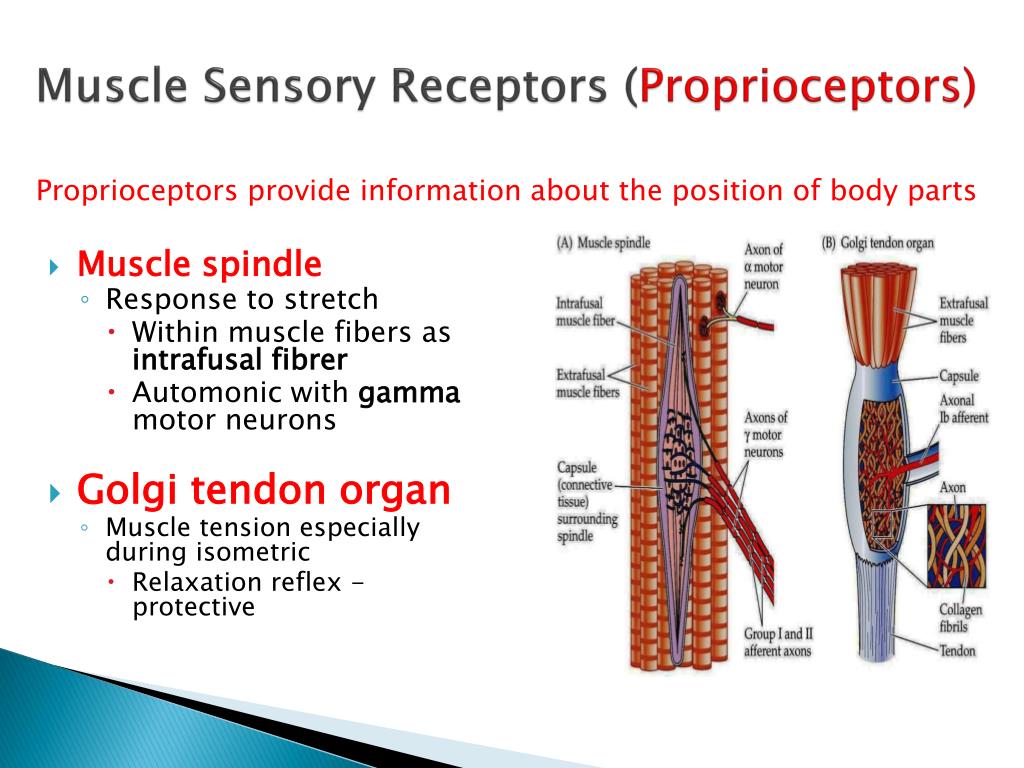
What stimulates the Golgi tendon?
Golgi tendon organs and the inverse myotatic reflex. Golgi tendon organs are located within the tendon; therefore they are in series with the muscle. They are stimulated by the stretching when extrafusal muscle fibres contract, causing muscle shortening and increased tension in the tendon.
What is the main function of a Golgi body?
Functions
- They condense the proteins synthesized in the ribosomes. ADVERTISEMENTS:
- They help in the formation of cell plate during cell division.
- They set aside some enzymes in tiny membrane hound vesicles which become lysomomes.
Which is true of Golgi tendon organs?
The golgi tendon organ is a proprioceptor, sense organ that receives information from the tendon, that senses TENSION. When you lift weights, the golgi tendon organ is the sense organ that tells you how much tension the muscle is exerting.
What is Golgi complex function?
The Golgi complex functions to: sort and package these molecules into vesicles for transport to other parts of the cell or secretion from the cell. As mentioned above, proteins that have been produced in the rough ER are placed into transition vesicles by the smooth ER.

What does the Golgi tendon regulate?
The Golgi tendon reflex assists in regulating muscle contraction force. It is associated with the Ib. Tendon organs signal muscle force through the entire physiological range, not only at high strain.
What is the function of Golgi tendon organs quizlet?
The function of the Golgi tendon organs is to prevent damage to tendons that occurs due to excessive muscle contractions. This is achieved by activating the inverse myotatic stretch reflex.
Where are Golgi tendon organs function?
The Golgi tendon organ is found in the tendon near the junction of tendon and muscle fibers. It responds to a tendon stretch, or a muscle contraction, by sending action potentials so that the muscle tension increases (Prochazka, Gillard, & Bennett, 1997).
What is the role of the Golgi tendon organ in controlling muscle contraction?
The Golgi Tendon Organ is a proprioceptive receptor that is located within the tendons found on each end of a muscle. It responds to increased muscle tension or contraction as exerted on the tendon, by inhibiting further muscle contraction.
What are the 5 functions of Golgi bodies?
Transporting, altering, and packing proteins and lipids to specific locations are the main duties of this cell organelle. Both plant and animal cells contain the Golgi apparatus, which is located in the cytoplasm of a cell.
What do Golgi tendons and muscle spindles do?
The muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organ (GTO) are both components of the nervous system which function to influence one's movement. The Golgi tendon organ and the muscle spindles function with each other reflexively to regulate the stiffness of muscles.
What is the role of the GTO?
GTOs sense muscular tension within muscles when they contract or are stretched. When the GTO is activated during contraction, it causes inhibition of the contraction (autogenic inhibition), which is an automatic reflex.
What is GTO in massage therapy?
GTO Release GTOs are nerve receptors that monitor muscle tension and if they detect excessive load or stretch, they will cause your muscle to relax so you do not tear a tendon or muscle. When applied during treatment, with firm pressure for 30 seconds, your muscles relax to reduce tone and spasm.
Is the knee jerk a Golgi tendon reflex?
0:351:532-Minute Neuroscience: Knee-jerk Reflex - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe knee-jerk reflex is considered a monosynaptic reflex.MoreThe knee-jerk reflex is considered a monosynaptic reflex.
What is Golgi tendon?
The Golgi tendon organ is a tree-like sensory ending enclosed in a spindle-like connective tissue capsule, that lies near the junction of a tendon with a muscle. In man, some 10 to 20 muscle fibres are connected to one tendon organ. A typical tendon organ in limb muscles has an ending of about 0.5 mm in length.
What would be the benefit of activating the Golgi tendon organ?
The GTO responds to increased muscle tension or contraction exerted on the tendon, by inhibiting further muscle contraction. When a muscle is stretched or pulled, this natural protective mechanism signals the central nervous system and causes the muscle to relax, protecting the muscle from damage.
What does the Golgi tendon organ do when excited?
When the Golgi tendon organ is excited for a prolonged period of time (at least 30 seconds according to National Academy of Sports Medicine), it provides an inhibitory effect to muscle spindles, which are trying to contract the muscle.
What is the function of the Golgi tendon organ chegg?
Function of Golgi tendon organ It senses the muscular tension in the muscle whenever it is contracted or stretched.
What is the function of tendons quizlet?
Tendons-connect muscle to bone (collagen only) function for stability of bone interaction. Ligaments-Connect bone to bone (collagen and elastin thus more flexible) Function is to exert mechanical advantage of muscle contraction over joints.
What is the most significant function of the Golgi apparatus quizlet?
Protein is needed for many cell functions such as repairing damage or directing chemical processes, Golgi apparatus:A major function is the modifying, sorting and packaging of proteins for secretion. It is also involved in the transport of lipids around the cell, and the creation of lysosomes.
How are golgi tendon organs activated quizlet?
The golgi tendon organs is going to be activated by the tension that is generated as the muscle contracts and the physiological effect of that sensory signal is going to be to diminish the output of the alpha motor neuron that supply the contracting muscle and thereby reduce the amount of tension that is generated.
How do GTOs and muscle spindles work together?
GTOs and muscle spindles work together through their reflexive actions to prevent injury. If you are a visual learner, feel free to refer to outside credible sources, such as YouTube videos, to get further clarification on this topic.
How does GTO work?
GTOs sense muscular tension within muscles when they contract or are stretched. When the GTO is activated during contraction, it causes inhibition of the contraction (autogenic inhibition), which is an automatic reflex. When the GTO is activated during stretching, it inhibits muscle spindle activity within the working muscle (agonist) so a deeper stretch can be achieved. GTOs are sensitive to changes in tension and rate of tension and, because they are located in the musculotendinous junctions, they are responsible for sending information to the brain as soon as they sense an overload. Static stretching is one example of how muscle tension signals a GTO response. So, when you hold a low-force stretch for more than seven seconds, the increase in muscle tension activates the GTO, which temporarily inhibits muscle spindle activity (thus reducing tension in the muscle), and allows for further stretching.
Where are the Golgi tendon organs located?
Golgi tendon organs (GTOs) are proprioceptors that are located in the tendon adjacent to the myotendinous junction. Image 1: Golgi Tendon Organ (neurotendinous spindle) from the human tendo calcaneus. The Golgi tendon organ is a tree-like sensory ending enclosed in a spindle-like connective tissue capsule, that lies near the junction ...
What is the Golgi organ?
The Golgi tendon organ is a tree-like sensory ending enclosed in a spindle-like connective tissue capsule, that lies near the junction of a tendon with a muscle. In man, some 10 to 20 muscle fibres are connected to one tendon organ. A typical tendon organ in limb muscles has an ending of about 0.5 mm in length.
What did Camillo Golgi discover?
Winner of Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine, Camillo Golgi, discovered (one of his discoveries) the Golgi Tendon Organ. The contributions of Camillo Golgi (1843–1926) to the study of the nervous system are a pillar of modern neuroscience. The Golgi impregnation first offered to microscopic studies individual neurons and glial cells in their entirety, and has therefore laid the foundation of neurohistology and neuroanatomy, opening a new era in neuroscience.
What organ is used to measure muscle tension?
When people lift weights, the golgi tendon organ is the sense organ that tells how much tension the muscle is exerting. If there is too much muscle tension the golgi tendon organ will inhibit the muscle from creating any force (via a reflex arc), thus protecting the you from injuring itself. This works in concert with the muscle spindles that monitor muscle length.
Which pathway is responsible for detecting muscle length and contraction changes?
Image 3: The dorsal column pathway is one of the neural pathways by which sensory information from the peripheral nerves is transmitted to the cerebral cortex. Conscious proprioception is transmitted in this pathway ie: Muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs which detect muscle length and contraction changes contributing to fine motor control and axial position.
Which organ is a muscle tension receptor?
Accordingly, the tendon organ is considered to be a muscle tension receptor rather than a muscle stretch receptor.
Why are GTOs important?
For this reason, GTOs, particularly those in the lower-limb extensors, are critical for sensing the forces exerted to resist imposed loads or the force of gravity acting on the body and regulating extensor activity required for maintaining vertical support and postural stability.
