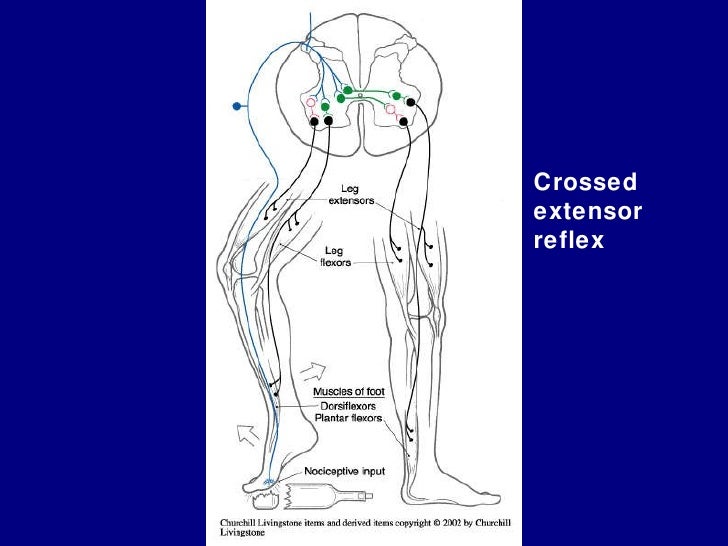
What is the function of the crossed extensor reflex? The crossed extensor reflex is a contralateral
Anatomical terms of location
Standard anatomical terms of location deal unambiguously with the anatomy of animals, including humans. All vertebrates (including humans) have the same basic body plan — they are bilaterally symmetrical. That is, they have mirror-image left and right halves if divided down the centre. For these reasons, the basic directional terms can be considered to be those used in vertebrates.
What does crossed adductor reflex mean?
What does crossed adductor reflex mean? Description: There is hyperreflexia of the right knee jerk (3+) with a rightsided crossed adductor response (the crossed adductor contraction occurred because of the increased right leg tone which resulted in reflex contraction of the adductor magnus with the very slight stretch of this muscle caused by ...
What is a crossed extensor reflex?
The crossed extensor reflex or crossed extensor response or crossed extension reflex is a reflex in which the contralateral limb compensates for loss of support when the ipsilateral limb withdraws from painful stimulus in a withdrawal reflex.
What are some examples of reflexes?
We have briefly explained some reflex action examples in humans in the following points:
- We close our eyes when a bright or shining light or torch hits our eyes.
- We suddenly withdraw our hands or legs when they touch something sharp, hot, or pricking objects.
- We cough or sneeze due to irritants, thread or foreign substances in the nasal passage.
- We perform batting of eyelids frequently when something irritates our eyes.
What are primitive motor reflexes?
Primitive reflexes are involuntary motor responses originating in the brainstem present after birth in early child development that facilitate survival. Several reflexes are important in the assessment of newborns and young infants.
What is the function of the crossed extensor reflex quizlet?
Causes extensor muscles on the side opposite (contralateral) side of the painful stimulus to contract. This causes the opposite leg to straighten to support shifting weight when one foot Is withdrawn from a painful stimulus.
Why is the crossed extension reflex important when stepping on a sharp object?
Pushing down hard on a sharp/unsafe object hurts more, but rapid flexion and extension of the opposite leg enables you to quickly transfer your body weight to the left foot and step away with the hurt right foot. This is the protective motor pattern of the Leg Cross Flexion- Extension Reflex.
How do you test a crossed extensor reflex?
This is a primitive reflex that is usually is only present until one month of age. The examiner holds one of the baby's legs extended and applies firm pressure to the sole of the foot of the same leg. The baby's free leg flexes, adducts and then extends.
Is crossed extensor reflex normal?
The crossed extensor reflex generally is considered an abnormal reflex except in the standing position. In the normal recumbent animal, the extension response is inhibited through descending pathways. Crossed extensor reflexes result from lesions in ipsilateral descending pathways, a sign of UMN disease.
What is the receptor for the crossed extensor reflex?
0:212:58Crossed Extensor Reflex - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhich shifts the foot away from the stimulus it's contracting the muscle here of the hamstring toMoreWhich shifts the foot away from the stimulus it's contracting the muscle here of the hamstring to flick that leg away now this is a simple reflex arc.
Is the crossed extensor reflex an example of postural reflex?
A crossed extensor reflex is a postural reflex initiated by withdrawal from a painful stimulus; the extensor muscles contract, but the corresponding flexors are inhibited.
What is the difference between a crossed extensor reflex and a withdrawal reflex?
During a withdrawal reflex, the flexors in the withdrawing limb contract and the extensors relax, while in the other limb, the opposite occurs as part of the crossed extensor reflex.
Is crossed extensor reflex autonomic?
Answer and Explanation: A crossed extensor reflex is an autonomic reaction to a stimulus that activates the side of the body that is opposite to the stimulus.
Is the crossed extensor reflex ipsilateral or contralateral?
Crossed Extensor Reflex: The crossed extensor reflex is a withdrawal reflex where the contralateral (opposite side) limb makes up for the loss of support created when the ipsilateral (same side) limb withdraws from a painful external stimulus.
Is crossed extensor reflex somatic?
The crossed extensor reflex is also known as the Cross-body Motor Reflex and is one of the Somatic Reflexes we discussed previously. Let's look at a practical example of stepping on a nail with your right foot.
How many synapses are involved in crossed extension reflex?
1 synapseThis means that there is only 1 synapse in the neural circuit needed to complete the reflex. It only takes about 50 milliseconds of time between the tap and the start of the leg kick...that is fast. The tap below the knee causes the thigh muscle to stretch. Information is sent to the spinal cord.
What do abnormal reflexes indicate?
When reflex responses are absent this could be a clue that the spinal cord, nerve root, peripheral nerve, or muscle has been damaged. When reflex response is abnormal, it may be due to the disruption of the sensory (feeling) or motor (movement) nerves or both.
What is crossed adductor reflex?
Adduction of the opposite thigh and extension of the opposite lower leg also can occur simultaneously if those reflexes are hyperactive. Note that this so-called crossed thigh adduction or leg extension tells you that the reflexes in the opposite leg are hyperactive.
Is crossed extensor reflex autonomic?
Answer and Explanation: A crossed extensor reflex is an autonomic reaction to a stimulus that activates the side of the body that is opposite to the stimulus.
Is crossed extensor reflex somatic?
The crossed extensor reflex is also known as the Cross-body Motor Reflex and is one of the Somatic Reflexes we discussed previously. Let's look at a practical example of stepping on a nail with your right foot.
Is crossed extensor reflex somatic or autonomic?
CardsTerm Somatic Reflexes are...Definition 1)Abdominal Reflex 2)Achilles Reflex 3)Corneal Reflex 4)Crossed-Extensor Reflex 5)Gag Reflex 6)Plantar Reflex 7)Patellar ReflexTerm Ciliospinal ReflexDefinition SympatheticTerm Salivary Reflexes are...Definition Parasympathetic11 more rows•Feb 23, 2010