What is the function of smooth muscle in the stomach?
The smooth muscle is responsible for movement of food by peristalsis and mechanical digestion by segmentation. In some regions, the circular layer of smooth muscle enlarges to form sphincters, circular muscles that control the opening and closing of the lumen (such as between the stomach and small intestine).
What is the function of smooth muscle tissue?
Smooth muscle lines many parts of the circulatory system, digestive system, and is even responsible for raising the hairs on your arm. In the circulatory system, smooth muscle plays a vital role in maintaining and controlling the blood pressure and flow of oxygen throughout the body.
How are smooth muscle fibers arranged in the gastrointestinal tract?
Gastrointestinal Motility and Smooth Muscle. Smooth muscle fibers are arranged in intertwined, rather indistinct bundles, aligned in most areas of the tube in circular and longitutinal layers. Individual smooth muscle fibers are connected to neighboring smooth muscle cells by gap junctions, which allow these cells to be electrically coupled.
What is the relationship between smooth muscle and gastrointestinal motility?
Gastrointestinal Motility and Smooth Muscle. The important consequence of this electrical coupling is that when an area of smooth muscle becomes depolarized, that depolarization spreads outward through adjacent sections of smooth muscle - this results in a well-coordinated contraction of, for example, an entire ring of circular smooth muscle.
Which muscle is responsible for movement of food?
How does food enter the body?
Is smooth muscle in the digestive tract?
Except for the first section of the esophagus, all the the muscle in the wall of the digestive tube is smooth muscle. Indeed, the patterns of motility seen in the gut are characteristic of smooth muscle, which has properties distinctly different from skeletal muscle.
What are three functions of smooth muscles?
For simplicity, the basic functions of smooth muscle in the organ systems are listed below.Gastrointestinal tract: Propulsion of the food bolus.Cardiovascular: Regulation of blood flow and pressure via vascular resistance.Renal: Regulation of urine flow.Genital: Contractions during pregnancy, propulsion of sperm.More items...
What do smooth muscles regulate?
The contractile function of vascular smooth muscle regulates the lumenal diameter of the small arteries-arterioles called resistance arteries, thereby contributing significantly to setting the level of blood pressure and blood flow to vascular beds.
What is smooth muscle?
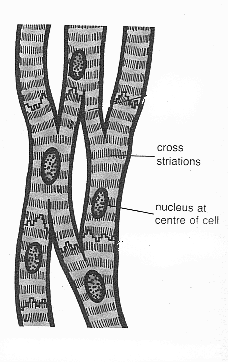
smooth muscle, also called involuntary muscle, muscle that shows no cross stripes under microscopic magnification. It consists of narrow spindle-shaped cells with a single, centrally located nucleus. Smooth muscle tissue, unlike striated muscle, contracts slowly and automatically.
Smooth Muscle Examples and Function
Understanding Smooth Muscles. There are three types of muscles in the body: smooth muscles, cardiac muscles and skeletal muscles. Smooth muscles are unique in their largely involuntary response, and in their structure. Smooth muscles have a much stronger ability to contract than skeletal muscles, and are able to maintain contraction longer.
Function of gastrointestinal smooth muscle: from signaling to ...
The action of smooth muscle in the intestinal wall produces tonic contractions that maintain organ dimension against an imposed load such as a bolus of food, as well as forceful contractions that produce muscle shortening to propel the bolus along the gastrointestinal tract. These functions are regu …
What is a Smooth Muscle and What are Its Functions
What is a Smooth Muscle? The human body contains three main types of muscular tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Smooth muscle is a type of non-striated muscle that is common in the walls of hollow organs and blood vessels.
What is the function of gastrointestinal smooth muscle?
Function of gastrointestinal smooth muscle: from signaling to contractile proteins.
What is the action of smooth muscle in the intestinal wall?
The action of smooth muscle in the intestinal wall produces tonic contractions that maintain organ dimension against an imposed load such as a bolus of food, as well as forceful contractions that produce muscle shortening to propel the bolus along the gastrointestinal tract .
Why is smooth muscle important?
Smooth muscle, because of its ability to contract and hold , is used for many function in many places of the body. Besides those listed above, smooth muscle is also responsible for contracting the irises, raising the small hairs on your arm, contracting the many sphincters in your body, and even moving fluids through organs by applying pressure to them. While smooth muscle doesn’t contract or release as quickly as skeletal or cardiac muscle, it is much more useful for providing consistent, elastic tension.
Which muscle lines the digestive system?
Smooth muscle also lines the majority of the digestive system, for similar reasons. However, the cells in the digestive system have different stimuli than those in the circulatory system. For instance, sheets of smooth muscle tissue in the gut react to you swallowing.
How does smooth muscle contract?
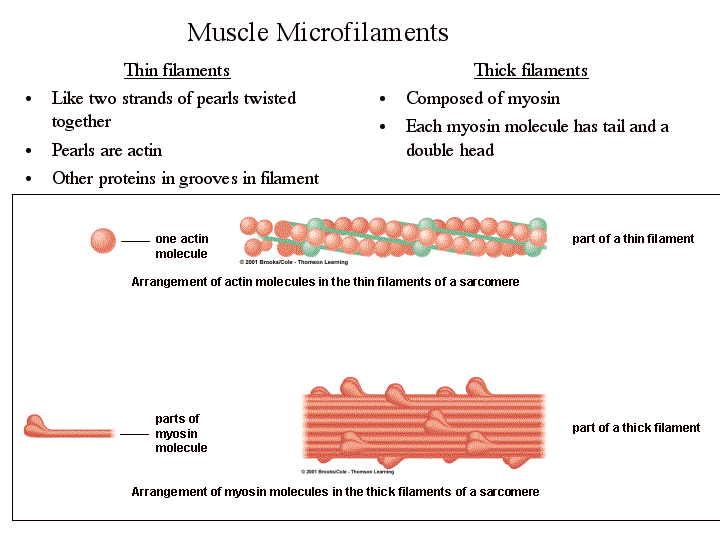
Like all muscle tissue, the function of smooth muscle is to contract. The image above shows how the actin and myosin fibers shorten, effectively shrinking the cell. However, there are some important differences in how the smooth muscle contracts, compared to other types of muscle. In skeletal muscle, a signal from the somatic nervous system traverses to the muscle, where it stimulates organelles in the muscle cell to release calcium. The calcium causes a protein to detach from actin , and myosin quickly binds to the opening on actin. Since there was always available ATP, the myosin uses it to quickly contract the cell.
What is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins. Smooth muscle contracts under certain stimuli as ATP is freed for use by the myosin. The amount of ATP released depends on the intensity of the stimuli, allowing smooth muscle to have a graded contraction as opposed to the “on-or-off” contraction of skeletal muscle.
Why is it important that the rest of the sheet of cells respond to a contraction?
B is correct. When a contraction happens in a smooth muscle tissue , it is important that the rest of the sheet of cells respond. The gap junctions found between cells allow for the passage of the nerve impulse or chemical signal which started the contraction. This ensures that many cells contract at once, producing the desired effect for the organism.
Why is smooth muscle adapted to many areas of the body?
This specialized function of contracting for long periods and hold that force is why smooth muscle has been adapted to many areas of the body. Smooth muscle lines many parts of the circulatory system, digestive system, and is even responsible for raising the hairs on your arm.
What is the ATP released by myosin?
Smooth muscle contracts under certain stimuli as ATP is freed for use by the myosin. The amount of ATP released depends on the intensity of the stimuli , allowing smooth muscle to have a graded contraction as opposed to the “on-or-off” contraction of skeletal muscle.
Which system innervates the smooth musculature?
The innervation of the smooth musculature is utmost complex. It lies under the influence of the visceral nervous system and works autonomously at the same time.
Where is smooth muscle found?
Smooth muscle is a type of tissue found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the intestines, uterus and stomach . You can also find smooth muscle in the walls of passageways, including arteries and veins of de cardiovascular system. This type of involuntary non-striated muscle is also found in the tracts of the urinary, respiratory and reproductive systems. In addition to that, you can find smooth muscle in the eyes, where it acts to change the size of the iris and the shape of the lens. The skin is also contains smooth muscle which allows hair to raise in response to cold temporatures or fear.
What is the function of myofibroblasts in smooth muscle?
They produce connective tissue proteins such as collagen and elastin for which reason they are also referred to as fixed (or stationary) connective tissue cells.
How thick is a smooth muscle cell?
The smooth muscle cell is 3-10 µm thick and 20-200 µm long. The cytoplasm is homogeneously eosinophilic and consists mainly of myofilaments. The nucleus is located in the center and takes a cigar-like shape during contraction. The cell membrane forms small pouch-like invaginations into the cytoplasm (caveolae) which are functionally equivalent to the T-tubules of the skeletal musculature. The smooth muscle cells are anchored to the surrounding connective tissue by a basal lamina.
What type of tissue does myofibroblasts produce?
Myofibroblasts produce connective tissue proteins such as collagen and elastin.
Which muscle group allows for cells to contract much stronger than those of striated musculature?
Fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows for cells to contract much stronger than those of striated musculature.
What is the cell membrane of skeletal muscle?
The cell membrane forms small pouch-like invaginations into the cytoplasm (caveolae) which are functionally equivalent to the T-tubules of the skeletal musculature. The smooth muscle cells are anchored to the surrounding connective tissue by a basal lamina. The smooth muscle fibers group in branching bundles.
Where is smooth muscle found?
Smooth muscle is a type of non-striated muscle that is found in the walls of hollow organs and blood vessels. Smooth muscle can be found throughout the body but is most common around the digestive tract, in the walls of blood vessels, arteries, and around other organs such as the eyes.
Where is single unit smooth muscle found?
Single-unit smooth muscle – a type of smooth muscle found in many organs, such as the stomach and intestines. It can be found both inside and outside these organ tissues.
What disorders affect smooth muscles?
Certain disorders can also affect the functioning of smooth muscles. For instance, a genetic condition called Multisystemic smooth muscle dysfunction syndrome (MSMDS) results in an embryo to not develop enough smooth muscles for the digestive system. Some autoimmune disorders such as hepatitis, lupus or cirrhosis can also cause Anti-smooth muscle antibodies (ASMA).
What are the three types of muscular tissue?
The human body contains three main types of muscular tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Smooth muscle is a type of non-striated muscle that is common in the walls of hollow organs and blood vessels. However, smooth muscle can be found throughout the body but is most common around the digestive tract, in the walls of blood vessels, arteries, and around other organs such as the eyes.
Which muscle is responsible for transporting blood throughout the body?
The vasculature system that transports blood throughout the body is controlled by smooth muscle. Smooth muscles contract to regulate blood pressure and other cardiovascular processes. They also aid in food digestion through peristalsis, which is the rhythmic wave-like contraction of muscles around the digestive tract.
What type of muscle is not striated?
As stated above, smooth muscle cells are not striated. This means they have no visible bands of contractile proteins like those found in skeletal muscles. These muscles are also involuntary, which means the contraction of these muscles is not dependent on conscious thought. They can contract in response to chemical or electrical signals, which they receive from autonomic nerves and hormones like epinephrine and vasopressin. Smooth muscle tissues are usually arranged as circular layers and tubes around the gut or as sheets between layers of connective tissue. Furthermore, this type of muscle has no more than one nucleus per cell.
Which muscle is responsible for movement of food?
The smooth muscle is responsible for movement of food by peristalsis and mechanical digestion by segmentation. In some regions, the circular layer of smooth muscle enlarges to form sphincters, circular muscles that control the opening and closing of the lumen (such as between the stomach and small intestine).
How does food enter the body?
Muscles and Digestion Food enters the body through the digestive system. There it is broken down into nutrients that can be absorbed into the body. However, the muscular system is needed to get food through the digestive system. Muscles that surround the stomach contract and move food to the small intestine.