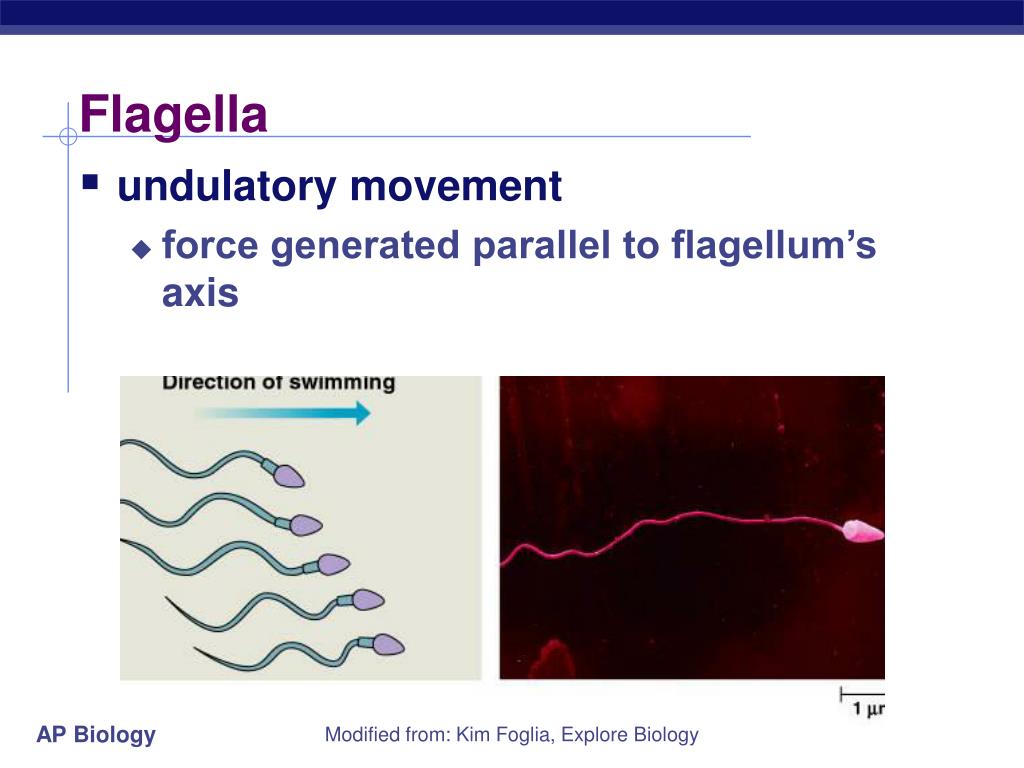
What is the function of the nucleus and the flagellum?
the nucleus is where DNA is stored and the flagellum is another major part commonly linked to the sperm cell. How does a sperm cell feature help carry out its function? How does the structure of the sperm cell help it to do its function? The flagellum moves the cell rapidly. Flagellum are made up of motor proteins. The flagellum of a sperm cell?
What is the function of flagella in a cell?
They are typically used to propel a cell through liquid (i.e. bacteria and sperm). However, flagella have many other specialized functions. Some eukaryotic cells use flagellum to increase reproduction rates. Other eukaryotic and bacterial flagella are used to sense changes in the environment,...
What is the function of the sheath of the sperm flagella?
Mammalian sperm flagella also possess a mitochondrial and a fibrous sheath that encircle most of the axoneme. These sheaths and the ODFs add mechanical rigidity to the flagellum creating the functional effect of increasing bend wavelength, which requires the entrainment of more dynein motors in the production of a single wave.
Do all sperm have a flagellum?
Without exception, sperm of all mammalian species use a flagellum for swimming. The mammalian sperm has a centrally located 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubule doublets and hundreds of accessory proteins that together constitute an axoneme.
What is the flagellum in sperm for quizlet?
The tail of a sperm cell is a flagellum, which provides motility for the sperm.
Does sperm cell need flagellum?
The sperm flagellum is essential for male fertility.
How does the flagellum in sperms function for locomotion?
The force for flagellar movement is exerted by the sliding of outer-doublet microtubules driven by the molecular motors, the dyneins. Dynein activity is regulated by the radial spoke/central pair apparatus through protein phosphorylation, resulting in flagellar bend propagation.
Where is the flagellum on a sperm?
In mammalian sperm flagella, ODFs and FS surround the axonemes. ODFs consist of nine fibers encompassing the axoneme in the midpiece, whereas FS is a structure lining the plasma membrane and surrounding the axoneme and ODFs (see Fig. 2).
Which part is the flagellum in sperm?
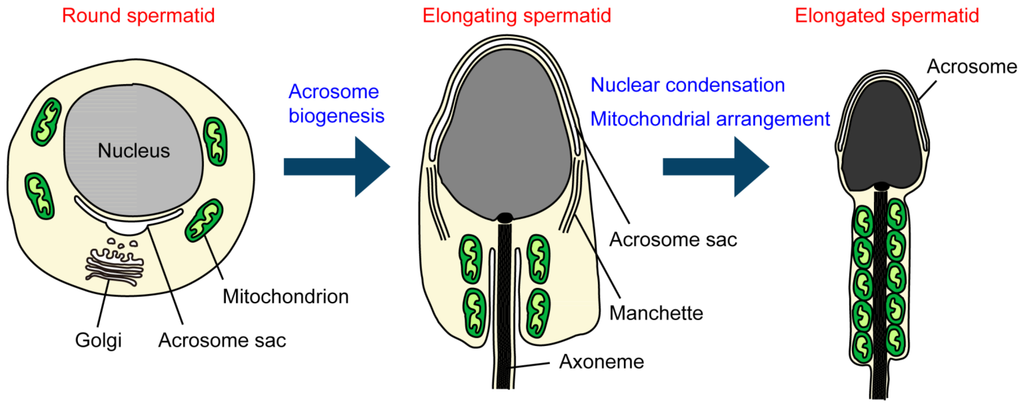
Motile cilia and flagella (sperm tail) contain a 9 + 2 microtubule structure. During steps 9–14 in the mouse, a transient microtubular platform, the manchette, surrounds the distal part of the sperm head participating in shaping the head and delivering the proteins to the developing tail.
How is a flagella helpful to bacteria and sperm cells?
Flagella are filamentous protein structures found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes, though they are most commonly found in bacteria. They are typically used to propel a cell through liquid (i.e. bacteria and sperm).
What allows a sperm cell to move?
The tip of the sperm head is the portion called the acrosome, which enables the sperm to penetrate the egg. The midpiece contains the mitochondria which supplies the energy the tail needs to move. The tail moves with whip-like movements back and forth to propel the sperm towards the egg.
Do all sperm have flagella?
sperm, also called spermatozoon, plural spermatozoa, male reproductive cell, produced by most animals. With the exception of nematode worms, decapods (e.g., crayfish), diplopods (e.g., millipedes), and mites, sperm are flagellated; that is, they have a whiplike tail.
Do sperm use flagella or cilia?
Most motile sperm cells use thin appendages named flagella or cilia for motility—in the following referred as flagella.
What will happen if flagellum in sperm cell is absent?
In particular, defects in flagella directly affect sperm motility, and often lead to failure of fertilization.
What would happen if flagellum was missing?
The absence of a flagellum leads to altered colony morphology, biofilm development and virulence in Vibrio cholerae O139 - PMC. The .
What is the flagellum?
Flagellum Definition. A flagellum is a microscopic hair-like organelle used by cells and microorganisms for movement. The word flagellum in Latin means whip, just like the whipping motion flagella (plural) often use for locomotion. Specialized flagella in some organisms are also used as sensory organelles that can detect changes in temperature ...
What is the function of flagella?
They are typically used to propel a cell through liquid (i.e. bacteria and sperm). However, flagella have many other specialized functions. Some eukaryotic cells use flagellum to increase reproduction rates. Other eukaryotic and bacterial flagella are used to sense changes in the environment, such as temperature or pH disturbances. Recent work with the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has shown that flagellum may also be used as a secretory organelle, but this discovery needs more time to be fully understood.
Why aren't peritrichous flagella polar?
Peritrichous flagella are not considered polar because they are located all over the organism. When these flagella rotate in a counterclockwise movement, they form a bundle that propels the organism in one direction. If a few of the flagellum break away and begin rotating clockwise, the organism then begins a tumbling motion. During this time, the organism cannot move in any real direction.
Why is ATP not needed in bacterial flagellum?
These flagella are made of a protein called flagellin. ATP isn’t needed because bacterial flagellum can use the energy of the proton-motive force. This means the energy is derived from ion gradients – usually hydrogen or sodium – which lie across cell membranes.
What is a monotrichous flagellum?
A. Monotrichous: A single flagellum at one end of the organism or the other.
What are the three parts of the flagella?
The flagellar structure consists of three different parts: rings embedded in the basal body, a hook near the surface of the organism to keep it in place, and the flagellar protein filaments. Every flagellum has these three things in common, regardless of organism. However, there are four distinct types of bacterial flagellum based on location:
What bacteria use windmills to propel up the urethra?
The bacteria Escherichia coli uses this windmill-like locomotion to propel up the urethra to cause urinary tract infections. Salmonella enterica, a harmful pathogen, uses several windmill-like flagella to infect human hosts. Comparison of flagellum motion in bacterial (prokaryotic) and eukaryotic organisms:
How does a bacterial flagellum grow?
A bacterial flagellum grows by filaments passing through the hollow interior until the desired length is reached.
What are Flagella?
The flagella, or flagellum for singular, are a whiplike extension used by different cells, as well as unicellular organisms, for movement. These organelles are found in the three different domains of life:
How does the flagella move?
The main flagella function is to assist the cell in movement. This function allows the cell to swim from one location to a more desirable one by rotating a rigid filament emerging from the cell. This movement is similar to the movement of a propeller in a boat. However, the direction of the flagellum differs in bacteria and archaeal flagella. Bacteria move forward using counterclockwise movement, whereas the archaea's flagellum moves in a clockwise motion to move forward. The movement of the flagella allows the differentiation between flagellum and cilia, which are other hair-like structures emerging from cells. The movement of cilia is generally a back-and-forth motion. However, the size of cilia and flagella is also another primary difference, as cilia are shorter than flagella.
What is the diameter of the archaeal flagella?
Archaeal flagella have a diameter of the filament of 10-14nm, smaller than eukaryotic flagellum. They are composed of a bundle of fibers that work as a single unit. Clockwise rotation pushes the organism forward; counterclockwise rotation of the flagella pulls the organism backward.
What is the protein that is added to the base of the filament?
Growth occurs by proteins called flagellin being added to the base of the filament.
Which organelle moves in coordination with each other?
Cilia move in coordination with each other; flagella move independently.
Where are flagella found?
As mentioned earlier, flagella are found in the three domains of life . The flagella and the flagellar arrangement can differ between all the domains, and even between species in the same domain. To add an extra variable, axial filaments add another dimension to the flagella arrangements.
What is the function of the sperm flagellum?
Functional anatomy of the mammalian sperm flagellum. The eukaryotic flagellum is the organelle responsible for the propulsion of the male gamete in most animals. Without exception, sperm of all mammalian species use a flagellum for swimming.
Which organelle is responsible for the propulsion of the male gamete in most animals?
The eukaryotic flagellum is the organelle responsible for the propulsion of the male gamete in most animals. Without exception, sperm of all mammalian species use a flagellum for swimming. The mammalian sperm has a centrally located 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubule doublets and hundreds of accessory proteins that together constitute an axoneme.
What is the role of the sheath in the central axoneme?
The sheaths also act as a retinaculum and maintain the integrity of the central axoneme when large bending torques are generated by dynein. Large torque production is crucial to the process of hyperactivation and the unique motility transitions associated with effective fertilizing capacity.
Function of flagella in prokaryotic cell
There are many gram negative and positive species of bacteria which are said to have flagella. The function of flagella in the cells of prokaryotes is to help in the movement of the bacteria and also helps them enabling the process of chemotaxis. The cells of them can either have only one flagellum or more.
Function of flagella in eukaryotic cells
The flagella in the eukaryotes are much different from that of the prokaryotes in serving its usage. The function of flagella in the eukaryotes strives to be a conserved one and serves for the use of getting transport system for proteins, to serve motility, and works also as a sensory.
Function of flagella in algae
The flagella is an organelle that helps in the cell to move back and forward On addition to this is also serves uses in organism. In an aqueous surrounding, the flagella mechanism even shows its reaction to the chemical, the mechanical, the light and the gravitational stimulus of then cell.
Function of flagella in cells
Flagella are said to be a hair like structure that is microscopic and is involved in getting to contribute in the cell movement.
Function of flagella in animal cell
The flagella are stricture to be defined by their use in the different types of cells rather than their structure.
What is the function of sperm?
The function of the sperm is to provide half of the genetic material to form a fertilized zygote or embryo upon fertilizing with an egg. It also provides centrioles to allow centrosome and microtubules to form to allow genetic material from the two to combine.
What is a Sperm Cell?
A sperm cell is a form of gamete or reproductive cell found in the male human body. The word sperm is derived from the Greek word sperma, meaning seed. It is a haploid (meaning it contains 23 chromosomes), which is half of the genetic material required to form a fertilized zygote via sexual reproduction. The other half of the genetic material comes from the egg, which the sperm must fertilize to form a fertilized zygote. While an egg cell can only contain an X chromosome, the sperm cell can have either an X or Y chromosome. Thus, the DNA carried in the sperm cell (XX for female or XY for male) determines the sex of the fertilized zygote.
What are the structures of the midpiece of sperm?
The midpiece of a sperm contains three primary structures: a typical centriole, an atypical centriole, and a central core with multiple mitochondria wrapped around it. In normal cells, mitochondria are the cell's powerhouse that stores and provides the energy needed for all cellular processes. Similarly, in a sperm cell, these multiple mitochondria in the midpiece store and provide energy for the sperm to transport itself into the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes to search for and fertilize the female egg.
How are sperm cells formed?
Sperm cells are formed via a process known as spermatogenesis. This process takes place in the seminiferous tubules in the testes of the male body. Firstly, the spermatogonia will turn into spermatocytes. These spermatocytes are the cells that undergo the primary event known as meiosis. In meiosis I and II, a parent sperm cell replicates its genetic material, allows any cross-over of genetic material to occur, and divides the genetic material into two and then further into four total daughter sperm cells known as spermatids. The daughter sperm cells or spermatids each contain 23 chromosomes each. They do not undergo any further cell division and have a minimal life span.
How is fertility measured?
Male fertility is measured by a sperm's quantity and quality. The quality of sperm is further measured by its size and the age of the male. As a man gets older, there is a higher risk of genetic mutation in the DNA inside the sperm. Also, an older male typically produces sperms with less volume and slower motility. All of these factors impact the sperm's ability to fertilize an egg and lead to pregnancy. A healthy human sperm ranges from 40 to 50 micrometers in length and can only be seen under a microscope. Conversely, a healthy human egg is 30x larger and visible to the naked eye.
What are the three features of a sperm cell?
The three anatomical features of a sperm cell are: 1) the head, 2) the mid-piece and lastly 3) the tail or the flagellum. The head contains the genetic material and acrosome. The mid piece contains the mitochondria. And, the tail is used to transport the sperm within the female reproductive tract.
What is the head of a chromosome?
The head is the portion that contains the nucleus and the vacuoles. The nucleus includes 23 densely structured chromosomes. At the tip of the head is a flat structure known as an acrosome. An acrosome is a sac that contains enzymes needed to penetrate the outer layer of an egg upon fertilization.