Just so, what is the function of sodium and potassium in action potential? The inward flow of sodium ions increases the concentration of positively charged cations in the cell and causes depolarization, where the potential of the cell is higher than the cell's resting potential.
What happens during an action potential?
- Definition
- Steps
- Phases
- Refractory period
- Propagation of action potential
- Synapse
- Summary
- Sources
What causes an action potential?
What causes an action potential? Action potentials are caused when different ions cross the neuron membrane. A stimulus first causes sodium channels to open. Because there are many more sodium ions on the outside, and the inside of the neuron is negative relative to the outside, sodium ions rush into the neuron.
What are the steps of an action potential?
What are the steps of an action potential quizlet?
- Step One: Reaching Threshold.
- Step Two: Depolarization.
- Step Three: Sodium Channels Close and Potassium Channels Open.
- Step Four: Active Sodium and Potassium Pumps Begin to Start Repolarization.
- Step Five: Hyperpolarization.
- Step Six: Resting Potential.
How do you explain an action potential?
There are three main events that take place during an action potential:
- A triggering event occurs that depolarizes the cell body. ...
- Depolarization - makes the cell less polar (membrane potential gets smaller as ions quickly begin to equalize the concentration gradients) . ...
- Repolarization - brings the cell back to resting potential. ...
- Hyperpolarization - makes the cell more negative than its typical resting membrane potential. ...
What is the role of sodium and potassium in an action potential?
The principal ions involved in an action potential are sodium and potassium cations; sodium ions enter the cell, and potassium ions leave, restoring equilibrium. Relatively few ions need to cross the membrane for the membrane voltage to change drastically.
What role does sodium play in generating an action potential?
In the open state, voltage-gated sodium channels form a pore in the cytoplasmic membrane that allows sodium ions to flow into the cell, depolarizing the cell and generating the upstroke of the action potential; however, most sodium channels rapidly transit into the “inactivated” state at depolarized potentials.
Why is potassium important for action potential?
The primary intracellular electrolyte, potassium produces a high osmotic pressure to maintain cell volume. Potassium is essential for maintaining a normal cell resting membrane potential and for generating and propagating action potentials in excitable tissues.
What does the sodium potassium pump do?
[3][4] The Na+K+-ATPase pump helps to maintain osmotic equilibrium and membrane potential in cells. The sodium and potassium move against the concentration gradients. The Na+ K+-ATPase pump maintains the gradient of a higher concentration of sodium extracellularly and a higher level of potassium intracellularly.
What is the role of sodium ions and sodium channels in generating an action potential?
When the cell membrane is depolarized by a few millivolts, sodium channels activate and inactivate within milliseconds. Influx of sodium ions through the integral membrane proteins comprising the channel depolarizes the membrane further and initiates the rising phase of the action potential.
What happens to the sodium and potassium ions when the neurons are stimulated How does their concentration inside and outside the cell change?
A stimulus first causes sodium channels to open. Because there are many more sodium ions on the outside, and the inside of the neuron is negative relative to the outside, sodium ions rush into the neuron. Remember, sodium has a positive charge, so the neuron becomes more positive and becomes depolarized.
What would happen if sodium and potassium channels open at the same time?
If the Na+ and K+ channels opened at the same time: - Positive ions would flow in and out of the cell simultaneously.
When sodium channels open during an action potential The opening is caused by?
depolarizationThe rising phase is caused by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. These ion channels are activated once the cell's membrane potential reaches threshold and open immediately. The electrochemical gradients drive sodium into the cell causing the depolarization. Animation 6.3.
How does action potential occur?
Going down the length of the axon, the action potential is propagated because more voltage-gated Na + channels are opened as the depolarization spreads. This spreading occurs because Na + enters through the channel and moves along the inside of the cell membrane. As the Na + moves, or flows, a short distance along the cell membrane, its positive charge depolarizes a little more of the cell membrane. As that depolarization spreads, new voltage-gated Na + channels open and more ions rush into the cell, spreading the depolarization a little farther.
Which protein moves sodium ions out of the cell?
Of special interest is the carrier protein referred to as the sodium/potassium pump that moves sodium ions (Na +) out of a cell and potassium ions (K +) into a cell, thus regulating ion concentration on both sides of the cell membrane.
Why is saltatory conduction faster than other types of conduction?
Saltatory conduction is faster because the action potential basically jumps from one node to the next (saltare = “to leap”), and the new influx of Na + renews the depolarized membrane. Along with the myelination of the axon, the diameter of the axon can influence the speed of conduction.
Why do mechanically gated channels open?
A mechanically gated channel opens because of a physical distortion of the cell membrane. Many channels associated with the sense of touch (somatosensation) are mechanically gated. For example, as pressure is applied to the skin, these channels open and allow ions to enter the cell.
How do muscle cells work?
Both of the cells make use of the cell membrane to regulate ion movement between the extracellular fluid and cytosol.
When the cell is at rest, and the ion channels are closed, ions are distributed across the membrane in
When the cell is at rest, and the ion channels are closed (except for leakage channels which randomly open), ions are distributed across the membrane in a very predictable way. The concentration of Na + outside the cell is 10 times greater than the concentration inside.
What are the functions of the nervous system?
The functions of the nervous system—sensation, integration, and response— depend on the functions of the neurons underlying these pathways. To understand how neurons are able to communicate, it is necessary to describe the role of an excitable membrane in generating these signals. The basis of this communication is the action potential, ...
Why do potassium ions leave the cell?
The potassium channels also open, and, in response to the positive interior of the cell and the diffusion pressure , potassium ions leave the cell.
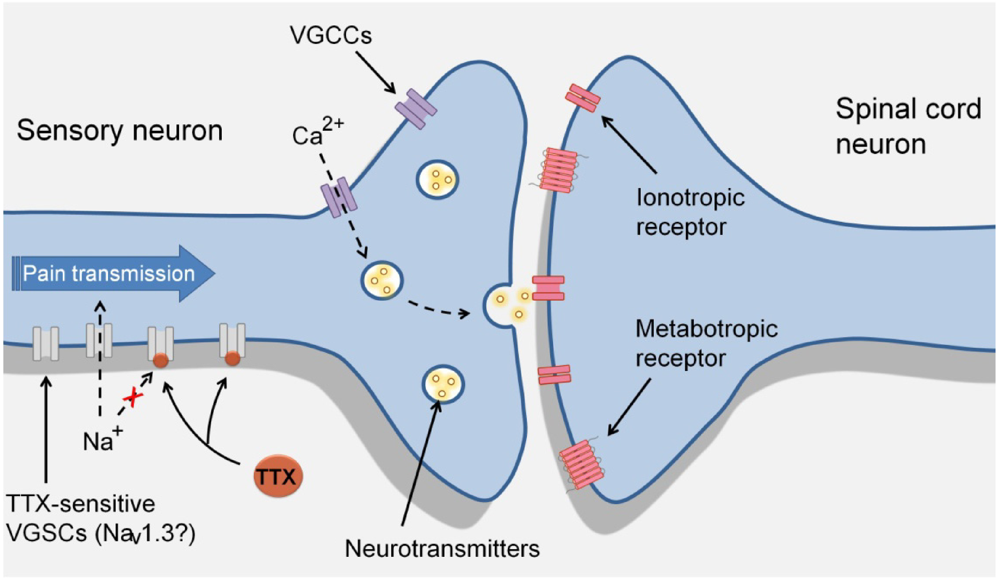
What happens when an action potential reaches the synaptic knob?
When an action potential reaches the synaptic knob, the calcium channels open, allowing calcium ions into the knob. This causes the release of neurotransmitters across the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitters briefly bind to the receptor molecules in the plasma membrane of the postsynaptic neuron.
How many axons are there in a multipolar neuron?
In a multipolar neuron, there are many dendrites and one axon. Bipolar neurons have one dendrite and one axon. Unipolar neurons have only one process; the most distal part of the structure is the dendrite, and the rest of the process functions as an axon. Compare and contrast white and gray matter.
What is the function of the somatic and autonomic nervous systems?
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. Its function is to integrate and evaluate incoming information and initiate an outgoing response. The PNS consists of the nerves outside the CNS, which originate from ...
Which type of nerve brings information to the CNS?
Afferent fibers include nerves bringing information to the CNS. Efferent fibers include nerves bringing information away from the CNS. The somatic and autonomic nervous systems each have afferent and efferent fibers in them. There are relatively few neurons in the brain.
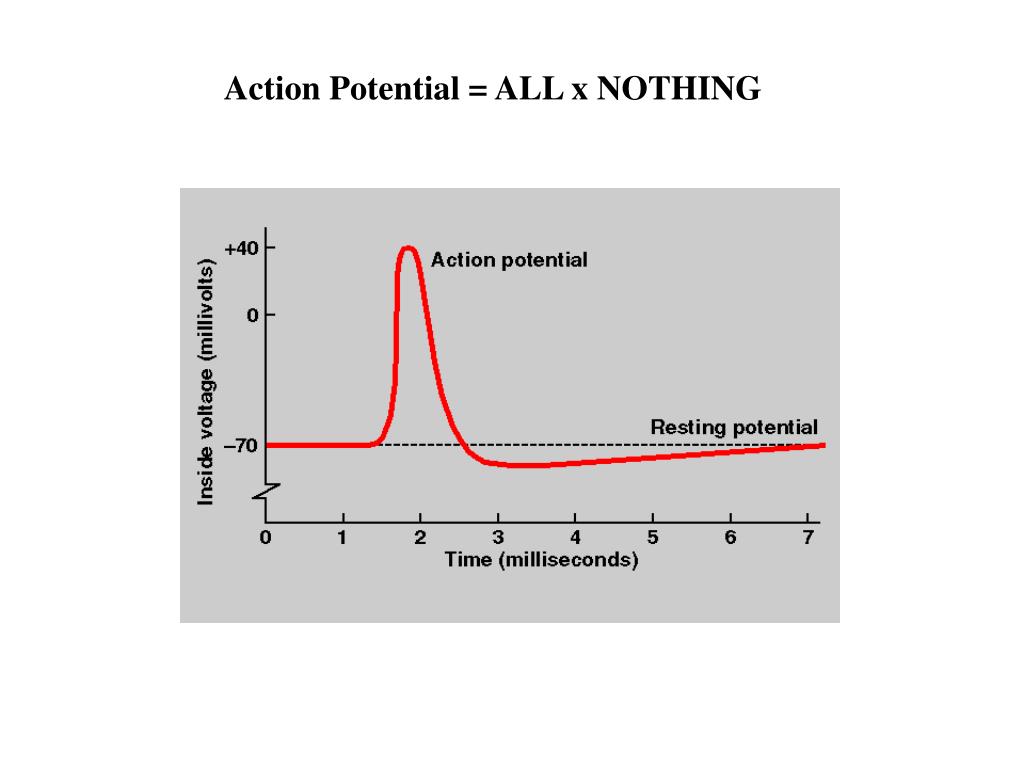
Why is action potential an all or none response?
The action potential is an all-or-none response because the cause of the action potential is the influx of sodium ions into the cell through the voltage-gated channels. These channels can be either open or closed. When they open, they stay open for a specific time, making each action potential the same.
What is the function of the nervous system?
The general function of the nervous system is communication. Communication is what makes possible control, which in turn allows integration, which allows homeostasis, which allows survival. The endocrine system also shares the function of communication.