The pons also serves to connect the cerebral cortex to the medulla oblongata The medulla oblongata is a long stem-like structure located in the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure …Medulla oblongata
See more

What is the function of the pons in sheep?
Pons in the sheep's brain is next to the medulla. It connects the medulla and the upper brainstem and relays messages between the cerebrum and cerebellum. The medulla in the sheep's brain is located right under the cerebellum. It controls vital functions like heartbeat and respiration.
What are the pons in the brain responsible for?
What Is The Main Function Of The Pons In Your Brain?The Pons Serves as a Communication Center for the Brain. ... The Pons Plays a Key Role in Regulating Breathing. ... The Pons Controls Some Aspects of Sleep/Wake Cycles. ... The Pons Is Vital to Experiencing Some Sensory Input.More items...
What is the function of the midbrain in a sheep brain?
Arousal, controlling autonomic functions, relaying sensory information between the cerebrum and cerebellum, and sleep.
What happens if pons is damaged?
Damage to the pons can result in serious problems as this brain area is important for connecting areas of the brain that control autonomic functions and movement. Injury to the pons may result in sleep disturbances, sensory problems, arousal dysfunction and coma.
Which involuntary actions does pons control?
Explanation: The pons contains nuclei that relay signals from the forebrain to the cerebellum, along with nuclei that deal primarily with sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, facial sensation, and posture.
Can you survive without the pons?
Because of the part that the Pons plays in hearing, eating, facial expression, and eye movement, the Pons is NOT something you could live without. It relays messages throughout the brain and controls too many important vital functions we as human beings need.
Where are pons present in the brain?
Your pons is one of the lowermost structures in your brain, located near the bottom of your skull. It's just above your medulla oblongata, which then connects to your spinal cord through the opening at the bottom of your skull.
Why is the pons called a bridge?
Pons is Latin for "bridge"; the structure was given its name by the Italian anatomist Costanzo Varolio, who thought that the most conspicuous portion of the pons resembled a bridge that connected the two cerebellar hemispheres.
Which part of the sheep's brain is the biggest?
The olfactory bulb, on the contrary, is comparatively larger in the sheep's brain when compared to the human brain, because animals usually rely more upon their senses and abilities of smell than humans do. Humans rely more upon other senses, such as sight and hearing, rather than smell like sheep and other animals.
What causes pons damage?
In central pontine myelinolysis (CPM), damage to the myelin sheath — the protective covering around nerve cells— happens and can lead to the injury and death of nerve cells in the pons. This damage most commonly occurs when your sodium levels rise too quickly, usually as a result of being treated for low sodium levels.
Can pons damage be reversed?
The disorder can't be cured, but its symptoms can be treated. CPM is one of the two types of osmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS). The other type, known as extrapontine myelinosis (EPM), occurs when myelin is destroyed in areas of the brain that aren't in the brain stem.
How does pons stroke affect?
Summary. A stroke in the pons region of the brain can cause serious symptoms. These may include problems with balance and coordination, double vision, loss of sensation, and weakness in half the body. Pons strokes can lead to brain damage.
What causes damage to the pons?
Damage to the pons most often results from tissue loss due to lack of blood flow (infarct) or bleeding (hemorrhage) – less frequently it can be caused by trauma. An infarct can be caused by several different conditions such as a blood clot (thrombosis) or stroke.
How does the pons regulate sleep?
The brain stem (especially the pons and medulla) also plays a special role in REM sleep; it sends signals to relax muscles essential for body posture and limb movements, so that we don't act out our dreams.
Where are the pons in the brain?
The pons is in the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata, and in front of the cerebellum. A separating groove between the pons and the medulla is the inferior pontine sulcus. The superior pontine sulcus separates the pons from the midbrain.
How is the pons involved with the eyes and ears?
How is the pons involved with the eyes and ears? The pons regulates head movements in response to visual and auditory stimuli.
How does the PONs help the brain?
It aids in many vital functions of the brain by transmitting signals between the forebrain and the cerebellum. If the pons was not functioning properly, these messages might not go through, and these functions could not be carried out. The same is true of sensory information passing between the right and left hemispheres of the brain.
What is the function of the pons?
The Pons Serves as a Communication Center for the Brain. The main function of the pons in your brainis serving as a relay center for many important messages that must go between different areas of the brain. It aids in many vital functions of the brain by transmitting signals between the forebrain and the cerebellum.
What is the pons?
The pons is a small but vital brain structure that houses bunches of nerve fibers. These fibers connect both the cerebrum and the cerebellum as well as the right and left hemispheres of the brain. They make it possible for these structures to send messages — including sensory and motor information — back and forth.
Why is the pons important?
The Pons Is Vital to Experiencing Some Sensory Input. The pons allows for the right and left hemispheres of the brain to exchange information about the senses, including sensory input and function. This includes hearing and taste, as well as balance.
What is the role of the pons in breathing?
The Pons Plays a Key Role in Regulating Breathing . The pons also contains a bundle of nerve cells known as the pneumotaxic center that is integral to the autonomic regulation of breathing. This includes how much air you breathe in and how soon you take another breath.
Which hemispheres of the brain are responsible for the transmission of sensory information?
The same is true of sensory information passing between the right and left hemispheres of the brain. These messages use the nerve fibers in the pons as a conduit, making the structure a key part of sensory function as well. The pons also contains a bundle of nerve cells known as the pneumotaxic center that is integral to the autonomic regulation ...
Can a stroke affect the pons?
Because of this, an injury to the pons may impact both sensory function and movement. Injuries to the Pons Can Disrupt Any or All of Its Functions. Strokes that affect the pons, called pontine strokes, are the most common way injuries occur that affect the pons.
What is the pons on the posterior side of the brain?
On the posterior side, it consists mainly of two pairs of thick stalks, which are known as cerebellar peduncles.
Which cranial nerve is the point of origin of the pons?
The different nerves that emerge from the pons include: Trigeminal nerve ― This is the fifth cranial nerve which is both sensory and motor in nature.
What is the function of the pontine nucleus?
Its function is mostly to provide input to the cerebellar cortex through structures known as the pontine nuclei, which allow the cerebellum to coordinate most of its control. The main function of pons is to basically act as a bridge or highway for relay of many signals to and from the cerebrum and the cerebellum.
Which part of the brain contains the cerebrum?
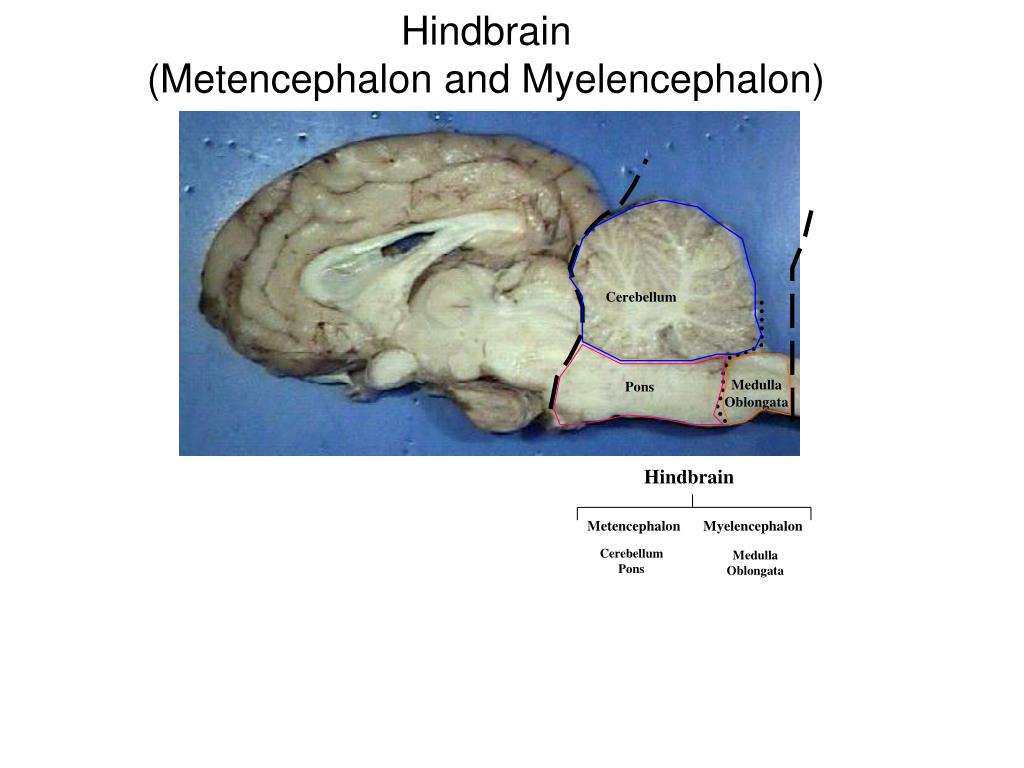
The forebrain contains the main part of the brain, which is the cerebrum that forms a bulk of the brain. The midbrain consists of the tectum, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. The hindbrain contains the medulla oblongata, pons, and the cerebellum.
What is the function of the dorsal part of the brain?
As a part of functions, it is said that the dorsal part of the midbrain and the brain stem is also an important center for consciousness and for maintaining alertness and fatigue levels of an individual. Hence, some experts believe that the pons may play a vital role in REM sleep cycle and in arousal as well.
Where is the pons located?
Pons is the region that is located superior to the medulla oblongata, inferior to the midbrain, and ventral to the cerebellum. In simple words, in humans, the pons is above the medulla oblongata, below the midbrain, and anterior to the cerebellum.
Which nerve is responsible for sideways movement of the eyes?
Abducens nerve ― This is a motor nerve which is responsible for sideways movement of the eyes. Facial nerve ― This is a motor nerve which affects the muscles of facial expression, like muscles that help in smiling, raising eyebrows, and bringing about various expressions on the face, like shock, fear, joy, etc.
What is the pons in biology?
Regina Bailey. Updated November 19, 2019. In Latin, the word pons literally means bridge. The pons is a portion of the hindbrain that connects the cerebral cortex with the medulla oblongata.
What is the damage to the myelin sheath of nerve cells in the pons?
Damage to the myelin sheath of nerve cells in the pons results in a condition called central pontine myelinolysis. The myelin sheath is an insulating layer of lipids and proteins that help neurons conduct nerve impulses more efficiently.
What connects the cerebrum to the cerebellum?
It connects the cerebrum to the cerebellum through the cerebral peduncle. The cerebral peduncle is the anterior portion of the midbrain that consists of large nerve tracts. The pons relays sensory information between the cerebrum and cerebellum. Functions under the control of the cerebellum include fine motor coordination and control, balance, ...
What nerves help us maintain equilibrium?
The vestibulocochlear nerve aids in hearing and helps us maintain our equilibrium. The pons helps to regulate the respiratory system by assisting the medulla oblongata in controlling breathing rate. The pons is also involved in the control of sleep cycles and the regulation of deep sleep. The pons activates inhibitory centers in ...
What happens if you get a pons injury?
Injury to the pons may result in sleep disturbances, sensory problems, arousal dysfunction and coma. Locked-in syndrome is a condition resulting from damage ...
Which ventricle runs posteriorly to the medulla and pons?
Sagittally, it is anterior to the cerebellum and posterior to the pituitary gland. The fourth ventricle runs posteriorly to the pons and medulla in the brainstem.
What are the divisions of the brain?
Divisions of the Brain 1 Forebrain: encompasses the cerebral cortex and brain lobes. 2 Midbrain: connects the forebrain to the hindbrain. 3 Hindbrain: regulates autonomic functions and coordinates movement.
What is a stroke involving the pons called?
The extent of damage depends on the location and size of the stroke. 4 . In rare instances, a stroke involving the pons, typically called a pontine stroke, may be the result of an injury to an artery caused by sudden head or neck trauma.
What are the symptoms of a stroke in the pons?
1 . Some of the symptoms of a pontine stroke include a combination of the following: 2 . Balance difficulty. Vertigo (spinning sensation) Dizziness.
What tests are used to diagnose pontine stroke?
Diagnosis of a pontine stroke requires a thorough neurologic examination. Some diagnostic imaging tests, such as brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and brain magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) or computerized tomography (CT) angiogram, can help confirm the diagnosis of a pontine stroke. 5
What is the name of the hindbrain?
In scientific terms, the pons is sometimes known as the hindbrain, a name that is based on the location of the pons in relation to the rest of the brain during the development of the brain in the embryo (developing baby). Verywell / Hilary Allison.
Why does the brainstem get injured?
This can happen because the blood vessels that supply blood to the pons and the rest of the brainstem are located in the back of the neck, and may become injured as result of neck trauma or sudden pressure or movements of the head or neck.
Can pontine stroke cause locked in syndrome?
A pontine stroke can cause a severe condition called locked-in syndrome. People who suffer from locked-in syndrome can be awake, alert, and able to think and understand, but are only able to move their eyes.
