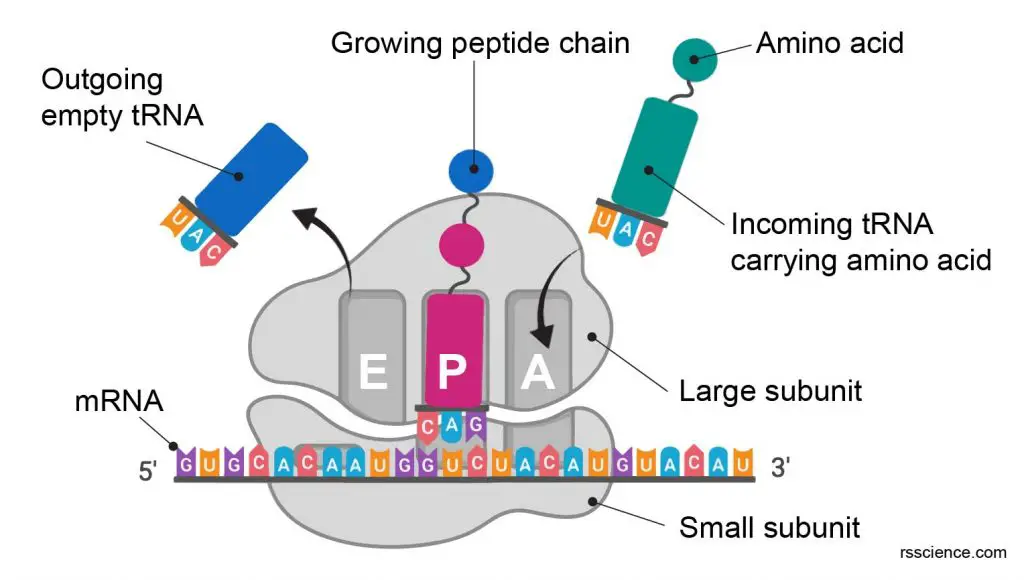
The P-site (for peptidyl) is the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. The other two sites are the A-site (aminoacyl), which is the first binding site in the ribosome, and the E-site (exit), the third. During protein translation, the P-site holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain.
What is the role of the P site in translation?
During protein translation, the P-site holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain Click to see full answer. Also know, what is the role of the A site in translation?
What is the function of E P and a site?
And the E site which is the exit site of the now uncharged tRNA after it gives its amino acid to the growing peptide chain. Additionally, what is the function of the E P and a site during translation?
What is the enzyme’s activity in translation?
The enzyme’s activity is to form peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids using tRNAs during translation. The enzyme’s activity uses two substrates of which one has the growing peptide chain and the other bears the amino acid that is added to the chain.
What is the site of translation in the cell?
The site of translation is ribosomes in the cell cytoplasm. Which one of the following does not play a role in translation? -tRNA -DNA -Anticodon -Amino acids -Ribosomes DNA Which of the following does not occur during RNA processing?

What is the role of the A-site in translation?
The role of the A-site (aminoacyl) in translation is that it will function as the entry site for a charged tRNA (a tRNA molecule that is bound to one amino acid). A peptide bond will be formed between the amino acid on the P site and the amino acid on the A site.
What is the function of A-site in ribosome?
The A-site (A for aminoacyl) of a ribosome is a binding site for charged t-RNA molecules during protein synthesis. One of three such binding sites, the A-site is the first location the t-RNA binds during the protein synthesis process, the other two sites being P-site (peptidyl) and E-site (exit).
What is the difference between P site and A-site of a ribosome?
The ribosome has mainly two important sites at which the synthesis of peptide chains takes place. P-site or the peptidyl site is the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. A-site or the aminoacyl site is the first binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. Initiation of the peptide synthesis starts at the P site.
What does EP and A-site stand for?
EP stands for 'Extended Play,' meaning that an EP is longer than a single but shorter than an album. They typically feature between 2-5 songs and are under 30 minutes in length.
What occurs in the E P and A sites of the ribosome?
The A site accepts an incoming tRNA bound to an amino acid. The P site holds a tRNA that carries a growing polypeptide (the first amino acid added is methionine (Met)). The E site is where a tRNA goes after it is empty, meaning that it has transferred its polypeptide to another tRNA (which now occupies the P site).
What is the function of the AP and E sites on the ribosome?
The P-site (for peptidyl) is the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. The other two sites are the A-site (aminoacyl), which is the first binding site in the ribosome, and the E-site (exit), the third. During protein translation, the P-site holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain.
Does tRNA move from A-site to P site?
tRNAs move through these sites (from A to P to E) as they deliver amino acids during translation. The ribosome is composed of a small and large subunit. The small subunit binds to an mRNA transcript and both subunits come together to provide three locations for tRNAs to bind (the A site, P site, and E site).
Which translation factor binds directly to the ribosomal P site?
Initiator tRNAInteractions with Initiator tRNA The initiator tRNA binds directly to the 30S subunit P site, which is mainly composed of 16S rRNA (Noller et al., 2005).
What does A-site stand for?
Society for Information Technology and Teacher Education.
What are the E P and A sites of the large subunit of the ribosome?
Elongation. Each ribosomal subunit has three binding sites for tRNA: designated the A (aminoacyl) site, which accepts the incoming aminoacylated tRNA; P (peptidyl) site, which holds the tRNA with the nascent peptide chain; and E (exit) site, which holds the deacylated tRNA before it leaves the ribosome.
Which step occurs in the A-site of the ribosome during translation quizlet?
Which step occurs in the A site of the ribosome during translation? - The tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide moves to this site as the ribosome slides to the next codon.
What is the role of the ribosomal P site in translation?
The ribosomal P-site plays a vital role in all phases of translation. Initiation involves recognition of the start codon (AUG) by initiator tRNA in the P-site, elongation involves passage of many elongator tRNAs through the P site, termination involves hydrolysis of the mature polypeptide from tRNA bound to the P-site, ...
What is the P site?
P-site. The P-site (for peptidyl) is the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. The other two sites are the A-site (aminoacyl), which is the first binding site in the ribosome, and the E-site (exit), the third. During protein translation, the P-site holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain.
What happens to the tRNA in the P-site?
During protein translation, the P-site holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain. When a stop codon is reached, the peptidyl-tRNA bond of the tRNA located in the P-site is cleaved releasing the newly synthesized protein. During the translocation step of the elongation phase, the mRNA is advanced by one codon, ...
Which antibiotics prevent peptide bond formation?
Macrolide, lincosamide and streptogramin classes of antibiotics prevent peptide bond formation and/or the translocation of tRNA from the A-site to the P-site on the ribosome that eventually leads to interference with the elongation step and thus the inhibition of protein translation.
Where is peptidyl tRNA bound?
Prior to peptide bond formation, an aminoacyl-tRNA is bound in the A-site, a peptidyl-tRNA is bound in the P-site, and a deacylated tRNA (ready to exit from the ribosome) is bound to the E-site. Translation moves the tRNA from the A-site through the P- and E-sites, with the exception of the initiator tRNA, which binds directly to the P-site.
Which ends of tRNA are in different sites?
In these hybrid states of binding, acceptor and anti-codon ends of tRNA are in different sites (A, P and E). Using chemical probing methods, a set of phylogenetically-conserved bases in ribosomal RNA where the tRNA binds has been examined, and is suggested to be directly involved in the binding of tRNA to the prokaryotic ribosome.
Which site binds to the incoming aminoacyl-tRNA?
The A-site binds to incoming aminoacyl-tRNA which has the anti-codon for the corresponding codon in the mRNA presented in the A-site . After peptide formation between the C-terminal carbonyl group of the growing polypeptide chain (attached to a P-site bound tRNA) and the amino group of the aminoacyl-tRNA (A-site bound), ...
What happens to tRNA at P site?
The tRNA at P site now has lost the methionine. As ribosome moves along the mRNA, tRNA at P site would go to E site and leaves (Exit).
Why does the ribosome slow down during translation?
It can be a lot slower sometimes since the ribosome have to slow down to allow time for certain proteins to fold into place during translation in order for them to achieve the right final conformation. ( EDIT: when I first read this question, I read it as if the word 'protein' was part of it.
What are the three tRNA binding sites?
The three tRNA-binding sites in ribosomes typically refer to: Aminoacyl-tRNA binding, or A-site. Peptidyl-tRNA binding, or P-site. tRNA exit site, or E-site. Structure of the ribosome: The three tRNAs bound to the ribosome are indicated in magenta (A-site), green (P-site) and yellow (E-site). mRNA is indicated in black.
How many sites does a ribosome have?
Ribosome has two subunits (small and large) three sites (A,P, E) for tRNA and one binding site for the mRNA. An initiator aminoacyl-tRNA, carrying amino acid methionine, binds with P site region of the small subunit,an mRNA binds from 5′ and the complex moves along the mRNA till it finds AUG codon.
Why do ribosomes need to be translated on the same mRNA?
1. It requires less mRNA to be transcribed in order to make the quantity of protein needed. You rarely ever need only one protein molecule to be made.
What is the function of ribosomes?
A ribosome is a complex cellular mechanism used to translate genetic code into chains of amino acids. Long chains of amino acids fold and function as proteins in cells. Ribosomes are a cell structure that makes protein. Protein is needed for many cell functions such as repairing damage or directing chemical processes.
Where are ribosomes located?
Ribosomes can be found floating within the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. The location of the ribosomes in a cell determines what kind of protein it makes. If the ribosomes are floating freely throughout the cell, it will make proteins that will be utilized within the cell itself.
Where does translation take place?
It is the second part of the central dogma in genetics. It takes place in the ribosomes found in the cytosol or those attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The functions of the ribosome are ...
What are the two factors that influence the translation process?
The translation process is aided by two major factors: A translator – this is the molecule that conducts the translation; substrate – this is where the mRNA is translated into a new protein (translator desk). The translation process is guided by machinery composed of:
What are the three stop codons in translation?
Termination of the translation process is triggered by an encounter of any of the three stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA). These triplet stop codons, however, are not recognized by the tRNA but by protein factors known as the release factors, (RF1 and RF2) found in the ribosomes.
What happens to the amino acid chain when the ribosomes are translated?
When the elongation process reaches the stop codon, the amino acid chain folds spontaneously to form a protein. The ribosomes then split into two subunits, but later rejoin before another mRNA is translated.
What protein splits the GTP that is bound to IF2?
A ribosomal protein splits the GTP that is bound to IF2 thus helping in driving the assembly of the two ribosomal subunits. The IF3 and IF2 are released. Figure: Diagram of Steps of Translation (Protein Synthesis).
What is the starting point of ribosome translation?
The ribosomal translation is initiated when the ribosomes recognize the starting point of mRNA, where it binds a molecule of tRNA that bears a single amino acid. In prokaryotes, the initial amino acid in N-formylmethionine. during elongation, the second amino acid is linked to the first one.
What is the initiator of fMet-tRNA?
The initiator fMet-tRNA has a normal methionine anticodon therefore it inserts the N-formylmethionine. This means that methionine is the first amino acid that is added and appears in the chain. Generally, there are three steps in the initiation process of translation;