
What is the purpose of an ovule in a flower?
Types of Ovules
- Orthotropous (Atropous) This is where the body of these ovules is straight so that the chalaza, where the nucellus and integuments merge, the funicle, which attaches the ovule to the ...
- Anatropous. ...
- Hemi-anatropous. ...
- Campylotropous. ...
- Amphitropous. ...
- Circinotropous. ...
What is the main function of ovary in a flower?
- Parietal - unilocular, syncarpous, no wall present separating carpals - cucumber
- Free central - multilocular, syncarpous, ovules centrally attached - primrose
- Axile - multilocular, syncarpous - lemon
- Basal - unilocular, monocarpous - marigold
- Marginal - unilocular, monocarpous - pea
What does the ovule do in the flower?
The ovule plays a vital role in sexual reproduction. Once a pollen grain lands on the stigma of a flower of its same species, it sends out a pollen tube down through the style. This tube then enters the ovary and reaches the ovule of the plant. Once that occurs, fertilization can arise as the nucleus of the pollen grain is sent down the tube to ...
What is the function of the placenta in a flower?
placenta, plural Placentas, orPlacentae, in botany, the surface of the carpel (highly modified leaf) to which the ovules (potential seeds) are attached. The placenta is usually located in a region corresponding somewhat to the margins of a leaf but is actually submarginal in position. The placentation, or arrangement of ovules within the ovary, is frequently of taxonomic value.
1. What are the functions of Ovule?
The primary function of the plant’s ovule is to take care of sexual reproduction, and also make it straightforward.The process of reproduction begi...
2. Mention some fun facts about Ovule.
The ovule itself is the reproductive organ that contains the egg cell which later develops into the seed. In angiosperms, the seed develops inside...
3. What is Nucellus?
Nucellus is one of the components of the ovule of a plant. As the largest part of the ovule, the nucellus contains both the embryo sac and the nutr...
4. Explain the process after pollination of ovules.
A chain of events takes place after pollination that leads to fruit formation. Once pollen reaches the stigma of a particular flower, certain event...
5. What Happens After the Pollination of Ovules?
After pollination, a chain of events takes place that leads to the formation of the fruit. When the pollen lands on the stigma of the flower of the...
6. How Many Types of Ovules are There?
There are categorically six types of ovules. These are orthotropous or anatropous ovules, anatropous ovule, hemi-anatropous ovule or hemitropous ov...
What is the ovule in seed plants?
Definition of Ovule. In the seed plants, the ovule is a structure rise and consists of the female reproductive cells. It has 3 parts: The integument, it forms its outer layer that we call a nucleus and also a remnant of the megasporangium.
What is the structure of an ovule?
Structure of Ovule. The ovule is an integument megasporangium. It contains the stalk and the body. We call the stalk as a funicle. One end of the funicle is having an attachment with the placenta and the other end is having an attachment with the body of it. However, the point where the funicle and the body attach is hilum.
What is the function of megaspores in the mitosis?
The megaspores remain in them and divide by the mitosis for producing the haploid female gametophyte or megagametophyte that also stays inside them. The remnants of the megasporangium tissue are surrounding the gametophyte. The gametophytes produce archegonia and these produce the egg cells.
What is the structure of a plant that develops into a seed during the fertilization process?
Firstly, the ovule is a structure of a plant that develops into a seed during the fertilization process. A mature one contains food tissue, one or two future seed coats cover it, and we call them integuments. A small opening present in the integuments lets the pollen tube to enter and discharge its sperm nuclei into the embryo sac.
What is the small opening in the integuments?
A small opening present in the integuments lets the pollen tube to enter and discharge its sperm nuclei into the embryo sac. Moreover, a large oval cell in which the development and the fertilization occurs. However, each of the these has an attachment between its base and the stalk i.e. funiculus that bears it.
How does pollen grain affect sexual reproduction?
It plays an important role in the process of sexual reproduction. Once a pollen grain falls on the stigma of a flower of its similar species. In addition , it sends out a pollen tube below through the style. Then this tube enters inside the ovary and then reaches into the ovule of the plant.
What is the point where the body and the funicle attach?
However, the point where the funicle and the body attach is hilum. Many times funicle gets fused with the body of the ovule one side and makes a ridge that we call as a raphe. The body of the ovule has 2 ends that are the basal end and the other one is the upper end we also call micropylar end.
Where are ovules kept in a flower?
These seeds later ripen and turn into an adult plant. In plants, ovules are kept in ovaries at the very bottom of a vase type structure known as a carpel, and this has a neck called a style with an opening at the top, which is called a stigma. What is ovule in a flower?
How does the ovule help plants reproduce?
The Plant Ovule plays an essential role in the sexual reproduction of plants. The process of reproduction becomes simple with the presence of an ovule. When the pollen grain lands on the stigma of the flower of the same species of flower, the plant brings out the pollen tube down through the style. Next, this pollen tube enters the ovary and reaches the ovule of the plant, and after this, fertilisation can occur as the nucleus of the pollen grain is sent down to merge with the nucleus in the embryo sac.
How many types of ovules are there?
Ans: There are categorically six types of ovules. These are orthotropous or anatropous ovules, anatropous ovule, hemi-anatropous ovule or hemitropous ovule, campylotropous ovule, amphitropous ovule, and circinotropous ovule. The body of the ovule is straight in the orthotropous ovule. In anatroposis, the body of the ovule is completely inverted. ...
What happens to the ovule after fertilisation?
In a flower, the ovule starts to swell after fertilisation, and it starts to toughen up in the due process of becoming a seed. The ovary starts growing around it and becomes a fruit. However, this is not true for all plants.
What is an ovule in a plant?
Read More. What is ovule? The Plant Ovule is a part of the female reproductive organ. It is that part of the plant where female reproductive cells are made and kept, and these cells and, in due course, these cells develop into seeds after fertilisation. These seeds later ripen and turn into an adult plant.
What happens after pollination?
Ans: After pollination, a chain of events takes place that leads to the formation of the fruit. When the pollen lands on the stigma of the flower of the same species, these events take place that ends in the final formation of seeds. The male gamete mixes with the egg cell and with the secondary nucleus and undergoes fertilisation. Only after the fertilisation occurs, the ovule develops into a seed. This seed is a source of food for the plant as well. After this, the ovule encloses an embryo inside the seed coat, and finally, the ovary develops into a fruit.
What is the meaning of the ovule?
Components. What is the meaning of ovule? It is part of the plant’s reproductive system and has many components, and this is primarily the ovule’s meaning. The plant ovule is made up of the female gametophyte, the integuments, and the nucellus. The gametophyte is also called an embryo sac, and it is found at the centre of the flowering plant.
Where are the ovules located in a flower?
In flowering plants, the ovule is located inside the portion of the flower called the gynoecium. The ovary of the gynoecium produces one or more ovules and ultimately becomes the fruit wall. Ovules are attached to the placenta in the ovary through a stalk-like structure known as a funiculus (plural, funiculi).
What is the ovule of a seed plant?
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the integument, forming its outer layer, the nucellus (or remnant of the megasporangium ), and the female gametophyte (formed from a haploid megaspore) in its center.
What is the orientation of an ovule?
Ovule orientation may be anatropous, such that when inverted the micropyle faces the placenta (this is the most common ovule orientation in flowering plants), amphitropous, campylotropous, or orthotropous ( anatropous are common and micropyle is in downward position and chalazal end in on the upper position hence, in amphitropous the anatropous arrangement is tilted 90 degrees and in orthotropus it is completely inverted) . The ovule appears to be a megasporangium with integuments surrounding it. Ovules are initially composed of diploid maternal tissue, which includes a megasporocyte (a cell that will undergo meiosis to produce megaspores). Megaspores remain inside the ovule and divide by mitosis to produce the haploid female gametophyte or megagametophyte, which also remains inside the ovule. The remnants of the megasporangium tissue (the nucellus) surround the megagametophyte. Megagametophytes produce archegonia (lost in some groups such as flowering plants), which produce egg cells. After fertilization, the ovule contains a diploid zygote and then, after cell division begins, an embryo of the next sporophyte generation. In flowering plants, a second sperm nucleus fuses with other nuclei in the megagametophyte forming a typically polyploid (often triploid) endosperm tissue, which serves as nourishment for the young sporophyte.
What is the purpose of the micropyle in a gymnosperm?
The micropyle opening allows the pollen (a male gametophyte) to enter the ovule for fertilization. In gymnosperms (e.g., conifers), the pollen is drawn into the ovule on a drop of fluid that exudes out of the micropyle, the so-called pollination drop mechanism. Subsequently, the micropyle closes. In angiosperms, only a pollen tube enters ...
What is meiosis in gymnosperms?
In gymnosperms, three of the four haploid spores produced in meiosis typically degenerate, leaving one surviving megaspore inside the nucellus.
What is the integument of an ovule?
Models of different ovules, Botanical Museum Greifswald. An integument is a protective layer of cells surrounding the ovule. Gymnosperms typically have one integument (unitegmic) while angiosperms typically have two integuments (bitegmic).
What is an ovule?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. A small body in seed-bearing plants that consists of the integument (s), nucellus, and embryosac (containing the egg cell) and develops into the seed after fertilization . For animal ovules, see Ovum.
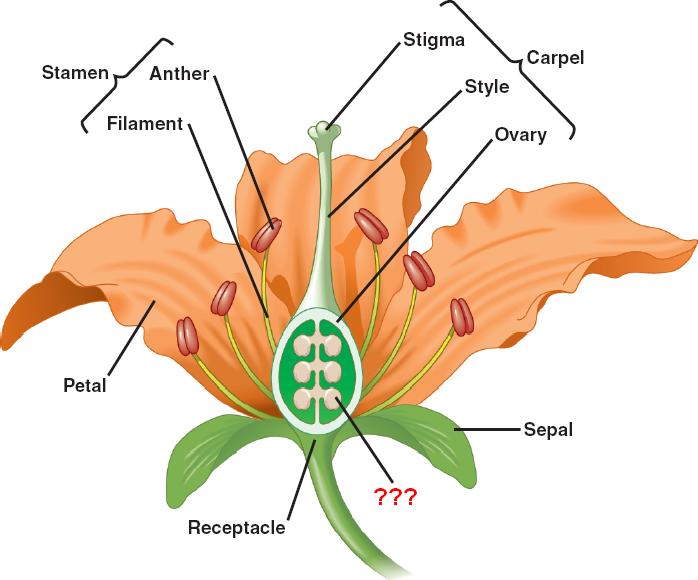
The Major Parts of a Flower
A flower is a reproductive structure of angiosperms, the most diverse and complex plant species in the world. Angiosperms are the most extensive group of plants on Earth and are responsible for the vast majority of fruit production. A flower is a unique structure that varies considerably among species.
Ovary of a Flower: Definition
What is the ovary of a flower? The definition of an ovary in a plant is a part of a plant that functions as the structure where fertilization and seed development occur. The ovary, in most cases, becomes the fruit for seed dispersal. The ovary is usually located at the base of the flower, below the stigma and style.
Where is the Ovary in a Flower?
The ovary in the flower is located in the inner whorl. The position of an ovary is based on the point of attachment of the petals, stamen, and sepals. If the ovary sits above the attachment, it is a superior ovary or hypogynous. If the petals, stamen, and sepals are attached at a mid-point, this is perigynous.
Structure and Function of Ovary in Flowers
The ovary of a flower is composed of a number of structures to ensure ovule development and the production of seed-bearing fruit. The outer layer of the ovary is called the ovary wall which eventually develops into the pericarp in fruits (outer, protective covering). The locule is the compartment that houses the ovule.
Ovule Functions in a Flower
The ovules of angiosperms function to produce a seed that remains dormant until germination outside the fruit. In this process, the seed is protected and nourished by the tissue (or endosperm) of the ovule. Unique to angiosperms, the ovule of a flower undergoes double fertilization.

Ovule Definition
Components of Ovules
- The ovule is made up of the nucellus, the integuments that form the outermost layer, and the female gametophyte (called an embryosac in flowering plants), which are found at the very center.
Related Biology Terms
- Anther – The part of the stamenthat contains pollen grains, or male gametophytes.
- Asexual Reproduction– Reproduction in which genetically identical offspring are produced from a single parent without the formation of gametes.
- Diploid – A nucleus, cell, or organismthat contains two sets of chromosomes, one from the female parent and another from the male parent.
- Anther – The part of the stamenthat contains pollen grains, or male gametophytes.
- Asexual Reproduction– Reproduction in which genetically identical offspring are produced from a single parent without the formation of gametes.
- Diploid – A nucleus, cell, or organismthat contains two sets of chromosomes, one from the female parent and another from the male parent.
- Pollination– The transfer of pollen to the female reproductive organs of the same plant or a different plant of the same species.
Quiz
- 1. The male gametophyte in a seed plant is the: A. Ovary B. Stigma C. Pollen grain D.Embryo sac 2. Which of the following is the type of ovule that is completely inverted? A. Amphitropous B. Anatropous C. Circinotropous D.Orthotropous 3. Which of the following becomes the plant’s seed after fertilization? A. The ovary B. The stigma C. The pollen grains D.The ovule