of the sinus, which may explain the high incidence of maxillary sinusitis.
Why maxillary air sinus is the commonest for infection?
Maxillary sinusitis is common due to the close anatomic relation of the frontal sinus, anterior ethmoidal sinus and the maxillary teeth, allowing for easy spread of infection.
What are the symptoms of maxillary sinusitis?
Pain, headache, nasal obstruction, a purulent nasal secretion and 'postnasal drip' (a discharge of 'mucopus' into the pharynx) are commonly found and there may also be fever and malaise. The pain is dull, heavy, throbbing and located over the cheek and in the upper teeth.
What is the function of maxilla?
The maxilla has several main functions, including: holding the top teeth in place. making the skull less heavy. increasing the volume and depth of your voice.
What is the function of the sinuses?
The sinuses are part of your nose and respiratory system. They connect to your nasal passages in a complex network of air flow and drainage passages. As you breathe in air through your nose and mouth, it moves through the sinus passages.
What is the hair that moves mucus through the sinuses?
Little hairs called cilia help the mucus move through the sinus cavities. The mucus from the sinuses drains into your nasal passages and then down the back of your throat to be swallowed.
What is the name of the hair that helps the mucus to move through the nasal cavity?
Both air and mucus flow through your sinuses and drain into your nose, through tiny openings called ostia (or singular, ostium). Little hairs called cilia help the mucus move through the sinus cavities.
What happens if you have a cold and a sinus infection?
People often develop sinusitis after they have a common cold. If the lining of your sinuses becomes blocked in a cold, the mucus gets thick and sticky.
How do you know if you have sinusitis?
Symptoms of a sinus infection are similar to those of a cold: Depending on which sinuses are infected, you may feel pain or pressure in your forehead, cheeks, ears, or teeth. You may have thick, sticky mucus coming from your nose. Your mucus may be cloudy, or have a greenish-yellow color.
How long does a sinus infection last?
A sinus infection can last from 10 days to as long as 8 weeks. This is called an acute sinus infection. Sometimes a sinus infection can become chronic, getting better and then worse again, off and on for months. Chronic sinusitis is medically defined as sinusitis that occurs more than four times a year.
How many people have sinus infections?
Sinus infections are common and can be a major health problem. According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI), 31 million people in the United States have sinus infections at a given time. You’re at higher risk for sinusitis if you: have allergies. smoke.
What is the purpose of sinuses?
The sinuses purpose is to humidify the air to the lungs, as well as create mucus secretion to eliminate unwanted particles from the body. They are a vital part of the respiratory process to bring the proper air, warm temperature and humidity into the lungs providing life to the body. Think of the sinuses as your body’s air filter. The sinuses also insulate their surrounding parts (nerves, eyes), increase voice resonance, and protect against trauma to the face. The also provide structural support for the skull and decrease the weight of the skull.
What is the best environment for sinuses?
The optimal state for sinuses could be described as “Hawaii Like”, a warm, moist, clean environment. This allows for the correct function for humidified air to the lungs. The opposite or worst environment for sinuses would include too dry, too hot and dry, too cold, floating irritants, smoke or a polluted environment. These environments creates congestion, irritation and inflammation, which is the precursor to sinusitis and sinus infections.
What is the membrane of the nose?
The Sinuses are lined with a Mucous Membrane, which is one continuous tissue extending from the tip of the nose to the smallest airway in the lungs. In a sense, it’s like Goretex, a strong protective shield. It allows you to breathe and it protects you from the elements. Because it connects all three parts of the respiratory tract, and when there is infection in the nose, it can easily affect the sinuses and lungs. That is why the common cold often results in a sinus infection, or in people with higher susceptibility, bronchitis or even an asthma attack.
What is the purpose of lining the mucous membrane?
Lining the mucous membrane are millions of tiny hair like strands whose role is to flush out pollutants and unwanted particles from the sinuses. Their wave-like action is like a cleaning crew of the mucus membrane (sinuses). The normal action rinses these pollutants down the drain to the stomach, which has powerful acids to neutralize these particles.
Which sinuses are located in the forehead?
Anatomy. Anteriorly, the frontal sinuses are contained by the forehead and the superciliary arches, superiorly and posteriorly by the anterior cranial fossa and inferiorly by the bony orbit, the anterior ethmoidal sinuses and the nasal cavity. Medially the sinuses face one another, separated by the midline.
Which sinuses are separated by the anterior wall?
The anterior wall separates this pair of sinuses from the nasal cavity, as does the hypophyseal fossa, the pituitary gland and the optic chiasm superior ly and the nasopharynx and pterygoid canal inferiorly.
What is the most posterior sinus in the head?
The most posterior of all the sinuses in the head, the sphenoidal sinuses are large and irregular, just like their septum, which is made by the sphenoid bone. Laterally, a cavernous sinus exists which is part of the middle cranial fossa and also the carotid artery and cranial nerves III, IV, V/I, V/II and VI can be found.
How many pairs of sinuses are there?
They are situated around the nasal cavity and they are all paired and sometimes symmetrical, while always being bilateral. There are four different pairs of sinuses and they are called the: This article will discuss detailed anatomy of the paranasal sinuses.
Which sinuses send lymphatic drainage to the submandibular lymph nodes?
The anterior and middle ethmoid sinuses send their lymphatic drainage to the submandibular lymph nodes while the posterior ethmoid sinus sends its own to the retropharyngeal lymph nodes.
Which sinus is superior to the ethmoid sinus?
Anatomy. Superior to the ethmoidal sinus is the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal bone, laterally the orbit can be found, while the nasal cavity is situated medially. The ethmoid sinuses are unique because they are the only paranasal sinuses that are more complex than just a single cavity.
What is the superior border of the sinus?
The superior border of this sinus is the bony orbit , the inferior is the maxillary alveolar bone and corresponding tooth roots, the medial border is made up of the nasal cavity and the lateral and anterior border are limited by the cheekbones. Posteriorly, two anatomical spaces known as the pterygopalatine fossa and the infratemporal fossa exist.
