
RNA polymerase Definition, Types, and Functions
- Definition of RNA polymerase. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) Polymerase (RNAP) enzyme is a multi-subunit enzyme which uses its function to catalyze the transcription process RNA produced from DNA template.
- Prokaryotic RNA polymerase. ...
- Eukaryotic RNA polymerase. ...
- Functions of RNA Polymerase. ...
- RNA polymerase vs DNA polymerase. ...
What is RNA polymerase and what does it do?
Jan 20, 2021 · RNA polymerases transcribe the information in DNA into RNA molecules that have a variety of functions, including messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomal RNA (for protein synthesis), ribozymes (for catalysis), and microRNA (for regulation of gene expression).
What helps RNA polymerase recognize the start of a gene?
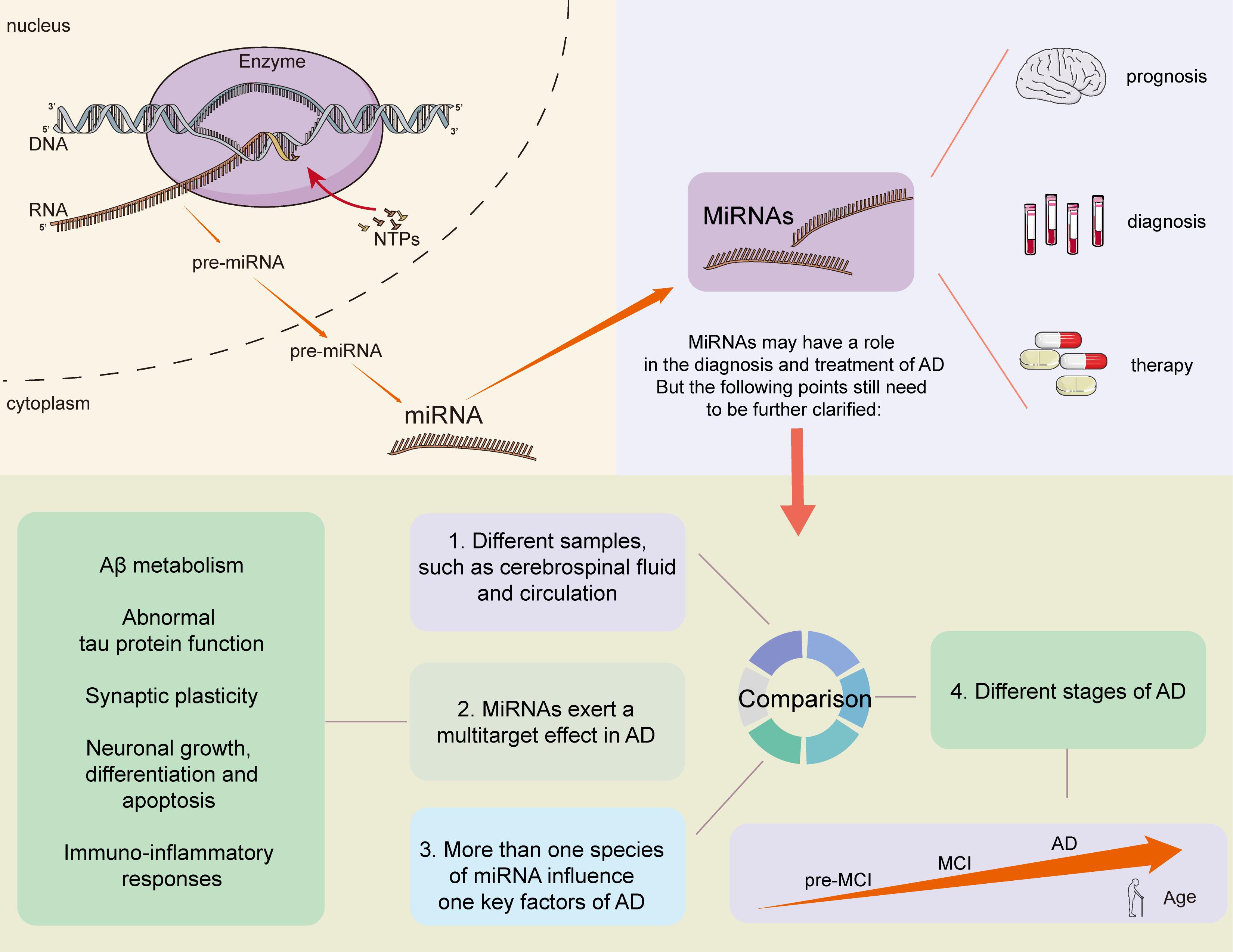
Nov 10, 2016 · A RNA polymerase (RNAP), or ribonucleic acid polymerase, is a multi subunit enzyme that catalyzes the process of transcription where an RNA polymer is synthesized from a DNA template. The sequence of the RNA polymer is complementary to that of the template DNA and is synthesized in a 5’→ 3′ orientation. This RNA strand is called the primary transcript and …
What does RNA polymerase I mean?
Jul 03, 2020 · RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
What is one of the primary functions of RNA molecules?
Abstract. RNA polymerase II is the core of the complex apparatus that is responsible for the regulated synthesis of mRNA. A comprehensive knowledge of RNA polymerase II is essential to our understanding of the molecular mechanisms through which a variety of transcription factors regulate eukaryotic gene expression.
What is the main function of RNA polymerase?
RNA polymerase is a multi-unit enzyme that synthesizes RNA molecules from a template of DNA through a process called transcription. The transcription of genetic information into RNA is the first step in gene expression that precedes translation, the process of decoding RNA into proteins.Mar 25, 2021
What are the two functions of RNA polymerase?
RNA polymerases transcribe the information in DNA into RNA molecules that have a variety of functions, including messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomal RNA (for protein synthesis), ribozymes (for catalysis), and microRNA (for regulation of gene expression).
What is the function of RNA polymerase quizlet?
What is the function of RNA Polymerase? RNA polymerase binds to DNA, separates the strands, then uses one of the strands as a template from which to assemble nucleotides into a complementary RNA strand.
What is the function of RNA polymerase first?
RNA polymerase I transcribes the genes that encode the structural RNAs for the subunits of the ribosome. RNA polymerase II transcribes the genes that encode proteins as well as a subset of small RNAs.
What is the role of RNA polymerase Brainly?
RNA polymerase is also important because it unzips and unwinds the DNA double helix so that it can insert the 'free' RNA nucleotides during transcription.Feb 15, 2018
What is the role of RNA polymerase during transcription?
The main enzyme involved in transcription is RNA polymerase, which uses a single-stranded DNA template to synthesize a complementary strand of RNA. Specifically, RNA polymerase builds an RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, adding each new nucleotide to the 3' end of the strand.
What is the function of RNA polymerase III and III?
RNAP II is responsible for transcription of most of the genes in eukaryotes, RNAP I transcribes multiple copies of the single gene for the large rRNA, and RNAP III transcribes short non-coding RNAs such as tRNAs, 5S rRNA, U6 snRNA and a limited number of others.
What are the function of RNA polymerase I and II in eukaryotes?
"Mention the function of RNA polymerase I and RNA polymerase II in eukaryotes." RNA polymerase I- Catalyese the synthesis of rRNA ( 28S, 18S and 8.8S ) : RNA polymerase II- Catalyses the synthesis of heterogeneous nuclear RNA/ hnRNA/ precursor Mrna.Mar 12, 2022
What are the function of RNA polymerase 1 and 2 in eukaryotes?
Abstract. All eukaryotes have three different RNA polymerases (RNAPs) which transcribe different types of genes. RNA polymerase I transcribes rRNA genes, RNA polymerase II transcribes mRNA, miRNA, snRNA, and snoRNA genes, and RNA polymerase III transcribes tRNA and 5S rRNA genes.
How does RNA polymerase work?
RNA polymerase then starts to synthesize the initial DNA-RNA heteroduplex, with ribonucleotides base-paired to the template DNA strand according to Watson-Crick base-pairing interactions. As noted above, RNA polymerase makes contacts with the promoter region. However these stabilizing contacts inhibit the enzyme's ability to access DNA further downstream and thus the synthesis of the full-length product. In order to continue RNA synthesis, RNA polymerase must escape the promoter. It must maintain promoter contacts while unwinding more downstream DNA for synthesis, "scrunching" more downstream DNA into the initiation complex. During the promoter escape transition, RNA polymerase is considered a "stressed intermediate." Thermodynamically the stress accumulates from the DNA-unwinding and DNA-compaction activities. Once the DNA-RNA heteroduplex is long enough (~10 bp), RNA polymerase releases its upstream contacts and effectively achieves the promoter escape transition into the elongation phase. The heteroduplex at the active center stabilizes the elongation complex.
What is RNA polymerase?
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol, and officially DNA-directed (dependent) RNA polymerase ), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as ...
What is the name of the RNA polymerase that unwinds the DNA double helix?
NCBI. proteins. RNA polymerase (purple ) unwinding the DNA double helix and uses one strand (darker orange) as a template to create the single-stranded messenger RNA (green) In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol, and officially DNA-directed (dependent) RNA polymerase ), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
How many nucleotides can RNAP build?
The process of adding nucleotides to the RNA strand is known as elongation; in eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides (the full length of the dystrophin gene).
How many subunits are in RNA polymerase?
RNA polymerase "core" from E. coli consists of five subunits: two alpha (α) subunits of 36 kDa, a beta (β) subunit of 150 kDa, a beta prime subunit (β′) of 155 kDa, and a small omega (ω) subunit. A sigma (σ) factor binds to the core, forming the holoenzyme.
Why is supercoiling important?
Supercoiling plays an important part in polymerase activity because of the unwinding and rewinding of DNA. Because regions of DNA in front of RNAP are unwound, there are compensatory positive supercoils. Regions behind RNAP are rewound and negative supercoils are present.
What is the sigma factor?
A sigma (σ) factor binds to the core, forming the holoenzyme. After transcription starts, the factor can unbind and let the core enzyme proceed with its work. The core RNA polymerase complex forms a "crab claw" or "clamp-jaw" structure with an internal channel running along the full length.
RNA Polymerase II Transcription: Overview
Transcription is the process by which DNA is converted into messenger RNA, or mRNA, which can then be converted into protein through the process of translation. The process of transcription occurs in the nucleus, using a multiprotein complex to transcribe a template strand of DNA into a pre-mRNA strand.
RNA Polymerase II Function
Eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases: RNA Polymerase I, RNA Polymerase II, and RNA Polymerase III, which all play different roles in the cell.
RNA Polymerase II Structure
Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase II. The red molecule in the middle is Alpha-Amanitin, a deadly toxin. The polymerase is the gray sections.
How does RNA polymerase work?
1. RNA polymerase unwinds the two DNA strands. 2. RNA polymerase copies the genectic instructions to form a strand of mRNA. 3. The mRNA carries the genetic instructions through the nuclear por complex into the cytoplasm to a ribosome subunit. 4. The mRNA attaches to a ribosome subunit.
Where does RNA synthesis take place?
In prokaryote cells, RNA synthesis and protein synthesis take place in the cytoplasm. In eukararyotes, RNA is produced in the cell's nucleus and then moves to the cytoplasm to play a role in the production of protein.
What is the process of translation?
What are the steps in the process of translation? 1. mRNA attaches to ribosome subunit; second ribsome subunit attaches to first forming a functional ribosome. 2. tRNa brings amino acids into ribsome.
Overview
Function
Control of the process of gene transcription affects patterns of gene expression and, thereby, allows a cellto adapt to a changing environment, perform specialized roles within an organism, and maintain basic metabolic processes necessary for survival. Therefore, it is hardly surprising that the activity of RNAP is long, complex, and highly regulated. In Escherichia coli bacteria, more than 1…
Structure
The 2006 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Roger D. Kornberg for creating detailed molecular images of RNA polymerase during various stages of the transcription process.
In most prokaryotes, a single RNA polymerase species transcribes all types of RNA. RNA polymerase "core" from E. coliconsists of five subunits: two alpha (α…
Action
RNA polymerase binding in bacteria involves the sigma factorrecognizing the core promoter region containing the −35 and −10 elements (located before the beginning of sequence to be transcribed) and also, at some promoters, the α subunit C-terminal domain recognizing promoter upstream elements. There are multiple interchangeable sigma factors, each of which recognizes a distinct se…
Other organisms
Given that DNA and RNA polymerases both carry out template-dependent nucleotide polymerization, it might be expected that the two types of enzymes would be structurally related. However, x-ray crystallographicstudies of both types of enzymes reveal that, other than containing a critical Mg ion at the catalytic site, they are virtually unrelated to each other; indeed template-depen…
History
RNAP was discovered independently by Charles Loe, Audrey Stevens, and Jerard Hurwitz in 1960. By this time, one half of the 1959 Nobel Prize in Medicine had been awarded to Severo Ochoa for the discovery of what was believed to be RNAP, but instead turned out to be polynucleotide phosphorylase.
Purification
RNA polymerase can be isolated in the following ways:
• By a phosphocellulose column.
• By glycerol gradient centrifugation.
• By a DNA column.
• By an ion chromatography column.
See also
• Alpha-amanitin
• Primase