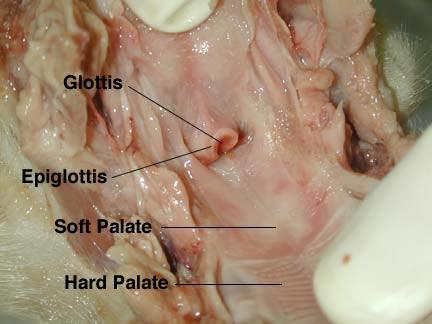
What is the difference between hard and soft palate?
- The anterosuperior border is attached to the hard palate via the palatine aponeurosis.
- The lateral borders feature two arches; palatoglossal (anteriorly) and palatopharyngeal (posteriorly). ...
- The posteroinferior border of the soft palate is free and faces towards the oropharynx. ...
What is the function of the soft palate?
The soft palate plays an essential role in blocking food and other substances from entering the nasal passages during swallowing and is important in the formation of certain sounds in speech production. Unlike the bony hard palate, the soft palate is very flexible.
How to raise soft palate?
- When you inhale, let your jaw drop easily (do not over-drop the jaw. ...
- Let your eyes widen as if you are overly alert (But think smirk, not eyes-popping out manic)
- Imagine that you are smiling from inside the face – a little like the ‘Mona Lisa’ (D.J Jones’s often refers to the ‘Mona Lisa Smile’).
What is the function of the soft palate and uvula?
Function. During swallowing, the soft palate and the uvula move together to close off the nasopharynx, and prevent food from entering the nasal cavity. It has also been proposed that the abundant amount of thin saliva produced by the uvula serves to keep the throat well lubricated. It has a function in speech as well.
What are the 2 functions of the soft palate?
The main functions of the soft palate are to aid speech, swallowing, and breathing. Cleft lip and cleft palate are common congenital abnormalities.
What is the function of the hard palate?
The hard palate provides space for the tongue to move freely and supplies a rigid floor to the nasal cavity so that pressures within the mouth do not close off the nasal passage. In many lower vertebrates the hard palate bears teeth.
What is the function of the soft palate quizlet?
During a swallow the soft palate is raised to prevent material moving into the nasal cavity (which poses infection risk). The position of the soft palate controls the relative degree of nasalisation of sounds.
What is a soft palate in mouth?
The back, muscular (not bony) part of the roof of the mouth.
What is the difference between the hard and soft palate?
The hard palate is the front part of the roof of the mouth, and the soft palate is the back part.
What is the soft palate made of?
Unlike the bony hard palate, the soft palate is very flexible. It is composed of a strong, thin, fibrous sheet, known as the palatine aponeurosis, and the glossopalatine and pharyngopalatine muscles. A small projection called the uvula hangs free from the posterior of the soft palate.
What is the difference between the hard palate and soft palate quizlet?
The hard palate is at the front, and the soft palate is at the back. The hard palate holds the root of the teeth. The soft palate pressed down for swallowing.
What is the function of the hard palate quizlet?
The hard palate holds the roots of the teeth and helps with mastication.
Where are the hard palate located and what are their functions?
Palate Anatomy With a hard palate comes a soft palate located in the back of your oral cavity with a much more fleshy-like surface. Your hard palate plays a significant role as it separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity while also aiding swallowing and speaking. Translation — it's a big deal.
How do I control my soft palate?
0:4911:02Component Focus #4 - “How Do I Control My Soft Palate?” - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBegin by touching the tip of your tongue to the top front teeth. Like. This then we are going toMoreBegin by touching the tip of your tongue to the top front teeth. Like. This then we are going to slide the tongue backwards slowly always maintaining contact with the top of the mouth.
Does the soft palate move?
The soft palate is moveable, consisting of muscle fibers sheathed in mucous membrane. It is responsible for closing off the nasal passages during the act of swallowing, and also for closing off the airway. During sneezing, it protects the nasal passage by diverting a portion of the excreted substance to the mouth.
Can the soft palate be removed?
A surgeon may recommend removing tissue from the soft palate or advancing or reducing the tongue. Our doctors carefully evaluate the anatomy of your upper airway and nose before recommending any invasive procedure, ensuring that it is the most appropriate option for you.
What is the function of the hard palate quizlet?
The hard palate holds the roots of the teeth and helps with mastication.
What is the hard palate called?
It forms the anterior two-thirds of the roof of the oral cavity. The hard palate is comprised of two facial bones: the palatine process of the maxilla and the paired palatine bones....Hard palate.BordersAnerior and lateral - maxillary teeth Posterior - soft palateClinical relationCleft palate2 more rows
Where is the hard palate?
roof of the mouthThe front, bony part of the roof of the mouth.
What do the hard and soft palate separate?
It is divided into two separate parts, namely, the “hard palate” and “soft palate.” The hard and soft palates separate the mouth (oral cavity) from the nasal cavity. The palate is a structure that forms the roof of the mouth.
What is the soft palate?
The soft palate is the muscular part at the back of the roof of the mouth. It sits behind the hard palate, which is the bony part of the roof of the mouth. The palates play important roles in swallowing, breathing, and speech.
How does the soft palate work when swallowing?
When a person swallows food or liquid, the soft palate rises to seal the opening of the airways to prevent pressure from escaping through the nose.
Why is my baby's palate not speaking?
A cleft palate can cause issues with speech and swallowing because the palate is unable to separate the respiratory tract from the digestive tract. Some babies with a cleft palate may have more frequent ear infections, hearing problems, or dental issues.
How does the mouth produce speech?
Speech is a highly complex process that involves the tongue, lips, and palate. These structures produce speech by directing airflow through the mouth to create certain sounds that form words. If a person has a cleft palate or another soft palate disorder, air can escape through the nose and affect the speech.
What is the roof of the mouth?
The hard and soft palates make up the roof of the mouth. The soft palate sits at the back of the mouth, behind the hard palate, which holds the teeth and gums.
What is the function of the uvula?
The function of the uvula is to block the nasal cavity when a person is eating or drinking. The soft palate comprises muscle and tissue, which make it mobile and flexible. When a person is swallowing or sucking, the soft palate completely separates the mouth from the throat, which helps keep food out of the respiratory tract.
Why do doctors recommend surgery for cleft lip?
Doctors recommend surgery to aid breathing, speech, language, and hearing. Sometimes, children with a cleft lip and palate need special dental care when they are older.
What are the Main Functions of the Soft Palate?
The soft palate is essential for the structure of the mouth. It provides several vital functions:
How to treat soft palate cancer?
Surgery is one of the treatment options for soft palate cancer. The goal of surgery is to remove as much of the soft palate cancer as possible. If the cancer is small, it may be extracted during a short operation that does not require a hospital stay.
How long does it take for a soft palate to heal?
In most circumstances, soft palate pain should not be a cause for concern. Usually, a person fully recovers within a few days to a week.
What is the most common type of soft palate cancer?
The most common type of soft palate cancer is squamous cell carcinoma. It is treated similarly to other cancers with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
Why does my soft palate swell?
It is common for the soft palate to show signs of swelling and inflammation if the body has a viral, bacterial, or fungal invasion.
Which two palates create the roof of the mouth?
The hard and soft palates create the roof of the mouth.
How many muscles and nerves work when you swallow?
When you swallow, more than 30 muscles and nerves work to send food toward the stomach rather than the nose or lungs. 2
Why is the soft palate important?
The soft palate, because of its position in the oral cavity and its flexibility, has an important function in the production of certain sounds used in human speech. When the soft palate is down, so that air can still go out through the nose, there is said to be a nasal stop.
What is the soft palate?
The soft palate, along with the hard palate, forms the palate, or the roof of the mouth, which separates the oral and nasal cavities.
What is the role of the soft palate in swallowing?
The soft palate plays an essential role in blocking food and other substances from entering the nasal passages during swallowing and is important in the formation of certain sounds in speech production. Unlike the bony hard palate, the soft palate is very flexible.
What happens when you elevate your soft palate?
During swallowing, the soft palate is pulled up, causing it to press against the posterior pharyngeal wall. When elevated in this way, it completely blocks and separates the nasal cavity and nasal portion of the pharynx from the mouth and the oral part of the pharynx. While elevated, the soft palate creates a vacuum in ...
Which part of the mouth separates the oral cavity?
The soft palate, along with the hard palate, forms the palate, or the roof of the mouth, which separates the oral and nasal cavities. The soft palate is continuous with the hard palate, which forms in the anterior roof of the mouth.
Is the soft palate raised or lowered?
The soft palatemay be raised or lowered. It is lowered in breathing and allows air to pass in and out through the nose. In the utterance of most speech sounds it is raised, so that air passing through the mouth alone forms the sound; if…
Is the soft palate flexible?
Unlike the bony hard palate, the soft palate is very flexible. It is composed of a strong, thin, fibrous sheet, known as the palatine aponeurosis, and the glossopalatine and pharyngopalatine muscles. A small projection called the uvula hangs free from the posterior of the soft palate.
What muscles attach to the soft palate?
Muscles of the soft palate – the tensor veli palatini (Figure 2) attaches to the scaphoid fossa and spine of the sphenoid and to the lateral surface of the cartilaginous portion of the auditory (Eustachian) tube. Its fibers descend between the lateral and medial pterygoid plates on the lateral aspect of the pharyngeal wall and give way to a tendon just above the pterygoid hamulus. The tendon hooks under the hamulus and turns medially to enter the soft palate, where it forms the palatine aponeurosis by fanning out and attaching to the posterior border of the hard palate. The palatine aponeurosis forms the basic structure of the soft palate to which other muscles gain attachment. Tensor veli palatini is supplied by the mandibular (V3) division of the trigeminal nerve and tenses the soft palate.
Which muscle is located in the soft palate?
The uvular muscle, also supplied by the pharyngeal plexus, lies entirely within the soft palate and elevates the uvula. In cases of unilateral paralysis of the soft palate, the uvula rises asymmetrically, being pulled away from the paralyzed side.
What is the name of the valve that narrows the opening from the nose into the throat?
A long palate narrows the opening from the nose into the throat. The excessive length of the soft palate and/or uvula acts as a noisy flutter valve during relaxed breathing.
What is the palate?
The palate forms the roof of the mouth and floor of the nasal cavity. The palate is divided anatomically into the bony hard palate anteriorly (part of the oral cavity) and the fleshy soft palate posteriorly (part of the oropharynx). The soft palate projects into the cavity of the pharynx from its attachment to the posterior edge of the hard palate. When elevated, it separates the oropharynx from the nasopharynx. Five paired muscles attach to the soft palate and contribute to its structure. In the midline the uvula projects downwards from its posterior free border.
Why is hypohyoid flap used?
Gangloff et al. 16) reported that hypo-hyoid myocutaneous flap was performed in order to reconstruct small or intermediate soft palate defects, and that its use was limited if patients had previously undergone thyroid surgery or radical neck dissection.
How to make your soft palate stiff?
The soft palate may be stiffened by inserting stiffening rods into the soft palate, or by injecting an irritating substance that causes stiffness in the injected area near the uvula.
Where is the palatoglossus located?
Palatoglossus descends from the inferior surface of the palatine aponeurosis and inclines slightly forwards to enter the posterolateral part of the tongue. The position of palatoglossus is evident on the inner surface of the oral cavity as a mucosal elevation, the palatoglossal ridge (anterior pillar of the fauces). The two palatoglossal ridges form the oropharyngeal isthmus, which marks the posterior boundary of the oral cavity. Innervated by fibers from the pharyngeal plexus, palatoglossus lowers the soft palate, raises the posterior part of the tongue and moves the palatoglossal ridge towards the midline, thus narrowing the isthmus.
Where is the soft palate located?
Overview. The soft palate is located in the upper portion of the back of the mouth, behind the teeth. Soft palate cancer begins in the cells of the soft palate. Your soft palate is located on the upper portion of the back of your mouth, behind your teeth. Soft palate cancer is considered a type of throat cancer.
Why does soft palate cancer happen?
Causes. Soft palate cancer forms when a genetic mutation turns normal, healthy cells into abnormal cells. Healthy cells grow and multiply at a set rate, eventually dying at a set time. Abnormal cells grow and multiply out of control, and they don't die.
How to reduce the risk of soft palate cancer?
Ways to reduce your risk of soft palate cancer include: Don't use tobacco. If you don't use tobacco, don't start. If you currently use tobacco of any kind, talk with your doctor about strategies to help you quit. Limit alcohol if you choose to drink. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
What is the treatment for soft palate cancer?
Doctors treat soft palate cancer similarly to the way they treat other types of throat cancers — often with a combination of surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
How to tell if you have cancer of the soft palate?
Some signs and symptoms of soft palate cancer can include the following: 1 Bleeding 2 Difficulty swallowing 3 Difficulty speaking 4 Bad breath 5 Mouth pain 6 Sores in your mouth that won't heal 7 Loose teeth 8 Pain when you swallow 9 Weight loss 10 Ear pain 11 Swelling in your neck that may hurt 12 White patches in your mouth that won't go away
How do you know if you have soft palate cancer?
Some signs and symptoms of soft palate cancer can include the following: Bleeding. Difficulty swallowing. Difficulty speaking. Bad breath. Mouth pain. Sores in your mouth that won't heal. Loose teeth. Pain when you swallow.