What is the major function of the epithelial tissue?
What are the functions of epithelial tissue class 9?
- They form the outer layer of skin.
- Form lining of mouth and alimentary canal,protect these organs.
- Help in absorption of water and nutrients.
- It forms barrier to keep different body system separate.
- Form lining of blood vessels,alveoli,kidney tubules.
What does stratified epithelium do?
The primary function of stratified epithelium is protection. As the epithelium has multiple layers, it protects the underlying tissues and internal organs against several physical and microbial damages. The columnar epithelium in the eyes protects the conjunctiva of the eyes and other delicate structures in the eyes.
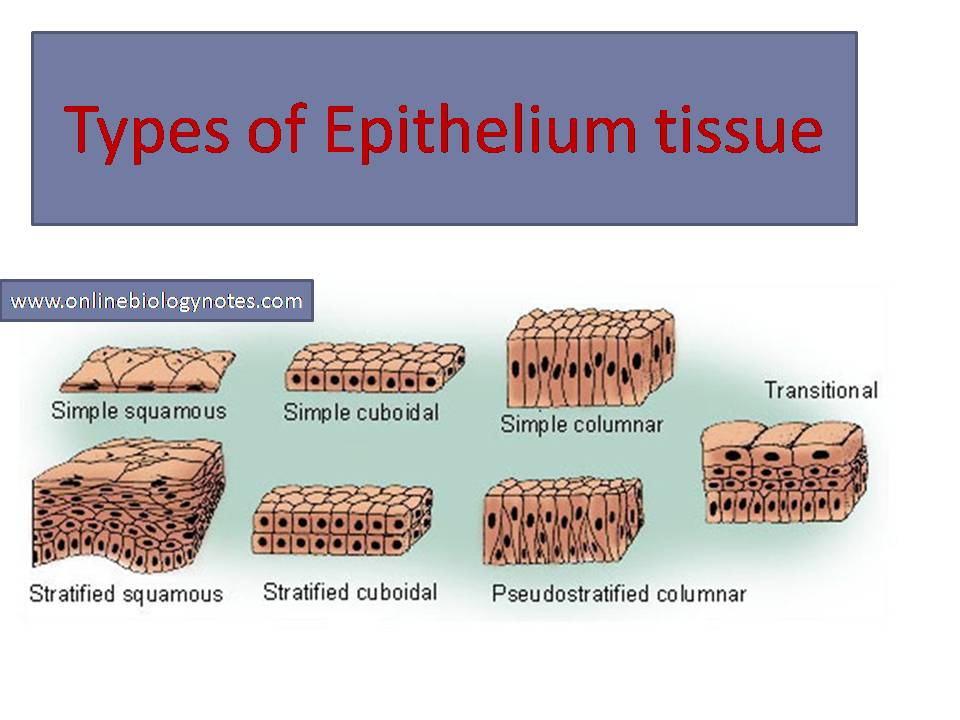
What are the 6 types of epithelial tissue?
Types of Epithelial Tissue
- Squamous Epithelium – These are thin, flat cells that are closely packed. ...
- Cuboidal Epithelium – These cells are cuboidal in shape. ...
- Columnar Epithelium – The columnar epithelium has cells that are pillar-like and column-like. ...
- Ciliated Epithelium – When the columnar epithelial tissues have cilia, then they are ciliated epithelium. ...
What are two ways to classify epithelium tissue?
Types of epithelium tissue:
- simple epithelium tissue
- compound epithelium tissue
- Specialized Epithelium
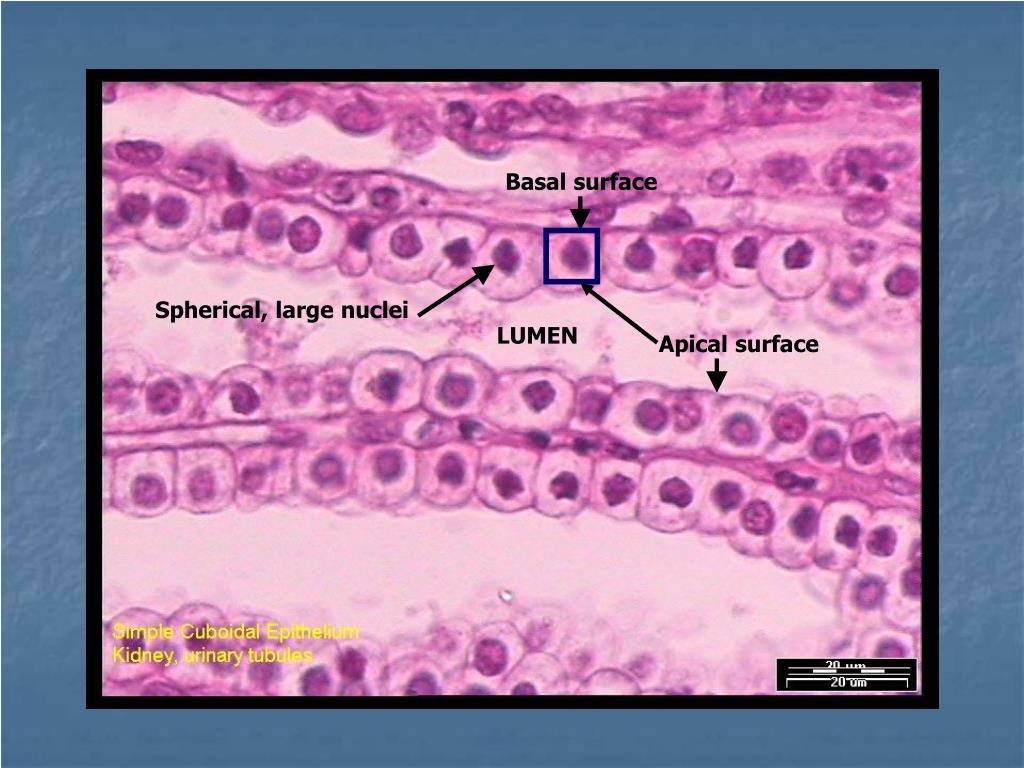
What is the main function of stratified cuboidal epithelium?
Stratified cuboidal epithelia is a rare type of epithelial tissue composed of cuboidally shaped cells arranged in multiple layers. They protect areas such as ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands.
What is stratified epithelium example?
Examples of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium include skin, epidermis of the palm of the hand and sole of the foot, and the masticatory mucosa.
What are stratified epithelial cells?
A stratified epithelium is a type of epithelial tissue that is composed of more than one layer of epithelial cells. The basal layer is the only one that is in contact with the basal lamina. This layer is also the one that undergoes mitotic division producinh cells in the upper layers.
What is the primary function of stratified epithelium quizlet?
Stratified Epithelium are more durable and function primarily to protect. Simple Epithelium are concerned with absorption, secretion, and filtration.
What are the 4 functions of epithelial tissue?
Forming sheets that cover the internal and external body surfaces (surface epithelium) and secreting organs (glandular epithelium). Functions of epithelial tissue are secretion, protection, absorption, transportation and special sensory receptive.
Where is stratified epithelial tissue found?
skinThe outer layer of your skin (the epidermis) is made of stratified squamous epithelial cells. Stratified cuboidal epithelium: This type of epithelium is not as common and is found in the excretory ducts of your salivary and sweat glands.
How is the structure of stratified epithelium related to its function?
Stratified squamous epithelium is a type of tissue found covering and lining parts of the body. In this tissue, cells are flattened, joined tightly together, and stacked. The major function of this tissue type is protection, as it is found in areas that undergo wear-and-tear.
How are simple and stratified epithelial tissue different?
The main difference between simple and stratified epithelium is that simple epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells while stratified epithelium is composed of multiple layers of cells.
What is the main function of most types of epithelial tissue?
The main functions of epithelia are protection from the environment, coverage, secretion and excretion, absorption, and filtration. Cells are bound together by tight junctions that form an impermeable barrier.
What is the main function of epithelial tissue quizlet?
Functions as protection, diffusion, filtration, absorption, secretion, and sensory reception.
What is stratified epithelium quizlet?
Stratified Epithelium. Contains two or more layers of cells that regenerate from the basal layer. Apical layer. Layer of cells that the shape and type of a tissue is named for. Protection.
What are the four types of stratified epithelium?
Stratified epitheliumSquamous. - nonkeratinized (covers the mucosa) - keratinized (skin)Cuboidal (lines excretory ducts of glands)Columnar (conjunctiva of the eyelids)Transitional (urinary tract)
How many stratified epithelium are there?
Stratified squamous keratinising epithelium There are around 8-10 layers of cells.
How many types of stratified epithelium are there?
There are four types of cells that can make up a stratified epithelium. The type of cell depends on the location of the tissue and its function.
What type of tissue is stratified squamous epithelium?
epithelial tissueA stratified epithelium is an epithelial tissue composed of more than one layer of epithelial cells. It differs from a simple epithelium in a way that the latter consists only one layer of epithelial cells.
What is stratified squamous epithelia?
Stratified squamous epithelia are tissues formed from multiple layers of cells resting on a basement membrane, with the superficial layer (s) consisting of squamous cells. Underlying cell layers can be made of cuboidal or columnar cells as well.
What are the different types of stratified squamous epithelia?
Types of Stratified Squamous Epithelia. These tissues can be classified as keratinized or non-keratinized based on the cytoskeletal structures found within the cell. Keratinized tissues are important where there is physical abrasion as well as the possibility of desiccation and water loss. Keratinized cells are specially structured ...
Where are epithelia found?
Epithelia consisting of multiple cell layers are generally found in regions where there is mechanical or chemical abrasion and stress and these tissues protect underlying structures from harm. Stratified squamous epithelia are found in nearly every organ system where the body comes into close contact with the outside environment – from ...
Which organs contain keratinized and non-keratinized stratified squamous epi?
Some organs, such as the anus, contain both keratinized and non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelia. Additionally, the amount of keratin deposition can vary depending on the level of abrasion. For instance, in people with a history of tobacco or alcohol abuse, the respiratory and digestive epithelia could become excessively keratinized.
Where are keratinized cells found?
They are also found in the oral cavity where eating, speaking and breathing could lead to significant loss of water.
What happens to cells during differentiation?
During differentiation, these cells also secrete glycolipids that fill interstitial spaces and isolate themselves. This is followed by nuclear disintegration and cell death. The external, dead layers of cells are periodically sloughed off and replaced.
Which layer of the cell is distinguished by the appearance of lipids and proteins that are secreted into the extra?
The third layer is distinguished by the appearance of lipids and proteins that are secreted into the extracellular matrix. The keratinized or corneal layer consists of dead cells containing abundant keratin, but no nucleus or cytoplasm. Oral mucosa.
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue has a number of functions, which include protection against abrasion, radiation damage, chemical stress and invasion by pathogens. A single organ can have different types of epithelial tissue based on the substances to which different surfaces are exposed. Protective tissue tends to be thicker, made of multiple layers of cells and often has inclusions such as keratin to provide mechanical strength and resistance. The skin of most mammals contains layers of thick keratinized dead epithelial cells protecting them against water loss and other stresses. Similarly, the esophagus is also exposed to a wide range of different textures, pH levels and chemical compositions from food and drink. Therefore, it also contains protective epithelium. Due to its involvement in the digestive process, however, it remains non-keratinized, and secretes mucus to smoothen the passage of food.
What is the simplest classification of epithelial tissue?
The simplest classification of these tissues is based on the number of cell layers. Simple epithelia. Stratified epithelia. When the epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells, it is called simple epithelial tissue ...
How many layers of epithelia are there?
Stratified epithelia consist of more than one layer of cells and only one layer is in direct contact with the basement membrane. Similarly, only one layer of cells has the apical surface exposed to the lumen of the organ or to the external environment. These tissues often have a protective role, and the extent of friction or abrasion often determines the number of layers of cells.
What is a single layer of epithelium called?
Stratified epithelia. When the epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells, it is called simple epithelial tissue and those containing two or more layers of cells are called stratified epithelial tissues. One particular type is called pseudostratified because a single layer of cells having varying heights gives the appearance ...
What are the different types of epithelial cells?
Epithelia can also be classified based on the shape of the cells, giving rise to three types: 1 Squamous epithelial tissue: consists of extremely thin cells that resemble the scales of a fish 2 Cuboidal epithelial tissue: contains cells that appear square in cross-section but are marginally longer than they are wide 3 Columnar epithelial tissue: consists of elongated cell involved in absorption of materials
What is pseudostratified epithelia?
Pseudostratified epithelia are formed of cells that have varying heights and therefore present the illusion of being stratified. However, every cell in this tissue makes contact with the basement membrane, thereby placing it among the simple epithelia.
Why is the basement membrane important?
The basement membrane compensates for the lack of blood vessels and nerves in the epithelium and is important for transport of nutrients, clearance of waste products, and transmission of neural and hormonal signals. It also plays an important role in anchoring the epithelium to the connective tissue underneath.
What is the epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue or epithelium (epi- upon; thele- nipple) is defined as one of the animal tissues that covers both external and internal surfaces of the animal body. It consists of a sheet of tightly packed cells with a minimum of intercellular material and rests upon a non-cellular basement membrane.
What are the characteristics of epithelial tissue?
The characteristics of epithelial tissues are as follows:#N#1. The cells are tightly packed, with little or no intercellular spaces ( 20 – 30 n m wide).#N#2. The cells adjacent to each other are held together by intercellular junctions.#N#3. The epithelial cells are polarised, i.e. , having an apical surface (free surface) that faces the inside of a cavity or outside of a surface and a basal surface (attached surface) that faces the underlying surface.# N#4. This tissue lies on a thin, non-cellular basement membrane.#N#5. Epithelial tissue lacks its own blood supply.#N#6. The materials between epithelial cells and the blood vessels of the connective tissues across the basement membrane are exchanged by the diffusion process.#N#7. Nerve endings may innervate the epithelial tissues.
What are the intercellular junctions between the epithelial cells?
The common intercellular junctions present between the epithelial cells are as follows: Tight junctions: In the apical region of the adjacent epithelial cells, the plasma membrane becomes tightly packed together. These junctions check the flow of materials between the cells and are also called occluding junctions.
How many types of epithelial tissue are there?
The epithelial tissues are broadly classified into three types:
How many different types of tissues are there in animals?
There are four different kinds of tissues in animals, i.e., epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue.
Where is the epithelial tissue located?
Location: It occurs in the inner surface of the urinary bladder, ureter, and renal pelvis. 3. Specialised Epithelial Tissue.
Which tissue is specialised to perform specific functions?
This epithelial tissue is specialised to perform specific functions, so they are specialised in structures also. They are as follows: