:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/ganglion-ciliare-3/BYySjgjRVXYjx901ThMA_Ganglio_ciliare_01.png)
What are the functions of the ciliary body?
The Anatomy of the Ciliary Body
- Anatomy. The ciliary body is part of the uvea of the eye, which also includes the iris and choroid. ...
- Function. One function of the ciliary body is to control the lens of the eye. ...
- Associated Conditions. The ciliary body can be affected by conditions including traumatic injury or melanoma. ...
- Tests. ...
What is the function of the ciliary body and muscle?
The ciliary muscle is in charge of changing the shape of the lens, while the ciliary processes participate in the production of the fluid in the eye also known as the aqueous humor. The ciliary body is attached to the lens by the collection of tiny fibrous cords known as the zonular fibers.
What are the cilia and what do they do?
Cilia are small, slender, hair-like structures present on the surface of all mammalian cells. They are primitive in nature and could be single or many. Cilia play a major role in locomotion. They are also involved in mechanoreception. The organisms that possess cilia are known as ciliates. They use their cilia for feeding and movement.
What connects the ciliary body to the lens?
The ciliary body is attached to the lens by the collection of tiny fibrous cords known as the zonular fibers. This attachment is crucial in changing the eye focus by changing the shape of the lens, a process known as accommodation. In order to provide these functions, ...
What is the function of the ciliary body quizlet?
One of the essential roles of the ciliary body is also the production of the aqueous humor, which is responsible for providing most of the nutrients for the lens and the cornea and involved in waste management of these areas. adjusts the shape of the lenses in order to focus the eyes.
What are two functions of ciliary muscles?
Ciliary muscles are involved in the accommodation reflex. Ciliary muscles help in changing shape of the lens to focus on the near object. It also controls the flow of aqueous humour into Schlemm's canal.
How does ciliary muscle focus our eye?
Ciliary muscles are attached to the lens in the eyes by zonular fibres. They can change the shape of the lens by contracting and help us focus the near objects. Contraction in ciliary muscles makes the lens more spherical and increases the focussing power.
Why are ciliary muscles important?
These muscles are important for moving the eyes as they place an image on the fovea to get maximum resolution. The ciliary muscle also contracts and relaxes its longitudinal fibers to increase and decrease the size of the pore in the trabecular meshwork.
What are the ciliary muscles?
Ciliary muscle (Musculus ciliaris) The intrinsic muscles of the eye are muscles that control the movements of the lens and pupil and thus participate in the accommodation of vision. There are three smooth muscles that comprise this group; ciliary, dilatator pupillae and sphincter pupillae muscles.
What type of muscles are ciliary muscles?
The ciliary muscle is composed of smooth muscle fibers oriented in longitudinal, radial, and circular directions. Interweaving occurs between fiber bundles and from layer to layer, such that various amounts of connective tissue are found among the muscle bundles.
How do ciliary muscles focus image of an object?
The ciliary muscles can contract and increase the curvature of the lens so that the lens thickens. The increased curvature of the lens allows the eye to focus on a close object. When the person then has to look at a faraway object, the muscles relax and the focus of the lens changes to an object further away.
What is the ciliary body?
The ciliary body is a disk-shaped tissue entirely hidden behind the iris. The inner part is the ciliary muscle, made of smooth muscle. 2 Smooth muscles contract and relax automatically, so you don’t have conscious control over them. Instead, the ciliary body functions in response to natural reflexes based on environmental stimuli.
What is the process of ciliary body?
Without it, it would be nearly impossible to read or see what’s right in front of you. 1. The ciliary body also produces a clear fluid called aqueous humor, which flows between the lens and cornea, providing nutrients and contributing to the fullness and shape of the eye.
What are the capillaries in the eye?
Groups of small blood vessels and capillaries toward the eye’s surface make up another section of the ciliary body. 1 The capillaries are responsible for exchanging fluids and other materials between the tissue and the blood cells.
Where is the ciliary body located?
The ciliary body is located in the middle of the eye, meaning it can be found on the eye’s inner wall, behind the iris. The ciliary body also forms a ring around the lens, helping the lens hold shape and adjust focus. Behind the ciliary body is the vitreous humor, a fluid made up of mostly water, which helps the eye retain its fullness. 3.
Which muscle is responsible for the round shape of the eye?
The ciliary body’s smooth muscles contract and relax to focus on near or far away objects. Muscle contractions are partly responsible for the round shape of the eye’s lenses since fine ligaments directly attach the lens to the ciliary body.
What is the secretion of aqueous humor?
The ciliary body’s capillaries secrete aqueous humor, a liquid in the front of the eye that’s responsible for keeping the eye healthy and inflated. 5 Aqueous humor also controls the eye’s pressure and supplies vital nutrients to the lens and cornea. 6.
What is the ciliary body?
Structurally, the ciliary body is a ring of tissue that surrounds the iris and connects it to the choroid. The ciliary body can’t be seen when you look at the eye, because it’s located behind the iris and sclera, which is the white part of the eye.
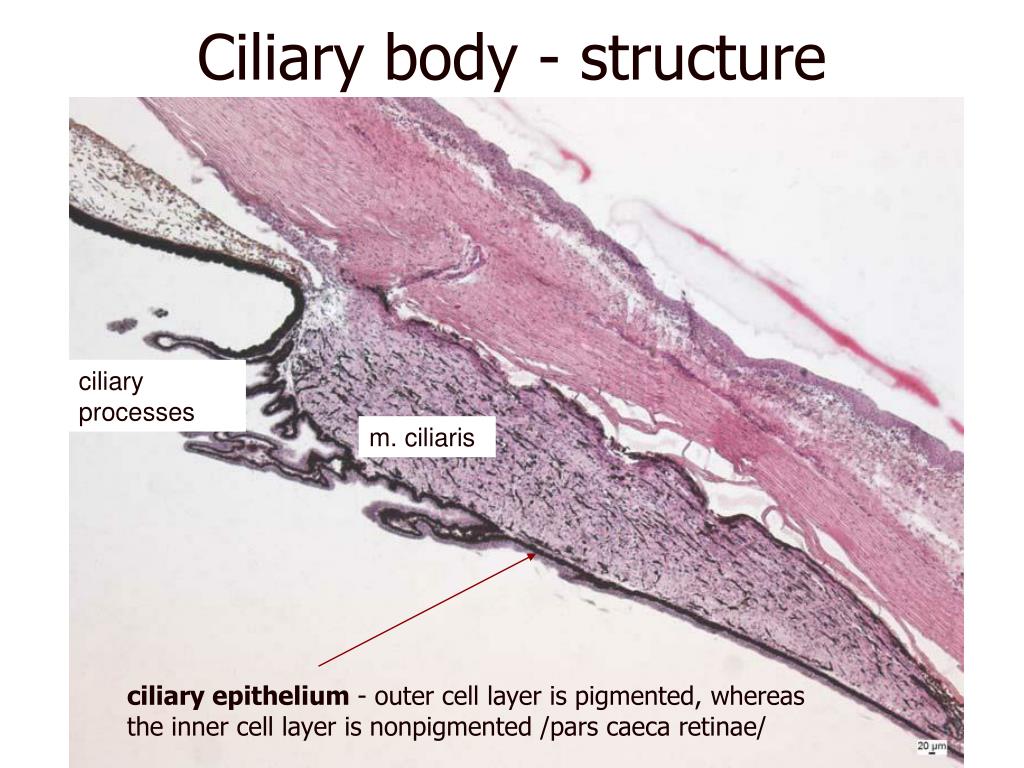
What is the structure of the ciliary body?
Structures contained within the ciliary body include: The ciliary muscle, which influences the shape of the lens inside the eye. Contraction of the ciliary muscle makes the lens become more convex, enabling the eye to focus on near objects. The ciliary muscle is connected to the lens by a series of very thin, radially-arranged fibers called ...
How does glaucoma affect the ciliary body?
How does glaucoma medication affect the ciliary body? Typically, the initial treatment used for glaucoma is medicated eye drops, which are designed to help regulate eye pressure by reducing the production of aqueous fluid by the ciliary body and/or increasing its drainage from the eye .
What is the muscle that holds the lens in place?
The ciliary muscle is connected to the lens by a series of very thin, radially-arranged fibers called the ciliary zonules (also called the zonular fibers or zonules of Zinn ), which hold the lens in place within the eye. The ciliary processes, which are about 70 ridges in the ciliary body that contain cells involved in the production ...
How many ridges are there in the ciliary system?
The ciliary processes, which are about 70 ridges in the ciliary body that contain cells involved in the production of the aqueous humor in the eye that controls eye pressure. SEE MORE: Eye anatomy.
What is accommodation in the eye?
Accommodation refers to the eye’s ability to automatically increase its focusing power to enable the eye to see near objects clearly. This action depends on the ciliary muscle. The ciliary body holds the lens of the eye in place behind the pupil using tiny fibers called ciliary zonules or zonules of Zinn. Aqueous fluid production occurs in the ...
What are the two parts of the eye?
The other two parts are the iris (the colored part of the eye), and the choroid (the part of the eye that nourishes the retin a). These two segments are connected together by the ciliary body.
What are the functions of the ciliary body?
6. The ciliary body is a circular band of muscle that is connected and sits immediately behind the iris. It does two things: 1. Controls lens shape by pulling or relaxing on the lens zonules. 2.
What is the function of the lens zonules?
1. Controls lens shape by pulling or relaxing on the lens zonules. 2. Produces aqueous humor which fills the posterior and anterior chambers and provides nutrition for avascular tissues in the eye such as the cornea.
What is the ciliary body?
The ciliary body is a ring-shaped thickened tissue which is present in the posterior chamber of the vitreous body and anterior part of human eye. The ciliary body receives the intervention through ciliary nerves. The blood is supplied through long posterior ciliary aqueous humor is secreted by th folds on the inner ciliary epithelium called ciliary processes. The aqueous humor then moves through the pupils into the anterior chamber of the eye. The Connective tissue used to attach the ciliary body with the lens is zonular fibers. It is also called as fibers of Zinn. The ciliary body contains the ciliary muscle. The ciliary muscle changes the shape of lens with respect to the focus of light in the light screen called retina. It is done by the relaxation of the ciliary muscle which makes changes in tension and changes the shape. The inner layer of the ciliary body is transparent and is covered by the vitreous body which is the continuation of the neural tissue of the retina. The outer layer of the ciliary body is retinal pigmented while the inner layer is unpigmented. The inner layer takes pigment which touches the iris. The ciliary nerves have ciliary ganglion.
What organs provide vision?
Eyes are the major visual organs which provides vision. Eye converts the light energy into electrochemical nerve impulse and transmits to brain through the optical nerve. The ciliary body only controls the accommodation of lens, production of aqueous humor. The ciliary body has a special smooth muscle called ciliary muscle. The ciliary body is a part of uvea which is the layer of tissue that delivers nutrients and oxygen to the eye tissues. The eye has 3 coats. The middle or vascular coat contains the ciliary body. When the ciliary body contract, it pulls itself forward and moves the axis of the eye.
What is the main action of the ciliary muscle?
The main action of ciliary muscle is changing the shape of the lens which occurs during the accommodation reflex . In addition, when contracting, the longitudinal fibers of ciliary muscle widen the iridocorneal space and canal of Schlemm which facilitates the draining of eye fluid.
What is the ciliary muscle?
The ciliary muscle occupies the biggest portion of the ciliary body, which lies between the anterior border of the choroid and iris. It is composed of smooth muscle fibers oriented in three different directions; longitudinal, radial and circular.
What muscle is responsible for the rounding of the eye?
The action of ciliary muscle is instructed by the parasympathetic fibers originating from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus in the midbrain. The contraction of this muscle loosens the zonular fibers allowing the lens to relax. When the lens relaxes, its degree of curvature increases, making it rounder.
How does the ciliary muscle change?
The state of the ciliary muscle changes depending if we observe distant or close objects. When looking at the distant object, the ciliary muscle is relaxed, the zonular fibers are tightened and the lens is flattened. In this state the refractive power of the lens is enough to form a clear image of the focused object on the retina. However, in order to focus on a close object, the inner structures of the eye must adapt, which is possible through the process of accommodation.
What are the intrinsic muscles of the eye?
The intrinsic muscles of the eye are muscles that control the movements of the lens and pupil and thus participate in the accommodation of vision. There are three smooth muscles that comprise this group; ciliary, dilatator pupillae and sphincter pupillae muscles. The ciliary muscle occupies the biggest portion of the ciliary body, ...
How many layers are there in the ciliary muscle?
The layers of ciliary muscle are described differently by several authors in the literature, but the most used classification divides this muscle into three separate layers;
Which muscle is responsible for near vision?
The contraction of the ciliary muscle loosens the zonular fibers increasing the convexity of the lens, which induces accommodation for near vision.
Why do we use scleral spur meshwork?
scleral spur and trabecular meshwork in order to enhance the outflow of aqueous through the tM and lower IOP.
What is the largest smooth muscle in the eye?
ciliary muscle. single smooth muscle mass; largest smooth muscle in the eye; densely innervated (autonomically-parasympathetic); similar to smooth muscle found in the parts of the body with diffuse innervation; gap and desmosomal junctions to aid the muscle in contracting in a uniform manner; contains fibers that are oriented in different ...
Do ciliary glands carry blood?
they are fenestrated, dilated, and carry tremendous amounts of blood (particularly in the ciliary processes).
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/major-arterial-circle-of-iris/ks7HPg8jceiAamXuyQ5Pw_Circulus_arteriosus_major_iridis_02.png)