What function does the cell wall perform in a plant?
The main functions of the cell wall are to provide structure, support, and protection for the cell. The cell wall in plants is composed mainly of cellulose and contains three layers in many plants. The three layers are the middle lamella, primary cell wall, and secondary cell wall. Bacterial cell walls are composed of peptidoglycan.
What does cell wall do for plant cell?
The cell wall surrounds the cell membrane and provides both strength and flexibility to plants. Moreover, the cell wall helps plants to maintain turgor pressure. Turgor pressure occurs when the fluid content of a cell pushes the cell membrane against the cell wall.
What are 3 functions of the cell wall?
It performs several important functions, the list of which is as follows:
- The cell wall of the plants provides rigidity, structure, and strength to the cell.
- Protection is provided by the cell wall against the physical shocks and mechanical strengths.
- Due to water intake, the cells start expanding. ...
- Prevention of water loss happens because of the presence of a cell wall.
Why does a plant cell have a cell wall?
The Tensile Strength of the Cell Wall Allows Plant Cells to Develop Turgor Pressure The aqueousextracellular environment of a plant cell consists of the fluid contained in the walls that surround the cell.
Why does the cell wall keep the shape of the plant?
Their shape is still being maintained by the cell wall so that, as soon as you water the plant, it can pick itself back up again. On the other hand, if you water too much, the cell wall also makes sure that the cell does not burst. It protects the cell from over-expansion.
Why is the cell wall important?
It protects the cell from over-expansion. The cell wall protects the plant and cells from the many insects and pathogens that could harm the plant, but the cell wall still has its vulnerable areas. There are holes all over the cell wall called plasmodesmata.
What is a Cell Wall?
Cells come in many different shapes and have different functions. Plant and animal cells are different, too. The main difference between plant and animal cells is that plant cells have a cell wall on the outer layer, whereas animal cells only have a cell membrane. The cell wall is a protective layer outside the cell membrane that also provides support for the cell's structure.
What is the primary cell wall made of?
The primary wall is the next layer. It is composed of cellulose in the form of microfibrils. These cellulose microfibrils weave together with glycans, increasing the strength of the cellulose. Pectins can also be found in the primary cell wall.
What are the cell walls of a redwood tree?
A redwood tree and a dandelion both have cell walls on the outside of all of their cells. The cell walls are there to give the plants their shape and support; however, the cell walls act and are constructed a little different to meet the needs of the particular plant. For instance, a 100-foot redwood tree needs a very strong and rigid plant cell wall so that it can grow to its great height and not fall over in the wind. On the other hand, a little yellow dandelion out in the field needs to have more plasticity so that it can bend, not break, as the wind blows through the field.
How many layers are there in the cell wall?
The cell wall can be divided into three layers, each of which is made for strength and protection. These layers and their compositions not only protect the cell but allow for the cell to function. The three layers are the middle lamella, the primary wall and the secondary wall.
What is the third layer of a plant?
The third and final layer is the secondary wall. This layer is extremely rigid and provides compression strength. It helps stop the plant from getting squished. The secondary wall has a very similar composition as the primary wall, only it has more stuff in it - it contains lignin, which is very hard and has considerable strength. The secondary wall also protects the plant from invading bacteria or fungi.
What are the functions of the cell wall?
The following points highlight the top seven functions of cell wall in the life of a plant. The functions are: 1. Gives Mechanical Strength 2. Maintains Cell Shape 3. Controls Cell Expansion 4. Controls Intercellular Transport 5. Protects Against Infective Organisms 6. Cell Wall has Signalling Device against Attack of Microorganism 7. Acts as a Reservoir of Food.
What is the mechanical strength of plant cell walls?
It is believed that the mechanical strength of plant cell walls is due to the presence of skeletal framework formed by cellulosic microfibrils. Cellulose is the major component of paper, cotton etc. Maximum strength is obtained from collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
Which polysaccharides are stored in the cell wall?
The foods may remain stored within the cell or as a component of the cell wall. The polysaccharides (mannans, xyloglucans and galactans) of cell wall are the example of the latter type. Mannans are cell wall storage polysaccharides. Endosperm of Ericaceae and Apiaceae contain 90% mannose approximately.
How does the covalent bond affect the cell wall?
The covalent bond affects the cell wall through the action of an enzyme – probably transglycosylase.
How is the cell wall of wood strengthened?
The cellulosic walls of wood are further strengthened by lignification. The large size and structural strength of a woody plant is achieved by the cell wall. In these plants the constituents of cell wall contributes 95% of the dry weight of wood. The rigidity of the whole plant and strength is due to cell wall.
Which structure maintains the shape of a cell?
Maintains Cell Shape: The various shapes of cell are attributable to cell wall. Isolated protoplasts are more or less spherical whose boundary is the plasma membrane. The plasma membrane is the most common site of cellulose synthesis and cellulose is one of the components of cell walls.
What are the walls of collenchyma cells?
The walls of collenchyma cells are thickened with pectin, hemicellulose, protein and cellulose. Collenchyma cells are living and retain their protoplast even when mature. Therefore, they can regulate the deposition and orientation of wall materials according to the need of developing organs.
What is the function of the cell wall?
The main function of the cell wall is to provide structural strength and support, and also provide a semi-permeable surface for molecules to pass in and out of the cell.
What is a Cell Wall?
A cell wall is defined as the non-living component, covering the outmost layer of a cell. Its composition varies according to the organism and is permeable in nature. The cell wall separates the interior contents of the cell from the exterior environment. It also provides shape, support, and protection to the cell and its organelles. However, this cellular component is present exclusively in eukaryotic plants, fungi, and few prokaryotic organisms.
What are the cell walls of prokaryotes made of?
The prokaryotic cell walls are composed of large polymers known as peptidoglycans. Cell walls in prokaryotes serve as a form of protection and prevent lysis (bursting of the cell and expulsion of cellular contents). Structurally, prokaryotic cell walls consist of two layers: An inner layer that is made up of peptidoglycans.
What is the primary cell wall?
Primary Cell Wall. The primary cell is situated closest to the inside of the cell and is the first-formed cell wall. It is mainly made up of cellulose, allowing the wall to stretch for the purpose of growth. Several primary cells contain pectic polysaccharides and structural proteins.
Why is water important in cell growth?
It helps to control cell expansion due to the intake of water. Also helps in preventing water loss from the cell. It is responsible for transporting substances between and across the cell. It acts as a barrier between the interior cellular components and the external environment.
How many layers are there in a plant cell wall?
A typical plant cell wall is composed of 3 layers namely the primary cell wall, the secondary cell wall, and the middle lamella.
Why are animal cells irregular?
An animal cell is irregular in their shape and this is mainly due to the lack of cell wall in their cells. The compositions of the cell wall usually vary along with organisms. Also, read Cell Wall and Cell Membrane.
What is the cell wall of plants?
The plant cell wall: Biosynthesis, construction, and functions. The plant cell wall is composed of multiple biopolymers, representing one of the most complex structural networks in nature. Hundreds of genes are involved in building such a natural masterpiece. However, the plant cell wall is the least understood cellular structure in plants.
What is the least understood cellular structure in plants?
However, the plant cell wall is the least understood cellular structure in plants. Due to great progress in plant functional genomics, many achievements have been made in uncovering cell wall biosynthesis, assembly, and architecture, as well as cell wall regulation and signaling.
What Is the Function of a Cell Wall?
The cell wall has several functions, including the maintenance of the cell structure and shape. The wall is rigid, so it protects the cell and its contents.
What is the purpose of cell walls?
In addition to the mechanical support, the wall acts as a framework that can prevent the cell from expanding or growing too quickly.
Why do plants have walls?
One of the main reasons for having a wall in a plant cell is that it can withstand turgor pressure, and this is where cellulose plays a crucial role. Turgor pressure is a force created by the inside of the cell pushing out. Cellulose microfibrils form a matrix with the proteins, hemicelluloses and pectins to provide the strong framework ...
What is the structure of cellulose?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate and consists of thousands of glucose monomers that form long chains. These chains come together and form cellulose microfibrils, which are several nanometers in diameter. The microfibrils help control the growth of the cell by limiting or allowing its expansion.
How does the cell wall affect antibiotics?
This helps to destroy the protective cell wall and stops the bacteria from growing.
How does the semi-permeable membrane help cells communicate?
Additionally, the semi-permeable membrane helps communication among cells by allowing signaling molecules to pass through the pores.
What is the cell wall?
The cell wall is an additional layer of protection on top of the cell membrane. You can find cell walls in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and they are most common in plants, algae, fungi and bacteria.
What is the cell wall?
A cell wall is a rigid, semi-permeable protective layer in some cell types. This outer covering is positioned next to the cell membrane (plasma membrane) in most plant cells, fungi, bacteria, algae, and some archaea. Animal cells however, do not have a cell wall. The cell wall has many important functions in a cell including protection, structure, ...
What are the layers of the plant cell wall?
From the outermost layer of the cell wall, these layers are identified as the middle lamella, primary cell wall, and secondary cell wall. While all plant cells have a middle lamella and primary cell wall, not all have a secondary cell wall.
How do pectins help cells?
Pectins aid in cell adhesion by helping the cell walls of adjacent cells to bind to one another. Primary cell wall: This layer is formed between the middle lamella and plasma membrane in growing plant cells.
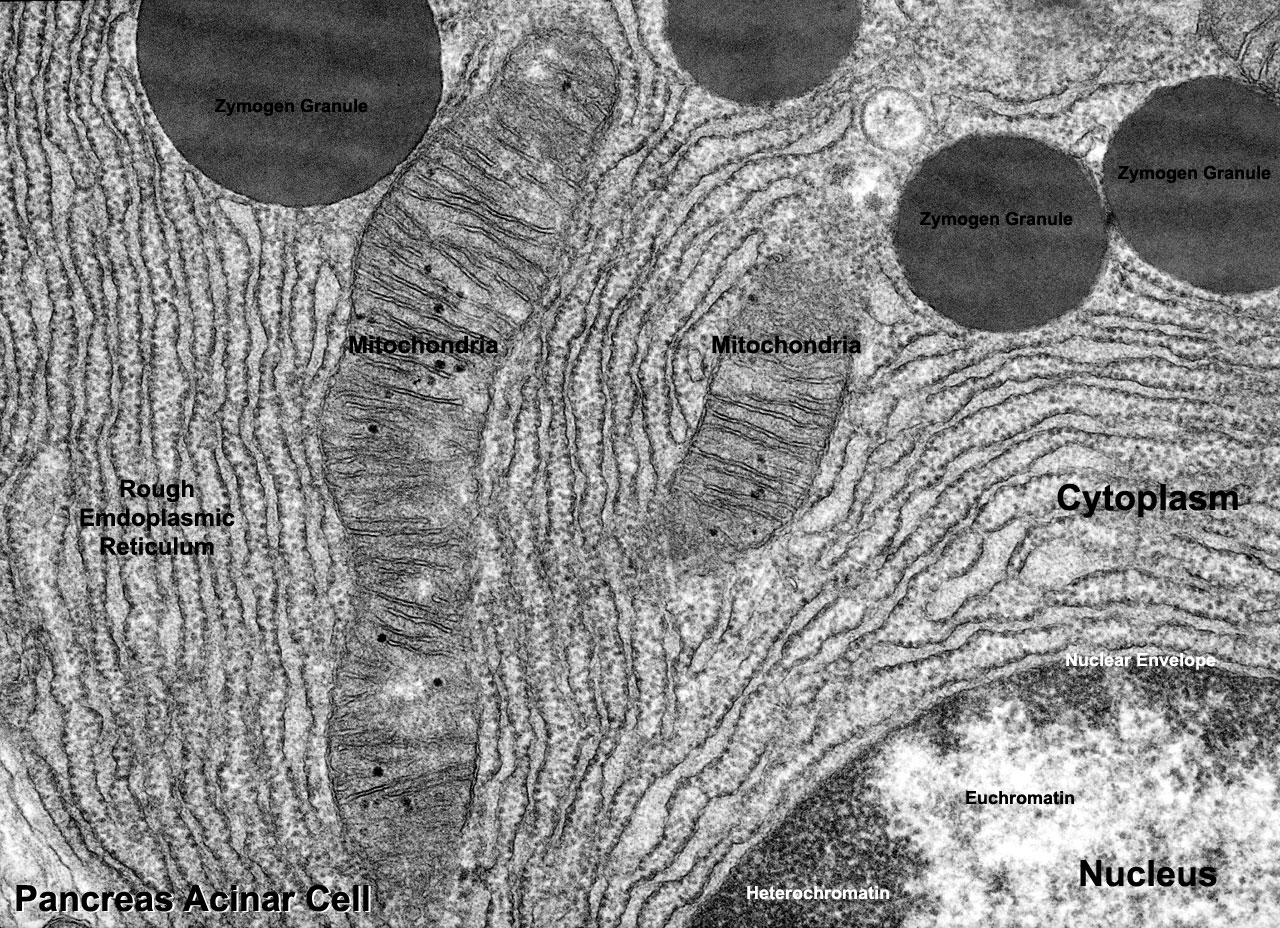
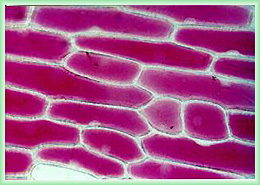
What is the cell wall in a micrograph?
This micrograph image shows a plant cell and its internal organelles. The cell wall appears as the thin layer between the cells and the nucleus is the prominent , round organelle with the smaller red nucleolus.
What is the force exerted against the cell wall as the contents of the cell push the plasma membrane against the cell?
It also controls the direction of cell growth. Withstand turgor pressure: Turgor pressure is the force exerted against the cell wall as the contents of the cell push the plasma membrane against the cell wall. This pressure helps a plant to remain rigid and erect, but can also cause a cell to rupture.
How do plants communicate?
Communication: Cells communicate with one another via plasmodesmata (pores or channels between plant cell walls that allow molecules and communication signals to pass between individual plant cells).
What are the components of a cell wall?
Cell wall composition varies depending on the organism. In plants, the cell wall is composed mainly of strong fibers of the carbohydrate polymer cellulose. Cellulose is the major component of cotton fiber and wood, and it is used in paper production. Bacterial cell walls are composed of a sugar and amino acid polymer called peptidoglycan. The main components of fungal cell walls are chitin, glucans, and proteins.
