What are the dangers of high prolactin levels?
What are the side effects of high prolactin levels in men?
- Headaches
- Visual impairment
- Reduced libido
- Fertility issues
- Erectile dysfunction
- Abnormal lack of body and facial hair
- Gynecomastia (commonly known as man-boobs)
What else can cause elevated prolactin levels?
These drugs include antipsychotics, drugs used to treat hypertension, and tranquilizers. Other causes of elevated prolactin levels are hypothyroidism and polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS. They might cause the prolactin level to slightly rise. Many other diseases can also cause a rise in prolactin levels.
What causes high prolactin levels?
What causes abnormally high levels of prolactin?
- Prolactinomas can cause elevated prolactin levels. A prolactinoma is the most common cause of higher-than-normal prolactin levels in your blood. ...
- Medications that can cause elevated prolactin levels. ...
- Health conditions that can cause elevated prolactin levels. ...
- Other pituitary gland tumors that can cause elevated prolactin levels. ...
How to reduce prolactin medically and naturally?
Reduce High Prolactin Levels Naturally And Get Pregnant
- Total Fertility Cleansing Kit. The first step to fertility health is to remove the toxins from your body that are causing infertility problems.
- ProlaClear Capsule. ProlaClear Capsule Is Especially Designed To Reduce High Prolactin Level, Inhibits Galactorrhea, Suppress Lactation And Balance Hormones Naturally.
- ProlaClear Tea. ...
- FertilCentrate Technique. ...

What is the main function of prolactin hormone?
Prolactin contributes to hundreds of physiologic functions, but the two primary responsibilities are milk production and the development of mammary glands within breast tissues. Prolactin promotes the growth of mammary alveoli, which are the components of the mammary gland, where the actual production of milk occurs.
What is the function of the prolactin-releasing factor?
PRF is a polypeptide hormone originating in the hypothalamus, and whose action is to stimulate the secretion of the prolactin in the pituitary gland.
What is the function of prolactin inhibiting hormone?
Prolactin Inhibiting Factor (PIF): Inhibits the release of prolactin and is purported to be dopamine which is secreted by the tuber infundibular neurons. Lactation: The production of milk through the actions of prolactin on breast tissue to create polyamines, casein, lactose and phospholipids.
What stimulates the release of prolactin releasing hormone?
The major physiological stimulus to prolactin secretion is suckling. Prolactin levels also rise during the latter half of pregnancy, an effect that is thought to be mediated by oestradiol. Like growth hormone, prolactin secretion is also increased during sleep and by stress and exercise.
Where is prolactin releasing hormone produced?
In humans, prolactin is produced both in the front portion of the pituitary gland (anterior pituitary gland) and in a range of sites elsewhere in the body. Lactotroph cells in the pituitary gland produce prolactin, where it is stored and then released into the bloodstream.
What happens when prolactin is high?
Too much prolactin reduces the production of the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Too much prolactin also can prevent the release of an egg during the menstrual cycle (anovulation) in females. In males, too much prolactin also can lead to decreased sperm production. Bone loss (osteoporosis).
Which hormone is also known as prolactin?
prolactin, also called luteotropic hormone (LTH) or luteotropin, a protein hormone produced by the pituitary gland of mammals that acts with other hormones to initiate secretion of milk by the mammary glands.
What causes high prolactin in females?
Hyperprolactinemia means you have higher-than-normal levels of prolactin in your blood. The most common cause is a prolactinoma, a benign (noncancerous) tumor in your pituitary gland. Certain health conditions and medications can also cause hyperprolactinemia.
What increases prolactin secretion?
The major physiological stimulus to prolactin secretion is suckling. Prolactin levels also rise during the latter half of pregnancy, an effect that is thought to be mediated by oestradiol. Like growth hormone, prolactin secretion is also increased during sleep and by stress and exercise.
What is prolactin release?
Prolactin is secreted from the pituitary gland in response to eating, mating, estrogen treatment, ovulation and nursing. It is secreted heavily in pulses in between these events. Prolactin plays an essential role in metabolism, regulation of the immune system and pancreatic development.
What is the function of prolactin and oxytocin?
The two primary hormones that are needed for lactation are prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin stimulates milk biosynthesis within the alveolar cells of the breast and oxytocin stimulates contraction of the myoepithelial cells that surround the alveoli, causing the milk to be ejected into the ducts leading to the nipple.
How is prolactin secretion controlled?
Prolactin secretion is photoperiodically controlled. In starlings under experimental photoperiodic manipulations, prolactin only increases to a peak under photoperiods that are also long enough to induce a molt (i.e., equal to or greater than 12L:12D), and then peak prolactin concentrations coincide fairly closely with the start of molt ( Dawson and Goldsmith, 1983 ). Under constant photoperiods of 12L:12D, starlings undergo repeated circannual cycles of gonadal maturation and molt; in this condition, prolactin also cycles with peak values coinciding with the onset of molt ( Dawson, 1997). Importantly, when starlings were actively immunized against vasoactive intestinal peptide (the prolactin-releasing hormone in birds) and transferred to a long photoperiod, the increase in normal prolactin was prevented and these birds did not molt (Dawson and Sharp, 1998 ).
Which hormones are involved in the luteal phase?
Whereas estrogens predominate in the follicular phase, progesterone predominates the luteal phase ( Fig. 5.5 ).
How many genes are there for peptide hormones?
About 50 peptide hormones can be found in a standard medical endocrinology textbook. While not an exhaustive list, these can provide an overview of patterns of biosynthesis encountered using fairly well-known examples. There are 65 genes for these 50 odd hormones ( Table 1 ), due in large part, to the existence of multiple genes for several hormones, including gonadotropin-releasing hormone, relaxin, growth hormone, placental lactogen, as well as the human chorionic gonadotropin β-subunit (2 GNRH, 3 RLXN, 2 GH, 3 CSH and 6 CGB genes, respectively). To a lesser extent, several heterodimeric hormones, luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and the inhibins, require products of two genes: LHB / CGA, FSHB / CGA, TSHB / CGA, CGB / CGA, and INHA / INHBA or INHA / INHBB, respectively. However, sharing a common subunit gene reduces the number of additional genes needed. Several genes, such as POMC, INHBA, and INHBB, encode more than one hormone, which further reduces the number of genes necessary to generate this group of peptide hormones.
What happens if estrogen levels drop too quickly?
Estrogen activity (E2) declines after ovulation. If it declines too quickly on days 15–19, there will be metrorrhagia. This can be due to insufficient rise in prolactin (PL, gray line), a sudden drop in GnRH and FSH that is intrinsic, or due to delayed CRH activity around day 18.
Which genes encode more than one hormone?
Several genes, such as POMC, INHBA, and INHBB, encode more than one hormone, which further reduces the number of genes necessary to generate this group of peptide hormones. Table 1. Peptide hormone genes and transcripts. Gene symbol a.
Is progesterone dominant in metrorrhagia?
In this final form of metrorrhagia, there is absolute progesterone predominance. If it arises from intrinsically strong luteal activity, the woman appears luteal in morphology: androgenic build, left > right asymmetry, tendency toward acne after adolescence, etc. If it is due to adaptative activity, there is typically a hyperprolactinemia as noted in metrorrhagia type 2C, but limited to neuroendocrine management of the luteal phase.
Does TRH release PRL?
Like the situation for GH, there is evidence for an endogenous factor or factors that stimulate PRL release. This PRL-releasing hormone (PRH) at first was thought to be the tripeptide TRH because administration of synthetic TRH stimulates PRL release as well as TSH release, at least under some conditions. However, the neuropeptide VIP stimulates PRL release during suckling when TRH is ineffective. Administration of TRH to suckling mice causes elevated TSH release but no increase in PRL release such as caused by VIP. Furthermore, TSH release is not observed during normal suckling, arguing against TRH as being responsible for PRL release at that time. A peptide first isolated as an orphan receptor was found to be a potent releaser of PRL both in vivo and in vitro. This prolactin-releasing peptide (PrRP) releases PRL when administered in low doses but is not as potent as TRH. PrRP apparently is widely distributed in the brain and can modulate many unrelated physiological events, including lactation, stress, body weight homeostasis, feeding behavior, and gastric motility. It is also a potent releaser of PRL in some nonmammals (see Chapter 5 ). Additional studies have shown that PrRP affects appetite (see Chapter 12 ). Tuberalin can stimulate release of PRL from lactotropes and is believed to be an important regulator related to photoperiodic effects on PRL release ( see pineal gland discussion, p 143).
What are the factors that stimulate prolactin release?
While many prolactin stimulating and enhancing factors are well known (such as thyrotropin-releasing hormone, oxytocin, vasoactive intestinal peptide and estrogen) those have primary functions other than stimulating prolactin release and the search for hypothetical releasing factor or factors continues.
When was the prolactin releasing peptide identified?
The prolactin-releasing peptide identified in 1998 was a candidate for this function, however as of 2008 it appears its function is not yet completely elucidated.
What is the name of the hormone that releases hormones?
Prolactin-releasing hormone. Prolactin-releasing hormone , also known as PRLH, is a hypothetical human hormone or hormone releasing factor. Existence of this factor has been hypothesized as prolactin is the only currently known hormone for which almost exclusively negative regulating factors are known (such as dopamine, leukemia inhibitory factor, ...
Is prolactin a negative hormone?
Existence of this factor has been hypothesized as prolactin is the only currently known hormone for which almost exclusively negative regulating factors are known (such as dopamine, leukemia inhibitory factor, some prostaglandins) but few stimulating factors. While many prolactin stimulating and enhancing factors are well known ...
What is the name of the hormone that makes prolactin?
Alternative names for prolactin. In everyday language, prolactin is referred to as the ‘milk hormone’; PRL; luteotropic hormone; LTH.
Which hormones decrease prolactin?
In addition to dopamine and oestrogen, a whole range of other hormones can both increase and decrease the amount of prolactin released in the body, with some examples being thyrotropin-releasing hormone, oxytocin and anti-diuretic hormone.
How is prolactin controlled?
One of the main regulators of the production of prolactin from the pituitary gland is the hormone called dopamine, which is produced by the hypothalamus, the part of the brain directly above the pituitary gland. Dopamine restrains prolactin production, so the more dopamine there is, the less prolactin is released. Prolactin itself enhances the secretion of dopamine, so this creates a negative feedback loop.
What happens if I have too much prolactin?
The condition of having too much prolactin circulating in the blood is called hyperprolactinaemia. The most common causes of hyperprolactinaemia include pregnancy, medications that reduce dopamine action in the body, thyroid underactivity and benign pituitary tumours (known as prolactinomas). Symptoms can include the unwanted production of milk, disturbances to the menstrual cycle and symptoms due to oestrogen deficiency (in women) or testosterone deficiency (in men). The vast majority of patients with a prolactinoma can be treated successfully using drugs which mimic the action of dopamine. The most commonly used is cabergoline.
What hormones increase prolactin production?
Oestrogen is another key regulator of prolactin and has been shown to increase the production and secretion of prolactin from the pituitary gland. Studies have shown small increases in prolactin in the blood circulation of women during stages of their reproductive cycle where oestrogen levels are at their highest.
Where is prolactin produced?
In humans, prolactin is produced both in the front portion of the pituitary gland ( anterior pituitary gland) and in a range of sites elsewhere in the body. Lactotroph cells in the pituitary gland produce prolactin, where it is stored and then released into the bloodstream. Human prolactin is also produced in the uterus, immune cells, brain, ...
Can low prolactin cause insufficient milk production?
A decrease in the amount of prolactin secreted can lead to insufficient milk being produced after giving birth . Most people with low prolactin levels do not have any specific medical problems, although preliminary evidence suggests they might have reduced immune responses to some infections.
What is prolactin hormone?
Prolactin is a protein hormone of the anterior pituitary gland that was originally named for its ability to promote lactation in response to the suckling stimulus of hungry young mammals . We now know that prolactin is not as simple as originally described. Indeed, chemically, prolactin appears in a multiplicity of posttranslational forms ranging from size variants to chemical modifications such as phosphorylation or glycosylation. It is not only synthesized in the pituitary gland, as originally described, but also within the central nervous system, the immune system, the uterus and its associated tissues of conception, and even the mammary gland itself. Moreover, its biological actions are not limited solely to reproduction because it has been shown to control a variety of behaviors and even play a role in homeostasis. Prolactin-releasing stimuli not only include the nursing stimulus, but light, audition, olfaction, and stress can serve a stimulatory role. Finally, although it is well known that dopamine of hypothalamic origin provides inhibitory control over the secretion of prolactin, other factors within the brain, pituitary gland, and peripheral organs have been shown to inhibit or stimulate prolactin secretion as well. It is the purpose of this review to provide a comprehensive survey of our current understanding of prolactin's function and its regulation and to expose some of the controversies still existing.
What is the function of prolactin?
Prolactin: structure, function, and regulation of secretion. Prolactin is a protein hormone of the anterior pituitary gland that was originally named for its ability to promote lactation in response to the suckling stimulus of hungry young mammals. We now know that prolactin is not as simple as originally described.
Does dopamine inhibit prolactin?
Finally, although it is well known that dopamine of hypothalamic origin provides inhibi tory control over the secretion of prolactin, other factors within the brain, pituitary gland, and peripheral organs have been shown to inhibit or stimulate prolactin secretion as well.
Is prolactin a simple hormone?
We now know that prolactin is not as simple as originally described. Indeed, chemically, prolactin appears in a …. Prolactin is a protein hormone of the anterior pituitary gland that was originally named for its ability to promote lactation in response to the suckling stimulus of hungry young mammals. We now know that prolactin is not as simple as ...
What is prolactin in physiology?
Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone that is responsible for lactation, breast development, and hundreds of other actions needed to maintain homeostasis. The chemical structures prolactin is similar to the structure of growth hormone and placental lactogen hormone.
What is the role of prolactin in breast development?
Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone that is responsible for lactation, breast development, and hundreds of other actions needed to maintain homeostasis. The chemical structures prolactin is similar to the structure of growth hormone and placental lactogen hormone.
How long does it take for prolactin to drop after breastfeeding?
If the mother does not nurse her baby, prolactin levels fall to non-pregnant levels after 1 to 2 weeks.
How much prolactin is in a male?
In males, serum prolactin levels range from 2 to 18 ng/ml, in females 2 to 30 ng/ml, and during the third trimester of pregnancy, 10 to 210 ng/ml. In cases of prolactinomas, the serum prolactin level is typically greater than 200 mg/mL.
What is the family of prolactin?
Together, they form the "prolactin/growth hormone/placental lactogen" family, which is characterized by a conserved helix bundle protein composition. All hormones in this family derive from a common ancestral gene. Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone that is responsible for lactation, breast development, and hundreds of other actions needed ...
Why do lactotrophs increase during pregnancy?
The number of lactotrophs will increase during pregnancy in response to the physiological need to develop breast tissues and to prepare for milk production. It should be noted that the increase in lactotrophs cells is not accompanied by an increase in angiogenesis.
Which hormones are released by the hypothalamus and have activity in modulating lactotophic activity?
Factors that stimulate production, upregulate prolactin gene transcription while factors that inhibit secretion downregulate prolactin gene transcription. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and dopamine are both released by the hypothalamus and have activity in modulating lactotophic activity.
Which hormone stimulates the mammary glands to synthesize milk?
Prolactin stimulates the mammary glands to synthesize milk.
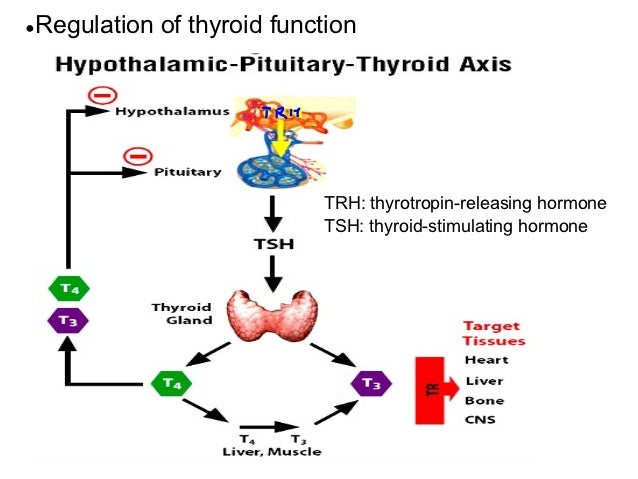
How is the release of thyroid hormones controlled?
Describe how release of thyroid hormones is controlled. The adrenal cortex releases cortisol, which stimulates the parathyroid glands to release TSH. The hypothalamus secretes TRH, which stimulates the pituitary to secrete TSH. The hypothalamus secretes TSH, which stimulates the pituitary to secrete TRH.
Which organ secretes TSH?
The hypothalamus secretes TSH, which stimulates the pituitary to secrete TRH.
Where does GH affect mitotics?
GH affects mitotic rates only in the epiphyseal regions of the bones.
