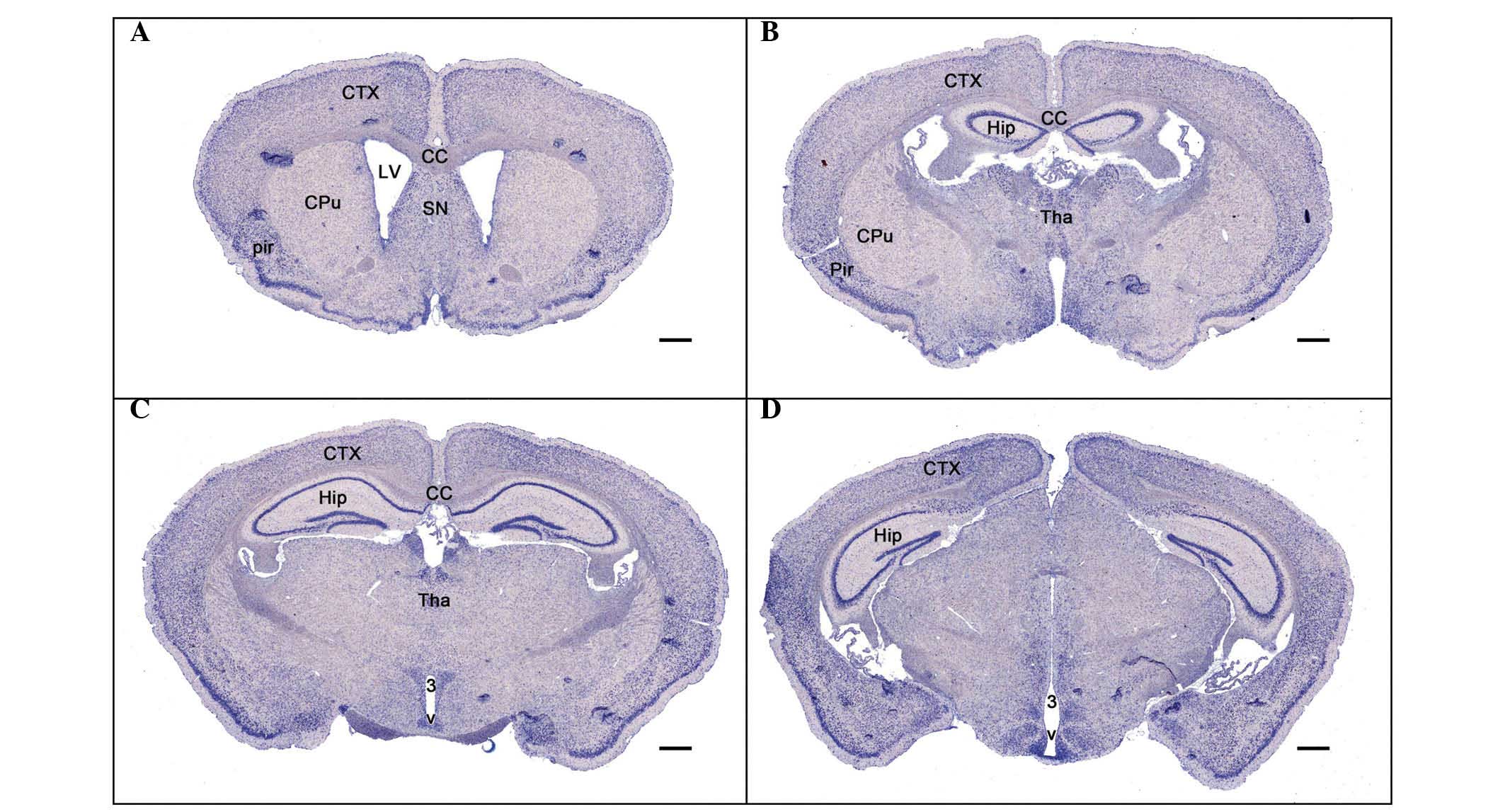
What is the corpus callosum and what does it do?
The corpus callosum is a large white matter tract that connects the two hemispheres of the brain. It is an incredibly important structural and functional part of the brain. It allows us to perceive depth and enables the two sides of our brain to communicate. The corpus callosum gets its name from the Latin language (“tough body”).
Would do you expain what the corpus callosum do?
The corpus callosum is a thick band of nerve fibers that divides the cerebral cortex lobes into left and right hemispheres. It connects the left and right sides of the brain, allowing for communication between both hemispheres. The corpus callosum transfers motor, sensory, and cognitive information between the brain hemispheres.
What happens if the corpus callosum is damaged?
The corpus callosum joins the two parts of the brains together. When severed or damaged, communication between the two parts is inhibited, causing problems if a situation requires the two parts of the brain to work in unison.
What are the functions of corpus luteum?
Corpus Luteum Function. The corpus luteum’s main function can be distilled down to its role in supporting the early pregnancy in the female body. It does so by releasing progesterone and estrogen. This mixture will cause the uterine mucosa to undergo all of the changes it needs to prepare for the successful implantation of a fertilized embryo.

What is the function of the corpus callosum in the brain quizlet?
The Corpus Callosum is the part of the mind that allows communication between the two hemispheres of the brain. It is responsible for transmitting neural messages between both the right and left hemispheres.
What does the corpus callosum do in everyday life?
The corpus callosum plays an important role in vision by combining the separate halves of our visual field, which process images separately in each hemisphere. It also allows us to identify the objects we see by connecting the visual cortex with the language centers of the brain.
What is the location and function of the corpus callosum?
What does the corpus callosum do? The corpus callosum connects the left side of the brain to the right side, each side being known as a hemisphere. The connection allows information to pass between the two halves.
What will happen if the corpus callosum is damaged?
Lesions of any part of the corpus callosum might lead to loss of contact between bilateral hemispheres that cause mental disorders, pseudobulbar palsy, speech and movement ataxia.
What happens if a person's corpus callosum is damaged?
Since each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body, the brain must coordinate movements with both sides. This coordination is mediated by the corpus callosum. If the corpus callosum is damaged, then signals cannot pass from one hemisphere to the other. This can lead to serious coordination problems.
How does the corpus callosum affect behavior?
Impaired social functioning is a well-known outcome of individuals with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Social deficits in nonliteral language comprehension, humor, social reasoning, and recognition of facial expression have all been documented in adults with agenesis of the corpus callosum.
Can you survive without a corpus callosum?
(Getty Images) The corpus callosum links one side of the brain to the other. It's not essential for survival, but in some people it's missing or malformed, causing mild to severe disabilities.
Can you live a normal life without a corpus callosum?
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a rare brain malformation that happens as your baby develops in the womb. It causes varying symptoms and challenges from mild to severe. Many children with this malformation can live a normal life.
How does the corpus callosum affect behavior?
Impaired social functioning is a well-known outcome of individuals with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Social deficits in nonliteral language comprehension, humor, social reasoning, and recognition of facial expression have all been documented in adults with agenesis of the corpus callosum.
What is an example of the corpus callosum?
For example, when you type on your keyboard, information about the feel of the keys is sent up from your right hand to the primary somatosensory cortex on the left side of your brain. That information, however, must then be shared with the right side of your brain as well.
Does the corpus callosum affect intelligence?
People with agenesis of the corpus callosum (AgCC) with normal general intelligence have deficits in complex cognitive processing, as well as in social cognition.
What happens if there is damage to the corpus callosum?
Damage of the corpus callosum typically occurs via intentional surgery. This results in a brain that cannot relay most of its messages from one hem...
What part of the brain is the corpus callosum located in?
The corpus callosum resides in the middle of the brain in between the left and right hemispheres. It makes up the roof of the lateral ventricles an...
Can you live without corpus callosum?
Patients who have had their corpus callosum split (and thus do not have a functioning corpus callosum) can still live full lives. These individuals...
What is the primary function of corpus callosum?
The primary function of the corpus callosum is to relay information between the right and left hemispheres. Each portion of the corpus callosum is...
How does the corpus callosum affect behavior?
The corpus callosum contributes to behavior by allowing the two halves of the brain to communicate. The brain must relay sensory information and co...
What is the corpus callosum and what is its normal function?
The corpus callosum is a c-shaped structure in the middle of the brain, composed of white matter, that is responsible for relaying messages from on...
What are the functions of the corpus callosum?
The corpus callosum is the largest fiber bundle in the brain, containing nearly 200 million axons. It is composed of white matter fiber tracts known as commissural fibers. It is involved in several functions of the body including: 1 Communication between brain hemispheres 2 Eye movement and vision 3 Maintaining the balance of arousal and attention 4 Tactile localization
How does the corpus callosum help us?
The corpus callosum plays an important role in vision by combining the separate halves of our visual field, which process images separately in each hemisphere. It also allows us to identify the objects we see by connecting the visual cortex with the language centers of the brain. In addition, the corpus callosum transfers tactile information (processed in the parietal lobes) between the brain hemispheres to enable us to locate touch .
How long does it take for a corpus callosum to develop?
The corpus callosum typically develops between 12 and 20 weeks and continues to experience structural changes even into adulthood. AgCC can be caused by a number of factors including chromosome mutations, prenatal infections, exposure of the fetus to certain toxins or medications, and abnormal brain development due to cysts.
What is the corpus callosum?
Regina Bailey. Updated January 29, 2020. The corpus callosum is a thick band of nerve fibers that divides the cerebral cortex lobes into left and right hemispheres. It connects the left and right sides of the brain, allowing for communication between both hemispheres. The corpus callosum transfers motor, sensory, ...
Which lobes of the brain are connected by the rostrum?
The rostrum and genu connect the left and right frontal lobes of the brain. The body and splenium connect the hemispheres of the temporal lobes and the hemispheres of the occipital lobes . The corpus callosum plays an important role in vision by combining the separate halves of our visual field, which process images separately in each hemisphere.
Where is the corpus callosum located?
Directionally, the corpus callosum is located underneath the cerebrum at the midline of the brain . It resides within the interhemispheric fissure, which is a deep furrow that separates the brain hemispheres.
What is the largest fiber bundle in the brain?
The corpus callosum is the largest fiber bundle in the brain, containing nearly 200 million axons. It is composed of white matter fiber tracts known as commissural fibers. It is involved in several functions of the body including:
What is the role of the corpus callosum in cognitive function?
Besides its importance in communication, the corpus callosum is hypothesized to play a primary role in cognition. Emerging evidence suggests that weakened integrity of the callosum contributes to a decline in cognitive function in aging adults.
Why is the corpus callosum important?
It is an incredibly important structural and functional part of the brain. It allows us to perceive depth and enables the two sides of our brain to communicate. The corpus callosum gets its name from the Latin language (“tough body”).
What are the four parts of the corpus callosum?
The corpus callosum is divided into four parts: rostrum, genu, body/trunk and splenium. The rostrum is continuous with the lamina terminalis and connects the orbital surfaces of the frontal lobes. The genu is the bend of the anterior corpus callosum and the forceps minor is a tract that projects fibres from the genu to connect ...
What is the superior aspect of the corpus callosum?
The superior aspect of the corpus callosum is covered with a thin layer of glial tissue under the pia mater, known as the indusium griseum, over which run on either side of the midline one or two strips of grey matter, i.e. the longitudinal striae.
Which part of the limbic system is attached to the fornix?
The cingulate gyrus is a component of the limbic system and lies superolateral to the corpus callosum. The callosal sulcus separates the two structures. The anterior part of the corpus callosum (rostrum, genu, body) is attached inferiorly to the fornix by the septum pellucidum while the splenium is attached inferiorly to the crura and ...
Where does the corpus callosum get its blood?
The vast majority of the blood supply to the corpus callosum comes from callosal branches of the pericallosal artery, whose course follows the outer border of the corpus callosum, first in the subcallosal area, then in the callosal sulcus or in the cingulate sulcus.
Which lobes of the hemispheres are connected by the rostrum and genu?
Eg the rostrum and genu connect the frontal lobes of the left and the right hemisphere, the body and the splenium connect the temporal lobes of the hemispheres as well as the occipital lobes. In this way the similar areas are interconnected and communicate in a way that there is a harmonization of their functions.
What is the largest collection of white matter within the brain?
The corpus callosum is the largest collection of white matter within the brain, and it has a high myelin content. Myelin is a fatty, protective coating around nerves that facilitates quicker transmission of information. White matter should not be confused with gray matter. The brain uses gray matter for computation, thinking, memory storage, ...
Why do surgeons cut the corpus callosum?
In modern neurosurgery, some surgeons have surgically cut the corpus callosum as a means for treating epileptic seizures. By disrupting contact between the two brain hemispheres, a seizure can be isolated and kept from spreading. Last medically reviewed on April 14, 2015.
What is white matter?
White matter should not be confused with gray matter. The brain uses gray matter for computation, thinking, memory storage, and more. White matter, like the corpus callosum, allows different parts of the brain to communicate with each other. Some congenital (birth) defects include a complete lack of this neural tissue.
How many axons are in the brain?
This bundle of nerve tissue contains over 200 million axons ...
What is the Corpus Callosum?
These messages can pass from one side of the brain to another via the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum is an important structure in the brain that plays a major role in nervous system communication, as well as contributing to its own important functions. In this lesson, investigate how the corpus callosum, its location, and its functions contribute to a well-functioning brain.
How does the corpus callosum contribute to behavior?
The corpus callosum contributes to behavior by allowing the two halves of the brain to communicate. The brain must relay sensory information and complex thought between the two halves of the brain in order to formulate a response, or behavior, to a stimulus. When the corpus callosum is absent, this communication cannot occur.
What is the structure that connects the two halves of the brain?
The two halves (or hemispheres) of the brain are connected via a c-shaped structure called the corpus callosum . The corpus callosum sits in the middle of the brain in between the right and left hemispheres and allows for neural messages to pass from one side to another. There are four parts of the corpus callosum:
How does corpus callosum damage occur?
Damage of the corpus callosum typically occurs via intentional surgery. This results in a brain that cannot relay most of its messages from one hemisphere to the next.
What is a split brain?
Split-brain patients are those who have had their corpus callosum severed in a procedure known as a corpus callosotomy. This procedure was typically performed on those suffering from serious seizure activity and was reserved as a last resort for those who could not find relief through safer alternatives. The surgery decreased the frequency of seizure activity but resulted in two halves of the brain that could no longer communicate. Sperry and other researchers observed these patients to understand what they could no longer do. This observation led to a deeper understanding of what the corpus callosum was responsible for.
Why did Sperry win the Nobel Prize?
Sperry eventually won a Nobel Prize for identifying the communicative properties of the corpus callosum and allowing scientists in the 1960s to understand that nerve fibers within the corpus callosum. Even with this information, scientists today are still learning the complexity and function of this important structure.
What is the term for the abnormal growth of the corpus callosum?
Dysgenesis of the corpus callosum occurs when the structure is abnormally developed. Usually, the corpus callosum will start to develop normally, but due to trauma, an underlying disease, or toxicity, will become abnormal as it continues to grow. Dysgenesis may be seen in children with other major diseases such as Dandy-Walker syndrome, a disease that results in malformed ventricles.
What is the corpus callosum?
The corpus callosum is the primary commissural region of the brain consisting of white matter tracts that connect the left and right cerebral hemispheres. It is composed of approximately 200 million heavily myelinated nerve fibers that form homotopic or heterotopic projections to contralateral neurons in the same anatomical layer.[1] During infancy, the corpus callosum expands rapidly due to an increase in the number of axons, axon diameter, and myelin. Although the development of the corpus callosum is complete by age four, growth continues until the third decade of life at a much slower rate.[1] Anatomically from anterior to posterior, the corpus callosum is composed of four parts based on previous histological findings: the rostrum, genu, body, and splenium, each responsible for connecting distinct areas of the cortex. The isthmus refers to the narrow region between the body and splenium in the posterior aspect of the corpus callosum.[2] Fibers of the genu cross over and give rise to the forceps minor, a connection between regions of the frontal cortices.[2] The fibers of the splenium move posteriorly and contribute to the forceps major, providing a connection between the occipital lobes.[3] The body fibers form the corona radiata as well as other large white matter pathways as they move transversely through the cerebral cortex. Finally, the orbital regions of the frontal lobes connect via the rostral fibers.[3] Due to its anatomical location, the corpus callosum is strongly related to the fornix and lateral ventricles. In conjunction with the fornix, the corpus callosum forms a physical barrier to separate the two lateral ventricles.[3]
What is age related alterations in axonal microstructure in the corpus callosum measured by?
Age-related alterations in axonal microstructure in the corpus callosum measured by high-gradient diffusion MRI.
Which artery provides arterial blood to the corpus callosum?
The internal carotid artery network provides arterial blood supply to a majority of the corpus callosum, specifically via the pericallosal artery (a branch of the anterior cerebral artery). The splenium is the exception as it receives vascular input from the vertebrobasilar system. The terminal and choroidal branches of the posterior cerebral artery supply the splenium with arterial blood. Venous drainage occurs via the callosal and callosal cingular veins and, ultimately, the internal cerebral veins. [7]
How many axons are in the corpus callosum?
There are approximately 200 million axons that form the corpus callosum, which arises primarily from neurons in neocortical layers II/III, V, and VI.[5] At 12 to 13 weeks of gestation, nerve fibers begin to cross the midline, giving rise to connections that later become the corpus callosum. By 18 weeks, all four components of the corpus callosum can be visualized using a transvaginal sonogram.[6] There is some debate about the anatomic direction in which development progresses; some data support the hypothesis that the corpus callosum develops in the cranial/caudal direction while others have observed the opposite developmental pattern. Interestingly, the corpus callosum is present in all primates and evolved with the neocortex. [7]
How many cerebral commissures are there in a rhesus monkey?
Cytological and quantitative characteristics of four cerebral commissures in the rhesus monkey.
What is NCBI bookshelf?
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
What is the structure and function of the corpus callosum?
Answer: The corpus callosum is the dense white matter tract that spans both hemispheres. Its main function is to allow communication between the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
What causes callosal agenesis?
Genetic factors that get damaged during development, prenatal exposure to toxins or metabolic disorders may all contribute to the likelihood that callosal agenesis develops.
How many divisions are there in the corpus callosum?
The corpus callosum can be divided into roughly four divisions. From rostral (anterior) most to causal (posterior) most, they are as follows:
What is the largest white matter tract in the human brain?
The largest white matter tract in the human brain is the corpus callosum. It is made up of more than 200 million axons. Anatomically speaking, the corpus callosum is the ventral base of the midline fissure (longitudinal fissure), the major division that separates the left and the right hemisphere. The corpus callosum also makes up ...
Which lobes are connected by the corpus callosum?
Splenium. At the posterior most end of the corpus callosum, the splenium connects the two occipital lobes. All four lobes are connected across the hemispheres by the corpus callosum at some point.
Where does the corpus callosum get its blood flow?
Specifically, the structure get its blood flow from the capillaries that branch of the pericallosal arteries, which stem off the anterior cerebral artery.
When is neural development affected in the fetus?
They believe that if neural development is affected early in the fetus, especially between the 3rd and 12th weeks of pregnancy. Children born with agenesis of the corpus callosum generally are generally healthy.
What is the corpus callosum?
The corpus callosum is an elongated structure perpendicular to the interhemispheric fissure, so that each of its ends enters a different hemisphere.
What happens when the corpus callosum is sectioned?
Callosotomy is what happens when, in a clinical or scientific context, the corpus callosum is sectioned. so he can no longer communicate both sides of the brain. This is an important change in the functioning of the central nervous system, since although there are other interhemispheric commissures, the corpus callosum is by far the largest.
What is the most visible part of the brain?
The corpus callosum is one of the most visible and striking parts of the brain when studying the human nervous system.
Why is the genu called the knee?
The genu, or knee of the corpus callosum is so called because it creates a very sharp curve back and forth, so that it is a little closer to the brain lobes than the rostrum. It is crossed by nerve fibers that keep the prefrontal cortex of the left and right hemisphere connected.
Which part of the corpus callosum is glued to the isthmus of the cingulate turn?
The splenium is easy to distinguish from the rest of the parts of the corpus callosum because it is the back end. which is glued to the isthmus of the cingulate turn and has a rounded ending. It has nerve associations with the temporal and occipital lobes of each hemisphere, and with the pineal gland.
Which structure is perpendicular to the interhemispheric fissure?
The corpus callosum is an elongated structure perpendicular to the interhemispheric fissure, so that each of its ends enters a different hemisphere.
How many cerebral hermispheres are there in the brain?
Bearing in mind that the anatomy of the brain is characterized by the existence of two cerebral hermispheres, one on the left and the other on the right, and that these are relatively isolated from each other (as they are separated in a good part of their surface by the interhemispheric fissure), we can already begin to intuit that the commissure fibres matter a lot, because information travels through them that only has a few very limited points in order to be able to access the other side of the brain.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/sulcus-calcarinus-2/L7TNDAd1a8vp4magfGipw_Sulcus_calcarinus_01.png)