What is the main function of both intracellular and extracellular fluids?
The main function of both intracellular and extracellular fluids is to provide nutrients to the cells in the body and lubrication to the body cavities. Intracellular Fluid: The intracellular fluid is a fluid found in the cell membrane, containing dissolved ions and other components, which are essential to cellular processes.
What is the intracellular fluid composed of?
Unlike extracellular fluid, the intracellular fluid has a high concentration of potassium and a low concentration of sodium. The cytosol is composed primarily of water, dissolved ions, small molecules, and large molecules soluble in water (such as proteins). Its molecules are important for cell metabolism.
What is intracellular fluid and how does it affect osmosis?
Intracellular fluid is the fluid inside a cell, which is made up of water, electrolytes, and proteins. Learn how to define intracellular fluid, explore its composition, and discover how electrolytes impact osmosis. Updated: 10/13/2021 What is Intracellular Fluid? Human cells are bathed in fluids both inside the cell and out.
What is the function of intracellular fluid in meiosis?
Functions. These processes include the synthesis of proteins known as genetic translation, the first stage of cellular respiration (glycocytosis) and cell division (mitosis and meiosis). The intracellular fluid allows the intracellular transport of the molecules through the cell and between the cellular organelles.
What are the functions of extracellular and intracellular fluids?
The main function of both intracellular and extracellular fluids is to provide nutrients to the cells in the body and lubrication to the body cavities.
What Is intracellular fluids?
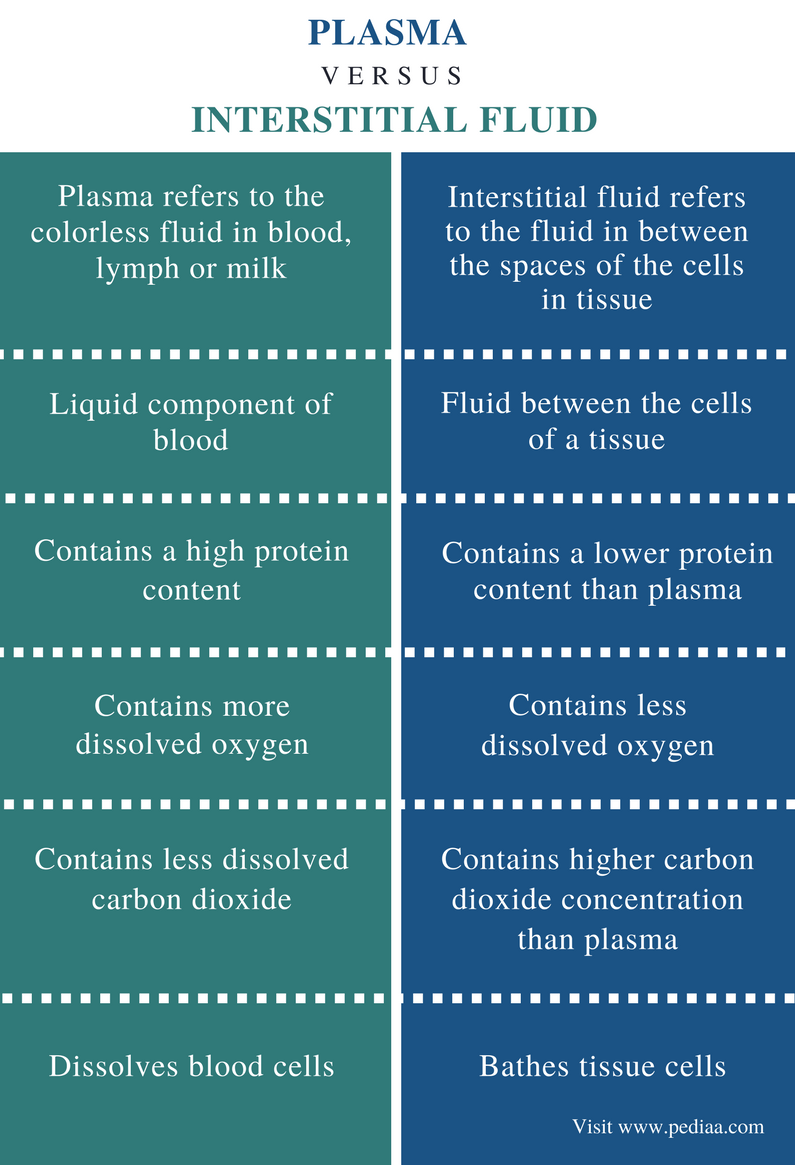
The intracellular fluid is the fluid contained within cells. The extracellular fluid—the fluid outside the cells—is divided into that found within the blood and that found outside the blood; the latter fluid is known as the interstitial fluid.
What is the most important intracellular fluid?
The major cation in the intracellular fluid is potassium. These electrolytes play an important role in maintaining homeostasis.
What is only found in intracellular fluid?
Intracellular fluid is the place where most of the fluid in the body is contained. This fluid is located within the cell membrane and contains water, electrolytes and proteins. Potassium, magnesium, and phosphate are the three most common electrolytes in the ICF.
What is the difference between intracellular fluid and intracellular fluid?
The intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment is the system that includes all fluid enclosed in cells by their plasma membranes. Extracellular fluid (ECF) surrounds all cells in the body.
What is the difference between intracellular fluid and intercellular fluid?
What is the Difference Between Intracellular and Interstitial Fluid? Intracellular fluid is the fluid that lies within cells. In contrast, interstitial fluid is the fluid present between blood vessels and cells.
Why does intracellular water matter?
The intracellular water is the location of important cellular processes, and although it has many functions, a very important one is that it allows molecules to be transported to the different organelles inside the cell.
Why is extracellular fluid important?
The extracellular fluid provides the medium for the exchange of substances between the ECF and the cells, and this can take place through dissolving, mixing and transporting in the fluid medium. Substances in the ECF include dissolved gases, nutrients, and electrolytes, all needed to maintain life.
What are the functions of body fluids?
The function of body fluid They deliver oxygen and nutrients to the cells, and take away waste materials, which are then eliminated with urination. When the body temperature rises, blood circulation to the skin increases, enabling heat dissipation though sweating, helping to keep the body at a constant temperature.
What are the examples of intracellular?
Occurring or being (situated) inside a cell or cells. For example, intracellular fluid pertains to the fluid inside the cell while intercellular fluid is the fluid between cells.
Is blood intracellular fluid?
Intravascular compartment The blood represents both the intracellular compartment (the fluid inside the blood cells) and the extracellular compartment (the blood plasma).
What does the term intracellular mean?
within a cellDefinition of intracellular : existing, occurring, or functioning within a cell intracellular parasites.
What are the examples of intracellular?
Occurring or being (situated) inside a cell or cells. For example, intracellular fluid pertains to the fluid inside the cell while intercellular fluid is the fluid between cells.
What does the term intracellular mean?
within a cellDefinition of intracellular : existing, occurring, or functioning within a cell intracellular parasites.
What's another word for intracellular fluid?
The bacterium usually doubles its intracellular fluid, called cytoplasm, too.
What is intracellular fluid and organelles?
The intracellular fluid of the cytosol or intracellular fluid (or cytoplasm ) is the fluid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes that encircle the various organelles of the cell. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into compartments.
What are examples of extracellular fluid?
Extracellular fluid refers to the fluid that is found outside of the cell. Extracellular fluid is found in blood plasma and in the interstitial spa...
What is meant by intercellular fluid?
Intracellular fluid refers to the fluid content found inside of the cell. Because intracellular fluid is found inside of the cell, it is sometimes...
What is the main function of intracellular fluid?
The main function of intracellular fluid is to help with the transport of gases, nutrients, and other molecules. Intracellular fluid is also import...
What is intracellular fluid?
Intracellular fluid is the fluid that exists within the cells of multi-celled organisms. The intracellular fluid is therefore stored within the intracellular compartments of the body. Intracellular fluid is often referred to as cytosol when discussing cellular functions. The cytosol and the organelles and molecules contained within are referred to collectively as the cytoplasm. The opposite of the intracellular fluid is the extracellular fluid, which exists on the outside of the cells in the extracellular compartment of the body. Many cellular mechanisms and enzymes work to move products and wastes from the intracellular fluid to the extracellular fluid, while at the same time bringing in new nutrients and solutes to the intracellular fluid.
What is the term for the fluid that surrounds the cells of the body but is separated still from the environment?
Related Biology Terms. Extracellular Fluid – Fluid that surrounds the cells of the body, but is separated still from the environment. Cytosol – The fluid containing nutrients, proteins, and other molecules in a cell, also called intracellular fluid.
How do cellular mechanisms and enzymes work?
Many cellular mechanisms and enzymes work to move products and wastes from the intracellular fluid to the extracellular fluid, while at the same time bringing in new nutrients and solutes to the intracellular fluid .
Is the cytosol interstitial or extracellular?
In the Cytosol. Answer to Question #1. B is correct. While the molecule has traveled a long way, it has one more membrane to traverse before it reaches the intracellular fluid, or cytosol. Currently, the molecule is in the interstitial fluid, a part of the extracellular fluid. This fluid exists between cells of the body ...
What Is Intracellular Fluid?
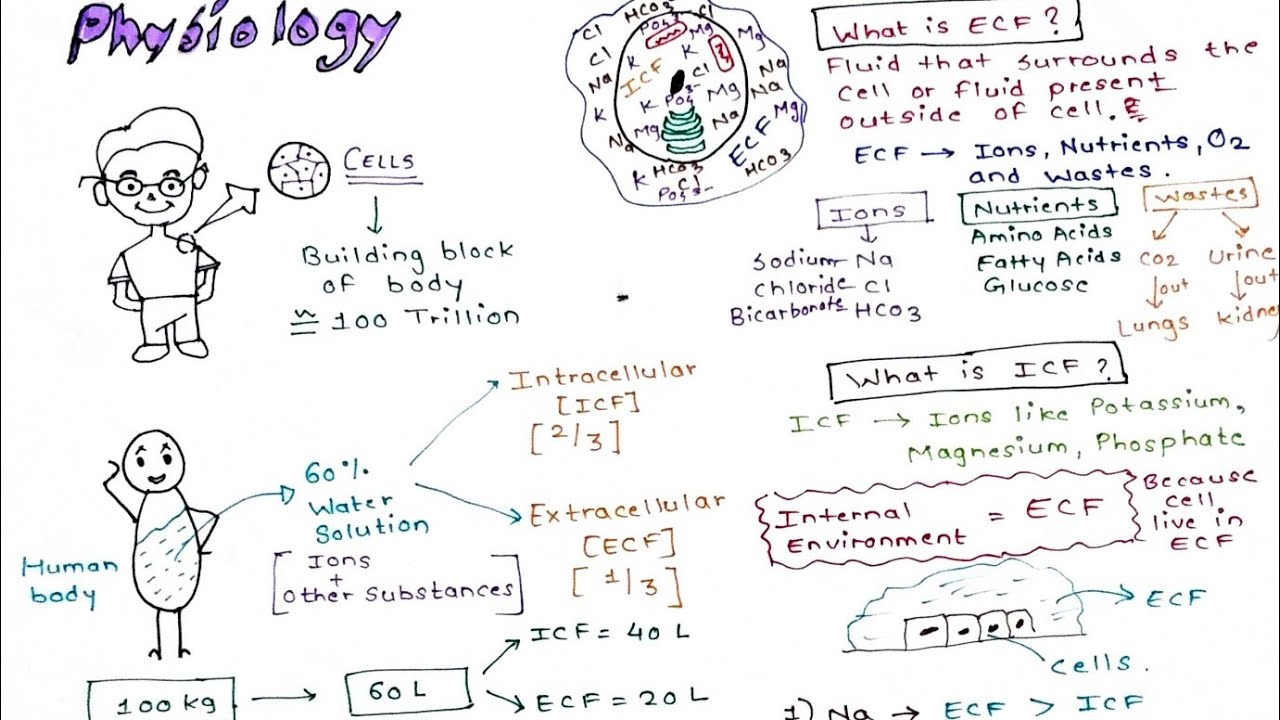
Living organisms like humans and other mammals are comprised largely of water. Indeed, nearly 75% of the body weight in humans is made of water. This water is divided into two main components of the human body: extracellular fluid and intracellular fluid.
Intracellular Fluid vs Extracellular Fluid
As mentioned earlier in this lesson, water comprises up to 75% of the total body weight in humans. These fluids are divided into intracellular and extracellular fluids. There are several important differences between intracellular fluid versus extracellular fluid.
Osmosis and Intracellular Fluid
Intracellular and extracellular fluids travel through the body via both active and passive transport. However, intracellular fluid often moves between cells by passively traveling across the cell membranes. The flow of intracellular fluid is controlled in part by osmosis.
Where is intracellular fluid stored?
Therefore, this fluid is stored within the intracellular compartments of the body. The intracellular compartment is the system that includes all the fluids enclosed in ...
What is the opposite of intracellular fluid?
The opposite of the intracellular fluid is the extracellular fluid, which is located outside the cells in the extracellular compartment. Many enzymes and cellular mechanisms work to transport both products and wastes from the intracellular fluid to the extracellular fluid, while bringing new nutrients and solutes to the intracellular fluid.
What is the fluid inside a cell called?
The fluid inside the cells is called intracellular fluid (IFC) and the fluid outside the cells is called the extracellular fluid (EFC). These two fluids are separated by a semipermeable membrane that surrounds the cell. This membrane makes it possible for the liquid to enter and exit, but at the same time prevents unwanted molecules ...
Why is it important to keep the water balance inside the cell?
Since the concentration of proteins is high within the intracellular fluid compared to the extracellular fluid, the differences in ion concentrations both inside and outside the cell become important in order to regulate osmosis. This allows you to keep the water balance inside the cell to protect it and not to explode.
What is the intracellular compartment?
The intracellular compartment is the system that includes all the fluids enclosed in the cells by their plasma membranes. Representation of eukaryotic human cells. When talking about cellular functions, this type of fluid is often referred to as a cytosol. The cytosol, organelles and molecules that are located inside are collectively referred ...
What is the role of the cytosol in eukaryotic cells?
Since the cytosol contains dissolved ions, it plays an important role in osmoregulation and cell signaling. It is also involved in the generation of action potentials as occurs in nerve, muscle and endocrine cells.
Why is the volume of cytosol stable?
The volume of this liquid is usually quite stable, since the amount of water found in the cells is regulated by the body. If the amount of water within a cell drops too low, the cytosol is too concentrated in solutes and can not carry out normal cellular activities.
What is Intracellular Fluid?
Human cells are bathed in fluids each within side the mobile and out. In fact, the water this is within side the mobile makes up approximately 42% of the entire frame weight. The fluid within side the mobile is known as intracellular fluid (ICF).
Composition of Intracellular Fluid
Intracellular fluid incorporates water and dissolved solutes and proteins. The solutes are electrolytes, which assist maintain our frame functioning properly. An electrolyte is an detail or compound that, while dissolved in fluid, breaks up into ions.
Osmosis and Intracellular Fluid
When water actions outside and inside the mobile, the manner is known as osmosis. Osmotic strain is the pressure that draws fluid from one compartment to every other. The degree of osmotic strain stays about same among the ICF and the ECF compartments.
What is intracellular fluid?
ICF is defined as all the body water within cells and, unlike the ECF compartment, is an inhomogeneous, multicompartmental entity, with different pH and ionic compositions depending upon the organ or tissue being considered. From: Oh's Intensive Care Manual (Seventh Edition), 2014.
How much does intracellular fluid volume increase?
Intracellular fluid volume increases from 25% of body weight in the young fetus to 33% at birth to approximately 37% of body weight at age 4 months. Except for a sudden increase during early childhood, the intracellular fluid volume remains relatively constant thereafter, approximating 40% of body weight.
Why is it unlikely that the loss of K + from the ICF was accompanied by a gain of Na +
It is also unlikely that the loss of K + from the ICF was accompanied by a gain of Na + because there was no significant change in ECF volume. Moreover, to gain Na + in the cells, there must be inhibition of the Na-K-ATPase.
What is the ICF volume?
The ICF volume represents the fluid content within the body's cells. This volume cannot be measured directly but is calculated as the difference between the measured TBW and the measured ECF volume. Potassium provides the osmotic skeleton for the ICF in much the same way that sodium provides the osmotic skeleton for the ECF. Because water is freely diffusible into and out of the cell, changes in the tonicity of the ECF are rapidly reflected by similar changes in ICF tonicity ( Saxton and Seldin, 1986). This is largely the result of the movement of water across the cell membrane with resultant changes of ICF volume. Thus, whereas plasma sodium concentration decreases in response to water retention, ICF volume increases (Humes, 1986 ). On the other hand, with water depletion resulting in hypernatremia, ICF volume decreases ( Humes, 1986 ). Relatively little is known about the organization of intracellular water into the various subcellular compartments and organelles.
What temperature does a cell dehydrate?
With intermediate cooling rates (1°-10° C/min), the cells dehydrate as the extracellular fluid turns to ice. The temperature falls fast enough, however, to freeze the intracellular water before cellular dehydration reaches the critical level to produce irreversible cell injury.
Why do cells die during cryolesion?
Some cells die as a direct result of dehydration, whereas others require the added insult provided during isotonic rehydration, which occurs during the thaw cycle. When the cryolesion thaws, the extracellular fluid melts first, briefly creating a relatively hypotonic environment.
Why does water freeze before intracellular fluid?
Because the composition of the intracellular and extracellular compartments differs markedly , the extracellular fluid freezes before the intracellular fluid.
Characteristics of intracellular fluid
Many textbooks refer to intracellular fluid as the cytosol, which is separated from the extracellular space (and the fluids contained in it) by the presence of the plasma membrane.
It's a small volume
The intracellular fluid, then, is contained in a fairly small space (the size of a cell) so it is, when considered for each individual cell, a very small volume, equivalent to 1 or 2 picoliters (1 picoliter is the millionth part of 1 microliter which, in turn, is one millionth of a liter).
Has a lot of dissolved substances
In addition to being made up of water, there is a huge amount of dissolved substances in the intracellular fluid: ions, proteins and other molecules. However, the viscosity of this liquid is very similar to that of water.
Exchange between the intracellular space and the extracellular space
Although intracellular and extracellular fluids are not in direct contact with each other, they exchange water and other substances constantly, either by active transport mechanisms (which require energy intake) or passive transport mechanisms (which occur in favor of a concentration gradient).
Waste and food
The existence of a transport medium that communicates the intracellular fluid with the extracellular one makes it possible for, for example, cells to dispose of some substances or “waste” that they no longer need into the environment that surrounds them and, at the same time, to take from their environment essential nutrients and solutes.
Composition of intracellular fluid
Intracellular fluid is mainly made up of water, after all, we know it for a reason as the universal solvent.
Features
The main function of the intracellular fluid (especially the water that composes it) is to provide a fluid support medium for the fundamental enzymatic reactions of a cell to occur.
What is intracellular fluid?
Intracellular fluid (ICF) represents about two thirds of the TBW, which is equivalent to 30% to 40% of total body weight. However, the proportion of ECF is much greater than that of ICF in preterm infants and reaches 60% of TBW at term. The membranes retaining this fluid allow the passive diffusion of water, whereas active transport mechanisms maintain an internal solute milieu different from that found outside the cells. K+, P 2-, and Mg 2+ are intracellular ions, and Na + and Cl - are predominantly extracellular.
What is the difference between intracellular and extracellular fluid?
Intracellular fluid (ICF) contains predominantly K+, while extracellular fluid (ECF) contains predominantly Na+ (Table 2.1), and it is this difference in ionic concentration between ICF and ECF that, first, allows the generation of the RMP and, second, provides the battery that drives the action potential.
What are the effects of transcellular potassium shifts?
Buffering of the ECF compartment, with reciprocal movement of potassium and hydrogen across the cell membrane, can result in a rise in serum potassium in the case of acidemia and a fall in serum potassium in the case of alkalemia. Two important hormones that are known to drive potassium into the ICF compartment are insulin and catecholamines.
What is the ICF volume?
The ICF volume represents the fluid content within the body's cells. This volume cannot be measured directly but is calculated as the difference between the measured TBW and the measured ECF volume. Potassium provides the osmotic skeleton for the ICF in much the same way that sodium provides the osmotic skeleton for the ECF. Because water is freely diffusible into and out of the cell, changes in the tonicity of the ECF are rapidly reflected by similar changes in ICF tonicity ( Saxton and Seldin, 1986). This is largely the result of the movement of water across the cell membrane with resultant changes of ICF volume. Thus, whereas plasma sodium concentration decreases in response to water retention, ICF volume increases (Humes, 1986 ). On the other hand, with water depletion resulting in hypernatremia, ICF volume decreases ( Humes, 1986 ). Relatively little is known about the organization of intracellular water into the various subcellular compartments and organelles.
What is the role of potassium in the cell?
As the most abundant cation in intracellular fluid, potassium plays an important role in a variety of cell functions. The high K + concentration in cells and the low K + concentration in extracellular fluid are essential to many of the electrical properties of cell membranes in both excitable (nerve, muscle) and nonexcitable tissues (transporting epithelia) ( 273, 454 ). Cell potassium also contributes importantly to the effective osmolality of intracellular fluid and thu s to the regulation of cell volume ( 273, 453, 454, 517 ). Changes in cell potassium tend to modify intracellular acidity, and thus potassium can indirectly influence a variety of metabolic processes by altering cytosolic hydrogen ion activity ( 2, 270 ). These important functions depend on the coordinated action of a variety of regulation mechanisms that serve to maintain constant total-body potassium content (50-55 mmol/kg body weight) and appropriate partition of potassium between extracellular and intracellular fluid ( 2, 151, 270, 296, 349, 398 ).
What temperature does a cell dehydrate?
With intermediate cooling rates (1°-10° C/min), the cells dehydrate as the extracellular fluid turns to ice. The temperature falls fast enough, however, to freeze the intracellular water before cellular dehydration reaches the critical level to produce irreversible cell injury.
Where does osmotic water flow occur?
Osmotic water flow occurs wherever there is a gradient of impermeable solute (such as Na +) across a water-permeable membrane (the body cell membranes). In the body the ECF and ICF compartments are always in osmotic equilibrium, even though the composition of the fluids within them is very different.
What is the function of intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid?
The main function of both intracellular and extracellular fluids is to provide nutrients to the cells in the body and lubrication to the body cavities.
What is the difference between intracellular and extracellular fluid?
The main difference between intercellular and extracellular fluid is that intracellular fluid is the liquid found inside the cell whereas extracellular fluid refers to all the body fluids outside the cell. The intracellular fluid is also known as the cytosol of the cell, comprising a complex mixture of organelles, proteins, and ions.
What is extracellular fluid?
The extracellular fluid (ECF) refers to all the fluid outside the cell. Tissue fluid and plasma are the two major components of the ECF. The cerebrospinal fluid found in the cavities of the brain and spinal cord is also included in the extracellular fluid. The composition of intracellular and extracellular fluid differs by the presence ...
What is the difference between cytosol and tissue fluid?
Cell membrane act as the margin of each fluid. Cytosol is the component of intracellular fluid whereas tissue fluid, blood plasma, and transcellular fluid are the components of the extracellular fluid. The concentration of potassium and magnesium ions in the intracellular fluid is high while the concentration of sodium and calcium ions are high in ...
What is the function of transcellular fluid?
The main function of the transcellular fluid is to lubricate the body cavities and provide nutrients.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane forms separate compartments inside the cell as well and these compartments are known as organelles. The content inside the cell, which is encircled by the cell membrane is also called the cytosol. The cytosol mainly comprises water. 70% of the total volume of the cytosol is made up of water.
What is the liquid in the blood?
The plasma is the liquid found in the blood. 90% of the plasma is composed of water. Blood cells, glucose, proteins such as fibrinogens, albumins, and globulins, oxygen, mineral ions such as sodium, potassium, enzymes, and hormones are suspended in the plasma .