Why does the ascending loop of Henle carry a thin segment?
The ascending loop of Henle carries a thin and thick segment. It helps in draining urine into the distal convoluted tubule. The sodium reabsorption in a thin ascending limb is quite passive and occurs paracellularly because of the difference in osmolarity between the tubule and interstitium.
What are the three parts of the Henle loop?
In the anatomy area, the loop of Henle is divided into three different sections- thin descending limb, thin ascending limb and thick ascending limb. The first portion of the loop is the thin descending limb which is permeable to water. The descending loop of Henle is an important function.
What is the function of the thick descending limb of Henle?
The thick descending limb of the loop of Henle expresses a sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter and helps reabsorb approximately a third of the filtered sodium and chloride from the fluid in the tubular lumen into the blood. Some of the Loops of Henle Functions are- Homeostatic mechanisms to regulate extracellular fluid volume
What is the main function of the loop of Henle in nephron?
The main role of the loop of Henle in nephron is to collect sodium chloride and water from urine. This allows the urine production that is more concentrated than blood by reducing the amount of water which is necessary for living.
What is the function of the ascending loop of Henle quizlet?
What is the role of the loop of Henle? responsible for reabsorbing approximately 25% of the filtered NaCl and water and a small amount of bicarbonate. However, another major function of the loop of Henle is to enable the kidney to produce either a dilute or a concentrated urine.
What is the most important function of the ascending limb of Henle?
The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is a direct continuation from the descending limb of loop of Henle, and one of the structures in the nephron of the kidney. The ascending limb has a thin and a thick segment. The ascending limb drains urine into the distal convoluted tubule.
What is the difference between ascending and descending loop of Henle?
The key difference between ascending and descending loop of Henle is that ascending loop of Henle is the thicker segment of the loop of Henle located just after the sharp bend of the loop while descending loop of Henle is the thinner segment located just before the sharp bend of the loop.
What are the three major functions of the loop of Henle?
Ion transport along the nephron is essential for the reabsorption of sodium and water, maintenance of plasma volume and blood pressure and production of urine.
What is absorbed in the ascending loop of Henle?
Abstract. Thick ascending limbs of Henle's loop have at least three major roles: (1) They reabsorb sodium chloride which dilutes the urine.
What substances are reabsorbed in the ascending loop of Henle?
Reabsorption in the thick ascending limb: A further 25% of the sodium and potassium is reabsorbed through the walls of the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle via: Three-ion cotransporter (sodium/potassium/chloride) and the sodium/potassium ATPase, which as before maintains the sodium concentration gradient.
Is water reabsorbed in the ascending loop of Henle?
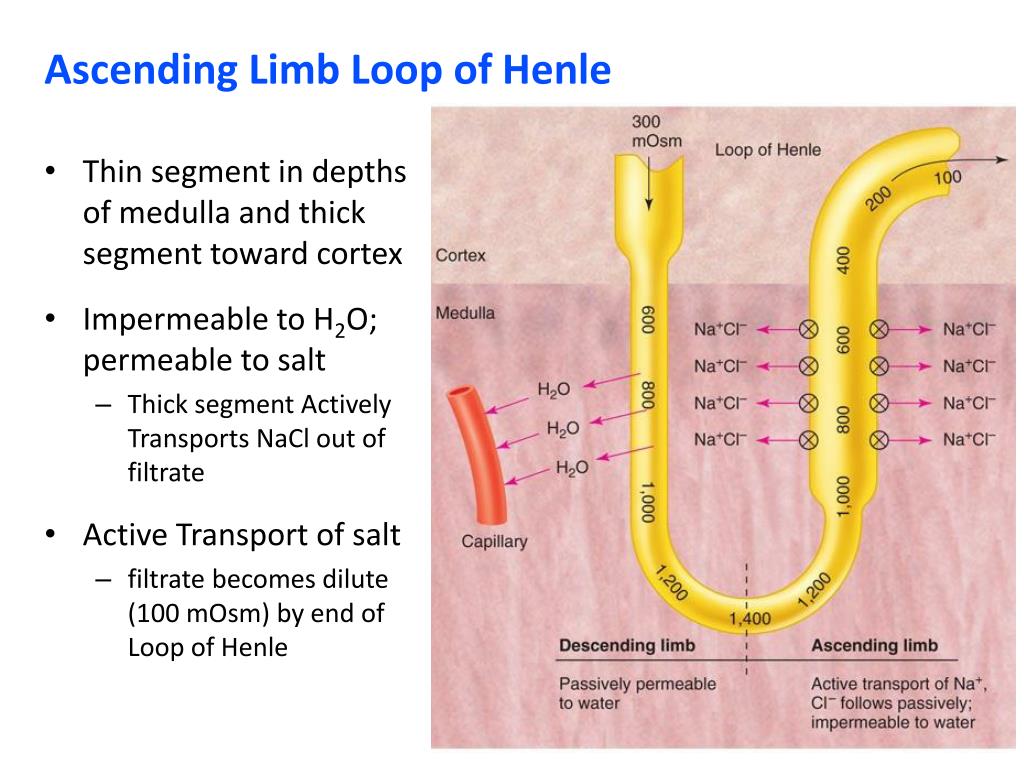
In the ascending portion, the loop becomes impermeable to water and the cells of the loop actively reabsorb solutes from the luminal fluid; therefore water is not reabsorbed and ions are readily reabsorbed.
Is the ascending limb permeable to water?
The ascending limb of loop of Henle is a segment of the nephron in the kidney divided into a thin and thick ascending limb. The thin ascending limb is impermeable to water and ions, except sodium and chloride, which cross by diffusion.
What is the difference between ascending and descending?
Descending can also be thought of as climbing down the stairs of numbers starting from the highest value. Moving down the slide is descending. The opposite of descending order is known as ascending order, in which the numbers are arranged from lower value to higher value.
Where is the ascending limb of the loop of Henle quizlet?
The thick ascending limb of nephron loop connects with the distal convoluted tubule, which connects with the urine connecting duct. The loop of henle dips down into the medulla, which is highly salty because of the ion absorption, Sodium is constantly being pumped out of the ascending limb into the medulla.
Is the ascending limb permeable to water?
The ascending limb of loop of Henle is a segment of the nephron in the kidney divided into a thin and thick ascending limb. The thin ascending limb is impermeable to water and ions, except sodium and chloride, which cross by diffusion.
Where is the ascending limb of the nephron loop quizlet?
Within the nephron, the tubular fluid flows from the DESCENDING LIMB OF THE NEPHRON LOOP; ASCENDING LIMB OF THE NEPHRON LOOP directly into the PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE; DESCENDING LIMB OF THE NEPHRON LOOP.
What does the descending loop of Henle do?
The descending portion of the loop of Henle is extremely permeable to water and is less permeable to ions, therefore water is easily reabsorbed here and solutes are not readily reabsorbed.
1. What are the major functions of the loop of henle?
Loop of Henle is found in the kidney location and has three major functions.Re-absorption: It absorbs 15% of filtered water and 25% of the filtered...
2. What activity happens in the ascending loop of henle?
The ascending loop of Henle carries a thin and thick segment. It helps in draining urine into the distal convoluted tubule. The sodium reabsorption...
3. What is the role of the ascending loop of henle?
The ascending Loop of Henle is impermeable to water. Here, the sodium chloride is transported from a thick portion of the ascending limb without ac...
4. What are the functions of nephron?
The primary function of the Nephron is to flush out the waste products such as solid waste and other excesses from the blood. Nephron is a basic st...
5. Mention one essential part of nephron?
An essential part of Nephron is Henle’s Loop, also known as Loop of Henle. The Henle’s loop carries both the descending limbs of Loop of Henle and...
6. What is PCT?
PCT or Proximal Convoluted Tubule is an essential part of Nephron. PCT can be described as a system that helps in the absorption and the reabsorpti...
7. Where are study notes available?
Biology is an important subject and it is necessary to have clear concepts of all the chapters. Practice is important so as to be able to do well a...
8. What are the three essential parts of nephron?
Nephron carries three different parts of tubules for secretion purpose. These three are-1. Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)The blood brought by the...
What are the three segments of the loop of the henle?
Anatomically, the loop of Henle can be divided into three main segments: the thin descending limb, the thin ascending limb, and the thick ascending limb (sometimes also called the diluting segment). Each nephron of the kidney contains blood vessels and a special tubule.
What is the liquid in the loop of Henle?
The liquid entering the loop of Henle is the solution of salt, urea, and other substances passed along by the proximal convoluted tubule, from which most of the dissolved components needed by the body—particularly glucose, amino acids, and sodium bicarbonate—have been reabsorbed into the blood.
What is the loop of a nephron?
Alternative Titles: Henle’s loop, nephronic loop. Loop of Henle, long U-shaped portion of the tubule that conducts urine within each nephron of the kidney of reptiles, birds, and mammals. The principal function of the loop of Henle is in the recovery of water and sodium chloride from urine.
Where does the glomerular filtrate enter the loop of Henle?
About one-third of the volume of the glomerular filtrate enters the descending limb of the loop of Henle. This fluid is isosmotic with plasma. The reabsorptive characteristics of the descending thin limb and those of the bend of the loop differ greatly…
Which segment of the loop is permeable to water?
The first segment of the loop, the thin descending limb, is permeable to water, and the liquid reaching the bend of the loop is much richer in salt and urea than the blood plasma is. As the liquid returns through the thin ascending limb, sodium chloride diffuses out of the tubule into the surrounding tissue, where its concentration is lower.
Which segment of the loop is responsible for the removal of salt?
In the third segment of the loop, the thick ascending limb, the tubule wall can, if necessary, effect further removal of salt, even against the concentration gradient, in an active-transport process requiring the expenditure of energy.
How does the filtrate of the nephron work?
As the filtrate flows through the tubule of the nephron, it becomes increasingly concentrated into urine. Waste products are transferred from the blood into the filtrate while nutrients are absorbed from the filtrate into the blood. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Read More on This Topic.
What is the ascending limb of the loop of Henle?
The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is a direct continuation from the descending limb of loop of Henle, and one of the structures in the nephron of the kidney. The ascending limb has a thin and a thick segment. The ascending limb drains urine into the distal convoluted tubule .
Which is thicker, ascending or descending?
The ascending limb is much thicker than the descending limb . At the junction of the thick ascending limb and the distal convoluted tubule are a subset of 15-25 cells known as the macula densa that are part of renal autoregulation through the mechanism of tubuloglomerular feedback .
Which limb is impermeable to water?
Thick ascending limb. Functionally, the parts of the ascending limb in the medulla and cortex are very similar. The medullary ascending limb is largely impermeable to water. Sodium (Na + ), potassium (K +) and chloride (Cl −) ions are reabsorbed by active transport.
What is the function of Tamm Horsfall protein?
The function of this protein is not well understood, but is responsible for creating urinary casts .
Is the ascending limb impermeable to water?
The thin ascending limb is impermeable to water; but is permeable to ions allowing for some sodium reabsorption. Na/K-ATPase is expressed at very low levels in this segment and thus this reabsorption is likely through passive diffusion. Salt moves out of the tubule and into the interstitium due to osmotic pressure created by the countercurrent system.
What is the loop of henle?
The Loop of Henle has a hairpin configuration with a thin descending limb and both a thin and thick ascending limb (TAL). The thin descending and ascending segments have thin, squamous epithelial membranes with minimal metabolic activity. On the other hand, the TAL has cuboidal epithelial membranes and is quite metabolically active.
What is the primary site of sodium reabsorption in the loop of henle?
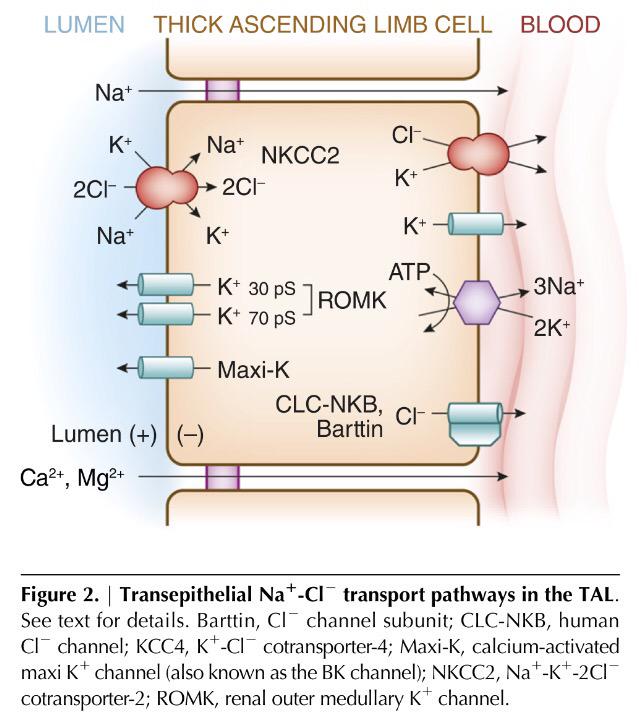
The primary site of sodium reabsorption in the Loop of Henle is the thick ascending limb (TAL). The TAL is impermeable to water. Sodium reabsorption is active – the driver is the Na + /K + ATPase on the basolateral membrane which actively pumps 3 Na+ ions out of the cell and 2 potassium (K+) ions into the cell. By creating a low intracellular concentration of sodium, the inside of the cell becomes negatively charged, creating an electrochemical gradient.
How do loop diuretics work?
They work by inhibiting NKCC2 transporters in the thick ascending limb, stopping sodium, potassium and chloride reabsorption. Less sodium reabsorption reduces the concentration of the renal medulla, decreasing water reabsorption in the DCT and CD. This leads to increased excretion of sodium in the urine and significant diuresis, reducing plasma volume. For this reason, loop diuretics such as furosemide are usually used to treat hypervolaemia, such as in heart or liver failure.
What is the role of the nephron in reabsorption?
Ion transport along the ne phron is essential for the reabsorption of sodium and water, maintenance of plasma volume and blood pressure and production of urine. The Loop of Henle contributes to the absorption of approximately 25% of filtered sodium and can be targeted by diuretic therapy.
What contributes to a hyperosmotic environment in the kidney medulla?
Pumping Na+ into the interstitial space – this contributes to a hyperosmotic environment in the kidney medulla
What are the side effects of loop diuretics?
An important side-effect of loop diuretics is hypokalaemia . This is because increasing sodium delivery to the DCT, also increases potassium excretion.
Is Na+ reabsorbable in the ascending limb?
The thin ascending limb is impermeable to water, due to it having no aquaporin channels. However, Na + reabsorption still occurs passively through epithelial Na+ (eNaC) channels. Chloride (Cl –) ions are also reabsorbed in the thin ascending limb through Cl– channels. There is also some paracellular movement of Na + and Cl – due to the difference in osmolarity between the tubule and the interstitium.
Which membrane of tubular epithelial cells in the ascending henle displays a mild intrinsic permeabil?
Importantly, the luminal membrane of tubular epithelial cells in the ascending henle display a mild intrinsic permeability to potassium, allowing backleak of some potassium ions into the lumen.
What is the thick ascending loop of the nephron?
The thick ascending loop of Henle is a major resorptive segment of the nephron and accounts for resorption of nearly a quarter of the filtered load of sodium, chloride, and potassium ions. In addition, Henle's thick segment is a major location of magnesium and calcium ion resorption.
Is the ascending henle impermeable to water?
Importantly, the ascending Henle is highly impermeable to water and the resorption of large amounts of sodium in the absence of water results in significant dilution of the tubular fluid.

Overview
Function
The thin ascending limb is impermeable to water; but is permeable to ions allowing for some sodium reabsorption. Na/K-ATPase is expressed at very low levels in this segment and thus this reabsorption is likely through passive diffusion. Salt moves out of the tubule and into the interstitium due to osmotic pressure created by the countercurrent system.
Functionally, the parts of the ascending limb in the medulla and cortex are very similar.
Structure
The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is a direct continuation from the descending limb of loop of Henle, and one of the structures in the nephron of the kidney. The ascending limb has a thin and a thick segment. The ascending limb drains urine into the distal convoluted tubule.
The thin ascending limb is found in the medulla of the kidney, and the thick ascending limb can be divided into a part that is in the renal medulla and a part that is in the renal cortex. The ascending …
Clinical significance
The thick ascending limb symporter: Na-K-Cl cotransporter.
See also
• Descending limb of loop of Henle
External links
• Nosek, Thomas M. "Section 7/7ch07/7ch07p11". Essentials of Human Physiology. Archived from the original on 2016-03-24.
• Histology image: 15804loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
• Overview at vet.cornell.edu