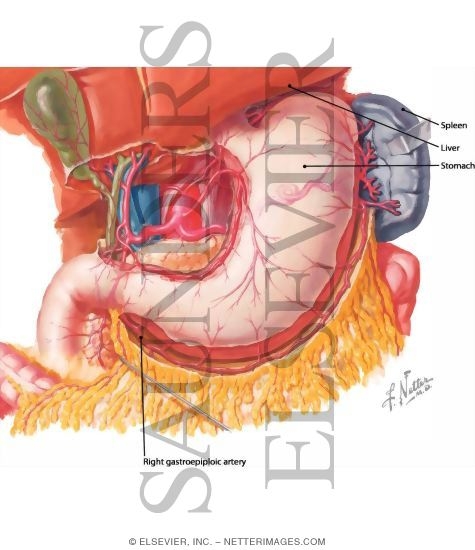
What is the function of lesser omentum
Greater omentum
The greater omentum is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum, which hangs down from the liver to the lesser curv…
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the duodenum may be the principal site for iron absorption.
What is the function of the omentum?
It can be defined as the doubled-up layer of tissue consisting of fat that supports and covers all the organs and intestines found in the lower abdominal area. The greater omentum is important for storing the different deposits of fat and the lesser omentum supports and holds the intestines and stomach.
What is the lesser omentum of the stomach?
The lesser omentum, also called the small omentum or gastrohepatic omentum, is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach (hepatogastric ligament) and the first part of the duodenum (hepatoduodenal ligament).
What are the ligaments of the lesser omentum?
The lesser omentum consists of two ligaments: medially located hepatogastric ligament, and laterally located hepatoduodenal ligament. The hepatogastric ligament connects the lesser curvature of the stomach to the visceral surface of the liver. The hepatoduodenal ligament passes from the duodenal bulb towards the visceral surface of the liver.
What is lesslesser omentum?
Lesser omentum, derived from the ventral mesentery. The peritoneum lines the walls of the abdominal cavity and covers much of the viscera. The parietal peritoneum lines the walls of the cavity and the visceral peritoneum covers the viscera. Between the parietal and visceral layers of peritoneum is a potential space (the peritoneal cavity).
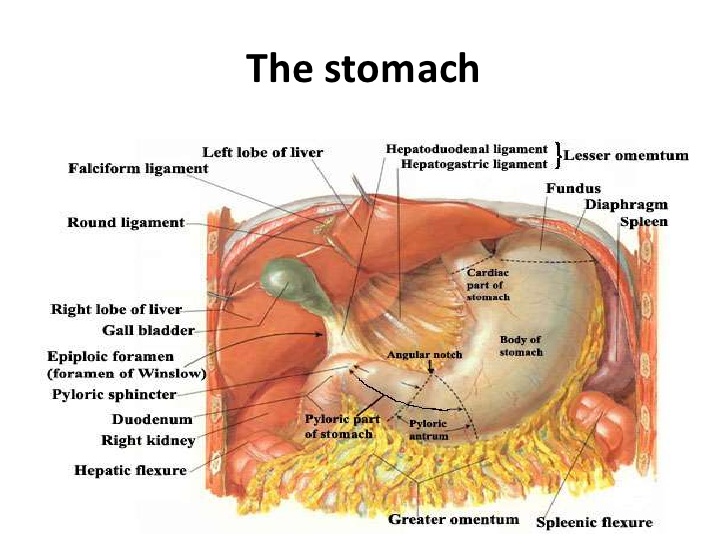
What is the function of the lesser omentum quizlet?
As discussed previously, the lesser omentum suspends the stomach and duodenum from the liver. It is a pathway for blood vessels entering the liver such as the hepatic portal vein and common hepatic artery. It also contains the common bile duct, lymph nodes and fat.
What is the main function of the omentum?
Therefore, the omentum has been recognised as having an important role in the immune defence, specifically in the peritoneal cavity. It plays this role by adhering to sites of inflammation, absorbing bacteria and other contaminants, and providing leukocytes for the local immune response [18].
What's in the lesser omentum?
The free border of the lesser omentum between the porta hepatis and the duodenum contains the hepatic artery, the portal vein, the common bile duct, lymph glands, lymph vessels, and nerves, forming the hepatic hilum. Behind this free edge is the opening into the lesser sac or foramen of Winslow.
What happens when you have your omentum removed?
An omentectomy may cause fluid retention due to blocked lymphatic blood vessels. You may have difficulty using the bathroom, both urinating and passing stool, during this period. As with any type of surgery, there's also the risk for an infection, bleeding or nerve damage.
Can you have your omentum removed?
There are two types of omentectomy. A supracolic omentectomy, or total omentectomy, removes the entire omentum. A partial omentectomy removes part of the omentum. An omentectomy is typically performed in combination with other treatments such as a hysterectomy or a salpingo-oophorectomy.
Why is omentum called the policeman?
The omentum is known as the policeman of the abdomen for its role in fighting intra-abdominal infection. Innervation: this flap is not innervated.
What is the difference between omentum and peritoneum?
Peritoneum is a serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity. Omentum is a fold of the peritoneal layer. It may be two-layered or four-layered with patches that give it a lacy appearance. The parietal peritoneum lines the pelvic and abdominal cavities.
Does the omentum show on CT scan?
On CT, the normal greater omentum appears as a band of fatty tissue with variable width. The CT appearance of omental pathology is dependent on the extent and duration of disease involvement. Early omental disease manifests as a smudged or permeated appearance of the omental fat (Fig. 3a).
Is omentum the same as belly fat?
what's an Omentum? Omentum Fat by any other name is still the same…Belly Fat, Beer Gut, Abdominal Fat, Spare Tire, Visceral Fat, Intra-Abdominal Adiposity (IAA)…it's the “sheet” of unhealthy fat located deep inside the abdomen, underneath the muscles in your stomach.
What is difference between peritoneum and omentum?
Peritoneum is a serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity. Omentum is a fold of the peritoneal layer. It may be two-layered or four-layered with patches that give it a lacy appearance. The parietal peritoneum lines the pelvic and abdominal cavities.
Why is omentum called the policeman?
In 1906, the greater omentum was described as the "abdominal policeman" by the surgeon James Rutherford Morrison. This is due to its immunological function, whereby omental tissue seems to "surveil" the abdomen for infection and cover areas of infection when found - walling it off with immunologically active tissue.
What is omentum in the body?
(oh-MEN-tum) A fold of the peritoneum (the thin tissue that lines the abdomen) that surrounds the stomach and other organs in the abdomen.
What is the lesser omentum?
The lesser omentum, also called the small omentum or gastrohepatic omentum, is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach (hepatogastric ligament) and the first part of the duodenum (hepatoduodenal ligament). The lesser omentum extends from the inferior and posterior surfaces ...
What is the free edge of the lesser omentum?
Behind this free edge is the opening into the lesser sac or foramen of Winslow.
What is the gastrohepatic ligament?
Gastrohepatic Ligament. The gastrohepatic ligament is part of the lesser omentum. It joins the gastroesophageal junction and lesser curvature of the stomach to the liver at the fissure of the ligamentum venosum superiorly and the porta hepatis inferiorly.
Which artery expands within the ventral mesentery?
Superior mesenteric artery (within dorsal mesentery) Inferior mesenteric artery (within mesocolon) The liver expands within the ventral mesentery, which later disintegrates, leaving only the falciform ligament and the lesser omentum. The primary gut elongates and herniates out into the umbilical cord.
Which ligament carries the short gastric and left gastroepiploic vessels to the stomach and sple?
The splenic artery and vein course along the body of the pancreas, and the tail of the pancreas lies within the splenorenal ligament. The gastrosplenic ligament carries the short gastric and left gastroepiploic vessels to the stomach and spleen. The splenic vein receives the inferior mesenteric vein and joins the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein.
Which ligament is bordered anteriorly to the right?
Splenorenal ligament. The lesser sac (omental bursa) is bordered anteriorly to the right by the lesser omentum, which conveys the common bile duct, hepatic artery, portal vein, and gastric vessels. The left borders include the gastrosplenic ligament (with short gastric vessels) and the splenorenal ligament (with splenic vessels).
What does the Histologic section of a normal spleen show?
Histologic section of a normal spleen viewed at low power shows white pulp and red pulp. A thin splenic capsule with slivers of branching trabeculae is also noted.
What is the omentum?
What is omentum. The omentum is part of the mesentery, which consists of two layers of peritoneum , a sheet of two serous membranes fused together that extends from the body wall to the digestive organs (Figures 1 and 2). The omentum pass from the stomach and the first part of the duodenum to other abdominal organs.
Where is the left omentum?
The left border of the greater omentum wraps around the spleen as the gastrosplenic ligament and continues dorsally as the splenorenal ligament (extending between the spleen and the left kidney) to the posterior body wall.
How many layers does the greater omentum have?
The greater omentum is a double sheet that folds back on itself, giving it a total of four layers. Hanging behind the anterior abdominal wall and in front of most of the small intestine, this omentum is usually a conspicuous feature when the peritoneal cavity is opened.
What is the space between the parietal and visceral layers of the peritoneum?
Between the parietal and visceral layers of peritoneum is a potential space (the peritoneal cavity). Abdominal viscera either are suspended in the peritoneal cavity by folds of peritoneum (omentum or mesenteries) or are outside the peritoneal cavity.
What is the term for the organs that are suspended in the peritoneal cavity?
Organs suspended in the cavity are referred to as intraperitoneal; organs outside the peritoneal cavity, with only one surface or part of one surface covered by peritoneum, are retroperitoneal. In the omentum, the leukocytes aggregate in the perivascular area to form what is termed milky spots 2).
How big is the omentum?
The size of the omentum varies from 300 gm to 2000 gm with a surface area of 300 cm 2 to 1500 cm 2 1).
Which mesentery supports the jejunum and ileum?
The long coils of the jejunum and ileum are supported by the mesentery. This sheet fans inferiorly from the posterior abdominal wall like long, pleated curtains. The transverse colon is held to the posterior abdominal wall by the transverse mesocolon, a nearly horizontal sheet that is fused to the underside of the greater omentum, so that it can be viewed only inferiorly. The sigmoid mesocolon is the mesentery that connects the sigmoid colon to the posterior pelvic wall.
Why is the greater omentum important?
Due to the milky spots of macrophage collections present in it , the Greater Omentum also contributes to the development of the immunity of the body. Moreover, it can also limit the spreading of intraperitoneal infections and help in the isolation of wounds. This, it does by wrapping itself around the areas of infection and trauma.
What is the omentum?
What is Omentum? What does Greater & Lesser Omentum do? Omentum (Latin for “apron”) is a body part which is composed of two different layers of fatty tissues and can be found in the lower abdominal area of the human body. Its primary function is to cover and support ...
What is the omentum called?
The Greater Omentum is often called by many other names like the Epiploon, Gastrocolic Omentum, Great Omentum or Omentum Majus and when it comes to animals, it takes the name – Caul. This part is the visceral peritoneum and looks like a long fold beginning near the stomach and hanging down.
Where do the two layers of the Lesser Omentum reach?
At the point where the two layers of the Lesser Omentum reach the duodenum and the lesser curvature of the stomach, they fuse and ascend to the porta hepatis in the form of a double fold.
Which is thinner, the stomach or the omentum?
The Lesser Omentum is much thinner than the Greater Omentum and continues with the two peritoneal layers covering the posteroinferior and anterosuperior surfaces of the stomach and the first part of the duodenum respectively.
How to measure omentum?
The perfect way to measure it is by sucking in the stomach as much as possible and then measure by the belly button as the Omentum cannot be sucked in. Shrinking the Omentum can be especially difficult if the person has other health problems.
How to shrink omentum?
Shrinking the Omentum can be especially difficult if the person has other health problems. The ideal way to maintain good health is to eat natural foods, i.e. those that do not contain high sugar or high fat and include many grains in the food menu. Find a regular sleep cycle is also a great way towards health. Another great way of reducing the size of the Omentum is to walk and regularly and keep the body as fit as possible.
Where is the lesser omentum located?
This is part of the peritoneum that is found in a double layer and goes from the beginning of the duodenum and stomach’s lesser curvature to the liver.
What is the omentum?
Omentum. The omentum is a part of the body that is found in your lower abdominal area. It is made up of two layers of fatty tissues and both supports and covers the organs and intestines found in this area of the body. There are two parts of the omentum, the greater omentum and the lesser omentum, which are responsible for storing fat deposits ...
What is the omentum called?
The greater omentum is also known as the epiploon, gastrocolic omentum, omentum majus or great omentum and is sometimes called the caul when referring to animals. This part of the body is visceral peritoneum in the form of a long fold hanging down and starting at the stomach.
What happens when an omentum is unhealthy?
When it is unhealthy, it can lead to health issues such as unhealthy arteries, inflammation or unstable blood sugar.
What are the divisions of the lesser omentum?
Divisions of Lesser Omentum. The lesser omentum contains several divisions of ligaments that are connected to the liver on one side, which is why each one contains the prefix “hepato.”. In most cases, the lesser omentum is only divided into two ligaments: the hepatogastric ligament connects with the stomach’s lesser curvature and ...
Which side of the duodenum is the greater omentum connected to?
On the left side, the greater omentum is connected to the gastrolienal ligament and on the right it reaches the beginning of the duodenum. In most cases, the greater omentum is thin with a cribriform appearance and has some adipose tissue.
Which part of the omentum stores fat?
There are two parts of the omentum, the greater omentum and the lesser omentum , which are responsible for storing fat deposits and connecting the intestines and stomach to the liver respectively. This article will explain on the structure and function of the greater omentum and the lesser omentum.
