
What are the functions performed by proteins in a cell?
The hundreds of different protein kinases in a eucaryotic cell are organized into complex networks of signaling pathways that help to coordinate the cell’s activities, drive the cell cycle, and relay signals into the cell from the cell’s environment. Many of the extracellular signals involved need to be both integrated and amplified by the cell.
What functions as factory to produce proteins in a cell?
5 rows · Mar 26, 2021 · Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of ...
Why are proteins important to cell function?
The collection of proteins within a cell determines its health and function. Proteins are responsible for nearly every task of cellular life, including cell shape and …
What are the five main functions of proteins?
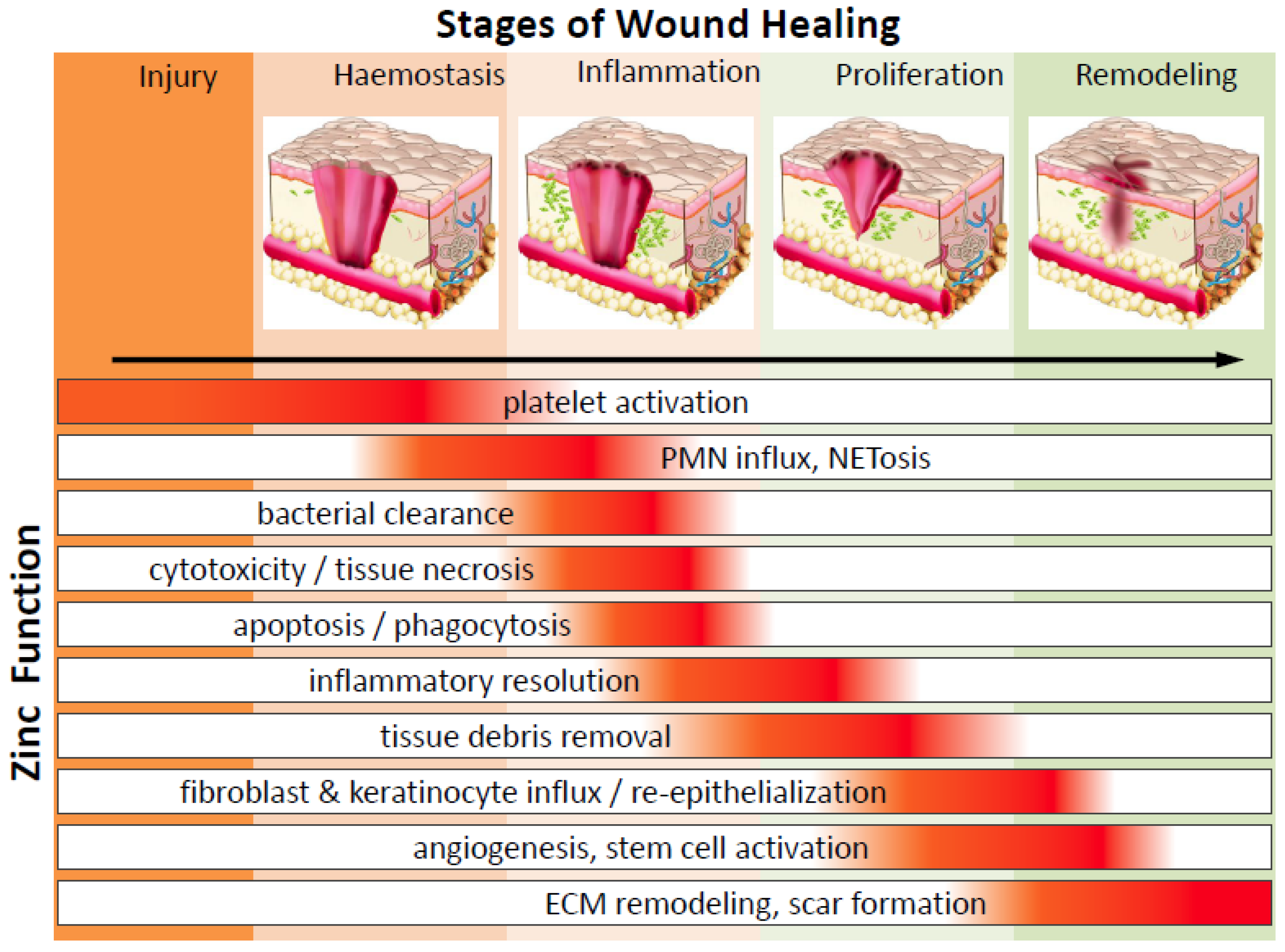
Mar 18, 2022 · Proteins have multiple functions, including: acting as enzymes and hormones, maintaining proper fluid and acid-base balance, providing nutrient transport, making antibodies, enabling wound healing and tissue regeneration, and providing energy when carbohydrate and fat intake is inadequate.
What is the main function of a proteins?
Protein has many roles in your body. It helps repair and build your body's tissues, allows metabolic reactions to take place and coordinates bodily functions. In addition to providing your body with a structural framework, proteins also maintain proper pH and fluid balance.Jun 20, 2018
What are three functions of proteins in cells?
Explanation: catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another.Apr 6, 2018
What are 5 functions of proteins in cells?
Every cell in your body contains protein, so meeting your protein requirement is essential for your health.Building Tissues and Muscles. Protein is necessary in building and repairing body tissues. ... Hormone Production. ... Enzymes. ... Immune Function. ... Energy.
What are the 4 main functions of proteins?
Terms in this set (4)Enzyme Activity. Responsible for reactions enzymes catalyze of nearby substrates.Cell to Cell Recognition. Recognize molecules on the surface of other cells.Cell Signalling. ... Transport Materials.
Which is one function of protein macromolecule?
Types of biological macromoleculesBiological macromoleculeBuilding blocksFunctionsProteinsAmino acidsProvide cell structure, send chemical signals, speed up chemical reactions, etcNucleic acidsNucleotidesStore and pass on genetic information2 more rows
What are 10 functions of proteins?
Functions of Proteins.Oxygen Transport.Proteins as Enzymes.Lysozyme - A Defensive Enzyme.Antibodies are Proteins.Structural Proteins.Contractile Proteins.Signal Proteins.More items...•Mar 22, 2016
What are the 6 main functions of proteins?
Proteins have multiple functions, including: acting as enzymes and hormones, maintaining proper fluid and acid-base balance, providing nutrient transport, making antibodies, enabling wound healing and tissue regeneration, and providing energy when carbohydrate and fat intake is inadequate.Mar 18, 2022
What are the 8 main functions of proteins?
Terms in this set (8)Enzymatic proteins. Selective acceleration of chemical reactions (ex: digestive enzymes)Structural proteins. Support (ex: silk fibers, collagen and elastin, and keratin)Storage proteins. ... Transport proteins. ... Hormonal proteins. ... Receptor proteins. ... Contractile and motor proteins. ... Defensive proteins.
What do proteins do?
Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs.
Which proteins provide structure and support for cells?
Growth hormone. Structural component. These proteins provide structure and support for cells. On a larger scale, they also allow the body to move. Actin. Transport/storage. These proteins bind and carry atoms and small molecules within cells and throughout the body. Ferritin.
Why do enzymes help the body?
Antibodies bind to specific foreign particles, such as viruses and bacteria, to help protect the body. Enzymes carry out almost all of the thousands of chemical reactions that take place in cells. They also assist with the formation of new molecules by reading the genetic information stored in DNA.
What determines the sequence of amino acids?
The sequence of amino acids determines each protein’s unique 3-dimensional structure and its specific function. Amino acids are coded by combinations of three DNA building blocks (nucleotides), determined by the sequence of genes.
How many different types of amino acids are there in a protein?
Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a protein. The sequence of amino acids determines each protein’s unique 3-dimensional structure and its specific function.
How Diverse Are Proteins?
Figure 1: The phosphorylation of a protein can make it active or inactive.
How Do Proteins Aid the Biochemical Reactions of a Cell?
Cells rely on thousands of different enzymes to catalyze metabolic reactions. Enzymes are proteins, and they make a biochemical reaction more likely to proceed by lowering the activation energy of the reaction, thereby making these reactions proceed thousands or even millions of times faster than they would without a catalyst.
What Do Proteins Do in the Plasma Membrane?
The proteins in the plasma membrane typically help the cell interact with its environment.
Conclusion
Proteins serve a variety of functions within cells. Some are involved in structural support and movement, others in enzymatic activity, and still others in interaction with the outside world. Indeed, the functions of individual proteins are as varied as their unique amino acid sequences and complex three-dimensional physical structures.
Why are proteins important?
Updated January 23, 2020. Proteins are very important molecules that are essential for all living organisms. By dry weight , proteins are the largest unit of cells. Proteins are involved in virtually all cell functions and a different type of protein is devoted to each role, with tasks ranging from general cellular support to cell signaling ...
What is the structure of a protein?
Protein Structure. The structure of a protein may be globular or fibrous depending on its particular role (every protein is specialized). Globular proteins are generally compact, soluble, and spherical in shape. Fibrous proteins are typically elongated and insoluble.
What are proteins made of?
Proteins. Proteins are biomolecules composed of amino acids that participate in nearly all cellular activities. Occurring in the cytoplasm, translation is the process through which proteins are synthesized. The typical protein is constructed from a single set of amino acids. Every protein is specially equipped for its function.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids are the building blocks of all proteins, no matter their function. Proteins are typically a chain of 20 amino acids. The human body can use combinations of these same 20 amino acids to make any protein it needs. Most amino acids follow a structural template in which an alpha carbon is bonded to the following forms: 1 A hydrogen atom (H) 2 A carboxyl group (-COOH) 3 An amino group (-NH2) 4 A "variable" group
What are some examples of proteins that are stored in the body?
Storage proteins reserve amino acids for the body until ready for use. Examples of storage proteins include ovalbumin, which is found in egg whites, and casein, a milk-based protein. Ferritin is another protein that stores iron in the transport protein, hemoglobin.
How many types of proteins are there in the human body?
Every protein is specially equipped for its function. Any protein in the human body can be created from permutations of only 20 amino acids. There are seven types of proteins: antibodies, contractile proteins, enzymes, hormonal proteins, structural proteins, storage proteins, and transport proteins.
How many amino acids are in a protein?
Amino acids are the building blocks of all proteins, no matter their function. Proteins are typically a chain of 20 amino acids. The human body can use combinations of these same 20 amino acids to make any protein it needs.
What are the functions of proteins in the body?
Proteins are responsible for hormone synthesis. Hormones are chemical messengers produced in one part of the body and then transported in the blood to a different part of the body. When the hormone gets to the target tissue/part of the body, it communicates a message to initiate a specific reaction or cellular process. For instance, after you eat a meal, your blood glucose levels rise. In response to the increased blood glucose, the pancreas releases the hormone insulin. Insulin tells the cells of the body that glucose is available and to take it up from the blood and store it or use it for making energy or building macromolecules. A major function of hormones is to turn enzymes on and off, so some proteins can even regulate the actions of other proteins. While not all hormones are made from proteins, many of them are. Other examples of hormones made from proteins include glucagon, melatonin, and thyroid hormone.
What are the roles of proteins in the cell membrane?
Proteins also play a role in nutrient transport. A cell’s membrane is usually not permeable to large molecules. To get the required nutrients and molecules into the cell, many transport proteins exist in the cell membrane. Some of these proteins act as channels that allow particular molecules to move in and out of cells. Others act as one-way taxis and require energy to function (Figure 6.3. 2 ).
How do proteins help us?
Some of the amino acids in proteins can be disassembled and used to make energy. In healthy people, protein contributes little to energy needs. If a person’s diet does not contain enough carbohydrates and fats their body will use amino acids to make energy. When proteins are needed for energy, they are taken form the blood and body tissues (e.g., muscle). To use proteins for energy, deamination is required. Deamination is a process where the amine group is removed from the amino acid and the nitrogen is transported to the kidney for excretion. The remaining components are metabolized for energy. To protect our body tissues from being broken down for energy, it is important to eat an adequate amount of fat and carbohydrate. It's also important to note that our body cannot store excess protein. Excess protein intake results in nitrogen excretion; the remaining components are used for energy or converted to fat for later use.
What are some of the tasks that proteins perform?
In other words, they are not part of the body structure, but have specific tasks to perform such as acting as transporter, antibodies, enzymes and more. You have already learned about some of these important proteins.
What is the function of enzymes?
Enzymes. Some proteins function as enzymes. Enzymes are proteins that conduct specific chemical reactions. An enzyme’s job is to provide a site for a chemical reaction and to lower the amount of energy and time it takes for that chemical reaction to happen (Figure 6.3. 1 ). This is why enzymes are sometimes called catalysts.
What are the learning objectives of protein?
Learning Objectives. Describe the various functions of protein in the body. Proteins build muscle and all body tissues. It is a crucial role of the proteins to provide the structure of virtually all body tissues. Some proteins have other "jobs" to do. In other words, they are not part of the body structure, but have specific tasks ...
Why do proteins attract water?
As a result, water moves toward areas that have higher concentrations of other solutes, such as proteins and glucose. Proteins attract fluid, so to keep the water evenly distributed between blood and cells, proteins continuously circulate at high concentrations in the blood. When protein intake is deficient it can cause edema (swelling).
Proteins Overview
Proteins are biomolecules that are present in all living organisms. They are involved in a wide variety of chemical processes that are essential for life. Protein is present in hair, skin, and connective tissues. It regulates digestion, cell activity and transports oxygen throughout the body.
Composition of Proteins
Proteins are made up of amino acids. Amino acids are compounds that contain an amino group and carboxyl, as shown in the diagram. Proteins are formed from long chains of amino acids, brought together by a particular bond known as a peptide bond. The bond forms between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another amino acid.
Major Functions of Proteins
What are some functions of proteins? The major functions of proteins are providing structure, regulating body processes, transporting materials, balancing fluids, helping with immunity, and providing energy. Each of the different functions is associated with a different, or multiple different, type of protein.
Why are proteins important to the body?
Protein has many roles in your body. It helps repair and build your body’s tissues, allows metabolic reactions to take place and coordinates bodily functions. In addition to providing your body with a structural framework, proteins also maintain proper pH and fluid balance.
Why do we need protein?
Your body needs protein for growth and maintenance of tissues. Yet, your body’s proteins are in a constant state of turnover. Under normal circumstances, your body breaks down the same amount of protein that it uses to build and repair tissues.
What are proteins made of?
They’re made and secreted by endocrine tissues or glands and then transported in your blood to their target tissues or organs where they bind to protein receptors on the cell surface.
What are the proteins that make up the connective tissue?
Some proteins are fibrous and provide cells and tissues with stiffness and rigidity. These proteins include keratin, collagen and elastin, which help form the connective framework of certain structures in your body ( 13. Trusted Source. ). Keratin is a structural protein that is found in your skin, hair and nails.
How many calories are in a gram of protein?
Protein contains four calories per gram, the same amount of energy that carbs provide. Fats supply the most energy, at nine calories per gram. However, the last thing your body wants to use for energy is protein since this valuable nutrient is widely used throughout your body.
What is fibrous protein?
Summary. A class of proteins known as fibrous proteins provide various parts of your body with structure, strength and elasticity. 5. Maintains Proper pH. Protein plays a vital role in regulating the concentrations of acids and bases in your blood and other bodily fluids ( 16.
What happens if you don't eat enough protein?
Trusted Source. ). If you don’t eat enough protein, your levels of albumin and globulin eventually decrease. Consequently, these proteins can no longer keep blood in your blood vessels, and the fluid is forced into the spaces between your cells.
What are the roles of membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins play key roles in cell communication (receptors are involved), cell-cell adhesion (CAMs play a big role), structural support, and transport (aquaporin is an example).
What is the role of membrane proteins in signalling?
In a signalling cascade, the news from the cell membrane is passed from one protein to another within the cell until the right protein (for example, one in the nucleus) gets the message, and the cell can react. Cell-cell adhesion and structural support are two more key roles membrane proteins play.
What is the cell membrane made of?
A cell membrane is composed of a lipid bilayer (two layers of lipid molecules) that surrounds the cell as a sphere. Integral proteins have a large hydrophobic (water-hating and lipid-loving) component that allows them to exist and function within the lipid membrane.
What is the castle of a cell?
Just as a castle is surrounded by a wall, a cell has a membrane that separates the inner cellular 'kingdom' from outside its walls. A castle depends on messengers who bring food and news from the outer world. The same is true for a cell. A cell's messengers are proteins that visit the cell membrane from outside the cell ( extracellular space ).
What is the function of receptors in the cell membrane?
Receptors are integral proteins in the cell membrane that receive signals from extracellular space so the cell can react . A hormone receptor might get a signal to grow, which sets off a chain of events within the cell called a signalling cascade.
What are integral proteins?
These proteins are called integral proteins. Unlike peripheral proteins, integral proteins are tightly associated with the membrane and don't move out of it. Unlike in our gatehouse analogy, where people are stationed at only one place along the castle wall, most integral proteins can move and flow within the membrane.
How does aquaporin work?
For example, aquaporin is a protein that forms channels that allow water to flow through the cell membrane. It works as the cell's plumber. Transport across the membrane works in two ways. One, active transport, means fuel must be used to transport a molecule across the membrane.
