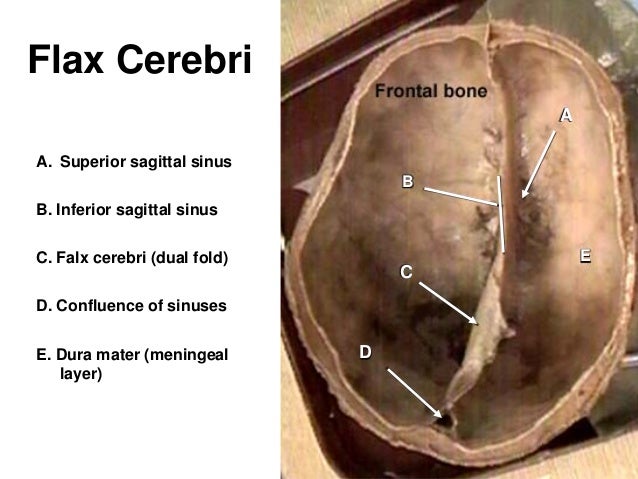
What is the falx cerebri function?
The falx cerebri separates the cerebral hemispheres and provides channels, known as dural sinuses, for blood and cerebral spinal fluid to drain.
What is the function of the tentorium cerebelli quizlet?
The falx cerebelli separates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum. The tentorium cerebelli separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum.
What does the falx cerebelli?
The falx cerebelli is a small infolding of the dura in the sagittal plane over the floor of the posterior cranial fossa. It partially separates the two cerebellar hemispheres 1.
What does the tentorium cerebelli cover?
The tentorium cerebelli (Fig. 8.32) is a horizontal projection of the meningeal dura mater that covers and separates the cerebellum in the posterior cranial fossa from the posterior parts of the cerebral hemispheres.
What is the FALX Cerebelli quizlet?
falx cerebelli. separates the two lobe of the cerebellum. tentorium cerebelli. separates the occipital lobe from the cerebellum, forms a "tent" over the cerebellum.
Where is the tentorium cerebelli located quizlet?
located at the back of the brain, immediately inferior to the occipital & temporal lobes, & within the posterior cranial fossa. It is separated from these lobes by the tentorium cerebelli, a tough layer of dura mater. It lies at the same level of & posterior to the pons, from which it is separated by the 4th ventricle.
What is the difference between cerebelli and cerebri?
The significant difference between cerebellum and cerebrum is their size. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, and it contributes nearly 80% of the total weight of the human brain. The cerebellum makes up the remaining part of the brain. The cerebrum controls voluntary movement, intelligence and memory.
What is the tentorium cerebelli made of?
dura materThe tentorium cerebelli (Latin for "tent of the cerebellum") is an invagination of the meningeal layer of the dura mater that separates the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum and brainstem.
What makes up the falx cerebelli?
Falx cerebri is a sickle-shaped vertical fold of dura that begins anteriorly at the crista galli and winds around the corpus callosum between the two cerebral hemispheres to reach the falcotentorial junction on the superior aspect of the tentorium cerebelli (Fig. 2.1A). It may be absent or very diminutive.
What is the tentorium of the brain?
The tentorium cerebelli, the second-largest dural reflection, is a crescent-shaped dura fold that extends over the posterior cranial fossa, separating the occipital and temporal cerebral hemisphere from the cerebellum and infratentorial brainstem [1,6].
Where is the FALX Cerebelli located?
occipital boneThe falx cerebelli is located below the tentorium cerebelli on the middle of the occipital bone. This small dural infolding extends into the space between the cerebellar hemispheres, attaching to the occipital crest of the skull and the posterior portion of the tentorium.
Where is the falx located in the brain?
The falx cerebri is situated in the longitudinal fissure, in between the cerebral hemispheres. The corpus callosum lies immediately inferior to the lower (free) margin of falx cerebri.
What is the tentorium cerebelli made of?
dura materThe tentorium cerebelli (Latin for "tent of the cerebellum") is an invagination of the meningeal layer of the dura mater that separates the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum and brainstem.
What is the location of the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli?
the brainThe falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli are thin dural structures found between parts of the brain. The cerebrum can be divided into left and right hemispheres. The falx cerebri (or falx) is a scythe-shaped band of dura matter that separates a part of the cerebral hemispheres.
What separates right and left hemispheres of brain?
A fissure or groove that separates the two hemispheres is called the great longitudinal fissure. The two sides of the brain are joined at the bottom by the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum connects the two halves of the brain and delivers messages from one half of the brain to the other.
What structure connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres?
the corpus callosumThe two hemispheres are connected by a thick band of nerve fibres called the corpus callosum. The brain halves are able to communicate with each other via this 'bridge'.
Why do primates have tentorium cerebelli?
As higher primates evolved from quadrupedal to bipedal locomotion with erect posture, the tentorium cerebelli came into play to support the extra weight of the brain that shifted from the anterior aspect, to the superior aspect of the cervical spine . Thereby, the tentorium cerebelli adds strength to the axial midline and dispels the burden of weight from supratentorial structures on the infratentorial structures .
Which part of the cranial fossa is attached to the tentorium cerebelli?
The tentorium cerebelli is attached almost along the entire circumference of the posterior cranial fossa with its outer (posterior and lateral) margins, which are fixed and convex. The inner (anterior) margin is free and concave, and forms a U-shaped hiatus.
What is the term for the downward displacement of the uncus of the temporal lobe?
An uncal herniation refers to the downward displacement of the uncus of the temporal lobe. It is caused by a unilateral mass effect from within the cerebral hemispheres, that pushes the uncus downwards and medially across the tentorial notch. The herniated uncus can compress the brainstem, oculomotor nerve (CN III) and posterior cerebral arteries in the ambient cistern .
What is the hiatus of the free anterior margin?
The free anterior margin contains a large U-shaped hiatus called the tentorial notch, which provides passage to the midbrain and the superior aspect of the cerebellar vermis. In addition, the splenium of the corpus callosum occupies a small part of the tentorial notch. The rim of the tentorial notch is attached to the apex of the petrous temporal bone and extends anteriorly as the anterior petroclinoidal ligament to attach to the anterior clinoid process.
What is the term for the downward displacement of the diencephalon and midbrain?
A central herniation refers to the downward displacement of the diencephalon and midbrain. In contrast to uncal herniation, central herniation is caused by a bilateral mass effect or diffuse brain edema, that pushes the diencephalon and midbrain centrally through the tentorial notch.
What is the dura mater?
The dura mater is a strong, double-layered membrane, composed of the periosteal layer, which adheres to the periosteum of the neurocranium , and the meningeal layer, which surrounds the brain and spinal cord. In some regions and fissures of the brain, the meningeal layer of dura mater projects inwards to form four dural partitions: the falx cerebri, falx cerebelli, tentorium cerebelli, and sellar diaphragm.
Where is the tentorium evaginated?
Near the apex of the petrous temporal bone, the lower layer of the tentorium is evaginated anterolaterally under the superior petrosal sinus to form a dural recess, the Meckel’s cave. Meckel's cave houses the posterior root of the trigeminal nerve and the trigeminal ganglion.