What is the function of the atrium and ventricles?
Atria receive blood returning to the heart from the body and ventricles pump blood from the heart to the body. The heart has a three-layered heart wall composed of connective tissue, endothelium, and cardiac muscle. It is the muscular middle layer known as myocardium that enables the heart to contract.
What is the function of Atria?
Atria are the upper chambers of the heart. They receive blood returning to the heart from other areas of the body and send blood to the ventricles.
What is the difference between the atria of the heart?
Atria are separated by an interatrial septum into the left atrium and the right atrium. The lower two chambers of the heart are called ventricles. Atria receive blood returning to the heart from the body and ventricles pump blood from the heart to the body. The atria of the heart receive blood returning to the heart from other areas of the body.
What is the difference between the left atrium and the ventricles?
Atria are separated by an interatrial septum into the left atrium and the right atrium. The lower two chambers of the heart are called ventricles. Atria receive blood returning to the heart from the body and ventricles pump blood from the heart to the body.

What is the function of the atria?
The atria perform three different functions during the various phases of the cardiac cycle, i.e. serving as reservoir during systole, passive conduit during early diastole, and booster function during late diastole.
What are the function of ventricles?
ventricle, muscular chamber that pumps blood out of the heart and into the circulatory system.
What are the functions of the atria and ventricles of the heart quizlet?
The atria of the heart receive blood from the veins and they are the reservoirs of blood, while the ventricles of the heart are major pumping chambers.
Which statement best describes the difference between atria and ventricles?
Which statement best describes the difference between atria and ventricles? Atria push blood from the veins to the ventricles, and ventricles push blood from the atria to the arteries.
What are the 4 main functions of the heart?
The four main functions of the heart are:Pumping oxygenated blood to other body parts.Pumping hormones and other vital substances to different parts of the body.Receiving deoxygenated blood and carrying metabolic waste products from the body and pumping it to the lungs for oxygenation.Maintaining blood pressure.
What is the main difference between your ventricles and your atria quizlet?
What is the main difference between your ventricles and your atria? Your atria bring blood into the heart; your ventricles pump it out.
What is the function of the atria quizlet?
What is the function of the atria? The atria receive blood returning to the heart from other areas of the body. R atrium: receives deoxygenated blood returning to the heart from the superior and inferior venae cavae. L atrium: receives oxygenated blood returning to the heart from the pulmonary veins.
What is the function of the right ventricle quizlet?
What is the function of the Right Ventricle? Receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium and pumps this blood through the pulmonary semilunar valve into the pulmonary trunk.
What are the 4 ventricles of brain?
There are four ventricles of the brain: the 2 lateral ventricles, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle. The ventricles are lined with a specialised membrane called the choroid plexus, which is made up of ependymal cells.
What's the definition of ventricle?
: a cavity of a bodily part or organ: as. a : a chamber of the heart which receives blood from a corresponding atrium and from which blood is forced into the arteries.
What are the ventricles of the brain called?
The ventricular system is composed of 2 lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, the cerebral aqueduct, and the fourth ventricle (see the images below).
Where are the ventricles of the brain?
The first and second ventricles are lateral ventricles. These C-shaped structures are located on each side of your cerebral cortex, the wrinkly outer layer of your brain. The third ventricle is a narrow, funnel-shaped structure situated between your right and left thalamus, just above your brain stem.
Why are the walls of the atria thinner than the ventricle walls?
The walls of the atria are thinner than the ventricle walls because they have less myocardium . The myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle fibers, which enable heart contractions. The thicker ventricle walls are needed to generate more power to force blood out of the heart chambers.
Which organ receives blood from the heart?
Right Atrium: Receives blood returning to the heart from the superior and inferior venae cavae. The superior vena cava returns de-oxygenated blood from the head, neck, arm and chest regions of the body to the right atrium. The inferior vena cava returns de-oxygenated blood from the lower body regions (legs, back, ...
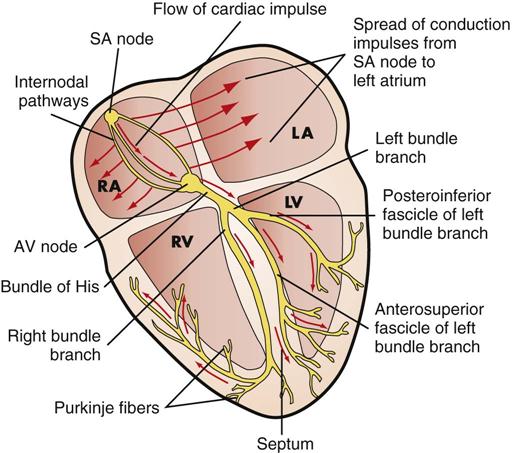
What is the heart's electrical impulse?
Cardiac conduction is the rate at which the heart conducts electrical impulses. Heart rate and heartbeat rhythm are controlled by electrical impulses generated by heart nodes. Heart nodal tissue is a specialized type of tissue that behaves as both muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Heart nodes are located in the right atrium of the heart. The sinoatrial (SA) node, commonly called the heart's pacemaker, is found in the upper wall of the right atrium. Electrical impulses originating from the SA node travel throughout the heart wall until they reach another node called the atrioventricular (AV) node. The AV node lies on the right side of the interatrial septum, near the lower portion of the right atrium. The AV node receives impulses from the SA node and delays the signal for a fraction of a second. This gives atria time to contract and send blood to the ventricles before the stimulation of ventricular contraction.
What are the two chambers of the heart?
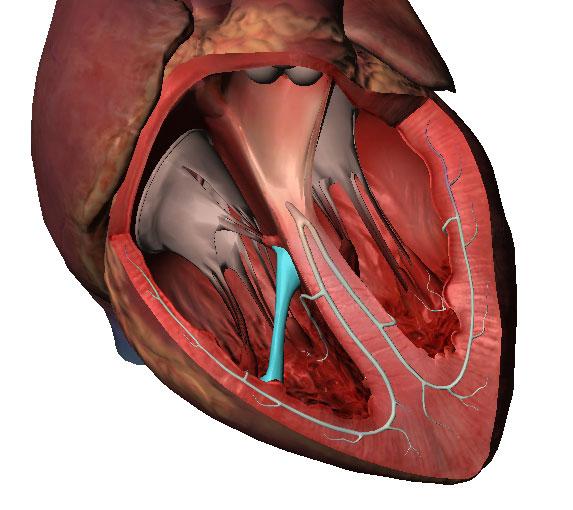
It is divided into four chambers that are connected by heart valves. The upper two heart chambers are called atria. At ria are separated by an interatrial septum into the left atrium and the right atrium. The lower two chambers of the heart are called ventricles. Atria receive blood returning to the heart from the body and ventricles pump blood ...
What are the layers of the heart?
The layers of the heart wall are the outer epicardium, the middle myocardium, and the inner endocardium. The walls of the atria are thinner than the ventricle walls because they have less myocardium .
Where are the heart nodes located?
Heart nodes are located in the right atrium of the heart . The sinoatrial (SA) node, commonly called the heart's pacemaker, is found in the upper wall of the right atrium. Electrical impulses originating from the SA node travel throughout the heart wall until they reach another node called the atrioventricular (AV) node.
Which organs receive blood returning to the heart from the body?
Atria receive blood returning to the heart from the body and ventricles pump blood from the heart to the body.
What is the function of the ventricles?
Function. The ventricles of the heart function to pump blood to the entire body. During the diastole phase of the cardiac cycle, the atria and ventricles are relaxed and the heart fills with blood. During the systole phase, the ventricles contract pumping blood to the major arteries (pulmonary and aorta ).
What is the heart's left ventricle?
Similarly, the heart's left ventricle receives blood from the corresponding left atrium and pumps that blood to the aorta. Heart failure can have devastating effects on the body. It can result from damage to the ventricles such that they cease to work properly. The lower two chambers of the heart are called heart ventricles.
How many ventricles does the heart have?
The heart has two ventricles which are its lower two chambers. These ventricles pump blood from the heart to the body. The heart's right ventricle receives blood from the corresponding right atrium and pumps that blood to the pulmonary artery. Similarly, the heart's left ventricle receives blood from the corresponding left atrium and pumps ...
What are the lower chambers of the heart called?
The lower two chambers of the heart are called heart ventricles. A ventricle is a cavity or chamber that can be filled with fluid, such as the cerebral ventricles. The heart ventricles are separated by a septum into the left ventricle and the right ventricle. The upper two heart chambers are called atria. Atria receive blood returning ...
What is the condition in which the heart beats irregularly?
Ventricular tachycardia is another disorder of the heart ventricles. In ventricular tachycardia, the heartbeat is accelerated but the heartbeats are regular. Ventricular tachycardia may lead to ventricular fibrillation, a condition in which the heart beats both rapidly and irregularly.
Which artery receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the main pulmonary artery?
Right ventricle: Receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the main pulmonary artery. Blood passes from the right atrium through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. Blood is then forced into the main pulmonary artery as the ventricles contract and the pulmonary valve opens. The pulmonary artery extends from the right ventricle and branches into the left and right pulmonary arteries. These arteries extend to the lungs. Here, oxygen-poor blood picks up oxygen and is returned to the heart via the pulmonary veins.
Why do ventricles become stiff?
Heart failure results from weakening or damaging of the heart muscle that causes ventricles to become stretched to the point that they cease to function properly. Heart failure may also occur when ventricles become stiff and unable to relax. This prevents them from filling properly with blood.
Which ventricles of the heart receive blood from the atria and pump it into the outflow vessels?
The left and right ventricles of the heart receive blood from the atria and pump it into the outflow vessels; the aorta and the pulmonary artery respectively.
Which part of the heart receives blood from the atria?
It is lined by pectinate muscles, and is derived from the embryonic atrium. Ventricles. The left and right ventricles of the heart receive blood from the atria and pump it into the outflow vessels; the aorta and the pulmonary artery respectively.
What is the septal wall in the right atrium?
The septal wall in the right atrium is marked by a small oval-shaped depression called the fossa ovalis. This is the remnant of the foramen ovale in the fetal heart, which allows right to left shunting of blood to bypass the lungs. It closes once the newborn takes its first breath.
What is a bridge in the heart?
Bridges – attached to the ventricle at both ends, but free in the middle. The most important example of this type is the moderator band, which spans between the interventricular septum and the anterior wall of the right ventricle. It has an important conductive function, containing the right bundle branches.
What is the right atrium?
Extending from the antero-medial portion of the chamber is the right auricle (right atrial appendage) – a muscular pouch that acts to increase the capacity of the atrium.
What is the left ventricle?
In the anatomical position, the left ventricle forms the apex of the heart, as well as the left and diaphragmatic borders. Much like the right ventricle, it can be divided into an inflow portion and an outflow portion. Inflow Portion.
Which ventricle forms the apex of the heart?
In the anatomical position, the left ventricle forms the apex of the heart, as well as the left and diaphragmatic borders. Much like the right ventricle, it can be divided into an inflow portion and an outflow portion.
Why are the atria important?
While each aspect of the heart plays an important role in the circulatory system, the atria are particularly important as they help to fill the ventricles prior to ventricular contraction. As such, the goal of this article is to discuss the embryology, anatomy, and blood supply of the atria of the heart. Furthermore, the physiological function, as ...
What is the cardiac atrium?
Much like the wide, open architectural atrium that functions as receiving sites for incoming guests, the cardiac atrium is a pair of chambers situated at the upper part of the heart that receives systemic and pulmonary blood.
How does the autonomic nervous system work?
The autonomic nervous system works in tandem to regulate the activities of the sinuatrial node. The heart is said to be in sinus rhythm as long as there are coordinated atrial contractions, followed by normal ventricular contractions. This can be demonstrated on an electrocardiograph by a P-wave preceding each QRS-complex, with normal intervals.
How does atrial dilation affect the heart?
Atrial dilatation and ischaemic tissue facilitate the development of re-entrant circuits. The dilatation results in stretching of the electrical pathway, which slows down the propagation of an action potential through a particular loop. As a result, some of the tissues exit the normal post action potential refractory period (i.e. completing repolarization) and can, therefore, be prematurely depolarized by an ectopic beat. The myocardium heals by forming fibrous tissue, which is a poor conductor of electricity. Consequently, the action potential has to find an alternative (possibly longer) route to travel; which leads to a similar situation described above.
What is the upper chamber of the heart called?
Each pump contains an upper chamber that functions as a receptacle for incoming blood, called the atrium , and a lower chamber that is responsible for pushing blood out of the heart called the ventricle. The heart is located in the mediastinum within a region known as the cardiac box; the boundaries of which include:
Which atrium is larger, the right or the left?
The left atrium. The left atrium is positioned slightly above and behind the right atrium. Although it is smaller in terms of the amount of blood it can hold, the left atrium has a thicker myocardial wall when compared to the right atrium.
What is the heart system?
The heart is at the center of this system, as it pumps blood through vascular channels towards the target tissue. Recall that the heart is a roughly pyramidal organ made up of two muscular pumps that are connected in-series – namely, the left and right heart. Each pump contains an upper chamber that functions as a receptacle for incoming blood, called the atrium, and a lower chamber that is responsible for pushing blood out of the heart called the ventricle. The heart is located in the mediastinum within a region known as the cardiac box; the boundaries of which include:
Which valves are opening to allow blood to flow through the left ventricle?
The atrioventricular valves have just opened, and blood is flowing rapidly through the mitral valve from the left atrium into the left ventricle.
What happens to the AV valves when the ventricular relaxes?
With continued ventricular relaxation, the pressure in the ventricles becomes less than that in the atria, causing the AV valves to open.
What is the term for the short period during ventricular systole?
isovolumetric relaxation. period when all four valves are closed and ventricular blood volume does not change. isovolumetric contraction. refers to the short period during ventricular systole when the ventricles are completely closed chambers. P wave.
What happens when the ventricular ejection has occurred?
Now that ventricular ejection has occurred, the ventricles enter diastole. Relaxation of the ventricles lowers their pressure. The drop in pressure and backflow of blood causes the semilunar valves to close. When the aortic valve closes, the volume of blood in the left ventricle remains constant until the mitral valve reopens.
What is the first phase of atrioventricular valve?
The atrioventricular valves have just opened, and blood is flowing rapidly through the mitral valve from the left atrium into the left ventricle. Phase 2: Isovolumetric Contraction.
What happens when all valves are closed?
With all the valves closed, contraction of the ventricles causes pressure in the ventricles to increase.