What is the function of Brunner's glands in the digestive system?
function in human digestive system. In small intestine Secretions from Brunner glands, in the submucosa of the duodenum, function principally to protect the intestinal walls from gastric juices.
Does Britannica have an article on Brunner glands?
Britannica does not currently have an article on this topic. In small intestine Secretions from Brunner glands, in the submucosa of the duodenum, function principally to protect the intestinal walls from gastric juices.
What is the function of the bicarbonate of Brunner's glands?
Brunner's glands (or duodenal glands) are compound tubular submucosal glands found in that portion of the duodenum which is above the hepatopancreatic sphincter (i.e sphincter of Oddi ). The main function of these glands is to produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion i.e. mucous (containing bicarbonate) in order to:
What is secretion from Brunner's glands?
Secretion from Brunner's glands contributes to a layer of mucus that forms a slippery, viscoelastic gel that lubricates the mucosal lining of the proximal intestinal tract. The unique capacity of this mucus layer to protect delicate underlying epithelial surfaces is due primarily to the gel-forming properties of its glycoprotein molecules.

Does brunners gland secrete mucus?
Secretion from Brunner's glands contributes to a layer of mucus that forms a slippery, viscoelastic gel that lubricates the mucosal lining of the proximal intestinal tract.
What hormones do Brunner's glands secrete?
Brunner's glands are compound racemose glands in the submucous layer of the duodenum. Secretin is a hormone released into the bloodstream by the duodenum (especially in response to acidity) to stimulate secretion by the liver and pancreas.
What is the function of Brunner's gland and the importance of Peyer's patches?
The main function of these glands is to produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion i.e. mucous (containing bicarbonate) in order to: protect the duodenum from the acidic content of chyme (which is introduced into the duodenum from the stomach);
What cells are in brunners glands?
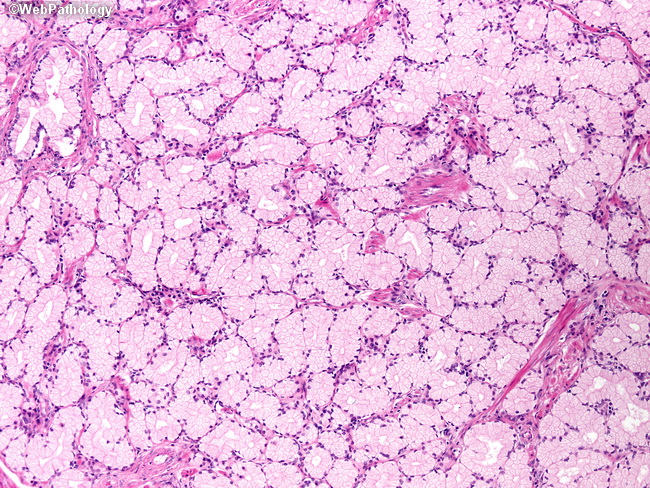
Brunner glands are composed of ramifying tubules lined principally by cells resembling the mucus-secreting cells of the gastric antral mucosa. Brunner glands also contain endocrine cells that store various polypeptides. Brunner glands lie predominantly in the duodenal submucosa, just beneath the muscularis mucosae.
Who discovered Brunner's gland?
The duodenal glands were first observed in 1679 by Wepfer (1) who described them during the autopsy of a beheaded woman. Wepfer described their arrangement in the duodenum and observed that when they were macerated in water, the duodenal glands discharged copious amounts of mucus.
Are Brunner's glands exocrine or endocrine?
Exocrine glandsExocrine glands have ducts - and they secrete onto a surface: examples of exocrine glands are: sebaceous and sweat glands (in the skin), salivary glands (oral), Brunner's glands.
Why are Brunner's glands primarily located in the duodenum?
Secretions from Brunner glands, in the submucosa of the duodenum, function principally to protect the intestinal walls from gastric juices.
What do Peyer's patches secrete?
T cells n Peyer's patches function similarly to LPLs (lipoprotein lipase) and other circulating T cells. However, the distinct feature of these T cells is to secrete tolerogenic cytokines like TGF-beta and IL-10 on exposure to common food allergens, as seen in some animal experiments.
Is Brunner's gland exocrine?
Brunner gland adenoma is a rare neoplasm derived from the exocrine glands of proximal duodenum.
Is Brunner's gland unicellular?
They are multicellular glands which are found in the submucosa region of the duodenum.
What two hormones does the duodenum secrete?
Upon entering the duodenum, the chyme causes the release of two hormones from the small intestine: secretin and cholecystokinin (CCK, previously known as pancreozymin) in response to acid and fat, respectively. These hormones have multiple effects on different tissues.
What are the two hormones secreted by the small intestine?
The mucosa of the small intestine secretes the hormones secretin and cholecystokinin.
What is secretin secreted by?
S cellsSecretin is secreted by S cells in the duodenum and affects numerous other organ systems. Secretin receptors (SR) are expressed in the basolateral domain of several cell types. [3] Besides regulating the growth of epithelial cells in the pancreas and biliary system, secretin additionally exerts trophic effects.
What enzymes are secreted by the duodenum?
The small intestines, where the duodenum is located, secretes sucrose, maltase, lactase, and peptidase enzymes to further break down food.
How can I check on my order?
Check your email or account page on our site for updates. You can also check on the status of your order by emailing us at [email protected] or call...
How long does it take to receive my order?
On average, orders for customers in the USA arrive in 2-5 business days and international expedited orders arrive in 7-14 business days. Orders pla...
What are your shipping costs?
Normal shipping starts at $8.00. However, for bulk orders and large orders, shipping will be calculated accordingly. Any necessary taxes will also...
Do you offer overnight/expedited shipping?
Yes. Overnight shipping is only guaranteed through Fedex, we can also expedite shipping with DHL, 3-5 days, and the price starts at $60 and will ul...
What are your international shipping costs?
International shipping starts at $17 for priority service and more expensive quicker delivery services are also available.
What is the main ingredient in CHOQ™ daily?
The core ingredient in CHOQ™ DAILY is PrimaVie® Purified Shilajit. A highly effective, clinically proven natural compound, Purified Shilajit is a p...
How does CHOQ™ Daily work?
Our team of seasoned herbalists created CHOQ™ Daily to help men optimize free and total testosterone levels, energy, and sports performance. The ke...
How is the duodenum distinguished from the jejunum?
The duodenum can be distinguished from the jejunum and ileum by the presence of Brunner's glands in the submucosa.
What are the symptoms of a Brunner hamartoma?
Most patients with Brunner gland hamartomas are asymptomatic or have nonspecific complaints such as nausea, bloating, or vague abdominal pain.
Which glands secrete alkaline fluid?
The Brunner glands, which empty into the intestinal glands, secrete an alkaline fluid composed of mucin, which exerts a physiologic anti-acid function by coating the duodenal epithelium, therefore protecting it from the acid chyme of the stomach.
How rare are hamartomas?
These hamartomas are rare, with approximately 150 cases described in the literature. It is estimated that they represent approximately 5–10% of benign duodenal tumors. They are variable in size, typically 1–3 cm, with only a few reported cases of lesions larger than 5 cm.
What is the function of the mucus gland?
The main function of these glands is to produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion i.e. mucous (containing bicarbonate) in order to: protect the duodenum from the acidic content of chyme (which is introduced into the duodenum from the stomach );
Can a Brunner hamartoma cause nausea?
Most patients with Brunner gland hamartomas are asymptomatic or have nonspecific complaints such as nausea, bloating, or vague abdominal pain. Most reports in the literature describe local surgical resection of Brunner gland hamartoma via duodenotomy.
Who is the Brunner gland named after?
They are the distinguishing feature of the duodenum, and are named for the Swiss physician who first described them, Johann Conrad Brunner . Human Brunner's gland.
What are Brunner’s Glands?
Brunner’s glands function to neutralize acids from your stomach. The chyme released from the upper stomach is very acidic. As this chyme enters into the beginning of the small intestine, called the duodenum, you are meant to have a protective coating there.
What is the name of the hormone that inhibits the secretion of acid and digestive enzymes in the stomach?
Urogastrone (another name for EGF), secreted by your Brunner’s glands, inhibits the chief cells in the upper stomach from secreting acid and digestive enzymes in order to protect your duodenum. Neutralizing that acid churn allows the nutrients consumed from fresh, enzymatically rich food to be absorbed.
What gland secretes a viscous solution?
This solution is secreted by your Brunner’s glands. Secretions of your Brunner’s glands are composed of a viscous, alkaline, slippery, and wet solution. You can note that inside this solution is a potent array of proteolytic enzymes. These secretions are produced by compound tubular organelle cells that exist above your sphincter of Oddi.
Why does Brunner's gland cause aging?
Many practitioners have observed that most aging occurs because Brunner’s glands functioning was compromised. Enterocrinin is a hormone that stimulates secretion of mucin and enzymes into your intestinal juices. Enterocrinin is released into the blood from your duodenum. As a result, this stimulates the acinar cells of your pancreas ...
Why is it important to have plenty of condiments full of enzymatic activity?
This is the law of adaptive secretion of digestive enzymes. As you bring in more exogenous enzymes, your body can conserve its own energy while digesting your food.
Why is the duodenum caustic?
In that case there would have been a highly caustic condition of the duodenum, due to the acid from the upper chamber of the stomach not being neutralized.
Where are Brunner's glands located?
So as you can observe, an extensive array of Brunner’s glands are located above the sphincter of Oddi. The sphincter of Oddi is the valve found within the pancreatic duct that is a portal which systematically opens and shuts itself. From the pancreatic duct, it empties into the beginning of the small intestine called the duodenum.
What are the secretory units of Brunner's glands?
Secretory units of Brunner's glands consist of epithelial tubules that show frequent distal branchings. The secretory units, with the exception of those found in rabbits and horses, consist primarily of a mucin producing cell type.
Where are Brunner's glands located?
Brunner's glands are unique to mammalian species and in eutherians are confined primarily to the submucosa of the proximal duodenum. In the majority of species examined, they begin at the gastrointestinal junction and extend for variable distances distally in the wall of the proximal small intestine. Ducts of individual glands empty either directly ...
Which chromosome is the Brunner gland located on?
Human Brunner's glands produce class III mucin glycoproteins and are thought to be the product of mucin gene MUC6 which is assigned to chromosome 11 (11p15-11p15.5 chromosome region).
Learn about this topic in these articles
Secretions from Brunner glands, in the submucosa of the duodenum, function principally to protect the intestinal walls from gastric juices. Lieberkühn glands, occupying the mucous membrane, secrete digestive enzymes, provide outlet ports for Brunner glands, and produce cells that replace surface-membrane cells shed from the tips of…
function in human digestive system
Secretions from Brunner glands, in the submucosa of the duodenum, function principally to protect the intestinal walls from gastric juices. Lieberkühn glands, occupying the mucous membrane, secrete digestive enzymes, provide outlet ports for Brunner glands, and produce cells that replace surface-membrane cells shed from the tips of…
What is the function of the Brunner's gland?
The primary physiological function of Brunner’s gland is to secrete alkaline mucus, which protects the duodenal mucosa from acid secreted in the stomach. Brunner’s gland hyperplasia is a type of proliferative disease of the duodenum, which is a very rare case. Brunner’s gland hyperplasia is usually asymptomatic, ...
Why is Brunner's gland hyperplasia chronic?
It is believed that the reason for Brunner’s gland hyperplasia is chronic inflammation, a chronic irritant because of excessive secretion of gastric acid, or a decrease in exocrine pancreatic function.
Why is there no consensus on Brunner's gland hyperplasia?
There is no consensus on the therapeutic principles of Brunner’s gland hyperplasia because follow-up research is insufficient since the disease is asymptomatic. Medical treatment serves to regulate gastric hyperacidity, which is one amongst the causes of Brunner’s gland hyperplasia. Thus, removal is the preferred method.
What is the Brunner gland?
Brunner’s glands are glands that secrete mucus. These glands are located in the deep mucous membrane (the mucous membrane is the membrane lining the various body cavities and covering the surface of the internal organs) and the submucosa of the duodenum, which flows into the intestinal glands. The primary physiological function ...
Why did they continue the frozen biopsy?
Even though the frozen biopsy showed no signs of malignancy, they decided to continue the operation because they might not rule out the chance of malignancy.
Can Brunner's gland be mistaken for malignancy?
Due to their rarity, these lesions can be mistaken for malignancy on radiographic and endoscopic examina tions. Symptomatic hyperplasia of Brunner’s gland associated with pancreatitis is very rare, and the literature is limited to a few clinical cases. Endoscopic ultrasound can be useful in obtaining a correct diagnosis.
Can Brunner's gland cause gastrointestinal bleeding?
Brunner’s gland hyperplasia may be a very rare lesion of the duodenum that is usually asymptomatic and is diagnosed incidentally during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. It can cause gastrointestinal bleeding , but the hemorrhagic shock may be a rare clinical manifestation of Brunner’s gland hyperplasia.
Why are Brunner's glands activated?
Brunner's glands are activated in response to acidic substances in the duodenum and different investigation s have found that the hormone secretin is a powerful activator of its secretion mechanisms. However, the mechanisms that trigger its activation are not yet understood with certainty.
Why does the duodenum get sore?
It occurs in patients with ulcers in the duodenum, generally due to hyperstimulation of the glands that secrete gastric acids to the stomach, resulting in hyperacidification and acute inflammation of the duodenum.
What glands are responsible for neutralizing acidity in the intestine?
Brunner's glands are responsible for neutralizing the acidity of gastric juices, therefore, mucus and alkaline substances such as bicarbonate that they secrete are one of the main mechanisms for the protection of the intestine against high concentrations of hydrochloric acid ( HCl).
What are the pathologies of Brunner's gland?
Pathologies caused by conditions in Brunner's glands range from hyperplasias due to hyperstimulation to the formation of tumors or neoplasms.
What is the effect of parasympathetic vagal stimulation on Brunner's glands?
Parasympathetic vagal (cholinergic) stimulation stimulates the secretion of cells in Brunner's glands, increasing the production of mucus and fluid that is released into the duodenum. The ingestion of irritating foods (physical or chemical) also stimulates the secretion in these glands.
What hormone is secreted by Brunner's glands?
The hormone urogastrone, secreted by Brunner's glands, has inhibitory effects on the secretion of acids in the stomach. The secretion of this hormone is sensitive to excessive alcohol consumption, which is why alcoholics usually suffer from irritations in the pancreas.
Which glands affect the duodenum?
There are multiple pathologies that affect the function of the duodenum by affecting Brunner's glands, since it receives pancreatic and bile secretions through the pancreatic and common bile ducts, respectively.

Overview
Brunner's glands (or duodenal glands) are compound tubular submucosal glands found in that portion of the duodenum which is above the hepatopancreatic sphincter (i.e sphincter of Oddi). It also contains submucosa which creates special glands. The main function of these glands is to produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion i.e. mucous (containing bicarbonate) in order to:
Structure
The duodenum can be distinguished from the jejunum and ileum by the presence of Brunner's glands in the submucosa.
Function
The Brunner glands, which empty into the intestinal glands, secrete an alkaline fluid composed of mucin, which exerts a physiologic anti-acid function by coating the duodenal epithelium, therefore protecting it from the acid chyme of the stomach. Furthermore, in response to the presence of acid in the duodenum, these glands secrete pepsinogen and urogastrone, which inhibit gastric acid secretion.
Clinical significance
Hyperplasia of Brunner glands with a lesion greater than 1 cm was initially described as a Brunner gland adenoma. Several features of these lesions favor their designation as hamartomas, including the lack of encapsulation; the mixture of acini, smooth muscles, adipose tissue, Paneth cells, and mucosal glands; and the lack of any cell atypia. These hamartomas are rare, with approximately 150 cases described in the literature. It is estimated that they represent approxim…
See also
• Peutz–Jeghers syndrome
External links
• Histology image: 11504loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: pyloro/duodenal junction, duodenum"
• Histology image: 11513loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: pyloro/duodenal junction"