What does the inferior extensor retinaculum do?
The inferior extensor retinaculum is the lower band of extensor retinaculum that attaches horizontally to the calcaneus (heel bone) and passes over and under the extensor muscle tendons in the ankle.
What are the flexor muscles of the forearm?
- Pronator teres muscle
- Flexor carpi radialis muscle
- Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle
- Palmaris longus muscle
- Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle
- Clinical note
What is a forearm flexor?
- "E/I" refers to "extrinsic" or "intrinsic". ...
- The brachioradialis, flexor of the forearm, is unusual in that it is located in the posterior compartment, but it is actually in the anterior portion of the forearm.
- The anconeus is considered by some as a part of the posterior compartment of the arm.
What are flexor and extensor muscles?
Flexors are muscles involved in flexing a muscle, like the biceps. These muscles extend two muscles further, e.g. Triceps. 3 Extensors are muscles involved in extending a muscle, like thetriceps. 4opens a joint and are the opposite to flexor muscles, which closes it.

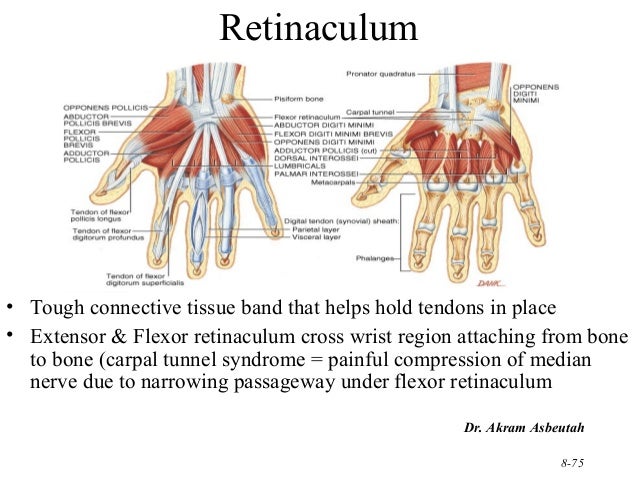
What is the function of the flexor retinaculum quizlet?
What is the function of the flexor retinaculum? 1. To keep the flexor muscles from "bowstringing" during flexion.
What is the function of the extensor and flexor retinaculum of the wrist?
The extensor retinaculum of the wrist is the broad ligamentous sheet located at the dorsal aspect of the wrist and functions to keep the extensor tendons in alignment and prevent bowstringing during movement.
Where is the flexor retinaculum?
The flexor retinaculum (also known as the transverse carpal ligament) is a rectangular-shaped fibrous band located at the ventral aspect of the wrist.
What is the function of the retinaculum of the foot?
Retinacula are thickenings of deep fascia in the region of joints, to keep the tendons in place as they cross the joints. Many retinacula are present in the vicinity of ankle joint. These retinacula are transverse bands across the ankle that holds down the tendons that cross from the leg to the foot.
What muscle attaches to the flexor retinaculum?
The thenar muscles attach to the radial half of the classic flexor retinaculum, composed of the distal portion of the flexor retinaculum (3) and the transverse carpal ligament (2), Bony attachments of transverse carpal ligament-pisiform (I'), hamate (H), tubercle of trapezium (7'), and tubercle of the scaphoid (S)--are ...
Which of the following structures pass through flexor retinaculum?
Structures passing deep to flexor retinaculum of the hand are: Median nerve. Radial bursa. Ulnar bursa.
Is flexor retinaculum a tendon?
On the radial side of the retinaculum is the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis, which lies in the groove on the greater multangular between the attachments of the ligament to the bone.
What is flexor retinaculum of leg?
A flexor retinaculum consists of a fibrous band of fascia, which is a sheet of dense connective tissue that covers or binds other body structures. The flexor retinaculum of the foot, also known as the laciniate ligament, covers the tendons of the flexor muscles of the ankle.
What passes through the flexor retinaculum of leg?
The flexor retinaculum (laciniate ligament; internal annular ligament) is a strong fibrous band, extending from the tibial malleolus above to the margin of the calcaneus below, converting a series of bony grooves in this situation into canals for the passage of the tendons of the Flexor muscles and the posterior tibial ...
What is the flexor retinaculum of the wrist?
The flexor retinaculum is a fibrous connective tissue band that forms the anterior roof of the carpal tunnel. Many experts consider the flexor retinaculum synonymous with the transverse carpal ligament and the annular ligament; for this discussion, they will be considered the same structure.
What is extensor retinaculum wrist?
The extensor retinaculum is a fibrous thickening of the investing fascia, extending around the wrist to become continuous with the volar carpal ligament.
What is the extensor retinaculum quizlet?
Extensor retinaculum. Definition. Thickening of fascia on the dorsal side of hand. Functions to keep extensor tendons in position to prevent bowstringing.
Which bones are attached to flexor and extensor retinaculum?
Structure. The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band that covers the carpal bones on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It attaches to the bones near the radius and ulna. On the ulnar side, the flexor retinaculum attaches to the pisiform bone and the hook of the hamate bone.
What is the flexor retinaculum?
A flexor retinaculum consists of a fibrous band of fascia, which is a sheet of dense connective tissue that covers or binds other body structures. The flexor retinaculum of the foot, also known as the laciniate ligament, covers the tendons of the flexor muscles of the ankle. The specific tendons covered are the tibialis posterior, ...
Where does the flexor retinaculum pass through?
They pass through the flexor retinaculum immediately posterior to (behind) the medial malleolus, which is the network of nerve tissue and muscle that surrounds the ankle joint.
Which tendons help to flex the foot?
The specific tendons covered are the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus, which all help to flex the foot so that the toes point downward. The function of the flexor retinaculum of the foot is to prevent subluxation, or partial dislocation, of these tendons.
Which ligament is the flexor retinaculum?
The flexor retinaculum is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament , and deeper with the palmar aponeurosis. The ulnar artery and ulnar nerve, and the cutaneous branches of the median and ulnar nerves, pass on top of the flexor retinaculum. On the radial side of the retinaculum is the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis, ...
Which bone attaches to the flexor retinaculum?
On the ulnar side, the flexor retinaculum attaches to the pisiform bone and the hook of the hamate bone. On the radial side, it attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and to the medial part of the palmar surface and the ridge of the trapezium bone . The flexor retinaculum is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament, ...
Where do the tendons of the palmaris longus and flexor carpi ulnaris?
The tendons of the palmaris longus and flexor carpi ulnaris are partly attached to the surface of the retinaculum; below, the short muscles of the thumb and little finger originate from the flexor retinaculum.
Can flexor retinaculum be severed?
When surgery is needed, the flexor retinaculum is either completely severed or lengthened. When surgery is done to divide the flexor retinaculum, by far the more common procedure, scar tissue will eventually fill the gap left by surgery.
What is retinaculum?
A retinaculum refers to any region on the body in which tendon groups from different muscles pass under one connective tissue band.
How long does it take for retinal amputation to manifest?
This complication is relatively rare and may manifest up to five weeks after the injury. To reduce the complications from retinaculum surgery, a procedure was developed that incorporates medial patellofemoral ligament overlap in addition to lateral retinaculum release.
What is the flexor retinaculum?
Gross anatomy. The flexor retinaculum encloses and forms the roof of the carpal tunnel. The ulna aspect of the flexor retinaculum forms the floor of Guyon's canal. It has superficial and deep layers, which are separate on the radial aspect, containing the tendon of flexor carpi radialis.
Where is the flexor retinaculum located?
The flexor retinaculum (also known as the transverse carpal ligament ) is a rectangular-shaped fibrous band located at the ventral aspect of the wrist.
What is the function of the flexor retinaculum?
The flexor retinaculum protects nine of the forearm flexor tendons and median nerve as they pass through the carpal tunnel.[1] If this tissue becomes inflamed, swollen, or fibrotic, the median nerve can become irritated or compressed, leading to carpal tunnel syndrome. Structure and Function.
How thick is the flexor retinaculum?
The flexor retinaculum thickens proximally to distally, ranging in thickness from 1.5 mm to 6.0 mm.[1] The structure is about 3 centimeters long and about 2.5 centimeters wide. The flexor retinaculum attaches laterally and medially to the carpals bone.
Where is the flexor digitorum superficialis?
The flexor digitorum superficialis, which is in the anterior compartment of the forearm, originates at the medial epicondyle of the humerus as well as parts of the radius and ulna.
Where is the ulnar artery?
The ulnar artery is one of the major blood vessels in the upper extremity and is close to the flexor retinaculum. The ulnar artery is a continuation of the brachial artery and is underneath the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. It lies on top of the flexor retinaculum lateral to the ulnar nerve.
Which part of the carpal tunnel is the flexor retinaculum attached to?
Specifically, the flexor retinaculum attaches to the scaphoid tuberosity and trapezial ridge radially and the pisiform and the hook of hamate ulnarly.[2] The flexor retinaculum forms the carpal tunnel's volar boundary, while the carpal bones form the dorsal boundary.
Which artery supplies the medial aspect of the forearm and forms the superficial palmar arch providing blood to the?
The ulnar artery supplies the medial aspect of the forearm and forms the superficial palmar arch providing blood to the hand.[3] . In some patients, there is a branch of the ulnar artery that passes over the retinaculum. Nerves. The flexor retinaculum is best known for sheltering the median nerve in the carpal tunnel.
Which muscle is associated with the front face of the eminence thenar?
Its front face gives rise to some muscles of the eminence thenar and of the eminence hypothenar and is related to the tendon of the long palmar muscle that adheres to it. The upper margin continues in the palmar carpal ligament, and the lower margin merges with the palmar aponeurosis.
What is the distal section of the flexor retinaculum?
The distal section of the flexor retinaculum consists of an aponeurosis between the thenar and hypo-thenar muscles. The thenar muscles (flexor pollicis brevis muscle and to a lesser degree abductor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis) originate from the radial side of this aponeurosis while, the hypothenar muscles (oppo- nens digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis) originate from the ulnar element of the aponeurosis. This section of the flexor retinaculum has a mean length of 0.99 ± 0.13 cm.
Which section of the flexor retinaculum has irregular boundaries?
The proximal section of the flexor retinaculum has irregular boundaries. This section is merged to and indivisible from the ante-brachial fascia. The density of this section varies considerably amongst various specimens.
How many borders does the flexor retinaculum have?
It is rectangular in shape and has roughly the shapes and size of a postage stamp.Like a postage stamp, it presents two surfaces and four borders.The flexor retinaculum is a robust fibrous band created by the thickening of deep fascia in front of the carpus (anatomical wrist).
Where do radial fibers come from?
The fibers arise from the pisiform to form a distinct head, on the ulnar element the majority of the radial fibers originate from the trapezium deep to the thenar musculature. A narrow strip of fibers emerges from the scaphoid tubercle. The proximal section of the flexor retinaculum has irregular boundaries.
What is it called when the flexor retinaculum is compressed?
When this occurs compression of the tibial nerve and artery occurs, which is known as tarsal tunnel syndrome .
What are the symptoms of a tear in the flexor retinaculum?
Symptoms of an isolated tear of the flexor retinaculum include pain, numbness, and tingling on the arch of the foot that’s provoked by walking, standing, and running. Due to the high number of proprioceptive nerve receptors in the fibrous band ankle instability can occur due to the altered feedback to the brain from the retinacula. This generally occurs in those that repeatably experience ankle sprains for no apparent reason.
What is the flexor of the foot?
The flexor retinaculum of the foot is a strong fibrous band that covers the tendons of the muscles that flex the foot such as walking on the toes like a ballerina. This retinaculum connects the inner ankle bone (medial malleolus) to the calcaneus (heel bone) and protects the tibial nerve and artery and when the retinaculum becomes injured or lacks mobility then the nerve can become compressed. When this retinaculum entraps the flexor tendons and nerve below this known as tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Why do we do proprioceptive exercises on the ankle?
Proprioceptive exercises of the ankle to improve feedback information to the brain and thus increasing stability

Overview
Function
The flexor retinaculum is the roof of the carpal tunnel, through which the median nerve and tendons of muscles which flex the hand pass.
Structure
The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band that covers the carpal bones on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It attaches to the bones near the radius and ulna. On the ulnar side, the flexor retinaculum attaches to the pisiform bone and the hook of the hamate bone. On the radial side, it attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and to the medial part of the palmar surface and the ridge of the trapezium bone.
Clinical significance
In carpal tunnel syndrome, one of the tendons or tissues in the carpal tunnel is inflamed, swollen, or fibrotic and puts pressure on the other structures in the tunnel, including the median nerve. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most commonly reported nerve entrapment syndrome. It is often associated with repetitive motions of the wrist and fingers. It is because of this that pianists, meat cutters, and people with jobs involving extensive typing are at particularly high risk. The tough fle…
See also
• Peroneal retinacula
• Extensor retinaculum of the hand
External links
• Anatomy figure: 08:04-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
• Hand kinesiology at the University of Kansas Medical Center
• lesson5flexretinac&palmapon at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)