The cell membrane has following functions:
- · It acts as a semipermeable membrane regulating the inflow and outflow of metabolites to and from the protoplasm.
- · It helps in electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation.
What does a cell membrane do in a bacterial cell?
The plasma membrane or bacterial cytoplasmic membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and thus has all of the general functions of a cell membrane such as acting as a permeability barrier for most molecules and serving as the location for the transport of molecules into the cell.
What are the parts and functions of the cell membrane?
What are the 6 functions of the cell membrane?
- Molecule Transport. Helps MOve food, water, or something across the membrane.
- Act as enzymes. Controls metabolic processes.
- Cell to cell communication and recognition. so that cells can work together in tissues.
- Signal Receptors.
- intercellular junctions.
- Attatchment to the cytoskeleton and ECM.
What is the main function of cell membrane?
The function of a cell membrane, also referred to as the plasma membrane, is to protect the structures within the cell, give shape to the cell and support its structure. The cell membrane is composed of a double layer of lipids and proteins.
What is the function and definition of cell membrane?
The cell membrane is a thin membrane that encases the cytoplasm of the cell, and holds the cytoplasm (as well as the cell’s organelles) within it, separating the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane is semi-permeable, meaning that it allows certain substances to move into the cell while it keeps certain other substances out of the cell.

What is the of cell membrane in bacterium?
Structure of cell membrane. ➢The structure of bacterial plasma membrane is that of. unit membrane, i.e., a fluid phospholipid bilayer, composed of phospholipids (40%) and peripheral and integral proteins (60%) molecules.
What are 3 functions of the cell membrane?
Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products, that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the ...
What are the 4 major functions of the cell membrane?
The four main functions of the plasma membrane include identification, communication, regulation of solute exchange through the membrane, and isolation of the cytoplasm from the external environment.
What is the importance of cell membrane?
The plasma membrane, or the cell membrane, provides protection for a cell. It also provides a fixed environment inside the cell. And that membrane has several different functions. One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
What are 5 functions of the cell membrane?
Terms in this set (5)protects the cell by acting as a barrier.regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell.receives chemical messengers from other cell.acts as a receptor.cell mobility, secretions, and absorptions of substances.
What are the main functions of a cell?
They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body's hereditary material and can make copies of themselves.
What is the main function of the cell membrane quizlet?
The primary function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer from tail to tail with embedded proteins, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells.
What are the three most important functions that a cell performs?
3 Major Functions of a CellEnergy Generation. Living cells exist in a perpetually active biological state. ... Molecular Transport. Each cell is surrounded by a membrane that delineates its boundaries and acts as a gatekeeper, controlling the movement of molecules into and out of the cell. ... Reproduction.
What is the cell membrane?
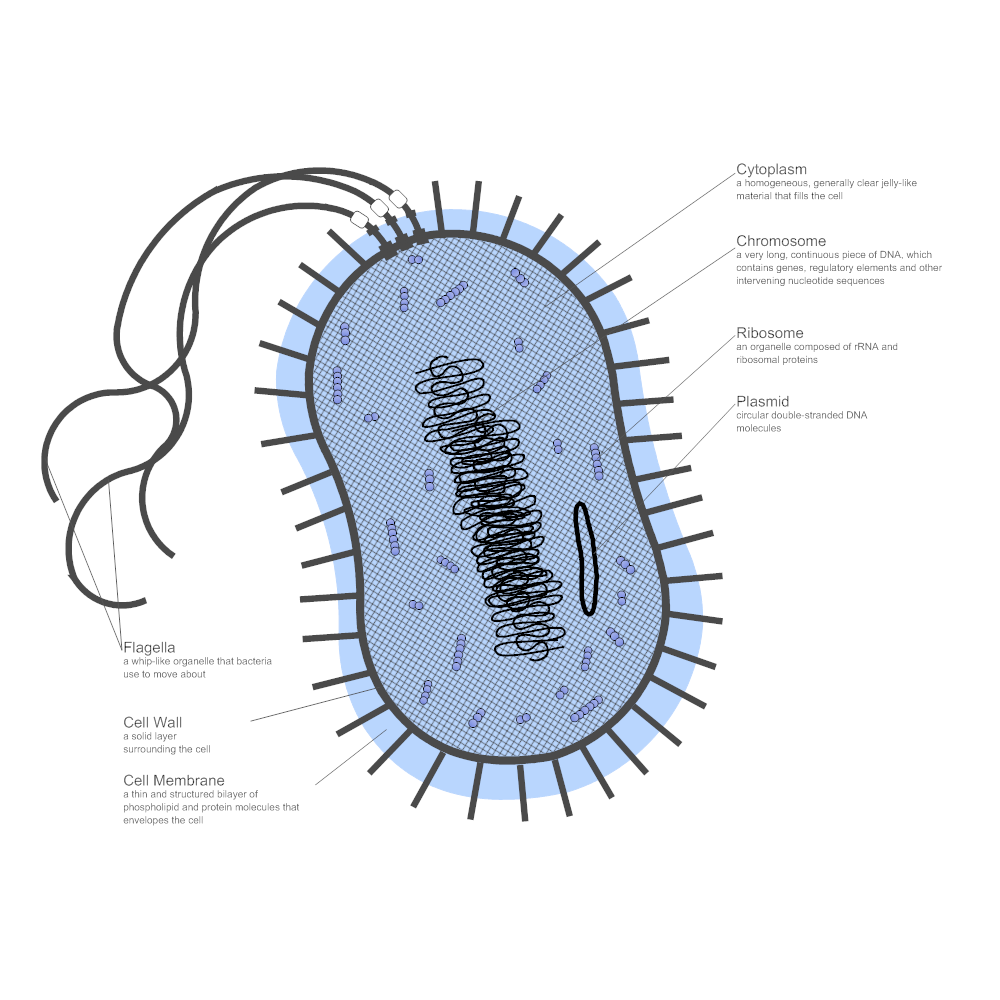
Cell membrane or plasma membrane is a thin (5–10 nm) semipermeable membrane that acts as an osmotic barrier. It lies beneath the cell wall separating it from the cell cytoplasm. Cell membrane primarily contains phospholipids and proteins. It also contains enzymes associated with DNA biosynthesis, cell wall polymers, and membrane lipids. Bacterial plasma membranes usually have a higher proportion of protein than eukaryotic membranes. They usually differ from eukaryotic membranes in lacking sterols, such as cholesterol, except in Mycoplasma. The cell membrane has following functions:
What is the outer layer of a cell?
The outer layer or cell envelope provides a structural and physi-ological barrier between the protoplasm (inside) of the cell and the external environment. The cell envelope protects bacteria against osmotic lysis and gives bacteria rigidity and shape. The cell envelope primarily consists of two components: a cell wall and cytoplasmic ...
What are the components of the cell envelope?
The cell envelope primarily consists of two components: a cell wall and cytoplasmic or plasma membrane. It encloses the proto-plasm, which consists of (i) cytoplasm, (ii) cytoplasmic inclu-sions (mesosomes, ribosomes, inclusion granules, vacuoles), and (iii) a single circular DNA (Fig. 2-7). Cell Membrane.
What is the function of the cell wall?
Function: Helps in attachment to solid surface. 7. Cell wall: It is an important structure of a bacteria. It give shape to the organism. On the basis of cell wall composition, bacteria are classified into two major group ie. Gram Positive and gram negative.
Which bacteria are semi-rigid extension of cell wall and cell membrane?
One bacteria may contains one or many prosthecae. Some prosthecae develop bud at the tip and hence helps in reproduction. Some prosthecate bacteria are: Caulibacter , Stella, Prosthecobacter, Hyphomicrobium.
What is the function of pili?
Function: Attachment: pili helps the bacteria to attach the host cell surface. Most of the human pathogens of respiratory tract, urinary tract are attached with the help of pili. Pili (fimbrae) possess antigenic property. Specialized function: some pili are modified for specialized function.
What is the function of a mesosome?
Mesosome: Mesosome is a spherical or round sac like structure found commonly in gram positive bacteria. Function: It is the site for respiration in bacterial cell. 12. Cytoplasm: It is colorless, viscus fluid present inside cell membrane. All the cell organelles and inclusions are found floating in cytoplasmic fluid.
What is the hollow tube that holds the chain of bacteria?
Some bacteria forming chain or trichome are enclosed by a hollow tube like structure known as Sheath.
Which layer of the cell wall is present in both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria?
Peptidoglycan layer is present in cell wall of both gram positive as well as gram negative bacteria. However, gram positive have thick layer of peptidoglycan.
What is the most important part of the cell?
Nucleus is the most important part of the cell. It controls and directs all the cellular activities and stores hereditary information of cell. Bacterial nucleus is known as nucleoid; it lacks nuclear membrane, nuceloplasm and nucleolus.
What is the function of the bacterial cell membrane?
This barrier prevents materials from simply diffusing into and out of the cell. This allows the cell to take up chemicals and nutrients needed for survival while keeping the vital cell components separated from the environment.
What is the cell membrane?
The answer is the cell membrane. The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that completely surrounds a bacterial cell. The word 'completely' is important here because any break in the bilayer will lead to the death of the bacteria.
How do bacteria increase the surface area of the cell membrane?
A bacterial cell can increase surface area of the cell membrane with only a small change in the volume of the cytoplasm by making many invaginations of the cell membrane. 'Invagination' is just a fancy word for 'folding the membrane.'.
How does antibacterial cleaning work?
In fact, some of our favorite antibacterial cleaning products kill bacterial cells by destroying or making holes in the cell membrane, allowing the bacterial cell contents to spill out . The phospholipid bilayer structure has both hydrophilic, or water-loving, and hydrophobic, or water-fearing, components.
What does it mean when a bacteria cell is larger?
Wait - what does that mean?! That means that as the cell gets larger, the rate of food uptake and waste excretion gets slower. The average bacterial cell has a large cell membrane surface area and a small internal cytoplasm volume. All that exposed cell membrane surface area can efficiently take up nutrients and deliver them to the cytoplasm where they're needed.
Why is the surface area of a cell important?
Finally, we learned that the surface area of the cell is crucial for the ability of the cell to absorb sufficient nutrients and that if a cell grows too large it can increase the membrane surface area through many tiny folds called invaginations.
What is the cytosol in a cell?
Cytosol is the water-like fluid found in bacterial cells. The cytosol contains all the other internal compounds and components the bacteria needs for survival. The fluid and all its dissolved or suspended particles is called the cytoplasm of the cell. Proteins, amino acids, sugars, nucleotides, salts, vitamins, enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, and internal bacterial structures all float around the cell in the cytoplasm. All of these components are vital to the life of the cell and are contained by the cell membrane.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
What are the proteins that interact with other cells?
Another is that the membrane of the cell, which would be the plasma membrane, will have proteins on it which interact with other cells. Those proteins can be glycoproteins, meaning there's a sugar and a protein moiety, or they could be lipid proteins, meaning that there's a fat and a protein.
Is the cell wall tougher than the plasma membrane?
In fact, they have a cell wall outside of them, and that cell wall is much tougher and is structurally more sound than a plasma membrane is. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.
Is cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
And there are different types of plasma membranes in different types of cells, and the plasma membrane has in it in general a lot of cholesterol as its lipid component. That's different from certain other membranes from within the cell.
How do bacteria cells function?
Bacteria cells function quite differently from human cells, from the function of the cell as a whole, right down to the individual structures in each cell. Bacteria exist in nature as individual cells.
What is the function of DNA in bacteria?
The main function of DNA in bacterial cells is the same as human cells, transcription into ribonucleic acid (RNA) followed by translation into amino acids and subsequent folding into proteins.
Why do bacteria have endospores?
Endospores are a bacteria cell's way of protecting itself against harsh changes in the environment or nutrient depletion. When a required nutrient in the environment becomes depleted or absent, signals get sent to the bacteria to begin endospore formation. An endospore protects the bacterial genetic material so that, when optimal conditions return, the bacterial cell can reform and thrive again.
What is the bilayer of a bacteria cell?
Bacterial cells consist of a phospholipid bilayer, and in some cases a layer of peptidoglycan. The phospholipid bilayer either allows or denies ions and other molecules entry to the cell, based on factors such as size and charge.
How does flagella help bacteria?
Flagella help bacteria move through the environment. The flagellum is a whip-like structure that can occur at one end, both ends, or all over the bacterial cell. The whipping action pushes the bacteria through the aqueous solution and improves the cells' chances of being in a nutrient-rich environment.
Where are ribosomes located in a cell?
Ribosomes exist in the cytoplasm of a bacterial cell and have a very important function. Ribosomes translate the amino acids from RNA. Once translated, the amino acids fold up into tertiary structures called proteins. The proteins in a bacterial cell have many important functions, including regulation of transcription and translation, ...
Do bacteria have organelles?
While some bacteria work together in a group, no bacteria forms multicellular tissues. Bacteria have organized structures within the cell, but do not have membrane-bound organelles, as with human cells.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus and mitochondria are two examples. Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized. In exocytosis, vesicles containing lipids and proteins fuse with ...
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.
What are the unique characteristics of the cell membrane of Archaea?
A unique characteristic of Archaea is the presence of ether linkages in the lipids of their cytoplasmic membranes which distinguishes archaea form eukaryotes and most bacteria. The structure of cytoplasmic membranes of many archaea is a lipid bilayer ...
What is the cytoplasmic membrane made of?
The cytoplasmic membrane in same of the archaeo bacteria or archaea are monolayers made of glycerol tetra-ether lipids. These monolayers are heat stable with hydrophilic portions (glycerol) at the cytoplasm and external interfaces and an internal hydrophobic portion (hydrocarbons).
What is the difference between bacterial and eukaryotic lipids?
The difference lies that bacterial and eukaryotic lipids are generally based on ester linkages. The archaeal lipids are mainly isopranyl glycerol ethers, which are synthesized by the condensation of glycerol or other alcohols with isopreroid hydrocarbons of 20, 25, or 40 carbon atoms. (Fig. 6.2)