
What is the function of the conjugation pilus Quizlet?
What is the function of the conjugation pilus? It pulls the F+ and F- cells together. What is required by an F- cell to become an F+ cell? What is the key difference between donor cells and recipient cells?
What is the function of conjugation pili in bacteria?
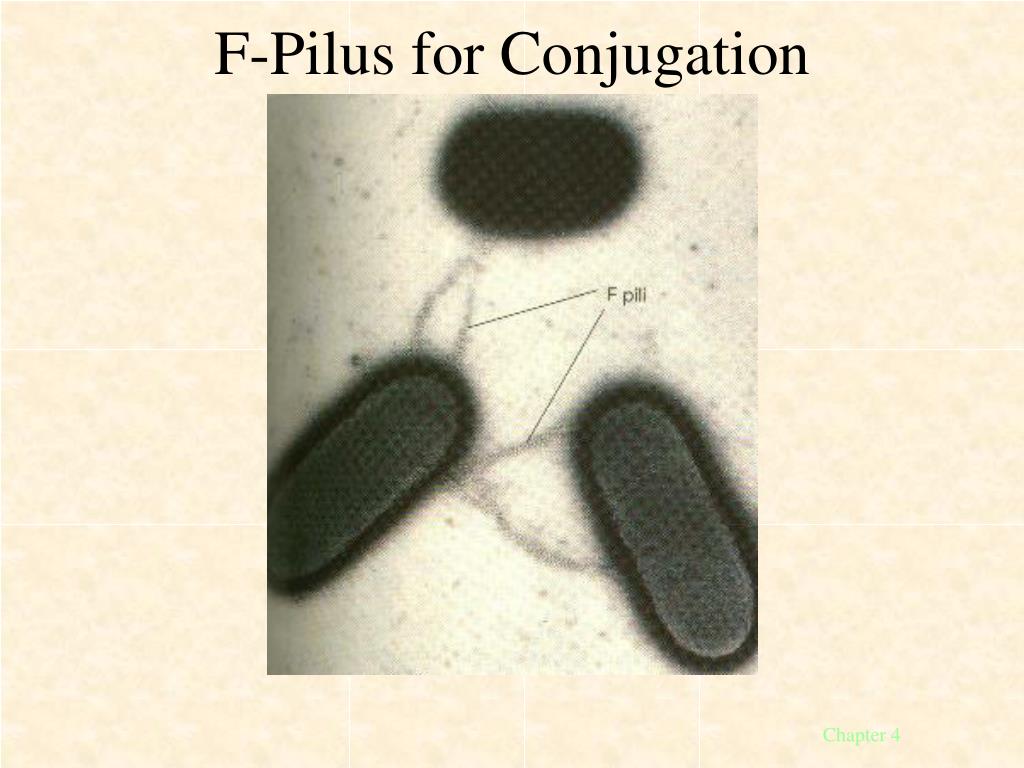
Conjugation pili allow for the transfer of DNA between bacteria, in the process of bacterial conjugation. 1) they initiate contacts between mating pairs. 2) they facilitate the transfer of genetic materials. 3) they draw mating cells into a close contact which increases the fertility of the union. Schematic drawing of bacterial conjugation.
What is the function of the F pilus?
F pilus in bacterial genetics, a hollow tubular pilus possessed by (male) F + cells, the carrier of the F plasmid (fertility plasmid). It forms a connection with a (female) F − cell in bacterial conjugation to allow the transfer of genetic material. pi´li incarna´ti a condition characterized by ingrown hairs.
What is bacterial conjugation and how does it work?
Schematic drawing of bacterial conjugation. Bacteria have evolved the process of conjugation as a way to increase genetic variability. The cell with the conjugation pilus, attaches to another cell, connecting the cytoplasm of each cell and allowing molecules of DNA to pass through the hollow pilus.
What is the function of conjugation pilus quizlet?
What is the function of the conjugation pilus? It carries the chromosome of F- cells. It pulls the F+ and F- cells together.
What is the function of conjugation in bacteria?
Conjugation is the process by which one bacterium transfers genetic material to another through direct contact. During conjugation, one bacterium serves as the donor of the genetic material, and the other serves as the recipient. The donor bacterium carries a DNA sequence called the fertility factor, or F-factor.
What does the pilus in bacteria do?
Pili are crucial virulence factors for many Gram-negative pathogens. These surface structures provide bacteria with a link to their external environments by enabling them to interact with, and attach to, host cells, other surfaces or each other, or by providing a conduit for secretion.
What are the two functions of pili?
Type IV pili are a type of Pili found in some Gram-positive bacteria (e.g., clostridia) and the majority of Gram-negative bacteria. They have several important functions ranging from their role in locomotion to DNA exchange.
What is conjugation and why is it important?
5.1. 3 Conjugation. Conjugation is an important process for genetic exchange between bacteria. The process needs mating of donor cell and recipient cell, and involves a cis-acting nick site (oriT) and the trans-acting functions given by a transfer protein.
What is conjugation in bacterial cells?
Bacterial conjugation, also referred to as bacterial sex, is a major horizontal gene transfer mechanism through which DNA is transferred from a donor to a recipient bacterium by direct contact.
What is a pilus bacterial conjugation?
Conjugative pili allow the transfer of DNA between bacteria, in the process of bacterial conjugation. They are sometimes called “sex pili”, in analogy to sexual reproduction, because they allow for the exchange of genes via the formation of “mating pairs”.
What is the meaning of pilus?
a hairDefinition of pilus : a hair or a structure (as on the surface of a bacterial cell) resembling a hair.
What is a pilus in biology?
A pilus (Latin for 'hair'; plural: pili) is a hair-like appendage found on the surface of many bacteria and archaea. The terms pilus and fimbria (Latin for 'fringe'; plural: fimbriae) can be used interchangeably, although some researchers reserve the term pilus for the appendage required for bacterial conjugation.
What is the function of the pili in a prokaryotic cell?
Prokaryotes often have appendages (protrusions) on their surface. Flagella and some pili are used for locomotion, fimbriae help the cell stick to a surface, and sex pili are used for DNA exchange.
What are the functions of pili and fimbriae?
Fimbriae and pili are hair-like appendages present on the bacterial cell wall similar to flagella. They are shorter than flagella and more in number. They are involved in the bacterial conjugation, attachment to the surface and motility.
What is difference between pili and fimbriae?
Difference between Fimbriae and Pili Pili are fine hair-like microfibers having pilin – a thick tubular structure while the fimbriae are tiny bristle-like fibers emerging from the surface of the bacterial cells. Pili are longer than fimbriae.
What is the value of conjugation to bacteria?
Conjugative plasmids act as vectors of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) between bacteria, trafficking beneficial accessory traits such as antibiotic resistance [1].
How do bacteria reproduce by conjugation?
In conjugation, one bacterium grows a duct, called a pilus, which attaches to the other bacterium. A genetic element known as a plasmid is then passed through the pilus from the donor cell to the recipient. In another case, viruses play a role in genetic exchange between bacteria.
Which of the following is used in conjugation bacteria?
Flagella helps in locomotion and pili helps in conjugation by forming sex pillus in bacteria.
What is bacterial conjugation quizlet?
conjugation. bacterial 'mating' process during which a one-way transfer of genetic material occurs through a sex pilus from the donor strain and the recipient strain.
Basic Biology of Oral Microbes
The pilus is a hair-like structure associated with bacterial adhesion and related to bacterial colonization and infection. Pili are primarily composed of oligomeric pilin proteins, which arrange helically to form a cylinder. New pilin protein molecules insert into the base of the pilus.
Neisseria
Pili are hair-like fibers consisting of thousands of protein subunits (pilin, 16–20 kDa). 20 Pathogenic Neisseria spp. have long pili (up to 4300 nm in length), termed type IV pili, that protrude from the bacterial surface (see Figure 179-6 ). Nonpathogenic Neisseria spp. may express both long and short pili (175–210 nm in length).
Aeromonas
Pili function as adhesive factors for mucosal surface attachment. Aeromonas species possess two major types of pili: short rigid pili (S/R type or type I) and long wavy flexible pili (L/W pili, which can be further separated into type IV and mini-pilin) ( Table 61.2 ). Straight (type I) pili (of 0.6–2.0 µm in length) are found in A. hydrophila.
Advances in Bacterial Pathogen Biology
Rebecca Lowry, ... Jonathan G. Shaw, in Advances in Microbial Physiology, 2014
Adhesive pili of the chaperone-usher family
Vasilios Kalas, ... Scott J. Hultgren, in Escherichia coli (Second Edition), 2013
Hair Loss in Children
Pili annulati refers to alternating bright and dark bands, with the bright areas corresponding to light scattered from clusters of air-filled cavities within the cortex. 34 Pili annulati is also known as ringed hair because of the alternating dilations of the medulla that produce the banded appearance.
pilus
A hair or hairlike structure, especially a proteinaceous structure projecting from the surface of a bacterium that is smaller than a flagellum and functions in DNA transfer during conjugation and, usually with other such structures, in adhesion.
pilus
a hair-like structure on the surface of bacteria which may be associated with bacterial CONJUGATION (the sex pilus) or with adhering bacteria to surfaces. See also FIMBRIA.
