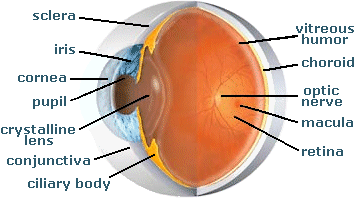
What does the cilliary muscles do?
The ciliary muscle is a muscle in the ciliary body, an area of the eye which helps people focus. Vision problems can occur if the ciliary muscle is damaged. An individual suffering from ciliary muscle problems may have trouble focusing on small print. Elderly individuals are particularly susceptible to developing vision problems.
What is the role of the ciliary muscle in the eye?
The ciliary muscle is a ring of smooth muscle in the eye 's middle layer ( vascular layer) that controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal.
What does ciliary muscle mean?
a muscle controlling the eye's accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances The ciliary muscle is a ring of striated smooth muscle in the eye's middle layer that controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humour into Schlemm's canal.
What is the function of the scalene muscles?
Scalenus posterior muscle
- Origin and insertion. The scalenus posterior is the smallest of the scalene muscles. ...
- Innervation. The scalenus posterior muscle is innervated by the anterior rami of spinal nerves C6-C8 .
- Blood supply. Just like the other scalenes, scalenus posterior receives its vascular supply from the ascending cervical branch of the inferior thyroid artery.
- Function. ...

What is ciliary muscle in short answer?
Ciliary muscle: A circular muscle that relaxes or tightens the zonules to enable the lens to change shape for focusing. The zonules are fibers that hold the lens suspended in position and enable it to change shape during accommodation.
What is the function of ciliary muscles Brainly?
The ciliary muscle is a muscle in the ciliary body, an area of the eye which helps people focus. With the assistance of the ciliary muscle, the lens of the eye can be flattened or rounded to allow people to focus on distant and near objects.
What is ciliary muscles Class 10th?
Solution : The muscles which hold the eye lens in its position, and bring about changes in the shape (curvature) of the eye lens, and hence of focal length are known as ciliary muscles . Answer.
What is the function of ciliary muscles Class 8?
The ciliary body produces the fluid in the eye called aqueous humor. It also contains the ciliary muscle, which changes the shape of the lens when your eyes focus on a near object. This process is called accommodation.
What is ciliary muscles Brainly?
The part of the eye that connects to the iris to the choroid is known as ciliary muscle. It is a circular muscle that relaxes or tightens the lens to change shape for focusing.
How do ciliary muscles focus our eyes Class 10?
The focusing of the eye is controlled by the ciliary muscle, which can change the thickness and curvature of the lens. This process of focusing is called accommodation. When the ciliary muscle is relaxed, the crystalline lens is fairly flat, and the focusing power of the eye is at its minimum.
Why do we have 2 eyes for vision and not just one?
Two eyes give us a wider field of view, i.e., approximately 200 degrees with our two eyes. It helps us by reducing parallax error in vision and increases our depth of perception, i.e., the ability to perceive the world in three dimension space.
What is the function of eye lens Class 10?
The lens is a transparent structure behind the iris, the coloured part of the eye. The lens bends light rays so that they form a clear image at the back of the eye – on the retina. As the lens is elastic, it can change shape, getting fatter to focus close objects and thinner for distant objects.
What is the only function of a muscle?
The muscular system's main function is to allow movement. When muscles contract, they contribute to gross and fine movement.
Which are functions of the muscular system Brainly?
Answer. The main function of the muscular system is movement. Muscles are the only tissue in the body that has the ability to contract and therefore move the other parts of the body. Related to the function of movement is themuscular system's second function: the maintenance of posture and body position..
What is the function of muscular system answer?
The muscular system is composed of specialized cells called muscle fibers. Their predominant function is contractibility. Muscles, attached to bones or internal organs and blood vessels, are responsible for movement. Nearly all movement in the body is the result of muscle contraction.
What is the function of muscle tissue apex?
The main function of muscle tissue is contraction.
What muscle is responsible for the rounding of the eye?
The action of ciliary muscle is instructed by the parasympathetic fibers originating from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus in the midbrain. The contraction of this muscle loosens the zonular fibers allowing the lens to relax. When the lens relaxes, its degree of curvature increases, making it rounder.
How does the ciliary muscle change?
The state of the ciliary muscle changes depending if we observe distant or close objects. When looking at the distant object, the ciliary muscle is relaxed, the zonular fibers are tightened and the lens is flattened. In this state the refractive power of the lens is enough to form a clear image of the focused object on the retina. However, in order to focus on a close object, the inner structures of the eye must adapt, which is possible through the process of accommodation.
What is the ciliary muscle?
The ciliary muscle occupies the biggest portion of the ciliary body, which lies between the anterior border of the choroid and iris. It is composed of smooth muscle fibers oriented in three different directions; longitudinal, radial and circular.
What is the main action of the ciliary muscle?
The main action of ciliary muscle is changing the shape of the lens which occurs during the accommodation reflex . In addition, when contracting, the longitudinal fibers of ciliary muscle widen the iridocorneal space and canal of Schlemm which facilitates the draining of eye fluid.
What are the intrinsic muscles of the eye?
The intrinsic muscles of the eye are muscles that control the movements of the lens and pupil and thus participate in the accommodation of vision. There are three smooth muscles that comprise this group; ciliary, dilatator pupillae and sphincter pupillae muscles. The ciliary muscle occupies the biggest portion of the ciliary body, ...
How many layers are there in the ciliary muscle?
The layers of ciliary muscle are described differently by several authors in the literature, but the most used classification divides this muscle into three separate layers;
Which muscle receives innervation from the sympathetic fibers of the autonomic nervous system?
There is a shred of existing evidence in the literature that ciliary muscle also receives innervation from the sympathetic fibers of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Allegedly these fibers provide the inhibitory impulses and thus inhibit the accommodation reflex.
What causes ciliary muscle contraction?
Parasympathetic activation of the M3 muscarinic receptors causes ciliary muscle con traction. The effect of contraction is to decrease the diameter of the ring of ciliary muscle causing relaxation of the zonule fibers, the lens becomes more spherical, increasing its power to refract light for near vision.
How does the ciliary muscle affect the lens?
When the ciliary muscle contracts , it pulls itself forward and moves the frontal region toward the axis of the eye. This releases the tension on the lens caused by the zonular fibers (fibers that hold or flatten the lens). This release of tension of the zonular fibers causes the lens to become more spherical, adapting to short range focus. Conversely, relaxation of the ciliary muscle causes the zonular fibers to become taut, flattening the lens, increasing the focal distance, increasing long range focus. Although Helmholtz's theory has been widely accepted since 1855, its mechanism still remains controversial. Alternative theories of accommodation have been proposed by others, including L. Johnson, M. Tscherning, and especially Ronald A. Schachar.
What muscle pulls the lens forward?
When the ciliary muscle contracts, it pulls itself forward and moves the frontal region toward the axis of the eye. This releases the tension on the lens caused by the zonular fibers (fibers that hold or flatten the lens).
Which nerve is responsible for the sympathetic postganglionic innervation of the ciliary ganglia?
The sympathetic postganglionic fibers are part of cranial nerve V 1 ( Nasociliary nerve of the trigeminal ), while presynaptic parasympathetic fibers to the ciliary ganglia are from the oculomotor nerve. The postganglionic sympathetic innervation arises from the superior cervical ganglia. Presynaptic parasympathetic signals ...
What is the ciliary muscle?
49151. Anatomical terms of muscle. The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscle in the eye's middle layer ( vascular layer ). It controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal.
What is the treatment for OAG?
Open-angle glaucoma (OAG) and closed-angle glaucoma (CAG) may be treated by muscarinic receptor agonists (e.g., pilocarpine ), which cause rapid miosis and contraction of the ciliary muscles, opening the trabecular meshwork, facilitating drainage of the aqueous humour into the canal of Schlemm and ultimately decreasing intraocular pressure.
Where does postganglionic innervation originate?
The postganglionic sympathetic innervation arises from the superior cervical ganglia. Presynaptic parasympathetic signals that originate in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus are carried by cranial nerve III (the oculomotor nerve) and travel through the ciliary ganglion via the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers which travel in ...
What is anterior segment dysgenesis?
Anterior segment dysgenesis (ASD) is a congenital (present at birth) condition that impacts the ciliary body. 4 Because ASD affects the development of the front of the eye, it can alter the ciliary body and the cornea, iris, and lens.
What happens if you hit your eye with an airbag?
Blunt trauma, such as an automobile airbag deploying or a hard hit to the head, or small projectiles getting lodged in the eye may damage the ciliary body . This can result in inflammation of the iris and changes in eye pressure (high or low). 7
What is the ciliary body?
The ciliary body is a disk-shaped tissue entirely hidden behind the iris. The inner part is the ciliary muscle, made of smooth muscle. 2 Smooth muscles contract and relax automatically, so you don’t have conscious control over them. Instead, the ciliary body functions in response to natural reflexes based on environmental stimuli.
What is the process of ciliary body?
Without it, it would be nearly impossible to read or see what’s right in front of you. 1. The ciliary body also produces a clear fluid called aqueous humor, which flows between the lens and cornea, providing nutrients and contributing to the fullness and shape of the eye.
What is the secretion of aqueous humor?
The ciliary body’s capillaries secrete aqueous humor, a liquid in the front of the eye that’s responsible for keeping the eye healthy and inflated. 5 Aqueous humor also controls the eye’s pressure and supplies vital nutrients to the lens and cornea. 6.
What are the capillaries in the eye?
Groups of small blood vessels and capillaries toward the eye’s surface make up another section of the ciliary body. 1 The capillaries are responsible for exchanging fluids and other materials between the tissue and the blood cells.
Is intraocular melanoma rare?
Although intraocular melanoma is the most frequent form of eye cancer in adults, it’s rare overall. 10 It grows in the eye’s pigmented cells (melanocytes) and can affect the iris, ciliary body, and choroid.
How does the ciliary body work?
The ciliary body is attached to the lens by the collection of tiny fibrous cords known as the zonular fibers. This attachment is crucial in changing the eye focus by changing the shape of the lens, a process known as accommodation . In order to provide these functions, the ciliary body needs to have rich vascularization and innervation; vascularisation is provided by the branches of the ophthalmic artery , while the nerve supply comes from the ciliary ganglion.
What is the ciliary body?
The ciliary body is an inner eye structure, located at the border between the choroid and the iris. It is composed of several unique structures that give the ciliary body its unique shape and function. These structures include the ciliary muscle, ciliary processes, ciliary vessels and ciliary epithelia. The ciliary muscle is in charge of changing the shape of the lens, while the ciliary processes participate in the production of the fluid in the eye also known as the aqueous humor.
What is the ciliary epithelium made of?
The ciliary epithelium is composed of two epithelial layers the pigmented layer and the non-pigmented layer. The pigmented one is the outer layer of the ciliary body and its processes contain cuboidal cells rich in melanin granules. The non-pigmented layer is the inner layer of columnar cells that are involved in the production of the aqueous humor.
Which vein drains blood from the ciliary body?
The blood from the ciliary body is drained by the vorticose veins. Vorticose veins drain their blood into superior orbital and inferior orbital veins.
Where is the ciliary body located?
The ciliary body is a ring-like thickening located between the anterior border of the choroid and the posterior aspect of the iris. On the cross-section, the ciliary body is triangular with its base near the iris and the apex near the choroid. Together with the iris and choroid, the ciliary body comprises the uveal tract. This tract is sandwiched between an outer layer (sclera) and an inner layer (retina).
Why do people get blind?
Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of blindness in the general population. Its most frequent cause is an obstruction of aqueous humor outflow through the trabecular meshwork. It can also be caused by the increased production of aqueous humor. The abnormal collection of aqueous humor increases the intraocular pressure which leads to the atrophy of the optic nerve (CN II) and progressive loss of vision.
Which nerves travel through the ciliary ganglion?
These fibers travel via the oculomotor nerve (CN III) to the ciliary ganglion. The ciliary ganglion then gives off short ciliary nerves (i.e. postganglionic fibers) that innervate the ciliary body.
What is the function of the ciliary muscles?
The main function of the ciliary musclesused to change the shape of the lens in the eye to help with focusing. Another functionof the ciliary muscles is to help regulate the flow of aqueous humor in the eye.
Which muscle controls the flow of aqueous humor?
The ciliary muscles also control the flow of the aqueous humor.
Where are the ciliary muscles located?
The ciliary muscles are the smooth muscles that are found in the middle of the eye layer.

Overview
The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscle in the eye's middle layer, uvea (vascular layer). It controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal. It also changes the shape of the lens within the eye but not the size of the pupil which is carried out by the sphincter pupillae muscl…
Structure
The ciliary muscle develops from mesenchyme within the choroid and is considered a cranial neural crest derivative.
The ciliary muscle receives parasympathetic fibers from the short ciliary nerves that arise from the ciliary ganglion. The parasympathetic postganglionic fibers are part of cranial nerve V1 (Nasociliary nerve of the trigeminal), while presyna…
Function
The ciliary fibers have circular (Ivanoff), longitudinal (meridional) and radial orientations.
According to Hermann von Helmholtz's theory, the circular ciliary muscle fibers affect zonular fibers in the eye (fibers that suspend the lens in position during accommodation), enabling changes in lens shape for light focusing. When the ciliary muscle contracts, it pulls itself forward and moves the frontal region toward the axis of the eye. This releases the tension on the lens cause…
Clinical significance
Open-angle glaucoma (OAG) and closed-angle glaucoma (CAG) may be treated by muscarinic receptor agonists (e.g., pilocarpine), which cause rapid miosis and contraction of the ciliary muscles, opening the trabecular meshwork, facilitating drainage of the aqueous humour into the canal of Schlemm and ultimately decreasing intraocular pressure.
History
The word ciliary had its origins around 1685–1695. The term cilia originated a few years later in 1705–1715, and is the Neo-Latin plural of cilium meaning eyelash. In Latin, cilia means upper eyelid and is perhaps a back formation from supercilium, meaning eyebrow. The suffix -ary originally occurred in loanwords from Middle English (-arie), Old French (-er, -eer, -ier, -aire, -er), and Latin (-ārius); it can generally mean "pertaining to, connected with", "contributing to", and "for the purpos…
Additional images
• The arteries of the choroid and iris. The greater part of the sclera has been removed.
• Iris, front view.
See also
• Accommodation reflex
• Cycloplegia
• Extraocular muscle
• Presbyopia
External links
• Lens, zonule fibers, and ciliary muscles—SEM Archived 2011-09-28 at the Wayback Machine