Enzymes that participate in the eukaryotic DNA replication process include:
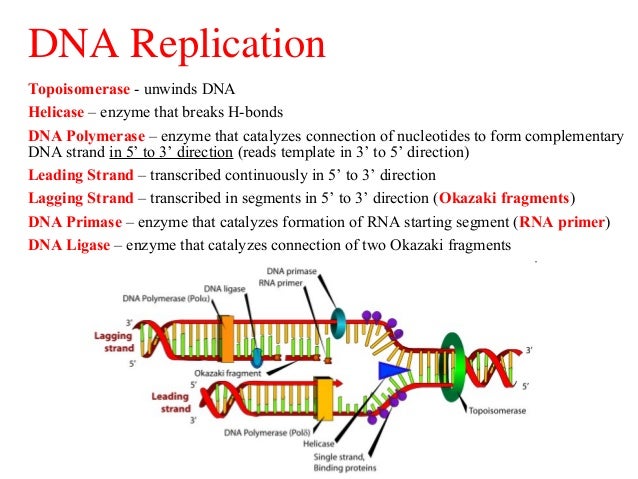
- DNA helicase - unwinds and separates double stranded DNA as it moves along the DNA. ...
- DNA primase - a type of RNA polymerase that generates RNA primers. ...
- DNA polymerases - synthesize new DNA molecules by adding nucleotides to leading and lagging DNA strands.
What does the helicase do during replication?
Upon the initiation of DNA replication, an enzyme called helicase is recruited to unzip the DNA strand into two single stranded DNA structures. Helicases are a class of enzymes that all perform the same function during DNA replication. Over 95 genes code for different helicases in human cells.
How does helicase actually "unwind" DNA?
- The first step in DNA replication is to ‘unzip’ the double helix structure of the DNA molecule.
- This is carried out by an enzyme called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the complementary bases of DNA together (A with T, C with G).
- The separation of the two single strands of DNA creates a ‘Y’ shape called a replication ‘fork’. ...
- 1. ...
What is the role of Okazaki fragments in DNA replication?
The process of DNA replication can be summarized as follows:
- DNA unwinds at the origin of replication.
- Helicase opens up the DNA-forming replication forks; these are extended in both directions.
- Single-strand binding proteins coat the DNA around the replication fork to prevent rewinding of the DNA.
- Topoisomerase binds at the region ahead of the replication fork to prevent supercoiling (over-winding).
What happens to histones during a DNA replication?
- Yes, genes code for histone proteins ( Histone gene, HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee ).
- Histone gene transcription is coupled with DNA replication and is regulated by the cell cycle.
- Most of the histone proteins are largely synthesized during the S phase

What is DNA Replication?
During its lifetime, the cell undergoes several stages of molecular characteristics, referred to as the cell cycle. The cell cycle is composed of 4 main stages: G1, S, G2, and M. All stages that occur prior to the last stage, M, in which the cell divides, occur to ensure the cell divides properly.
Molecular Mechanism of DNA Replication
DNA replication is dependent on many enzymes, in order to be carried out efficiently. DNA is double stranded in nature, and in order to be replicated, this structure has to be unzipped. The site of initial unwinding is referred to as the origin of replication.
Helicases in DNA Replication
The first step of DNA replication is to unwind the double stranded structure, in order to promote semi-conservative replication. This process is mediated by an enzyme, referred to as the helicase enzyme.
What is DNA Double Helix?
DNA is a double stranded molecule, where the shape of it, is sometimes referred to as the double helix. DNA is composed of monomers, referred to as nucleotides. Nucleotides are further composed of a sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogen containing base.
Answer
The function of Helicase in the process of DNA replication is to untwist the double helix and separating the two DNA strands. This action of helicase creates the replication forks and replication bubbles where the process of replication is initiated.
Did this page answer your question?
To support your homeschooling, we're including unlimited answers with your free account for the time being.
Molecular Mechanism of DNA Replication
Helicases in DNA Replication
- The first step of DNA replication is to unwind the double stranded structure, in order to promote semi-conservative replication. This process is mediated by an enzyme, referred to as the helicase enzyme. Helicase, in DNA replication, breaks the hydrogen bonds that hold the double strand together to expose the single strands, in order to kickstart r...
What Is DNA Double Helix?
- DNA is a double stranded molecule, where the shape of it, is sometimes referred to as the double helix. DNA is composed of monomers, referred to as nucleotides. Nucleotides are further composed of a sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogen containing base. The sequence of nitrogen containing bases in DNA is what is known as the genetic code, and is vital for DNA function in di…