
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is an important nutrient. In fact, every part of your body needs it to function properly. As a supplement, niacin may help lower cholesterol, ease arthritis and boost brain function, among other benefits. However, it can also cause serious side effects if you take large doses.
What are The Amazing health benefits of niacin?
The 12 Proven Health Benefits of Niacin
- Improves cholesterol. Niacin has been a useful ingredient to lower LDL and triglycerides for decades. ...
- Reduces the risk of heart disease. Due to the positive effect niacin has on cholesterol levels, the B vitamin may also reduce heart disease risk.
- Decreases the risk of type 1 diabetes. ...
- Increases cognitive function. ...
- Improves skin health. ...
How does niacin affect your body?
What Are the Dangers of Taking Niacin for Blood Pressure?
- Low Blood Pressure. Niacin can have a blood-pressure lowering effect on the body, which can be beneficial to your high blood pressure symptoms when taken in the correct dosage.
- Medication Interactions. ...
- Niacin Flush. ...
- Organ Damage. ...
What foods have a high source of niacin?
Therefore, here is a list of top 20 foods high in niacin:
- Rice Bran – 34mg/100g (170%DV)
- Shiitake Mushrooms – 14,1mg/100g (71%DV)
- Peanuts, dry-roasted, without salt – 13,5mg/100g (68%DV)
- Spirulina – 12,8mg/100g (64%DV)
- Sunflower Seeds, dry roasted – 7mg/100g (35%DV)
- Millet, raw – 4,7mg/100g (24%DV)
- Barley, pearled, raw – 4,6mg/100g (23%DV)
- Sesame Seeds, whole, dried – 4,5mg/100g (23%DV)
What are the effects of taking niacin?
- Increase HDL (good) cholesterol. It prevents the breakdown of apolipoprotein A1, which is used to make HDL (good) cholesterol. ...
- Reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol. Niacin speeds the breakdown of apolipoprotein B in LDL (bad) cholesterol, causing less to be released by the liver. ...
- Lower triglycerides. ...
What is niacin and its function?
Niacin works in the body as a coenzyme, with more than 400 enzymes dependent on it for various reactions. Niacin helps to convert nutrients into energy, create cholesterol and fats, create and repair DNA, and exert antioxidant effects. [
What are two functions of niacin?
Niacin is involved in many bodily processes and it's important to help our cells grow and function. Our bodies also use niacin to convert nutrients into energy, to make fats and cholesterol and to form and repair our genetic material (DNA).
What happens to niacin in the body?
Niacin is naturally present in many foods, added to some food products, and available as a dietary supplement. All tissues in the body convert absorbed niacin into its main metabolically active form, the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD).
Is vitamin B12 and niacin the same thing?
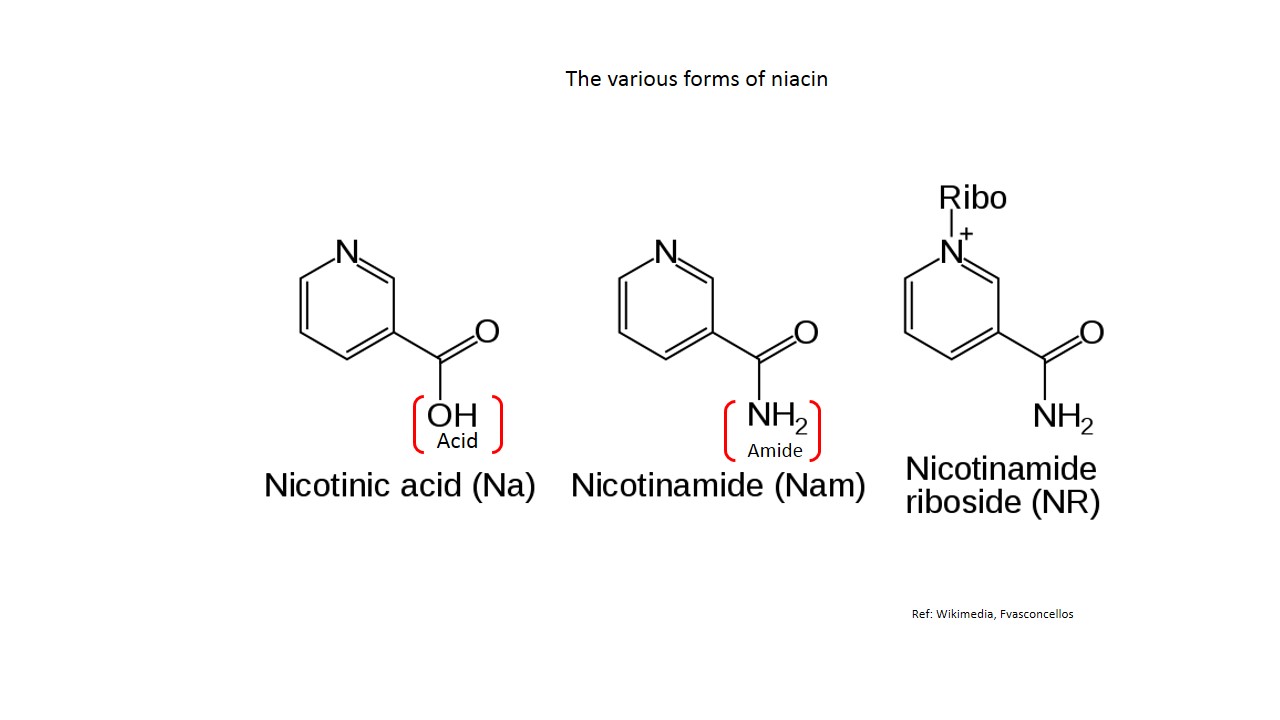
Vitamin B3 is a member of the vitamin family and includes three forms of vitamers: nicotinamide, niacin, and nicotinamide riboside. Vitamin B12 is a type of vitamin involved in metabolism in our body.
How does niacin help anxiety?
Niacin is a precursor to several neurotransmitters in the brain, which may have an impact on mood. Niacin sensitivity is inversely correlated with severity of symptoms, and flush deficits were significantly associated with depressed mood and anxiety.
Why do men take niacin?
Because niacin helps improve blood flow, it may also be good for impotence. In a study published by the Journal of Sexual Medicine, a daily dose of up to 1,500 mg of niacin was enough to improve sexual function among men who had both ED and dyslipidemia.
What are the cons of taking niacin?
Many people are not aware that large doses of niacin vitamins can result in health problems. Some of the common symptoms of over-consumption of niacin include headache, fatigue, diarrhea, heartburn, skin rashes, vomiting, blurred vision, drowsiness, peptic ulcers and organ damage.
Who should not take niacin?
People with any health condition including liver or kidney disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or cardiovascular problems need to talk to a doctor before using niacin supplements. Do not treat high cholesterol on your own with over-the-counter niacin supplements.
Does niacin help you sleep?
There is evidence to suggest that vitamin B3 can assist with sleeping, which means that another unique property about niacin is its ability to be a wonderful and natural sleeping aid via its interaction with tryptophan.
Does niacin help hair growth?
Niacin serves another purpose: assisting in healthy hair growth. It improves blood circulation, and therefore brings oxygen to the hair follicles, resulting in hair development. 2 It's often recommended to those who have alopecia, with the goal of fuller, thicker hair.
When should I take niacin morning or night?
In general, the immediate-release form of niacin should be taken after your evening meal and the extended-release form should be taken at bedtime after a low-fat snack. Taking it in the morning or on an empty stomach might cause you to experience more side effects such as flushing and stomach upset.
Is niacin good for your kidneys?
Niacin also lowers serum phosphorus levels in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), dyslipidemia, and diabetes mellitus [4], [5]. Furthermore, niacin plays a key role in cardiovascular diseases and cardiovascular-related mortality by modifying both dyslipidemia and phosphorus levels [6], [7], [8], [9].
What is a function of niacin quizlet?
niacin participates in protein synthesis. folate and vitamin b12 function as coenzymes in the formation of red blood cells, and the replenishment of cells.
What are two functions of zinc?
Zinc, a nutrient found throughout your body, helps your immune system and metabolism function. Zinc is also important to wound healing and your sense of taste and smell. With a varied diet, your body usually gets enough zinc.
What are 3 functions of zinc?
Zinc is a trace mineral, meaning that the body only needs small amounts, and yet it is necessary for almost 100 enzymes to carry out vital chemical reactions. It is a major player in the creation of DNA, growth of cells, building proteins, healing damaged tissue, and supporting a healthy immune system.
What is the name of the B3 vitamin?
Niacin (also known as vitamin B3) is one of the water-soluble B vitamins. Niacin is the generic name for nicotinic acid (pyridine-3-carboxylic acid), nicotinamide (niacinamide or pyridine-3-carboxamide), and related derivatives, such as nicotinamide riboside [ 1-3 ]. Niacin is naturally present in many foods, added to some food products, and available as a dietary supplement.
How much niacin is in a serving of nuts?
Plant-based foods, such as nuts, legumes, and grains, provide about 2-5 mg niacin per serving, mainly as nicotinic acid. In some grain products, however, naturally present niacin is largely bound to polysaccharides and glycopeptides that make it only about 30% bioavailable [ 3, 4 ].
How much tryptophan is in turkey?
Turkey is an example of a food high in tryptophan; a 3-oz portion of turkey breast meat provides about 180 mg tryptophan, which could be equivalent to 3 mg niacin [ 9 ].
What is a DRI for niacin?
DRI is the general term for a set of reference values used for planning and assessing nutrient intakes of healthy people. These values, which vary by age and sex, include:
How to determine if niacin is in your blood?
Levels of niacin in the blood are not reliable indicators of niacin status. The most sensitive and reliable measure of niacin status is the urinary excretion of its two major methylated metabolites, N1-methyl-nicotinamide and N1-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide [ 2 ]. Excretion rates in adults of more than 17.5 micromol/day of these two metabolites reflect adequate niacin status, while excretion rates between 5.8 and 17.5 micromol/day reflect low niacin status. An adult has deficient niacin status when urinary-excretion rates are less than 5.8 micromol/day. Indicators of inadequacy such as this and other biochemical signs (e.g., a 2-pyridone oxidation product of N1-methyl-nicotinamide below detection limits in plasma or low erythrocyte NAD concentrations) occur well before overt clinical signs of deficiency [ 2 ]. Another measure of niacin status takes into account the fact that NAD levels decline as niacin status deteriorates, whereas NADP levels remain relatively constant [ 1, 3, 5 ]. A “niacin number” (the ratio of NAD to NADP concentrations in whole blood x 100) below 130 suggests niacin deficiency [ 6, 7 ]. A “niacin index” (the ratio of erythrocyte NAD to NADP concentrations) below 1 suggests that an individual is at risk of developing niacin deficiency [ 8 ]. No functional biochemical tests that reflect total body stores of niacin are available [ 5 ].
Why are people undernourished?
People who are undernourished because they live in poverty or have anorexia, alcohol use disorder, AIDS, inflammatory bowel disease, or liver cirrhosis often have inadequate intakes of niacin and other nutrients [ 2, 19, 21, 22 ]. People with inadequate riboflavin, pyridoxine, and/or iron intakes.
How many enzymes are required for NAD?
More than 400 enzymes require NAD to catalyze reactions in the body, which is more than for any other vitamin-derived coenzyme [ 1 ]. NAD is also converted into another active form, the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), in all tissues except skeletal muscle [ 4 ].
What is the role of niacin in the body?
The key role of niacin in your body is to synthesize the coenzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), which are involved in over 400 biochemical reactions in your body — mainly related to obtaining energy from the food you eat ( 1 ).
Why does the brain need niacin?
Your brain needs niacin — as a part of the coenzymes NAD and NADP — to get energy and function properly.
What is the B3 vitamin?
Niacin is one of the eight B vitamins, and it’s also called vitamin B3. There are two main chemical forms and each has different effects on your body. Both forms are found in foods as well as supplements. Nicotinic acid: As a supplement, nicotinic acid is a form of niacin used to reduce cholesterol levels and lower your risk of heart disease ( 1.
What is niacin used for?
Niacin helps protect skin cells from sun damage, whether it’s used orally or applied as a lotion ( 17 ).
How does niacin help with energy?
As with all B vitamins, niacin helps convert food into energy by aiding enzymes.
What is the best way to get niacin?
Niacin is one of eight B vitamins that are important for every part of your body. Luckily, you can get all the niacin you need through your diet. Foods that provide niacin include meat, fish and nuts. However, supplemental forms are sometimes recommended to treat certain medical conditions, including high cholesterol.
What foods contain niacin?
Many foods contain niacin, especially meat, nuts, and legumes. Some foods are also fortified with extra B vitamins.
Did You Know?
Many B vitamins are thought to help increase energy, including niacin. Because niacin is water-soluble (less risk of building up in the body to a toxic level), many people don’t think twice about taking a supplement that may contain 100 times the RDA for the vitamin. Although niacin assists several enzymes in converting food into ATP, a form of energy, taking doses well beyond the RDA will not offer a special boost in energy levels. Eating a balanced diet with a variety of foods is often all that is needed to obtain niacin’s energy-boosting benefit.
How does niacin work?
Niacin works in the body as a coenzyme, with more than 400 enzymes dependent on it for various reactions. Niacin helps to convert nutrients into energy, create cholesterol and fats, create and repair DNA, and exert antioxidant effects. [1,2]
Why is niacin deficiency rare?
A niacin deficiency is rare in the United States and other industrialized countries because it is well-absorbed from most foods (with the exception of some cereal grains in which niacin is bound to its fibers, decreasing the absorption) and is added to many foods and multivitamins.
What is the B3 vitamin?
Niacin – Vitamin B3. Niacin, or vitamin B3, is a water-soluble B vitamin found naturally in some foods, added to foods, and sold as a supplement. The two most common forms of niacin in food and supplements are nicotinic acid and nicotinamide. The body can also convert tryptophan—an amino acid—to nicotinamide.
How much niacin is in a niacin diet?
RDA: Niacin is measured in milligrams (mg) of niacin equivalents (NE). One NE equals 1 milligram of niacin or 60 mg of tryptophan. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for adults 19+ years is 16 mg NE for men, 14 mg NE for women, 18 mg NE for pregnant women, and 17 mg NE for lactating women.
What are the symptoms of niacin deficiency?
A severe niacin deficiency leads to pellagra, a condition that causes a dark, sometimes scaly rash to develop on skin areas exposed to sunlight; bright redness of the tongue; and constipation/diarrhea. Other signs of severe niacin deficiency include: Depression. Headache. Fatigue.
Why is niacin rare?
A niacin deficiency is rare because it is found in many foods, both from animals and plants.
What is niacin and what does it do?
Niacin (also called vitamin B3) helps turn the food you eat into the energy you need. Niacin is important for the development and function of the cells in your body.
How much niacin do I need?
The amount of niacin you need depends on your age and sex. Average daily recommended amounts are listed below in milligrams (mg) of niacin equivalents (NE) (except for infants in their first 6 months).
What foods provide niacin?
Niacin is found naturally in many foods, and is added to some foods. You can get recommended amounts of niacin by eating a variety of foods, including the following:
What kinds of niacin dietary supplements are available?
The two main forms of niacin in dietary supplements are nicotinic acid and nicotinamide.
What are some effects of niacin on health?
Scientists are studying niacin to better understand how it affects health. Here is an example of what this research has shown.
Can niacin be harmful?
The niacin that food and beverages naturally contain is safe. However, dietary supplements with 30 mg or more of nicotinic acid can make the skin on your face, arms, and chest turn red and burn, tingle, and itch. These symptoms can also lead to headaches, rashes, and dizziness.
What is vitamin B3?
Niacin (Vitamin B3) helps turn food into energy. Learn how much you need, good sources, deficiency symptoms, and health effects here.
What is niacin?
Niacin is the generic name used for a group of water-soluble compounds (nicotinamide and nicotinic acid) that belong to the family of B- vitamins.
What are the functions of niacin?
Niacin is involved in many bodily processes and it’s important to help our cells grow and function . Our bodies also use niacin to convert nutrients into energy, to make fats and cholesterol and to form and repair our genetic material ( DNA ).
How much niacin do I need per day?
How much niacin you need per day changes according to your age, sex, life-stage and other individual factors such as physical activity.
What foods contain Niacin?
We can get niacin from a variety of foods but some of the richest sources include:
Does niacin interact with other nutrients?
Our bodies can make 1 mg of niacin from each 60 mg of tryptophan, with the help of iron, vitamin B6 and riboflavin. Having good amounts of these micronutrients in our diets is important to ensure that our bodies can make niacin when there’s not enough from foods.
What happens if I have too much niacin?
It is highly unlikely to get harmful amounts of niacin through foods alone. Even if we exceed our daily needs, our bodies remove the niacin surplus through urine.
When should I pay extra attention to my niacin intake?
Niacin deficiency is not a risk for the general population since most people can get the recommended amounts of this vitamin from a varied and balanced diet.
What foods can help with high cholesterol?
Rice. Fish. Lean meats. Legumes. Peanuts. Poultry. NIACIN AND HEART DISEASE. For many years, doses of 1 to 3 grams of nicotinic acid per day has been used as a treatment for high blood cholesterol. Niacin can help in increasing level of good cholesterol (HDL cholesterol) in the blood.
What causes pellagra?
A deficiency of niacin causes pellagra. The symptoms include:
Why is niacin important?
Niacin helps the digestive system, skin, and nerves to function. It is also important for changing food to energy.
How do vitamins leave the body?
Leftover amounts of the vitamin leave the body through the urine. The body keeps a small reserve of these vitamins. They have to be taken on a regular basis to maintain the reserve.
How to get the daily requirement of vitamins?
Ask your provider which amount is best for you. The best way to get the daily requirement of essential vitamins is to eat a balanced diet that contains a variety of foods.
What is the RDA for nutrition?
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA): average daily level of intake that is enough to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97% to 98%) healthy people . Adequate Intake (AI): when there is not enough evidence to develop an RDA, the AI is set at a level that is thought to ensure enough nutrition.
Does niacin help with cholesterol?
Niacin can help in increasing the level of good cholesterol (HDL cholesterol) in the blood. It can also bring down the amount of unhealthy fat in the blood. Always talk to your health care provider before starting any supplements.
What is Niacin?
There are eight essential B vitamins, and Niacin is one of them. Niacin is a B3 vitamin, which is a water-soluble vitamin.
Why is pellagra so common?
Pellagra is a common disease known due to the lack of niacin in the diet. The condition causes sores, inflammation, dementia, and diarrhea. Studies show that pellagra often affects developing countries due to the lack of resources and access to niacin foods and supplements.
What is the best treatment for pellagra?
Niacin supplements and nad therapy are the most effective option for treating pellagra.
What happens if you don't take B3?
Without vitamin B3, the body can be at risk of heart conditions, poor cholesterol levels, bad skin health, and cognitive function. A niacin deficiency can lead to medical conditions, such as pellagra. Niacin intake is essential for your health.
How does niacin work?
Niacin works to convert food into energy. Thus, niacin can provide you energy with food consumption.
How to get more niacin?
To obtain more niacin, the following doses are the general daily amounts to respect: 1 Children: 250mg daily, for those over 16 years of age 2 Adults: 250mg daily, which can be increased
What are the two types of niacin?
Within niacin, there are two chemical formations, nicotinic acid, and niacinamide. Both are in food or supplements that contain niacin, but both have diverse effects and health benefits.
What is niacin used for?
Niacin or vitamin B3 is also used for treating various infections and extreme fluid loss conditions like diarrhoea, cholera, etc.
What is the role of vitamin B3 in the body?
Vitamin B3 carries out a pivotal fundamental role, in maintaining optimal energy metabolism in the body. Also known as niacin, it primarily exists in two forms – nicotinamide and nicotinic acid. These are converted into two central compounds in the system – NADP and NADPH, which work as electron carriers, essential for the processing ...
What is the B3 complex?
Vitamin B3, or well known as vitamin B3 complex is one of the eight essential water-soluble vitamins. The term complex denotes the three forms of the B3 vitamin which are niacin (nicotinic acid), nicotinamide (niacinamide), and nicotinamide riboside. These three forms of vitamin B3 are converted within the body to synthesize Nicotinamide Adenine ...
Why is B3 important for the digestive system?
Vitamin B3 is extremely important for the healthy functioning of the gastrointestinal system by improving digestion, proper absorption of the food juices into the body and excretion of the waste products from the intestines. It also prevents constipation and reduces flatulence.
Why is vitamin B3 bad?
Nowadays, several developing countries are also facing vitamin B3 deficiencies due to a rising number of populations suffering from malnutrition, poverty, and alcoholism.
What is the best way to prevent deficiency syndrome?
Like any other water-soluble vitamins, this vitamin B3 complex also gets washed away from the body, hence one should consume a diet rich in vitamin B3 food options to prevent the deficiency syndromes. Vitamin B3 is not only found in a variety of processed and fortified foods and energy drinks but also in innumerable natural food ...
What is the importance of vitamin B3?
Vitamin B3 holds high significance as it is extremely necessary for the healthy functioning of the neural system, digestive system, lower cholesterol, good for skin, hair and is also required for enzyme synthesis. Like all other vitamins, B3 also plays an important role in breaking down food to synthesize energy and helps in the signalling of cells, synthesizing and repairing DNA and aids in the functioning of more than 200 enzymes. Also Read: Vitamin B1 – Functions, Food Sources, Deficiencies and Toxicity
What is the name of the vitamin B3?
Niacinamide is one of the two forms of vitamin B3 — the other being nicotinic acid. Vitamin B3 is also known as niacin.
Why is B3 important?
Vitamin B3 plays a vital role in converting the food you eat into usable energy and helps your body’s cells carry out important chemical reactions ( 1. Trusted Source. ). Since it’s water-soluble, your body doesn’t store this vitamin, which is why you need to eat nicotinic acid or niacinamide daily.
How much tryptophan is needed to make vitamin B3?
However, the conversion of tryptophan to vitamin B3 is inefficient, as it takes 60 mg of tryptophan to make just 1 mg of vitamin B3 ( 1 ).
Why is niacinamide important?
Niacinamide plays an important role in keeping your skin healthy.
What is a saline solution used for?
It has been used to treat skin conditions like acne and rosacea, a facial skin disorder characterized by redness ( 5, 6 ).
How many B vitamins are in a B complex?
The vitamin is also included in B-complex supplements, which contain all eight B vitamins.
Is niacinamide good for melanoma?
Niacinamide may benefit those with certain skin conditions and reduce the risk of melanoma in high-risk individuals. It may also be useful for people with chronic kidney disease and, to a lesser extent, type 1 diabetes.

Overview
Deficiency
Infants
Children
- 1–3 years: 6 mg NE/day
4–8 years: 8 mg NE/day
Adolescents and adults
- Men ages 14 years and older: 16 mg NE/day
Women ages 14 years and older: 14 mg NE/day - Pregnant women: 18 mg NE/day
Breastfeeding women: 17 mg NE/day
Improves blood fat levels
- Niacin may help to improve your blood fat levels by:
increasing your HDL (good) cholesterol - reducing your LDL (bad) LDL cholesterol
This may translate to a decrease in heart disease risk, although several studies have found no link between niacin supplementation and a decrease in heart disease risk or deaths ( 4, 5 ).
May reduce blood pressure
- One role of niacin is to release prostaglandins, or chemicals that help your blood vessels widen …
In one observational study of over 12,000 adults, researchers found that each 1 mg increase in daily niacin intake was associated with a 2% decrease in high blood pressure risk — with the lowest overall high blood pressure risk seen at a daily niacin intake of 14.3 to 16.7 mg per day ( … - A high quality study also noted that single doses of 100 mg and 500 mg of niacin slightly reduce…
However, more research is needed to confirm these effects.
May help treat type 1 diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which your body attacks and destroys insulin-crea…
There’s research to suggest that niacin could help protect those cells and possibly even lower the risk of type 1 diabetes in children who have a higher chance of developing this condition ( 10 ). - However, for people with type 2 diabetes, the role of niacin is more complicated.
On one hand, it can help lower the high cholesterol levels that are often seen in people with type 2 diabetes. On the other, it has the potential to increase blood sugar levels. As a result, people with diabetes who take niacin to treat high cholesterol also need to monitor their blood sugar carefull…
Boosts brain function
- Your brain needs niacin — as a part of the coenzymes NAD and NADP — to get energy and functi…
In fact, brain fog and even psychiatric symptoms are associated with niacin deficiency ( 1, 13 ). - Some types of schizophrenia can be treated with niacin, as it helps undo damage to brain cells t…
Preliminary research shows that it could also help keep the brain healthy in cases of Alzheimer’s disease. However, results are mixed ( 15, 16 ).
Improves skin health
- Niacin helps protect skin cells from sun damage, whether it’s used orally or applied as a lotion ( …
It may help prevent certain types of skin cancer as well. One high quality study in over 300 people at high risk of skin cancer found that taking 500 mg of nicotinamide twice daily reduced rates of nonmelanoma skin cancer compared to a control ( 18 ). - Niacin can help treat many conditions. It appears to exert positive effects on blood fat and bloo…
Niacin is found in a variety of foods, especially meat, poultry, fish, nuts, and legumes. Some foods may also be fortified with niacin and other vitamins, like breakfast cereals ( 1 ).
Just one thing
- Try this today: Concerned you may not be getting enough niacin? Keep a log of your food intake for a day or two. If you regularly eat animal protein, nuts, seeds, or niacin-fortified foods, you are probably getting enough. If not, you may want to speak with a healthcare professional about supplementation.
Recommended Amounts
Food Sources
Supplements
- Niacin is available as a supplementin the form of nicotinic acid or nicotinamide. Sometimes the amounts in supplements are far beyond the RDA, causing unpleasant side effects of flushing. Niacin supplements are also available as a prescription medicine that is used to treat high cholesterol; this typically comes in an extended release form of nicotinic acid that allows slower…
Signs of Deficiency and Toxicity
- Deficiency
A niacin deficiency is rare in the United States and other industrialized countries because it is well-absorbed from most foods (with the exception of some cereal grains in which niacin is bound to its fibers, decreasing the absorption) and is added to many foods and multivitamins. A severe ni… - Toxicity
Toxicity when eating foods containing niacin is rare, but can occur from long-term use of high-dose supplements. A reddened skin flush with itchiness or tingling on the face, arms, and chest is a common sign. Flushing occurs mainly when taking high-dosage supplements in the form of ni…
Did You Know?
- Many B vitamins are thought to help increase energy, including niacin. Because niacin is water-soluble (less risk of building up in the body to a toxic level), many people don’t think twice about t...
- Corn is naturally high in niacin, but it is bound to carbohydrates which makes it difficult for the human body to absorb. However, when corn is nixtamalized (a traditional process in tortilla …
- Many B vitamins are thought to help increase energy, including niacin. Because niacin is water-soluble (less risk of building up in the body to a toxic level), many people don’t think twice about t...
- Corn is naturally high in niacin, but it is bound to carbohydrates which makes it difficult for the human body to absorb. However, when corn is nixtamalized (a traditional process in tortilla makin...
Terms of Use
- The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The N…