Explore
The temporal bone is a thick, hard bone that forms part of the side and base of the skull. This bone protects nerves and structures in the ear that control hearing and balance.
What does temporal bone mean?
The superior temporal lobe is one of three parts of the temporal lobe of the brain. Its main function is largely auditory, as it is the first spot of the brain that intercepts auditory signals. Both sides of the superior temporal lobe have different functions, as the right side deals more with emotions while the left side deals more with ...
What is the function of the superior temporal lobe?
The tympanic antrum is bounded above by a thin plate of bone, the tegmen tympani, which separates it from the middle fossa of the base of the skull; below by the mastoid process; laterally by the squama just below the temporal line, and medially by the lateral semicircular canal of the internal ear which projects into its cavity.
Which bone is above the temporal bone?
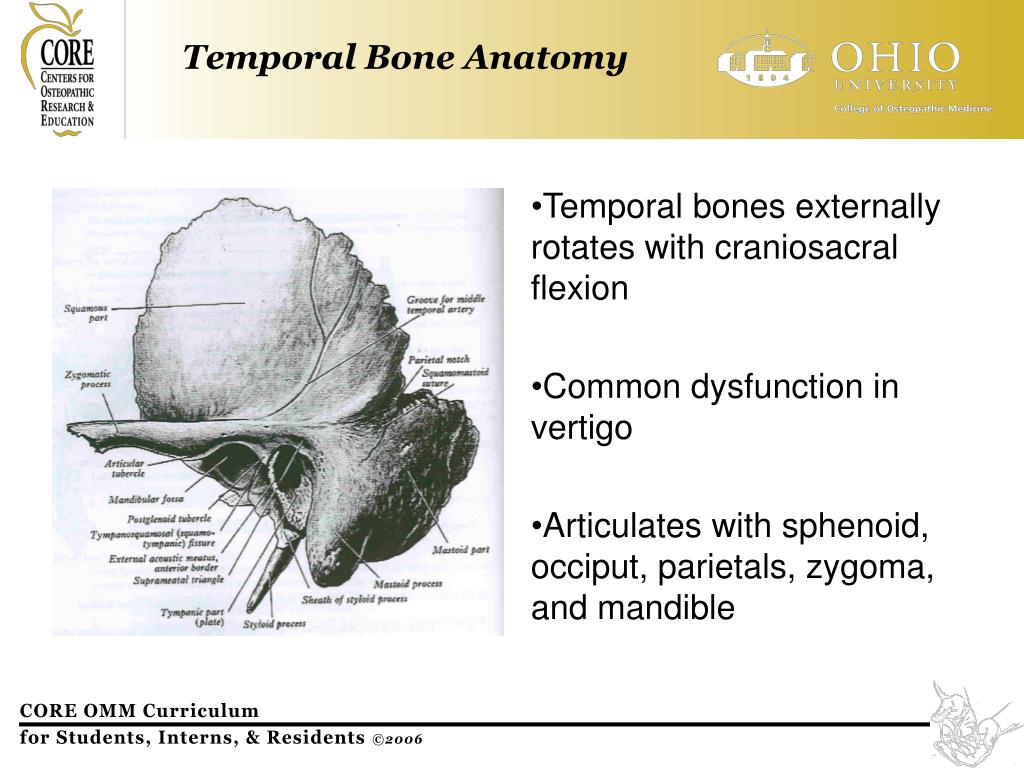
- It is anatomically divided into four regions called the squamous, mastoid, temporal, and petrous parts.
- The flattened squamous part forms the superior region of the bone that helps protect the sides of the brain ( temporal lobe ).
- The thick, mastoid part forms the lower, posterior portion of the bone. ...
What are the parts of the temporal bone?
See more
Where is the temporal bone of the ear located?
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears.
What is found in the temporal bone?
Structure & Location. In anatomy, each temporal bone is composed of five parts: the squama, the petrous, mastoid, and tympanic parts, as well as the styloid process.
What type of bone is your temporal bone?
The temporal bones are a pair of bilateral, symmetrical bones that constitute a large portion of the lateral wall and base of the skull . They are highly irregular bones with extensive muscular attachments and articulations with surrounding bones.
What are the 3 primary parts of the temporal bone?
The temporal bone is divided into several main parts/portions 1-3:squamous part (temporal squama)petrous part (petrous pyramid)tympanic part.mastoid part (usually considered a separate part but it is formed by both the squamous and petrous parts)
What happens if the temporal bone is damaged?
A temporal bone fracture may cause facial paralysis, hearing loss, bruising behind the ear, and bleeding from the ear. Doctors use computed tomography (CT) to diagnose temporal bone fractures. Treatment, sometimes including surgery, is needed if the fracture causes problems.
How do you remember the temporal bone?
0:497:07Skull Bones Mnemonic (Cranial and Facial Bones) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd it also covers the frontal lobe of my brain. And guess what anatomist called this bone theyMoreAnd it also covers the frontal lobe of my brain. And guess what anatomist called this bone they called it the frontal bone aren't those anatomist. So clever forehead. And frontal both start with F.
Why is the temporal bone most fragile?
Because the temporal bone encloses the middle and internal ear, these structures can be damaged by penetrating or concussive trauma to the tympanic membrane through the external acoustic meatus without temporal bone fracture.
Can you break your temporal bone?
Temporal bone fractures can occur after severe blunt trauma to the head and sometimes involve structures of the ear, causing hearing loss, vertigo, balance disturbance, or facial paralysis.
What causes temporal bone pain?
What are the causes & diagnosis of Temporalis Tendonitis? stress, tooth grinding, direct trauma to the Temporalis muscle, excessive gum chewing. In rare cases a condition called Coronoid Process Hyperplasia may be the cause of Temporal Tendinitis.
Which part of the temporal bone is related with hearing and balancing?
On each side, the sense organs for hearing and balance are contained within a complicated cavity in the petrous temporal bone that's shaped like this. The cavity is known as the bony labyrinth. The bony labyrinth consists of a central chamber, the vestibule, the three semicircular canals, and the spiral cochlea.
How thick is the temporal bone?
Bone thickness ranged between 1 and 8 mm across all age groups. In the group 5 to 6 years, the average temporal bone thickness was 3.42 ± 1.16 mm. Also in our study, a similar range of bone thicknesses was observed in the younger age groups.
What bone is above your ear?
temporal boneThe temporal bone is an area of the skull above the ear.
Which features are found in the petrous part of the temporal bone?
The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior, the components of the inner ear.
Does the temporal bone have a sinus?
Explanation: There are four paranasal sinuses in the head: the frontal, maxillary, sphenoid, and ethmoid sinuses. They function in lightening the skull, and creating mucous for the nasal cavity. The temporal bone does not contain a sinus.
Which features are found in the tympanic part of the temporal bone?
The tympanic part of the temporal bone is composed of anterior and posterior surfaces and superior, inferior and lateral borders.
What are the parts of the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe can be divided through its traditional Broadmann's area or simply by the superior, middle and inferior temporal gyrus (STG, MTG, ITG, respectively), parahippocampal/entorhinal gyri and fusiform gyrus.
What is the temporal bone?
The temporal bone consists of a pair of bones that help make up the skull. Many cranial nerves and blood vessels pass through the temporal bone. Injuries to this bone can cause a loss of function in the facial muscles, as well as hearing loss and heavy bleeding. Keep reading to learn more about the anatomy and function of the temporal bone.
What happens when blood vessels pass through temporal bone?
Many blood vessels and nerves pass through the temporal bone, so damage to it can have serious consequences involving blood loss and nerve damage.
What are the bones of the skull?
The other major bones in the skull are: 1 the two parietal bones that make up the top of the skull 2 the occipital bone at the back and base of the skull 3 the frontal bone at the forehead 4 the sphenoid bone at the temple 5 the ethmoid bone behind the eye
Why do people get temporal fractures?
Temporal bone fractures can occur due to motor vehicle accidents, assaults, or falls. About one-quarter. of temporal bone fractures occur as a result of sports injuries, gunshot wounds, and cycling accidents, among other injuries. more likely than females to sustain a temporal bone fracture.
What bones make up the skull?
The temporal bones help make up the skull.
How to detect ear tumors?
To detect these tumors, doctors examine the ear and often also use medical imaging methods. Different types of tumor have different treatment and management options.
Can a temporal fracture be life threatening?
Doctors treating a temporal bone fracture must first make sure that the injury is not life threatening. They will manage the bone fracture once they are confident that the person is in a stable condition. Temporal bone fractures can involve damage to certain nerves or lead to bleeding in the brain.
What is the temporal bone?
The temporal bones are a pair of bilateral, symmetrical bones that constitute a large portion of the lateral wall and base of the skull . They are highly irregular bones with extensive muscular attachments and articulations with surrounding bones. There are a number of openings and canals in the temporal bone through which structures enter ...
What is the squamous part of the temporal bone?
Squamous part. The squamous part is the anterior superior portion of the temporal bone that forms the lateral part of the middle cranial fossa. It has the appearance of a large flattened plate. Its external surface is smooth and slightly convex.
What part of the temporal bone is split into two?
This part of the temporal bone is usually split into two: the petrous part and the mastoid part.
What is the groove on the external surface of the bone?
Above the external acoustic meatus, there is a groove on the external surface of the bone for the middle temporal artery. The internal surface of the squamous part is concave shaped. Its surface has impressions that follow the groove and contour of the temporal lobe of the cerebrum that rests against it.
What is the socket for articulation of the temporal bone with the head of the mandible?
The mandibular notch (fossa), the socket for articulation of the temporal bone with the head of the mandible , is also present on the squamous part of the temporal bone.
Which part of the temporal bone fuses with the petrous part internally?
The tympanic part of the temporal bone fuses with the petrous part internally, and the squamous and mastoid parts posteriorly. Its posterior surface forms the anterior wall, floor and part of the posterior wall of the external acoustic meatus.
Where is the petrous part of the cranial cavity?
Petrous part. The petrous part is a wedge shaped mass of bone located between the sphenoid and occipital bones within the cranial cavity. It is the most medial part of the temporal bone, and it is the landmark dividing the middle and posterior cranial fossae from each other.
Where is the temporal bone located?
The temporal bone or os temporale is a paired, irregular bone and the thickest in the human body, located at the sides and base of the skull. It provides space for important cranial arteries, veins, and nerves. The os temporale also provides attachment points for numerous muscles. It joins or articulates with the occipital, parietal, sphenoid, ...
What are the parts of a temporal bone?
Because of its shape, it is split into five different parts: Squamous portion or part. Petrous portion or part. Mastoid portion or part. Tympanic portion or part.
What is the inner surface of the temporal squama?
The inner surface of the temporal squama is convex. At the bottom of the squama, the zygomatic process of the temporal bone juts towards the cheekbone (zygoma), forming the posterior portion of the zygomatic arch. This zygomatic process is part of the squamous portion of the left and right temporal bones.
What is the back of the temporal bone called?
At the back of the temporal bone is the mastoid part. It contains special cells called mastoid air cells. These sometimes fill with fluid that can become infected. An infection here is called mastoiditis.
What is the petrous part of the skull?
The petrous part of the temporal bone or petrous temporal bone is part of the skull base, situated between the paired sphenoid bone and singular occipital bone. It has a pyramid shape with a base and an apex.
What is the term for the formation of air cells in bone?
The formation of air cells in bone is known as pneumatization and this phenomenon occurs throughout the temporal bone. Pneumatization stops around puberty.
Where is the tympanic part?
The tympanic part sits just below the squama and in front of the mastoid part. It surrounds the external auditory canal and makes up part of the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone. The mandibular fossa contributes to the articulation between the mandible and the skull at the temporomandibular joint.
Where does temporal bone come from?
In evolutionary terms, the temporal bone is derived from the fusion of many bones that are often separate in non-human mammals: The squamosal bone, which is homologous with the squama, and forms the side of the cranium in many bony fish and tetrapods.
How many centers does the temporal bone have?
The temporal bone is ossified from eight centers, exclusive of those for the internal ear and the tympanic ossicles: one for the squama including the zygomatic process, one for the tympanic part, four for the petrous and mastoid parts, and two for the styloid process.
What is a glomus jugulare tumor?
Glomus jugulare tumor: A glomus jugulare tumor is a tumor of the part of the temporal bone in the skull that involves the middle and inner ear structures. This tumor can affect the ear, upper neck, base of the skull, and the surrounding blood vessels and nerves. A glomus jugulare tumor grows in the temporal bone of the skull, ...
What is the tympanic ring?
The tympanic ring is an incomplete circle, in the concavity of which is a groove, the tympanic sulcus, for the attachment of the circumference of the eardrum (tympanic membrane). This ring expands to form the tympanic part, and is ossified in membrane from a single center which appears about the third month.
When does the tympanic ring join the squama?
The tympanic ring unites with the squama shortly before birth; the petromastoid part and squama join during the first year, and the tympanohyal portion of the styloid process about the same time [Fig. 7, 8]. The stylohyal does not unite with the rest of the bone until after puberty, and in some skulls never at all.
Which part of the tympanic bone is shaped like a pyramid?
Fused with the squamous and mastoid parts and between the sphenoid and occipital bones lies the petrous part, which is shaped like a pyramid. The tympanic part is relatively small and lies inferior to the squamous part, anterior to the mastoid part, and superior to the styloid process.
What is the name of the suture that separates the occipital bone and mastoid portion?
Occipitomastoid suture. It separates occipital bone and mastoid portion of temporal bone.
What are the functions of the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobes main functions are visual, olfactory, and auditory processing and memory creation. It also plays important roles in emotional responses and communication.
Where are the temporal lobes located?
The temporal lobes can be found on the sides of the head by the ears. There is one lobe in each hemisphere of the brain.
Which lobe of the brain processes information in different ways?
The temporal lobes on each side of the brain process information in different ways and have slightly different jobs.
Which part of the brain is responsible for voluntary muscle movements?
Cerebellum: this is a small part of the brain located at the back just above the brainstem; it has two hemispheres like the cerebrum and helps coordinate voluntary muscle movements like posture and balance.
Which part of the brain is responsible for emotion regulation?
Amygdala: This is vital for emotion and memory regulation and is where the "fight or flight" response occurs
Which part of the brain is responsible for movement, temperature regulation, speech, judgment, thinking, hearing, vision, and?
Cerebrum: this is the main and largest part of the brain; it is made of white and grey matter and is responsible for movement, temperature regulation, speech, judgment, thinking, hearing, vision, problem-solving, and much more.
How many lobes does the cerebrum have?
The Cerebrum has four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal.
What is the shape of the temporal bone?
In the temporal bone, a pyramid, a drum and a scaly part are distinguished. The pyramid, or rocky part (pars petrosa), has a triangular shape, located obliquely in the horizontal plane. The tip of the pyramid is directed forward and medially, and the base is back and lateral. At the top of the pyramid is the inner opening ...
What is the scaly part of the parietal bone?
The scaly part (pars squamosa) is a convex outwardly shaped plate having a beveled free upper edge for connection to the parietal bone and a large wing of the sphenoid bone. The external temporal surface of the scales is smooth.
What is the mandibular fossa?
Behind the zygomatic process, at its base, is the mandibular fossa (fossa mandibularis) for articulation with the condylar process of the lower jaw to form the temporomandibular joint. Channels of the temporal bone. Several channels of the temporal bone pass through the pyramid for cranial nerves and blood vessels.
What bone is paired with the sphenoid bone?
The temporal bone (os temporale) is paired, it forms part of the base and lateral wall of the skull between the sphenoid bone in front and the occipital bone behind. It accommodates the organs of hearing and balance. In the temporal bone, a pyramid, a drum and a scaly part are distinguished. The pyramid, or rocky part (pars petrosa), has ...
Which cell communicates with the drum cavity?
The most compartmental cell - the mastoid cave ( Antrum mastoideum) communicates with the drum cavity. Medially mastoid process is limited by a deep mastoid fillet (incisure mastoidea). The median of this notch is the furrow of the occipital artery (sulcus arteriae occipitalis).
Which part of the auditory system is a curved bone plate?
The drum part (pars tympanica) is formed by a curved narrow bone plate, which in front, below and behind restricts the external auditory opening (porus acusticus externus) leading to the external auditory meatus (meatus acusticus externus).
Where does the canalis facialis begin?
The canalis canalis facialis begins in the internal auditory canal. It goes first transversely with respect to the long axis of the pyramid to the level of the cleft of the canal of the large stony nerve. Having reached the cleft, the channel forms a knee, then it is guided at a right angle back and laterally.