How to use biceps and triceps correctly?
- Use a low anchor and focus on pushing toward the ceiling.
- Separate the rope when your triceps are overhead and fully contracted.
- On the way down, don't try to force a deeper stretch than your arms will allow. Your arms should move through this movement without any pain.
Is the bicep and bicep brachii the same thing?
The biceps brachii is a unique muscle with 2 proximal tendons and a single distal tendon. Although these tendons are part of the same muscle, they have significantly different functions. It is hypothesized that the long head of the biceps acts as a pain generator in the shoulder, though the biomechanical function is still under debate.
How to exercise the femoral biceps?
The 20 Best Exercises for Biceps Femoris Workout
- Barbell Squat. Squats with a barbell is one of the main basic exercises in powerlifting and bodybuilding for training the muscles of the legs and buttocks.
- Dumbbell Squat. Squatting with dumbbells is an exercise that affects the muscles of the legs and buttocks. ...
- Lying Leg Curl. ...
- Deadlift. ...
- Stiff-Leg Deadlift. ...
- Hip Abduction Machine. ...
- Leg Press. ...
What do the triceps and biceps muscles do?
- Movement- The biceps and triceps contract to move the upper arm.
- Production of heat- The muscles produce heat for the upper arm.
- Posture maintenance- It requires energy from the muscles to keep arms steady.

What are the functions of the biceps femoris quizlet?
The function of the biceps femoris is to: extend the thigh and flex the leg.
Where is the action of the biceps femoris?
In general, the biceps femoris muscle acts on both the knee and hip joints. Although, due to its attachments, the short head of this muscle acts only on the knee joint while the long head acts on both. When acting on the hip joint, biceps femoris produces the movement of hip extension.
What activity uses the biceps femoris?
The functions of the biceps femoris are in controlling knee and hip joint movements. It is a commonly injured muscle in high-intensity sports.
What is a biceps femoris in anatomy?
Description. Biceps femoris is a muscle of the posterior compartment of the thigh, and lies in the posterolateral aspect. It arises proximally by two 'heads', termed the 'long head' (superficial) and the 'short head' (deep). It is part of the hamstrings.
What happens when the biceps femoris contracts?
These muscles produce flexion at the knee and extension at the hip when they contract. When the thigh is flexed, the hamstring muscles (especially the biceps femoris) help tilt the pelvis backward.
Why is it called biceps femoris?
The biceps femoris muscle of the leg derives its name from having two heads of origin, long and short. The long head arises from the medial facet on the ischial tuberosity in continuity with the tendon of origin of semitendinosus.
What does the biceps femoris extend?
Both heads of the biceps femoris perform knee flexion. Since the long head originates in the pelvis it is involved in hip extension. The long head of the biceps femoris is a weaker knee flexor when the hip is extended (because of active insufficiency).
What muscles flex the knee?
The knee flexors include the set of hamstrings, gracilis, sartorius, gastrocnemius, plantaris, and popliteus. Interestingly, most of these knee flexors also internally or externally rotate the knee. This important set of motions will be discussed in an upcoming section.
Is the bicep femoris two muscles?
The biceps femoris is a double-headed muscle located on the back of thigh. It consists of two parts: the long head, attached to the ischium (the lower and back part of the hip bone), and the short head, which is attached to the femur bone.
Which of the following statements is true about the biceps femoris muscle?
Which of the following statements is true about the biceps femoris muscle? Selected Answer: Correct It is best developed through hamstring curls or leg curls.
How do I activate my biceps femoris?
Begin by flexing your knees slightly, and then flex at the hip, moving your butt back as far as possible, lowering your torso as far as flexibility allows. Your back should remain in absolute extension at all times, and the bar should remain in contact with the legs.
What part of the name biceps femoris indicates its location?
Biceps femoris muscleBiceps femorisPosterior view of right leg. Long head of muscle highlighted in red, short head (yellow) labeled in the lower part of the imageDetailsOrigintuberosity of the ischium, linea aspera, femurInsertionthe head of the fibula which articulates with the back of the lateral tibial condyle10 more rows
In what movements are the biceps femoris and the semitendinosus antagonists?
Antagonists to flexion at the hip include the gluteus maximus, the hamstrings (specifically the long head of biceps femoris), and the semimembranosus and semitendinosus, which all act to extend at the hip.
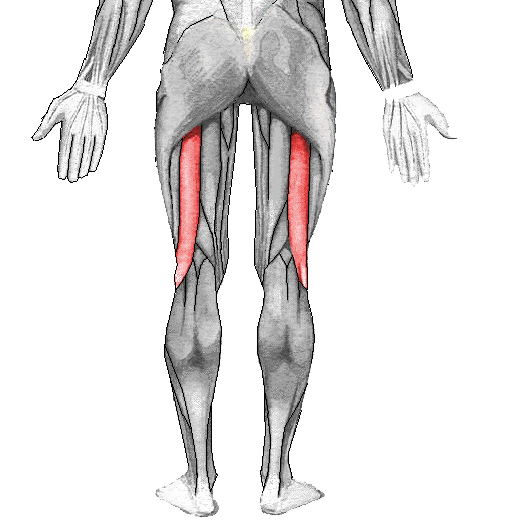
What is biceps femoris?
The biceps femoris is a long muscle in the posterior compartment of the thigh responsible for movement at both the hip and knee joints. Along with...
Where is the biceps femoris located?
The biceps femoris muscle is located in the posterior compartment of the thigh, also known as the hamstrings. The hamstrings are made up of three s...
What does the biceps femoris do?
The biceps femoris is responsible for movement at both the hip joint and knee joint. At the hip, the long head of the biceps femoris allows for thi...
What are the most important facts to know about biceps femoris?
The biceps femoris muscle, located in the posterior portion of the thigh, is composed of a long head that originates from the ischial tuberosity an...
Why does my bicep hurt?
Pain in the biceps femoris can be caused by several reasons. The most common condition is a strained muscle caused by improper lifting or too much exercise. Overuse of the biceps femoris can result in torn muscles and ligaments. Last medically reviewed on January 20, 2018.
What is the long head of the hamstring?
The long head is a part of the hamstring muscle group that occupies the posterior section of the thigh. The hamstring muscles may be considered extensors of the thigh.
Where is the biceps femoris located?
Biceps femoris. The biceps femoris is a double-headed muscle located on the back of thigh. It consists of two parts: the long head, attached to the ischium (the lower and back part of the hip bone), and the short head, which is attached to the femur bone. The long head is a part of the hamstring muscle group that occupies the posterior section ...
How to strengthen biceps femoris?
You can strengthen the biceps femoris with common squats and hip hinges. Perform hamstring curls by looping a resistance band around a stable object and hooking it around your ankle. Lie on your stomach on a mat and bend and extend your knee to work against the resistance. Leg curls using a stability ball are another way to build strength in the biceps femoris. Lie on your back and prop your heels up on the ball with straight legs. Bend the knees to curl the ball closer to your rear. To stretch the biceps femoris, put one leg up on a raised surface -- a bench or chair -- and gently lean forward over it to feel a mild pull in the back of your leg. Repeat on the other side.
What muscles are involved in running?
The hamstrings consist of three muscles: the semitendinosus, semimembranosus and biceps femoris. The biceps femoris is a two-headed muscle that lies in the outer-middle section of the back of the thigh. It is intrinsic to knee flexion.
Where does the biceps femoris attach to the ischium?
The long head of the biceps femoris attaches to the ischium -- the lower and back part of the hip bone. The short head attaches to the femur, or thigh bone. The point of innervation, where the muscle fibers and neurons connect, is the tibial part of the sciatic nerve, which runs down the back of the thigh from the hip to the sole of the foot. This point is where the muscle receives the signal to contract.
Which muscle helps you bend your knee?
Both heads of the biceps femoris enable you to bend and extend the knee. The long head of the muscle also assists you in extending the hip. If you bend your knee slightly, the biceps femoris helps you rotate the leg outward.
Who is Andrea Cespedes?
Andrea Cespedes is a professionally trained chef who has focused studies in nutrition. With more than 20 years of experience in the fitness industry, she coaches cycling and running and teaches Pilates and yoga. She is an American Council on Exercise-certified personal trainer, RYT-200 and has degrees from Princeton and Columbia University.
What is biceps femoris?
The biceps femoris is a long muscle in the posterior compartment of the thigh responsible for movement at both the hip and knee joints. Along with the semitendinosus and semimembranosus, the biceps femoris makes up the hamstrings muscle. The muscles of the hamstring border the popliteal fossa, which is a triangular space behind the knee. The lateral border of the popliteal fossa is created by the biceps femoris.
Where is the biceps femoris located?
The biceps femoris muscle is located in the posterior compartment of the thigh, also known as the hamstrings. The hamstrings are made up of three separate muscles: the semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris. The biceps femoris has two heads, a short head and a long head, that originate from different locations but share the same insertion site. There, they join to form the biceps femoris tendon. The biceps femoris tendon then joins with the lateral collateral ligament to insert at the lateral aspect of the head of the fibula (i.e., outer lower leg bone). The two heads originate at different locations, with the long head originating at the ischial tuberosity, and the short head originating at the linea aspera of the femur (i.e., thighbone). The ischial tuberosity is a rounded portion of the ischium, or part of the pelvic bone. Comparatively, the linea aspera of the femur is a lip, or ridge, at the posterior shaft of the femur.
What are the most important facts to know about biceps femoris?
The biceps femoris muscle alongside the semitendinosus and semimembranosus form the hamstrings muscle. These muscles are responsible for thigh extension, knee flexion, and external rotation of both the hip and leg.
Which artery supplies blood to the long head and short head of the biceps femoris?
The inferior gluteal artery, popliteal artery, and perforating branches from the inferior gluteal and profunda femoris arteries supply blood to both the long head and short head of the biceps femoris.
What is the difference between a long and short head?
The innervation (i.e., nerve supply) differs between the long head and short head. The long head is innervated by the tibial portion of the sacral nerve (L5-S2), while the short head is innervated by the common fibular, or peroneal, division of the sacral nerve (L5-S2).
What muscle allows you to rotate your knee away from the body toward the side?
Your biceps femoris muscle allows you to rotate your knee away from the body toward the side. You use this muscle to sit cross-legged on the floor, to perform plie squats and to perform the mountain pose in yoga. Bending your legs and pressing your feet together is made possible by this muscle, as are a number of other lateral rotation functions of the knee and hip working together.
What muscle allows you to bend your knee?
As the biceps femoris muscle contracts, the muscle shortens, allowing you to lift your leg or bend your knee. As the muscle elongates or stretches, you're able to extend the leg away from your body. The long head of the biceps femoris muscle allows you to extend your leg while the short head bi ceps femoris allows you to rotate your knee laterally and flex your knee.
What muscle is used to extend the leg?
The biceps femoris muscle works in conjunction with multiple thigh and hip muscles. The main function of this muscle is to enable you to extend your leg and thigh at the hip joint. The biceps femoris allows you to lift your leg upward from the floor, to kick a ball and any other movement that requires extension of the leg away from your body. Lifting your knee requires flexion, initiated by a shortening of the hamstring muscles, including the biceps femoris.
Where is the biceps femoris located?
The long- and short-headed biceps femoris muscle located on the back of the thigh originates at the buttocks and extends to an insertion point at the back of the knee. Specifically, the upper portion or head of the biceps femoris starts at the bottom end of the back of the pelvis at a point called the ischial tuberosity, near the coccyx or tailbone. The other end of the muscle attaches to the top ends or the heads of the fibula and tibia just below the back of your knee joint.
Who is Denise Stern?
Denise Stern is an experienced freelance writer and editor. She has written professionally for more than seven years. Stern regularly provides content for health-related and elder-care websites and has an associate and specialized business degree in health information management and technology.
What is the function of the biceps femoris?
The biceps femoris has three primary functions: extending the thigh, bending the knee, and rotating the knee toward the outside of the body. The long head is involved in thigh extension and is known as an extensor muscle. Lastly, you have learned that the biceps femoris carries the sciatic nerve down the leg and that it is supplied by three primary arteries, including the profunda femoris.
What is the biceps femoris?
Wow! Who knew this one muscle was so complex and so important? You have learned that the biceps femoris is one of three muscles that make up the hamstring on the back of the thigh. It runs from the bottom of your tailbone to the back of the knee. Also, it has two points of origin, the long head and the short head. Muscles with two points of origin are called biceps.
What arteries are used to flow blood to the biceps?
The blood flow to the biceps femoris comes from three arteries. These arteries are the inferior gluteal artery, the profunda femoris artery, and the popliteal artery. Some identify the profunda femoris as the deep femoral artery. More specifically, the profunda femoris branches into the perforating arteries, which actually supply blood to a portion of the biceps femoris.
Where does the biceps femoris start?
The biceps femoris starts right about at the point where the buttock area ends (the coccyx) and the thigh begins. It then progresses down to the back of the knee and attaches to the lower leg bones. It is part of the large muscle group (the hamstring) that covers the back of the thigh.
Where is the femoris bicep located?
As we said above, the femoris bicep has two points of origin of heads. The long head begins on the lower portion of the pelvis. The short head begins at about the middle of the femur. The femur is the large bone in your upper leg. These two smaller portions of the muscle join together and progress down toward the point of insertion, at the back of the knee. Insertion is the location at which a muscle terminates, or ends. Here, they attach primarily to the fibula, but some smaller portions attach to the tibia. The tibia and fibula are the two bones located in the lower portion of the leg.
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
Is the bicep part of the hamstring?
Yes, technically the biceps femoris is part of the hamstring, so both your coach and the doctor are correct. However, your doctor is being more specific. The biceps femoris is one of a trio of muscles that make up the hamstring muscle group. The hamstring is comprised of three muscles; the biceps femoris, the semitendinosus, and the semimembranosus. But wait, you're still confused. You thought your bicep muscle was in your upper arm? In anatomy of the body, we describe any muscle that has two heads, or points of origin, as a bicep. The biceps femoris has two points of origin.
How many heads does the biceps femoris have?
Clinical relevance[edit| edit source] We know that biceps femoris muscle usually has 2 heads, namely short head and long head of biceps femoris. These two heads insert on the head of fibula, where at the site of insertion they divide into two portions by fibular collateral ligaments.
What causes a snapping biceps femoris?
These two heads insert on the head of fibula, where at the site of insertion they divide into two portions by fibular collateral ligaments. Any sort of subluxation or dislocation of biceps femoris tendon or abnormal insertion of the tendon, and any or no trauma, meniscal instability can lead to Snapping Biceps Femoris Tendon. It is an unusual condition with symptoms of pain on the lateral side of knee, fibular head will be prominent, painful snap on lateral aspect of knee during active and passive knee flexion at 90 degrees and difficulty in performing ADL’s or sport related activities. As it is a rare phenomenon and there are very few articles published related to this condition. Furthermore, the exact pathology leading to snapping biceps femoris tendon is still unknown. However, according to researches, occurrence of this condition could be either due to overuse, prolong sporting or congenital.
Where is the biceps femoris located?
Biceps femoris is a muscle of the posterior compartment of the thigh, and lies in the posterolateral aspect. It arises proximally by two 'heads', termed the 'long head' (superficial) and the 'short head' (deep). It is part of the hamstrings. [1] [2] [1] Anatomy[edit| edit source] Origin[edit| edit source]
How do the head and tibia provide stability?
Both heads provide rotary stability by preventing forward dislocation of the tibia on the femur during flexion
How to palpate ASIS?
With one hand, palpate the patient's ASIS and iliac crest with your thumb and index finger
Where is the pain in the lower biceps?
Pain referred from TrPs in the lower half of the biceps femoris (long or short head) focuses on the back of the knee and may extend up the posterolateral area of the thigh as far as the crease of the buttock.
What is the short head of the femur?
Short head: linea aspera and lateral supracondylar line of the femur
How many muscles are there in mastication?
There are four muscles of mastication. Select the exception.
Which brachii is the antagonist?
biceps brachii is the antagonist and triceps brachii is the agonist.
How many parts does the insertion of a muscle have?
the insertion of the muscle is split into two parts.
Which direction does lateral flexion of the head go?
lateral flexion of the head to the left and rotation of the head to the right.
Where does the sacroiliac muscle originate?
This muscle extends and rotates the vertebral column toward the opposite side of the body. Its origin is on the sacrum and transverse processes of each vertebra and its insertion is the spinous processes of more superior vertebrae