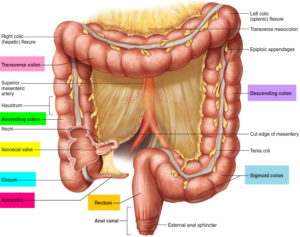
The appendix (or vermiform appendix; also cecal [or caecal] appendix; vermix; or vermiform process) is a finger-like, blind-ended tube connected to the cecum, from which it develops in the embryo. The cecum is a pouchlike structure of the colon, located at the junction of the small and the large intestines.
Full Answer
Do humans have a cecum or just an appendix?
The cecum or caecum is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix, to which it is joined).The word cecum (/ ˈ s iː k əm /, plural ceca / ˈ s iː k ə /) stems from the Latin caecus meaning blind.It receives chyme from the ileum, and connects to ...
What is the function of the cecum and appendix?
Cecum and Appendix Function. The cecum is the first part of the large intestine. It has an appendix consist of friendly bacteria. It stores friendly bacterial. These bacteria digest the remaining port of food. Food absorbs and left sold material. This sold material was removed from the body through the anus. The cecum is a pouch-like structure.
What causes an enlarged cecum?
The following symptoms may be experienced with cecal volvulus:
- ballooning abdomen (abdominal distension)
- constipation
- diarrhea
- trouble passing gas
- severe abdominal pain
- vomiting
Why is the cecum important?
- Introduction. A polyp is an abnormal tissue growth and is commonly found in the intestine ( Haggar & Boushey, 2009 ).
- Material & Methods. This study was approved by the institutional review board of the Seoul National University Hospital (IRB No. ...
- Results. ...
- Discussion. ...
- Conclusions. ...
- Supplemental Information. ...
Is the cecum the same as the appendix?
Cecum and appendix are situated at the junction of the small intestine and large intestine. The key difference between the cecum and appendix is cecum is a pouch-like structure while appendix is worm-shaped tube-like structure.
What is cecum function?
The main functions of the cecum are to absorb fluids and salts that remain after completion of intestinal digestion and absorption and to mix its contents with a lubricating substance, mucus. The internal wall of the cecum is composed of a thick mucous membrane, through which water and salts are absorbed.
What was the function of appendix?
The function of the appendix is unknown. One theory is that the appendix acts as a storehouse for good bacteria, “rebooting” the digestive system after diarrheal illnesses. Other experts believe the appendix is just a useless remnant from our evolutionary past.
What happens when the cecum is removed?
In our study we demonstrated that removal of the cecum resulted in a conspicuous decrease in both richness and evenness of bacterial communities of the colon, as well as a pronounced change in the composition of the bacterial community structure.
Can u live without cecum?
People can live without a colon, but may need to wear a bag outside their body to collect stool. However, a surgical procedure can be performed to create a pouch in the small intestine that takes the place of the colon, and in this case, wearing a bag is not necessary, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Do you need your cecum?
The function of the cecum is to aid in digestion. It is the first part of the colon (large intestine) to receive digested materials from the small intestine, and it pushes these materials into the ascending colon.
What happens when appendix is removed?
Your belly may be swollen and may be painful. If you had laparoscopic surgery, you may have pain in your shoulder for about 24 hours. You may also feel sick to your stomach and have diarrhea, constipation, gas, or a headache. This usually goes away in a few days.
Can you live without appendix?
You can live a normal life without your appendix. Changes in diet or exercise are usually not needed.
Why do people get their appendix removed?
The appendix is a small, finger-shaped organ that comes out of the first part of the large intestine. It needs to be removed when it becomes swollen or infected. If the appendix is not removed, it can leak bacteria and infect your entire belly, which can be very life threatening.
What causes inflammation of the cecum?
Inflammation of the colon, or colitis, may occur for many reasons. It may be due to a short-term infection from consuming contaminated food, or a sign of a chronic condition, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. Colitis symptoms may include abdominal cramping, diarrhea, nausea, and bloating.
Are polyps in the cecum cancerous?
Most colon polyps are harmless. But over time, some colon polyps can develop into colon cancer, which may be fatal when found in its later stages.
Why is the cecum removed?
Ileocecal resection is the surgical removal of the cecum along with the most distal portion of the small bowel—specifically, the terminal ileum (TI). This is the most common operation performed for Crohn disease, though other indications also exist (see below).
Does a colonoscopy look at the cecum?
Colonoscopy enables visual inspection of the entire large bowel (also called the colon or large intestine) from the distal rectum to the cecum. It remains the gold standard for the detection of polyps and colorectal cancer. The procedure is a safe and effective means of evaluating the large bowel.
Where is the cecum found and what is its function?
A pouch that forms the first part of the large intestine. It connects the small intestine to the colon, which is part of the large intestine. The cecum connects the small intestine to the colon.
What causes inflammation of the cecum?
Inflammation of the colon, or colitis, may occur for many reasons. It may be due to a short-term infection from consuming contaminated food, or a sign of a chronic condition, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. Colitis symptoms may include abdominal cramping, diarrhea, nausea, and bloating.
What causes cecum pain?
Some circumstances or conditions can make it more likely a person who is predisposed will experience a problem related to mobile cecum, such as becoming pregnant, undergoing abdominal surgery, or getting an infection. Other factors, such as a high-fiber diet, may also play a role.
What is the role of the cecum in digestion?
During digestion, the small intestine absorbs nutrients from solid foods, and passes the solid waste products and liquid into the large intestine for absorption into the body. The cecum acts as a receptacle for the liquid products passed into the large intestine.
What is the role of the cecum in the body?
More than just a reservoir for liquids, the cecum is responsible for the absorption of salts and electrolytes into the body from liquids. The muscle tissue of the cecum contracts, causing the liquid products to churn. This churning extracts salts and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium. These salts are then absorbed into the mucus membrane of the cecum. Humans lose salts and electrolytes as they sweat, and must replace these nutrients to carry electrical charges between cells. The cecum separates these salts from the liquids consumed and absorbs them into the body.
How does the cecum work?
Humans lose salts and electrolytes as they sweat, and must replace these nutrients to carry electrical charges between cells. The cecum separates these salts from the liquids consumed and absorbs them into the body. 00:00. 00:00 12:50. GO LIVE.
What valve separates the cecum from the small intestine?
Separating the cecum from the small intestine is the ileocecal valve, also called Bauhin’s valve, and the appendix protrudes from the lower part of the cecum.
What is the function of the duodenum?
It is the first part of the large intestine that digesting food enters after leaving the small intestine, and is shaped like a sac. Separating the cecum from the small intestine is the ileocecal valve, also called Bauhin’s valve, and the appendix protrudes from ...
What animals take in cellulose?
Animals, both herbivores and omnivores, take in cellulose when eating plants. Bacteria and enzymes in the cecum of these animals cause fermentation that breaks down cellulose fibers, which then allows the rest of the large intestine to digest the nutrients from cellulose.
What is the purpose of the mucus membrane in the large intestine?
The large intestine extracts liquid from the waste products, making it necessary for the mucus to lubricate the solid waste and allow it to pass through the rest of the large intestine .
What is the difference between the appendix and the cecum?
The key difference between the cecum and appendix is cecum is a pouch-like structure while appendix is worm-shaped tube-like structure.
What is the purpose of the cecum?
The cecum is considered as the junction between the small intestine and large intestine. The main function of the cecum is to provide the space for mixing bacteria with partially digested food coming from the small intestine ...
What is Appendix?
Appendix is a worm-shaped blind-ended tube that is connected to the cecum of the digestive tract. Appendix is also known as a cecal appendix or vermiform appendix. The normal length of the human appendix is 9 mm. But it can vary from 2 to 20 mm. The diameter usually lies between 7 to 8 mm. Appendix is located on the right side of the body in the lower quadrant of the abdomen near the right hip bone.
How does the cecum work?
When partially digested food (known as chyme) enters into the cecum, bacteria are mixed with the chyme by the cecum wall contraction.
What are the parts of the gastrointestinal tract?
The gastrointestinal tract is composed of different components such as mouth, O esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine, Liver, Pancreas, Gallbladder, etc. Cecum and appendix are two parts of the large intestine. Cecum is the pouch-like region of the large intestine that is located at the junction of the small intestine ...
Why is the appendix important?
The appendix is associated with two common diseases namely appendicitis and appendix cancers. Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix due to blockage of the tube by the stones of the faeces.
Where is the cecum located?
The cecum is situated in between the ascending colon and vermiform appendix. And it is located in the lower right quadrant of the abdominal cavity inferior and lateral to the ileum. The cecum is composed of four layers; the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis and serosa.
What is the fold of the peritoneum that connects these organs to the posterior abdominal wall?
Intestinal mesenteries are folds of peritoneum that connect these organs to the posterior abdominal wall.
What is the term for a sac-like bulge of the intestinal wall protruding outward?
Diverticulosis: An intestinal diverticulum is a sac-like bulge of the intestinal wall protruding outward. Diverticula arise because of the increased intestinal pressures associated with a low-fiber diet and when the transport of intestinal content is slower. The condition is typically asymptomatic.
Which attaches to the transverse mesocolon?
Mesocolic taenia: attaches to the transverse mesocolon (which anchors the transverse colon to the posterior abdominal wall)
What is the inflammation of the diverticula?
Diverticulitis: inflammation of diverticula that occurs when the diverticula become occluded. Diverticulitis often presents with lower abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits and may become complicated by abscess, perforation, fistula, and bowel obstruction.
Which is thinner, the large or the small intestine?
The walls of the large intestine are thinner than those of the small intestine.
Where is the intestinal pouch?
Intestinal pouch between the terminal ileum (at the ileocecal junction) and the ascending colon
Where do large intestines develop?
The large intestines develop from the primitive midgut and hindgut:
What is the cecum of the colon?
What is the cecum. The cecum is a small blind pouch about 6 cm (2.4 inch) long at the beginning of the large intestine (the ascending colon). Attached to the cecum is a twisted, coiled tube called the appendix or vermiform appendix, measuring about 8 cm (3 in.) in length. The base of the appendix lies on the posteromedial wall ...
Where is the appendix located?
The base of the appendix lies on the posteromedial wall of the cecum about 1 to 2 centimeters below the ileocecal junction. The tip of the appendix frequently floats in the peritoneal cavity and can be located in a retrocecal position. It has a short triangular mesentery called the mesoappendix. The end of the small intestine is ...
What is a cecum inflammation?
Cecum inflammation. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) encompasses two types of idiopathic intestinal disease that are differentiated by their location and depth of involvement in the bowel wall 12). Ulcerative colitis involves diffuse inflammation of the colonic mucosa. Most often ulcerative colitis affects the rectum (proctitis), ...
What happens to the chyme after a meal?
Immediately after a meal, a gastroileal reflex intensifies peristalsis in the ileum and forces any chyme into the cecum. The hormone gastrin also relaxes the sphincter.
What is the end of the small intestine called?
It has a short triangular mesentery called the mesoappendix. The end of the small intestine is the ileocecal junction, where the terminal ileum joins the cecum of the large intestine. The muscularis of the ileum is thickened at this point to form a sphincter, the ileocecal valve, which protrudes into the cecum.
What valve regulates the passage of food residue into the large intestine?
The ileocecal valve regulates the passage of food residue into the large intestine and prevents feces from backing up into the ileum. As the cecum fills with residue, the pressure pinches the ileocecal valve shut and prevents the reflux of cecal contents into the ileum.
What is the term for a disease that results in transmural ulceration of the GI tract?
Crohn disease (Crohn’s disease) results in transmural ulceration of any portion of the gastrointestinal tract (GI) most often affecting the terminal ileum and colon 13). Both diseases are classified by extent (mild, moderate, or severe) and location.
What Is the Function of the Appendix?
The muscles lining your GI tract, along with the hormones and enzymes that the system produces, allow your GI tract to break down and process food. Your appendix doesn't directly help with digestion.
Why is the appendix important?
According to the so-called "safe house" theory, the appendix protects a collection of beneficial gut bacteria when certain diseases wipe them out from elsewhere in the GI tract. Once the immune system has rid the body of the infection, the bacteria emerge from the appendix biofilm and recolonize the gut. ( 6)
What is the appendix attached to?
The finger-shaped appendix is attached to a part of your large intestine called the cecum — a small pouch typically considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. (1)
Why does my appendix hurt?
The infection or obstruction causes the bacteria in the appendix to grow out of control, and the organ can fill with pus and swell. Appendicitis causes intense abdominal pain and other GI symptoms, including vomiting and diarrhea. Removal of the appendix (an appendectomy) is often the necessary course of action, though increasingly, ...
What is the name of the pouch that is attached to the McBurney's point?
( 3) The finger-shaped appendix is attached to a part of your large intestine called the cecum — a small pouch typically considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. (1)
What happens when the appendix bursts?
When the appendix bursts, it spreads its content throughout the abdomen, potentially infecting the peritoneum, which is the silk-like membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. A peritoneum infection, called peritonitis, can then lead to sepsis, a complication that's potentially deadly if not treated aggressively. ( 9)
What is the condition called when the appendix is infected?
Sometimes, the appendix can become inflamed and infected, resulting in a condition called appendicitis.
What is the function of the cecum?
It is separated from the ileum (the final portion of the small intestine) by the ileocecal valve (also called Bauhin valve), which limits the rate of food passage into the cecum and may help prevent material from returning to the small intestine . The main functions of the cecum are to absorb fluids and salts that remain after completion ...
What is the cecum of the intestine?
The cecum, the first part of the large intestine, is a sac with a closed end that occupies the right iliac fossa, the hollow of the inner side of the ilium ( the upper part of the hipbone). Guarding the opening of the ileum (the terminal portion…
How many cecums are there in a rock hyrax?
Cecum number can also vary; for example, the rock hyrax ( Procavia capensis) has two ceca, whereas certain insectivores (such as hedgehogs, moles, and shrews) lack a cecum. The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Adam Augustyn, Managing Editor, Reference Content.
What is the internal wall of the cecum?
The internal wall of the cecum is composed of a thick mucous membrane, through which water and salts are absorbed. Beneath that lining is a deep layer of muscle tissue that produces churning and kneading motions. Variations in cecum size and structure occur among animals.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
