
Where are dendritic cells typically found?
Derived from precursors in the bone marrow, dendritic cells (DC) are professional antigen-presenting cells typically found in the mucosa, skin, and lymphoid tissues. As antigen-presenting cells, these cells are primarily involved in processing antigen before presenting them to T cells in order to activate immune response.
What are all the organelles of a dendritic cell?
List of Cell Organelles and their Functions
- Plasma Membrane. The plasma membrane is also termed as a Cell Membrane or Cytoplasmic Membrane. ...
- Cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is present both in plant and animal cells. ...
- Nucleus. ...
- Endoplasmic Reticulum. ...
- Golgi Apparatus. ...
- Cilia and Flagella. ...
- Centrosome and Centrioles. ...
- A Brief Summary on Cell Organelles. ...
What are the main functions of epidermal cells?
Epidermal cells include several types of cells that make up the epidermis of plants. Although they serve a number of important functions, their primary role is to protect from a variety of harmful factors (environmental stressors) including microbes, chemical compounds as well as ultraviolet light among others.
What is the difference between dendritic and Langerhans cells?
What is the difference between Langerhans cells and dendritic cells? Dendritic cells (DCs) 3 are professional APCs that play a crucial role in activating adaptive immune responses. Langerhans cells (LCs) are a subset of immature DCs that reside in the epidermis.

What is the function of epidermal dendritic cells quizlet?
Epidermal dendritic cells help activate the immune system within the body. Spiky hemispheres that in conjunction with sensory nerve endings form a sensitive touch receptor.
What do epidermal dendritic cells do?
Dendritic cells (DCs) are specialized antigen presenting cells abundant in peripheral tissues such as skin where they function as immune sentinels. Skin DCs migrate to draining lymph node where they interact with naïve T cells to induce immune responses to microorganisms, vaccines, tumours and self-antigens.
Where are dendritic cells function?
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as accessory cells) of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems.
What is the function of dendritic cells Langerhans cells in the epidermis quizlet?
Langerhans cells (a type of dendritic cell) and dermal dendritic cells initiate an immune response by presenting processed antigen to T cells, thus providing a defense against environmental antigens.
Where are epidermal dendritic cells found?
Origin, Transcription Factor, and Survival Factor Requirements of Skin Dendritic Cell Populations. LC are radio-resistant cells that reside in the supra-basal layer of the epidermis, closely attached to the surrounding keratinocytes via E-cadherin containing adherens junctions.
Are dendritic cells in the epidermis?
Using the latter it has been shown that there are three forms of dendritic cells in human epidermis. The first two, the melanocyte and Langerhans' cell, vary in number and location in different regions of the body while the indeterminate type remains rather constant and is located in the lower levels of the epidermis.
What do dendritic cells activate?
Dendritic cells (DCs) are a type of innate immune cells with major relevance in the establishment of an adaptive response, as they are responsible for the activation of lymphocytes.
What is the role of dendritic cells in immune defense quizlet?
Dendritic cells are a part of a class of immune cells called APCs, or antigen presenting cells. They degrade pathogens so T cells can recognize them and be able to mark future pathogens (of the same type) for degradation.
What are the dendritic cells?
Dendritic cells (DCs), named for their probing, 'tree-like' or dendritic shapes, are responsible for the initiation of adaptive immune responses and hence function as the 'sentinels' of the immune system. Paul Langerhans first described DCs in human skin in 1868 but thought they were cutaneous nerve cells.
Which epidermal cells are also known as epidermal dendritic cells?
Langerhans cells are dendritic antigen-processing and antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis. They form 2–8% of the total epidermal cell population, mostly found in a suprabasal position.
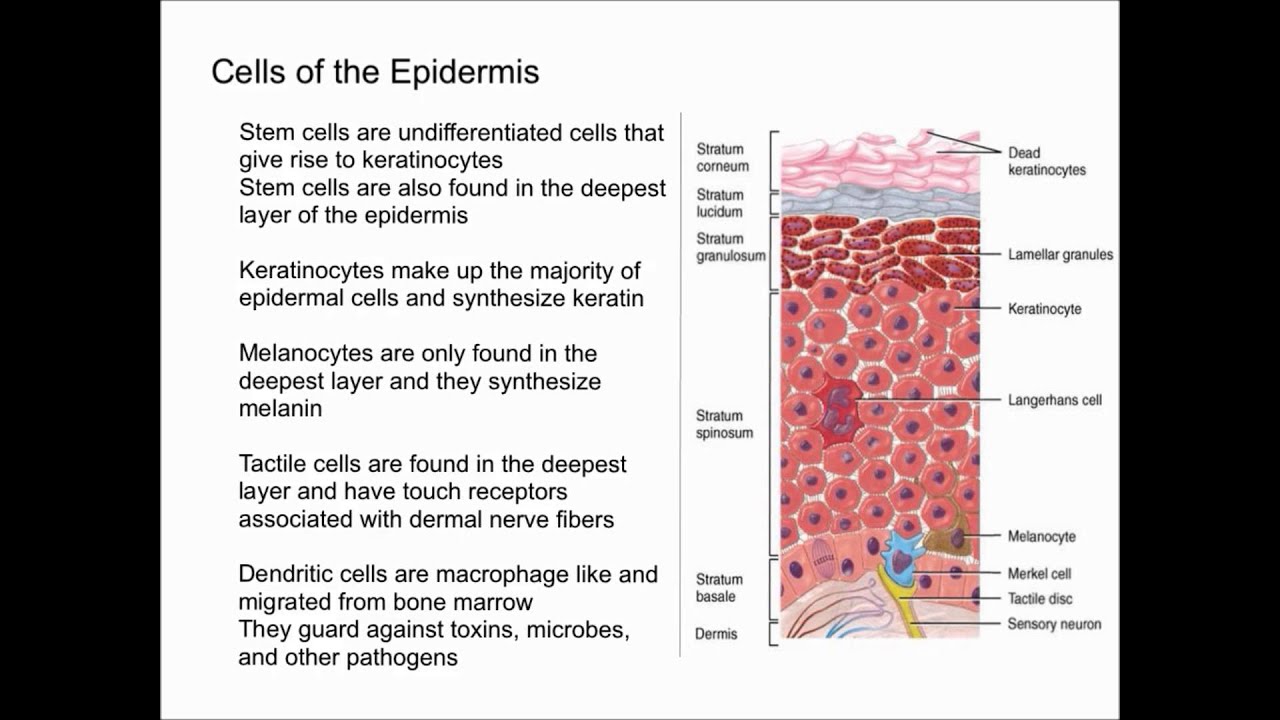
What is the function of dendritic cells found within the stratum spinosum of the epidermis?
These are found in the stratum spinosum layer of the epidermis. They are irregularly shaped dendritic cells, without keratin filaments of melanosomes, and they are antigen presenting cells. They play a role in facilitating skin allergic reactions.
What is the function of dendritic cells found within the stratum spinosum?
Langerhans cells, dendritic cells, are the skins first line defenders and play a significant role in antigen presentation. These cells need special stains to visualize, primarily found in the stratum spinosum.
Where are epidermal dendritic cells located quizlet?
Epidermal dendritic cells are found in the stratum spinosum and they serve to eat and destroy foreign or dangerous particles. The Merkel Cell is found in the Stratum basale and is for stimulation of nerves. Explain how hemoglobin and melanin contribute to skin color.
What layer of epidermis are dendritic cells found?
Stratum spinosum, 8-10 cell layers, also known as the prickle cell layer contains irregular, polyhedral cells with cytoplasmic processes, sometimes called “spines”, that extend outward and contact neighboring cells by desmosomes. Dendritic cells can be found in this layer.
What is the function of Langerhans cells?
Langerhans cells (LCs) reside in the epidermis as a dense network of immune system sentinels. These cells determine the appropriate adaptive immune response (inflammation or tolerance) by interpreting the microenvironmental context in which they encounter foreign substances.
What are skin dendritic cells called?
A key cell type of the resident skin immune system is the dendritic cell, which in normal skin is located in two distinct microanatomical compartments: Langerhans cells (LC) mainly in the epidermis and dermal dendritic cells (DDC) in the dermis.
Why are dendritic cells important?
Dendritic cells have an important function in the innate immune system where they carry out surveillance duties, looking for antigens in the form of endogenous toxins and exogenous foreign substances. The presence of an antigen – or its surface proteins – stimulates an immune response. This is because certain patterns of molecules on the antigen or on damaged cell membranes make them recognizable. In the image, the orange antigens with many surface proteins have been detected by antibodies – the Y-shaped blue-green particles. Antibodies are a later stage of immunity that will be described further on.
What is the role of dendritic cells in the immune system?
They are bone marrow and lymph -derived leukocytes or white blood cells. Dendritic cells play a primary role in immune responses. The ease with which they can be grown in laboratories together with their strong antigen-killing features makes them a promising anti-cancer agent.
What are dendritic cells?
Dendritic cells are formed from precursor cells in the bone marrow and lymph tissue and are one of three types of antigen-presenting cells.
What are the three types of antigen-presenting cells?
The three types of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) are dendritic cells, macrophages, and B-cells.
Why do tumors suppress the immune system?
This is because tumor cells hide behind their own anti-inflammatory cytokines. Not only are they very hard for an APC to recognize, they also block the natural inflammatory response of healthy immune cells.
Where do plasmacytoid cells originate?
Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells originate in the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, and tonsils) and the bone marrow. Lymph vessels and nodes (green) follow the same routes as our blood vessels (blue and red). Lymph – circulatory system of immunity.
Which cells scavenge and destroy harmful or foreign particles and release chemicals that attract more white blood cells?
Macrophages and neutrophils scavenge and destroy harmful or foreign particles and release chemicals that attract more white blood cells. Dendritic cells perform phagocytosis and preserve information from ingested particles that can kick-start adaptive (acquired) immune responses. Cytokines are signaling molecules.
Which layer of the epidermis is located closest to the dermis?
deepest layer of the epidermis that is situated closest to the dermis
How many layers are there in the superficial layer of the epidermis?
superficial layer of the epidermis made up of 20-30 cell layers of dead, keratin-filled cells
What are the loops in the dermal papillae?
dermal papillae contain capillary loops to nourish the epidermis
What is a dendritic cell?
Dendritic cells (dendron in Greek means tree) are cells with multiple long cell hi processes. The processes are like huge trees with their branches reaching out to the sky. These are professional “antigen presenting cells”.
Which cells pass information about foreign antigens to the effector cells?
The dendritic cells will then pass the information about the foreign antigens to the “effector cells” (those who know karate, and have all kinds of poisons and guns and knives) who are alerted to the danger, and they will then “do the necessary”.
What cells are responsible for phagocytizing pathogens?
Dendritic cells patrol the body, phagocytize pathogens, digest them and present the peptide on proteins that extend from the cells (MHC II molecules). The peptides are recognized by Th cells, which then activate the adaptive immune system and prompting the developing of antibody-producing plasma cells and cytotoxic T cells that will attack infected body cells. Dendritic cells are the only ones that can alert naive Th cells to the presence of a novel infection. No dendritic cells, no Th activation and very little immune response.
Where are epidermal dendritic cells found?from biologydictionary.net
Epidermal Dendritic Cells. Epidermal or dermal dendritic cells are found in different forms on and within the skin. All epidermal dendritic cells activate T-cells on or in the epidermis and dermis. One example is the Langerhans cell (LC).
Why are dendritic cells important?from biologydictionary.net
Dendritic cells have an important function in the innate immune system where they carry out surveillance duties, looking for antigens in the form of endogenous toxins and exogenous foreign substances. The presence of an antigen – or its surface proteins – stimulates an immune response. This is because certain patterns of molecules on the antigen or on damaged cell membranes make them recognizable. In the image, the orange antigens with many surface proteins have been detected by antibodies – the Y-shaped blue-green particles. Antibodies are a later stage of immunity that will be described further on.
What is the name of the neoplasm of a dendritic cell?from biologydictionary.net
Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is a rare form of blood cancer. As its name suggests, the source of the cancer is the plasmacytoid form of dendritic cells.
What type of cells are we born with?from biologydictionary.net
We are also born with phagocytic cells – macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells, monocytes, dendritic cells, etcetera. Phagocytes envelop and digest foreign particles, dead and damaged cells, and toxins. Dendritic cells are phagocytic and phagocytes are part of our innate immune system.
What are plasmacytoid dendritic cells?from biologydictionary.net
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce cytokines like type I interferon and tumoral necrosis factor. Cytokines stimulate the production of natural killer cells, B lymphocytes, and myeloid dendritic cells. They also have particularly strong antiviral properties.
What is the function of a macrophage in a pink antigen invasion?from biologydictionary.net
The macrophage has receptors for the LPS pattern that detect the PAMPS. Upon detection, the macrophage then secretes cytokines in response. Cytokines tell other cells that an attack is underway. The macrophage catches and digests the bacteria ( phagocytosis ).
What is the name of the ulcer that cuts off blood supply to the skin?from woundsource.com
A decubitus ulcer forms where the pressure from body the body's weight presses the skin against a firm surface, such as a bed or wheelchair. Pressure cuts off the blood supply to the skin and injures tissue cells. Initially, the skin usually looks red or a bit discolored. Eventually, if the pressure isn't relieved, ...
Why do the cells of the epidermis renew themselves?from health.howstuffworks.com
Because they're also the first to encounter damage, the cells of the epidermis are constantly renewing themselves, with dead skin cells falling off by the tens of thousands each minute. One of the most basic functions of the epidermis is waterproofing [source: The Merck Manuals ].
What is the substance in your epidermis layer that determines skin color?from health.howstuffworks.com
More About Melanin. Melanin is the substance in your epidermis layer that determines skin color.
What is the purpose of a nail plate seal?from nailcarehq.com
A thin layer of dead tissue riding on the nail plate to form a seal between the nail plate and eponychium to prevent pathogens from infecting the matrix area.
How many layers of keratin are in a nail?from nailcarehq.com
The average person has 50 layers of keratin cells that make up the nail plate.
How does skin regulate temperature?from owlcation.com
It Helps Regulate Our Temperature. Your body is protected from extreme heat and extreme cold by the skin. Skin plays a vital role in maintaining constant body temperature. Your body could quickly become overheated or very cold without the skin. The skin has roughly about 2.5 million sweat glands.
What is the role of skin in the human body?from owlcation.com
In addition to covering the entire human body as a single entity, skin plays a vital role in protecting us and keeping our bodies healthy. This article discusses the three layers of human skin, explains what each one does, and explores several ways in which our skin helps ...
Where is the living skin at the base of the nail plate?from nailcarehq.com
Living skin at the base of the nail plate that covers the matrix area. This should NOT be confused with the “cuticle”.
Definition
Dendritic Cells Function
- Dendritic cells function within the immune system. They are phagocytes and antigen-presenting or accessory cells (messengers and activators) in our innate and adaptive immune mechanisms. Dendritic cells are formed from precursor cells in the bone marrow and lymph tissueand are one of three types of antigen-presenting cells. Antigen-presenting cells...
Dendritic Cell Types
- In humans, dendritic cell types exist in three main groups. These are conventional dendritic cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and epidermal (dermal) dendritic cells.
The Immune Response
- In humans, the immune response protects us from toxins produced inside the body and foreign particles and single-celled organisms that enter the body from outside. Antigens, as already mentioned, all have generic forms of surface proteins. Foreign microorganisms have PAMPs (pathogen-associated molecular patterns) and damaged cells or cancer cells have DAMPs (dam…
Immunity and Vaccination
- Vaccinations work either to provide an active acquired immune response or a passive response. When ready-made antibodies are injected into the body, they recognize a specific pathogen and attack it. This type of vaccination is relatively short-lived. Other types of vaccines introduce a very small amount of pathogen – either alive but only mildly pathogenic (weak) or inactivated. It is the…
Dendritic Cells in Cancer Therapy
- The use of dendritic cells in cancer therapy is under a lot of scrutiny. We need to understand how they work at a much deeper level to move towards personalized cancer treatment in the form of a vaccine or even a preventive pill. Cancer vaccination is a form of immunotherapy. The ability of dendritic cells to regulate our immune responses is very relevant, as somewhere along the canc…
Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm
- Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is a rare form of blood cancer. As its name suggests, the source of the cancer is the plasmacytoid form of dendritic cells. In BPDCN, cancer is caused specifically by plasmacytoid dendritic cells that produce high levels of type I interferon. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm is more likely to affect middle-aged or older males. I…