
What does the dorsal root ganglia do?
Sensory ganglia, or dorsal root ganglia, send sensory information to the central nervous system. This information includes touch, smell, taste, sound, and visual stimuli. They also deliver information about body position and sensory feedback relating to organs.
What are ganglion's functions?
The term "ganglion" refers to the peripheral nervous system. However, in the brain (part of the central nervous system), the "basal ganglia" is a group of nuclei interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, associated with a variety of functions: motor control, cognition, emotions, and learning.
What is the function of the dorsal and ventral roots?
What is the function of the dorsal and ventral roots? Each spinal nerve is formed by the combination of nerve fibers from the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord. The dorsal roots carry afferent sensory axons, while the ventral roots carry efferent motor axons. How many dorsal root ganglion are there?
What does the dorsal root ganglia mainly contain?
The dorsal root ganglia mainly contain: axons of sensory neurons. cell bodies of sensory neurons. axons of motor neurons. synapses cell bodies of motor neurons.

What is the function of the dorsal root ganglion quizlet?
The dorsal root ganglion contains cell bodies of sensory neurons. Ventral root joins with the dorsal root to form the spinal nerve. Divides into the ventral and dorsal rami. Smaller dorsal ramus supplies all structures of the back.
What is the function of a ganglion?
Ganglia is the plural of the word ganglion. Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies found throughout the body. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and carry nerve signals to and from the central nervous system.
What is the dorsal root ganglion made of?
The dorsal root ganglia (DRG) are a collection of cell bodies of the afferent sensory fibers, which lie between adjacent vertebrae.
What is the function of the dorsal?
The function of the dorsal cavity gives rise to sensation and perception of the nervous system. The nerves originate at the spinal cord, then travel long distances to innervate different regions of the body.
What is dorsal ganglion?
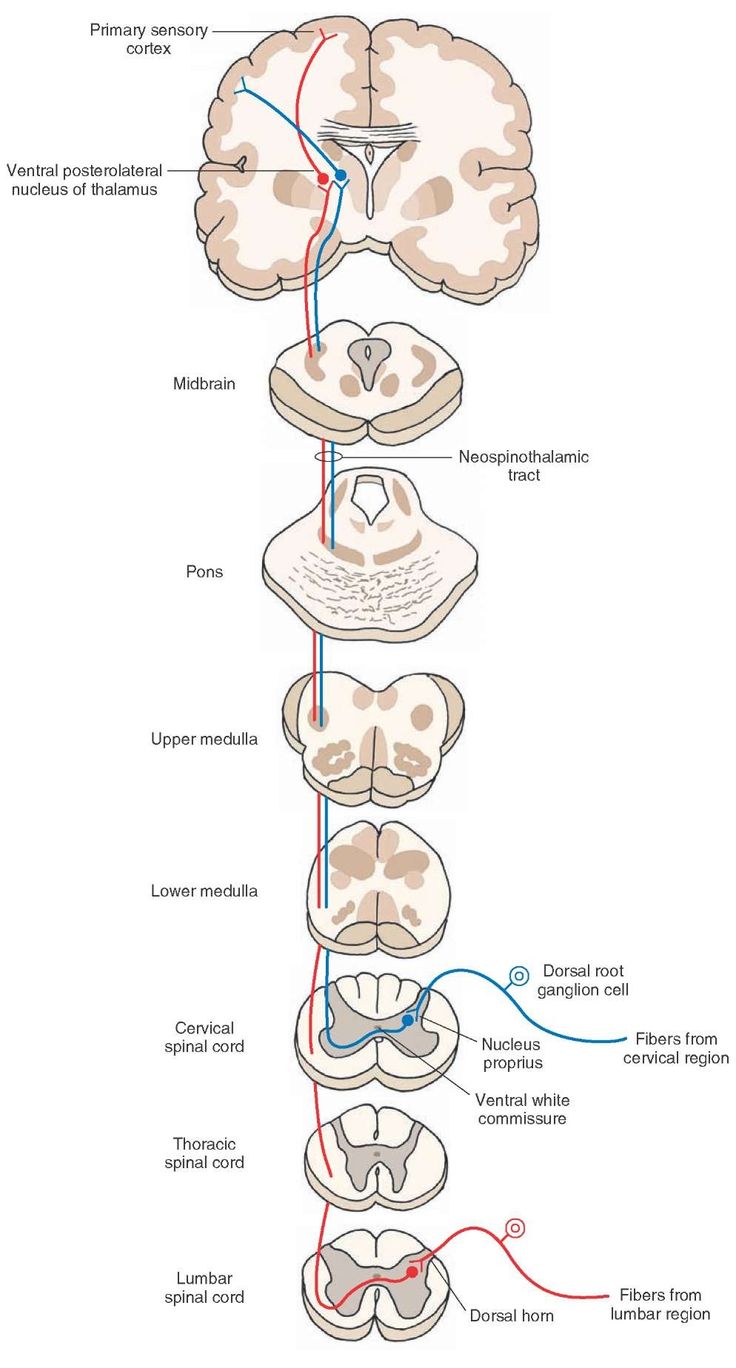
As the dorsal root emerges from the intervertebral neural foramina, it forms the dorsal root gangliondorsal root ganglionA dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Dorsal_root_ganglionDorsal root ganglion - Wikipedia (DRG). The DRG is a group of cell bodies responsible for the transmission of sensory messages from receptors such as thermoreceptors, nociceptors, proprioceptors, and chemoreceptors, to the CNS for a response.
What is the difference between nerve and ganglion?
Both nerves and ganglia are structures found in the nervous system. However, a ganglion refers to a collection of nerve cells outside of the CNS whereas a nerve is the axon of a neuron. An afferent neuron, by the way, carries impulses whereas an efferent neuron is involved in motor functions.
Where is a dorsal root ganglion?
spinal nerveA dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia.
Is dorsal root ganglion CNS or PNS?
peripheral nervous systemThe dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) are located in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), between the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and the peripheral nerve terminals, and contain various cell types such as satellite glial cells, endothelial cells, macrophages and primary sensory neurons.
What happens to the body if the dorsal root or ganglion is damaged?
When a dorsal root or ganglion is damaged, the sensory information may be altered as it is passed into the spinal cord, or it is not transmitted to the spinal cord at all. This results in reduced or no ability to sense stimuli from that peripheral nerve.
Is dorsal root ganglion sympathetic or parasympathetic?
Ganglion: Collection of neuron cell bodies located in the peripheral nervousnervousAfferent nerve fibers are the axons (nerve fibers) carried by a sensory nerve that relay sensory information from sensory receptors to regions of the brain. Afferent projections arrive at a particular brain region. Efferent nerve fibers are carried by efferent nerves and exit a region to act on muscles and glands.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Afferent_nerve_fiberAfferent nerve fiber - Wikipedia system (PNS). Types: Sensory ganglia: Dorsal root gangliaDorsal root gangliaA dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Dorsal_root_ganglionDorsal root ganglion - Wikipedia of spinal nerves and the ganglia of selected cranial nerves. Autonomic ganglia: Sympathetic (close to the spinal cord), Parasympathetic (near on in the viscera).
What happens in the dorsal root?
The dorsal root transmits sensory information, forming the afferent sensory root of a spinal nerve.
What is the dorsal root ganglion quizlet?
dorsal root gangliadorsal root gangliaA dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Dorsal_root_ganglionDorsal root ganglion - Wikipedia are cell bodies of sensory neurons whose axons conduct impulses inward from peripheral body parts. dermatome. the area of skin that the sensory nerve fibers of a particular spinal nerve innervate.
What is a ganglion quizlet?
A ganglion is a swelling along a nerve containing the cell bodies of peripheral neurons.
What do ganglia and nuclei do?
The basal ganglia and related nuclei consist of a variety of subcortical cell groups engaged primarily in motormotorThe primary function of the motor cortex is to generate signals to direct the movement of the body. It is part of the frontal lobe and is anterior to the central sulcus. It consists of the primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, and the supplementary motor area.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › ...Physiology, Motor Cortical - PubMed control, together with a wider variety of roles such as motor learning, executive functions and behavior, and emotions.
What is a ganglion in medical terms?
Ganglion cysts are lumps that most commonly develop in the wrist. They're typically round or oval and are filled with a jelly-like fluid. Ganglion cysts are noncancerous lumps that most commonly develop along the tendons or joints of your wrists or hands. They also may occur in the ankles and feet.
What are ganglia quizlet?
Ganglia Structure. Collection of neuronal cell bodies outside of the CNS. Ganglia Function. Regulate and maintain the neuronal cell integrity in the PNS.
What is the function of the dorsal and ventral roots?
The dorsal roots are responsible for sensory functions, such as feeling pain, touch, and temperature changes. The ventral roots are responsible for...
What are ganglia and where are they located?
Ganglia are located throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems. They are the bundles of axons from neurons and glial cells in the centra...
What is the definition of ganglia?
Ganglia in the central nervous system corresponds to bundles of axons from neurons and glial cells. In the peripheral nervous system, ganglia refer...
What happens if dorsal root ganglia is damaged?
If the dorsal root ganglia is damaged, it can cause feelings of numbness in certain areas in the body. It can also cause the inability to feel temp...
Why do we need dorsal root ganglia?
While the message is eventually read by your brain, and you might have a conscious reaction (ouch!) to a painful stimulus like a thumbtack, the dorsal root ganglia help your body initiate that lightning fast reaction before your brain even has time to register it . Dorsal root ganglia, and the short circuit of afferent and efferent nerves to the spine, are an evolutionary adaptation to help prevent us from harming ourselves. Even from something as small as a thumbtack.
Where is the dorsal root located?
Dorsal root ganglia are located at the juncture between the spinal cord and the individual branching spinal nerves, and form a small bulge at the base of each spinal nerve. The dorsal root ganglia project outward from the spaces between each vertebral bone in the spinal column, or backbone.
What are the two types of nerves that send messages to the brain?
In order to understand how dorsal root ganglia function, we'll need to define a couple of terms: afferent nerves, which send messages toward the brain; and efferent nerves, which send messages away from the brain.
What are the nerve cells that transmit sensory information?
Within the peripheral nervous system, there are special nerve cell clusters called dorsal root ganglia that help transmit the sensory messages of pain and touch. Dorsal root ganglia are also known as spinal ganglia, or posterior root ganglia.
What are the nerves that send and receive messages to and from various parts of the body?
All along our spinal cord, we have specialized nerves that send and receive messages to and from various parts of our body. There are particular nerve cell clusters called dorsal root ganglia that are present in the root of these spinal nerves. In this lesson, we'll discuss the function and definition of a dorsal root ganglion.
How does the Ganglion respond to pain?
The ganglion collects and transmits messages of pain and touch very quickly to the spinal cord, rather than all the way back to the brain. This shorter distance allows for a very rapid response to a painful stimulus. It allows you, for example, to quickly pull your hand away from a hot stove or a thumbtack.
Where do peripheral nerves spread?
These peripheral nerves spread out to the edges, or extremities, of the body to the organs, and to the surface of the skin. Unlike the central nervous system, peripheral nerves aren't protected by the spinal column or the skull.
What are the functions of the dorsal root ganglion?
The functions of the dorsal root ganglion are important to understand with respect to other terms, such as afferent and efferent nerves. Afferent nerves are those that send messages to the CNS , whereas efferent nerves bring messages from the C NS. Axons are the projections from nerve cells that connect the cell to the CNS through the spine. Our bodies' extremities and organs are connected to the CNS through these axons, and when impulses from our extremities occur, they travel through these axons to the CNS. From there, afferent nerves work to send information to the CNS and efferent nerves are sent from the CNS to the extremities.
How does the dorsal root ganglia work?
The dorsal root ganglion consists of the cell bodies of sensory neurons, which form a single fiber. This nerve fiber further splits into two fibers, where one fiber carries impulses away from the cell body, and the second fiber carries them to the cell body. This split occurs very close to the spinal cord, thus allowing very fast communication between the sensory fiber s and the CNS. Blood supply to the dorsal root ganglion is achieved via the segmental arteries. Unlike the rest of the nervous system, these blood vessels are very permeable, which greatly contributes to the rapid communication that can be achieved.
What nerve sends messages to the CNS?
Afferent nerves send messages to the CNS, and efferent nerves send messages from the CNS to the rest of the body. Axons are projections from nerve cells. When your finger touches an unpleasant stimuli, like a needle tip, the efferent nerves transmit this information to the dorsal root ganglia, which then responds by sending out signals through the afferent nerves to remove your finger. The quickness of this process is due to the development of the dorsal root ganglion.
What are the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord?
Dorsal roots of the spinal nerve are responsible for sensory perception and ventral roots correspond to motor control and functions. The dorsal root ganglia, also termed spinal ganglia, are nerve clusters within the PNS that are responsible for signaling impulses pertaining to pain, touch, and temperature sensation to the spinal cord. The ventral horn of the spinal cord is responsible for relaying information from the ventral root to the CNS, thus being important for motor-related functions.
Why does my dorsal root ganglia feel numb?
If damaged, the dorsal root ganglia would not function appropriately. This could result in the overall feeling of numbness in certain areas in the body, or the abnormal feelings of too much or too little pain. Furthermore, there could be an inability to feel temperature changes. This may occur due to damage to the spinal cord via the spine, such as crashes or compressions to the spine.
What are the ganglia in the spinal cord?
Importantly, these ganglia are responsible for our sensory and motor functions. In the spinal cord, there are spinal nerves that contain dorsal and ventral roots. Dorsal roots of the spinal nerve are responsible for sensory functions, whereas the ventral roots correspond to motor functions. Dorsal root ganglia (also known as spinal ganglia or sensory ganglia) are important nerve clusters within the PNS that aid in signaling pertaining to pain and touch to the spinal cord as opposed to the brain, allowing for a rapid response. This is greatly useful in the event of a painful experience, such as when your hand is too close to something hot. The ventral horn is where all the motor neurons synapse through the ventral roots, thus being responsible for motor-related functions.
How does the spinal cord respond to pain?
When your fingertip touches the sharp needle, impulses from the fingertip corresponding to pain travel through a long axon, an efferent nerve, to the CNS, indicating an unpleasant experience. The spinal nerves rapidly respond to the impulse via the removal of your finger tip from the unpleasant stimuli. The quickness at which this process is achieved is primarily due to the dorsal root ganglion's proximity to the spinal cord, in addition to the permeability of the blood vessels in this structure. The entire process of pain perception may even feel like a reflex, given how quick it happens. This is primarily because of the dorsal root ganglion, which is an evolutionary adaptation to reacting quickly to unpleasant and painful stimuli.
Where is the dorsal root ganglion located?
A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia.
What type of neurons are in the dorsal root ganglion?
The neurons comprising the dorsal root ganglion are of the pseudo-unipolar type, meaning they have a cell body (soma) with two branches that act as a single axon, often referred to as a distal process and a proximal process .
What are the axons of dorsal root ganglion neurons?
The axons of dorsal root ganglion neurons are known as afferents. In the peripheral nervous system, afferents refer to the axons that relay sensory information into the central nervous system (i.e. the brain and the spinal cord ).
What is the name of the nerve that runs through the dorsal root?
A spinal nerve with its ventral and dorsal roots. The dorsal root ganglion is the "spinal ganglion", following the dorsal root. A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve.
What is the distal section of the axon?
The distal section of the axon may either be a bare nerve ending or encapsulated by a structure that helps relay specific information to nerve. Two examples where the nerve ending of the distal process is encapsulated as such are, Meissner's corpuscles, which render the distal processes of mechanosensory neurons sensitive to stroking only, and Pacinian corpuscles, which make neurons more sensitive to vibration.
Which ganglion contains cationic channels?
The presence of these channels in the posterior root ganglion gives reason to believe that other sensory neurons may contain them as well.
What is the effect of compression on the dorsal root ganglion?
Compression of the dorsal root ganglion by a mechanical stimulus lowers the voltage threshold needed to evoke a response and causes action potentials to be fired. This firing may even persist after the removal of the stimulus.
Where does the dorsal root ganglia get its blood?
The dorsal root ganglia receive their blood supply from nutrient arteries that branch directly from the dorsal division of each spinal segmental artery. Compression of the spinal nerve, distal to the dorsal root ganglion, showed a marked decrease in blood flow, ranging up to 45% less compared to compression proximal to the dorsal root ganglion, which showed only a 10-15% decrease (Yoshizawa, Kobayashi, & Hachiya, 1991 ). The ganglion has more abundant intrinsic vessels than the nerve root, consisting of continuous and fenestrated capillaries. The implications of these types of capillaries being associated with the dorsal root ganglion suggest the blood-nerve barrier surrounding the ganglia is not as impervious as originally thought, similar to the peripheral nerve; thus, the dorsal root ganglion may be subject to more hemodynamic stress and/or damage ( Bergman & Alexander, 1941 ). This is especially true in patients with diabetes mellitus, where it was noted in postmortem studies, diabetic patients had statistically significant thickened dorsal root ganglion perineural capillary basement membranes when compared to nondiabetics ( Johnson, 1983 ). This finding is no surprise compared to findings with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, but the significance also may implicate dorsal root ganglion pathology for neuropathic manifestations of dysesthesia and anesthesia in diabetics.
What is the dorsal root?
Each dorsal root of the spinal cord contains at the level of the intervertebral foramen an elongated thickening called spinal ganglion or dorsal root ganglion (DRG) (Fig. 1 ). This thickening, which is sheathed by the continuation of the surrounding membranes of the cord into the epineurium and perineurium of the peripheral nerves, is caused by the accumulation of cell bodies of primary sensory neurons (DRG cells) ( Fig. 2 ). These originally bipolar cells later on become (pseudo-)unipolar. The single axonal process soon divides in a T-like fashion into a peripheral branch, which is connected to somatic and visceral receptors, and a central branch, which enters the cord. The continuity of peripheral and central branches constitutes the major afferent axonal pathway to the cord. The dorsal spinal root comprises the trajectory of this axonal bundle between its entry into the cord and the intervertebral foramen. Shortly distal to the DRG, it fuses with the ventral spinal root to form the spinal nerve. Contrary to the DRG and the distal part of the dorsal root, both of which remain at the level of the intervertebral foramen, the proximal part of the dorsal root lengthens considerably during development due to the ascensus of the cord. The more caudal the cord level, the longer the corresponding proximal dorsal root. The so-called root sheath covers this part of the dorsal root, which traverses the subarachnoid space to the cord. The latter is considered a continuation of both pia and arachnoid mater but possibly also of the deep perineurium. The proximal part of each dorsal root (belonging to one ganglion) is actually composed of a number of smaller rootlets that enter the dorsolateral cord in a row ( Fig. 1 ). The rostrocaudal extent of this row macroscopically demarcates the rostrocaudal extent of a cord segment. Therefore, a cord segment owes its distinction to its sensory connection (through dorsal root and DRG) with its peripheral dermatomal field.
What neuron is used in a ganglion?
Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neuron preparations isolated from avian, reptilian, amphibian, and mammalian species have been widely used by neuroscientists in their studies of a variety of research questions. Using mammalian DRG neurons, electrophysiologists and molecular biologists have studied voltage-dependent ion channels, including sodium (1–12 ), calcium ( 1, 13–16 ), chloride ( 17, 18) and potassium ( 19, 20 ), as well as ion channels activated by neurotransmitters such as GABA ( 17, 21–27 ), glycine ( 28 ), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ( 29 ). As the isolation and culture procedures of rat DRG neurons are relatively easy to master and can be tailored to various rat ages, this preparation is ideal for many different research projects.
What is the function of DRG neurons?
Thus, DRG neurons serve as important centers of communication between the peripheral and central nervous systems.
What part of the spinal nerve is the proximal part of?
Shortly distal to the DRG, it fuses with the ventral spinal root to form the spinal nerve. Contrary to the DRG and the distal part of the dorsal root, both of which remain at the level of the intervertebral foramen, the proximal part of the dorsal root lengthens considerably during development due to the ascensus of the cord.
What is the DRG in biology?
The dorsal root ganglia (DRG) are a collection of cell bodies of the afferent sensory fibers, which lie between adjacent vertebrae.
Where are DRG neurons located?
Mammalian DRG neuronal cell bodies are clustered in connective tissue and embedded between the spinal column vertebrae on either side of the spinal cord. DRG neurons receive sensory input from mechanoreceptors, free nerve endings, nociceptors, and other peripheral sensory transducers. Information is subsequently transmitted by DRG axonal processes which give rise to a variety of ascending nerve tracts, such as the spinothalamic and proprioceptive tracts. The DRG axons ultimately make synaptic contact with nuclei of the dorsal column ( 30) or thalamus, at which point the information is transmitted to the cerebral cortex for further processing. Thus, DRG neurons serve as important centers of communication between the peripheral and central nervous systems. The study of the physiological properties of these ganglia, as well as their responses to pharmacological and toxicological agents, is of great medical relevance.
What are the functions of the dorsal root ganglia?
The functions of dorsal root ganglia are all#N#associated with the perception of sensations. These include: 1 Nociception 2 Perception of mechanical stimulus#N#upon compression 3 First processing center of the#N#sensory information 4 Role in reflex action
Where is the dorsal root ganglion located?
It is located in close proximity to the spinal cord. As the dorsal root of spinal nerve emerges from the intervertebral neural foramen, it expands to form the ganglion.
What is the grey matter of the spinal cord?
As these cells develop from the neural crest cells, the cells in the dorsal root ganglion are also regarded as the grey matter of. the spinal cord. It is considered that this part of the spinal cord’s grey. matter migrated to the periphery during the later phase of pregnancy.
What is a ganglion in the spinal cord?
Benefits. A ganglion is the collection of cell bodies of neurons located outside the central nervous system. A dorsal root ganglion is the one associated with the dorsal or posterior root of the nerves originating from the spinal cord. All the posterior roots of spinal nerves contain a ganglion.
What are the two types of cells in a dorsal root ganglion?
Two types of cells can be seen in a slide of a dorsal root ganglion. These are the neuron cells and the satellite cells. The neurons cells or cell bodies are the larger cells. having a big nucleus. Upon careful examination, a nucleolus can also be seen. inside each nucleus.
Which ganglion has a number of sensory receptors that are activated by different stimuli?
The endings of the fibers originating from the dorsal root ganglion have a number of sensory receptors that are activated by different stimuli. Some of these receptors are ion channels that can be activated by the compression of the dorsal root ganglion.
Which nerve is associated with sensory functions?
As we already know that the dorsal root of the spinal nerve is associated with the sensory functions, all the functions associated with the dorsal root ganglion are also related to different sensations.
How do you isolate a DRG?
The meninges surround the spinal cord in situ, and cover DRG once the cord is taken out. To extract the meninges, use fine forceps to carefully peel them back from one end of the spinal column segment to the other. If they prove difficult to identify, try grasping at the vertebrae between the DRG using fine forceps.
Which of the following describes the dorsal root ganglia?
Which of the following describes the dorsal root ganglion? It is a collection of cell bodies from sensory neurons.
Is myelination possible in mouse dorsal root ganglia?
Myelination in mouse dorsal root ganglion/Schwann cell cocultures The established protocols for in vitro studies of peripheral nerve myelination with rat embryonic dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and postnatal Schwann cell cocultures do not work with mouse cells.
Overview
Function
Proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors are expressed by DRG sensory neurons and might play a role in acid-induced nociception.
The nerve endings of dorsal root ganglion neurons have a variety of sensory receptors that are activated by mechanical, thermal, chemical, and noxious stimuli. In these sensory neurons, a group of ion channels thought to be responsible for somatosensory transduction have been identi…
Structure
The neurons comprising the dorsal root ganglion are of the pseudo-unipolar type, meaning they have a cell body (soma) with two branches that act as a single axon, often referred to as a distal process and a proximal process.
Unlike the majority of neurons found in the central nervous system, an action potential in posterior root ganglion neuron may initiate in the distal process in the periphery, bypass the cell body, an…
See also
• Anterior root of spinal nerve
• Knee jerk
Additional images
• Medulla spinalis
• The formation of the spinal nerve from the posterior and anterior roots
• Scheme showing structure of a typical spinal nerve.
External links
• Anatomy figure: 02:04-09 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
• Histology image: 04401loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
• Photo of model at Ohio State University