What is the function of the sensory association area?
What is the function of the somatic sensory association area? This part of the brain is essential for receiving sensory information from the body and processing it to initiate important movements that are required to deal a particular situation. It receives sensations of touch, pain, and vibration from the entire body. Read, more on it here.
What is the function of visual association area?
This associationarea lies in the large parietal and occipital cortical space bounded by the somatosensory cortex anteri-orly, the visual cortex posteriorly, and the auditory cortex laterally. As would be expected, it provides a high level of interpretative meaning for signals from all the surrounding sensory areas.
What is the function of the Motor Association area?
Association areas are all the areas in cerebral cortex except primary sensory area and primary motor area. It receives information from sensory areas and it is involved in “higher” functions such as perception, thoughts and decision-making, etc.
What is the definition of association areas?
parts of the cerebral cortex that receive inputs from multiple areas; association areas integrate incoming sensory information, and also form connections between sensory and motor areas. Because they are involved in organizing information that comes from various other areas of the brain, association areas are often linked to complex functions.

Where is the somatosensory cortex function?
0:102:002-Minute Neuroscience: Primary Somatosensory Cortex - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe primary somatosensory cortex is located in a Ridge of cortex called the post central gyrus it isMoreThe primary somatosensory cortex is located in a Ridge of cortex called the post central gyrus it is situated just posterior to the central sulcus a prominent fissure that runs down the side of the
Where is the somatosensory association area located?
superior parietal lobeThe somatosensory association cortex is located in the superior parietal lobe (a.k.a. posterior parietal cortex), which is posterior to SI. The highest degree of convergence of somatosensory information occurs in the posterior parietal cortex.
What is the somatosensory area of the brain and where is it?
The primary somatosensory cortex is called S1. This area of the cerebral cortex receives sensory information from the somatic senses, plus proprioceptive senses and some visceral senses. It is located on the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe, as shown in Figure 4.3. 6.
What do the association areas control?
The association cortices include most of the cerebral surface of the human brain and are largely responsible for the complex processing that goes on between the arrival of input in the primary sensory cortices and the generation of behavior.
What lobe is the somatosensory association area?
In neuroanatomy, the primary somatosensory cortex is located in the postcentral gyrus of the brain's parietal lobe, and is part of the somatosensory system.
What are the 3 systems of the somatosensory system?
The somatosensory system is regulated by receptors that are spread throughout the body and measure a number of different sensory modalities in the body. These sensations can be divided into three main divisions: external stimuli, internal stimuli, and the sense of where the body is in space.
What part of the brain processes somatosensory information?
parietal lobeThe parietal lobe is separated from the occipital lobe by the parieto-occipital sulcus and is behind the central sulcus. It is responsible for processing sensory information and contains the somatosensory cortex.
Where are association areas located in the brain?
The anterior association area is in the frontal lobes. It is rostral to the postcentral gyri, Rolandic fissure, and premotor areas. It has Sylvian fissure as its posterior boundary. It is referred to as prefrontal cortex.
Where is the somatosensory cortex located quizlet?
The primary somatosensory cortex is located behind and parallel to the primary motor cortex, in front of the parietal lobe. It receives and processes sensory information from the skin and body, enabling us to perceive bodily sensations.
What is the somatosensory cortex?
Performance focused athletes. Student learning. The somatosensory cortex is a part of your brain that receives and processes sensory information from the entire body. Other names of somatosensory cortex include somesthetic area and somatic sensory area. This part of the brain is essential for receiving.
Where does the primary somatosensory area receive fibers?
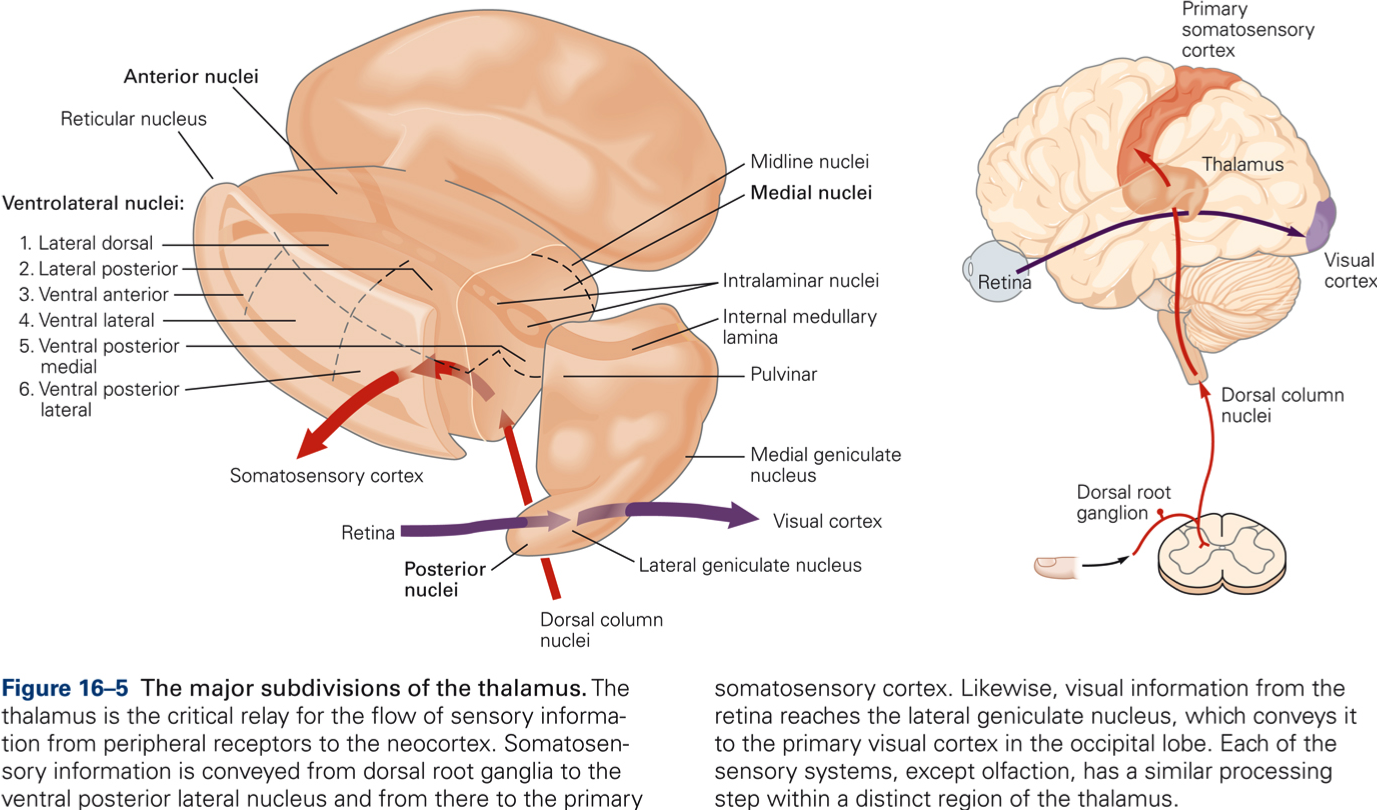
Primary Somatosensory Cortex (S1) The primary somatosensory area receives projection fibers from the ventral posterior lateral and ventral posterior medial nuclei of thalamus. These nuclei receive fibers from the contralateral half of the body in the form of medial, trigeminal and spinal lemnisci.
What is the cause of a somatosensory lesion?
Unilateral lesion of the somatosensory cortex causes sensory disturbances on the contralateral side of the body. The person remains unable to judge degrees of pressure, warmth, unable to localize pain and tactile stimuli accurately, and unable to judge the weights and shapes of the objects. Loss of muscle tone may also be a symptom of lesions of somatosensory cortex.
What part of the brain processes sensory information?
The somatosensory cortex is a part of your brain that receives and processes sensory information from the entire body. Other names of somatosensory cortex include somesthetic area and somatic sensory area.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the discrete localization of different sensations that arise in different parts of the?
Pinpoint the location of pain, tingling, touch, temperature, and other sensations is the function of somatosensory cortex , specifically area S1.
Which artery supplies the lateral surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres?
The arterial supply to most of the primary somatosensory area (S1) and the secondary somatosensory area (S2) is derived from the medial cerebral artery. This artery supplies the lateral surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres.
Which lobe of the brain is the somatosensory cortex located in?
The somatosensory cortex is a part of the forebrain. It is present in the parietal lobe.
What is the somatosensory system?
The somatosensory system is made up of primary, secondary and tertiary neurons that enable touching and sensitive to temperature, position, and balance possible (3). They are distributed throughout the body and include sensory receptors neurons on the surface and deeper neurons within the central nervous system (CNS).
What is the primary somatosensory cortex?
The primary somatosensory cortex of the human brain is made up of Brodmann areas 3, 1 and 2. Brodmann area, one section of the cerebral cortex is familiar with its histological structure or cytoarchitecture and organization of cells (2).
What is the somatic sense of pain?
Derived#N#from the Latin words "to harm or hurt", nociception is the somatic#N#sense of pain. In this case, the primary somatosensory cortex responds to#N#certain harmful or potentially harmful stimuli (1). For example, if you are cut or some#N#chili powder is poured to your eyes, nociceptors generate projections along the#N#spinal cord to the primary somatosensory cortex. These may result in a variety#N#of physiological and behavioral responses.
Which cortex is prone to a lesion?
to neurosurgeons, the primary somatosensory cortex is prone to the lesion. 1. Agraphesthesia. This is one kind of disorder of directional cutaneous kinesthesia (proprioception) or disorientation of sensation of the skin across the skin space (2).
Which part of the brain is responsible for the processing of somatic sensations?
The primary somatosensory cortex is mainly responsible for the processing of somatic sensations. According to research, somatic sensations are bodily sensations of touch, pain, temperature, vibration and proprioception (1).
Why are hands and lips expanded on a good homunculus?
Hands and lips are expanded on a good homunculus. This is because several neurons in the cerebral cortex are assigned to process signals from these body parts (3). Brodmann. areas 3, 1 and 2 also comprise of cells that run to the secondary somatosensory.
What is the somatic N pathway?
Somatic#N#pathways also called somatosensory pathways, convey information between the#N#brain and nerve cells in the skin and other body organs (3). There are two main somatic#N#pathways namely anterolateral pathway and posterior column-medial lemniscal#N#pathway.
Why are association areas called association areas?
These areas are called association areas because they receive and analyze signals simultaneously from multiple regions of both the motor and sensory cortices as well as from subcortical structures.
What is the association area of the parieto-occipitotemporal area?
This associationarea lies in the large parietal and occipital cortical space bounded by the somatosensory cortex anteri-orly, the visual cortex posteriorly, and the auditory cortex laterally. As would be expected, it provides a high level of interpretative meaning for signals from all the surrounding sensory areas. However, even the parieto-occipitotemporal association area has its own functional subareas, which are shown in Figure 57–5.
What is the prefrontal association area?
We learned that the prefrontal association area functions in close association with the motor cortex to plan complex patterns and sequences of motor movements. To aid in this function, it receives strong input through a massive subcortical bundle of nerve fibers connecting the parieto-occipitotemporal association area with the prefrontal association area. Through this bundle, the prefrontal cortex receives much preanalyzed sensory information, especially information on the spatial coordinates of the body that is necessary for planning effective movements. Much of the output from the prefrontal area into the motor control system passes through the caudate portion of the basal ganglia-thalamic feedback circuit for motor planning, which provides many of the sequential and parallel compo-nents of movement stimulation.
What is Broca's area?
Broca’s Area. A special region in the frontal cortex,called Broca’s area, provides the neural circuitry forword formation. This area, shown in Figure 57–5, islocated partly in the posterior lateral prefrontal cortex and partly in the premotor area. It is here that plans and motor patterns for expressing individual words or even short phrases are initiated and executed. This area also works in close association with Wernicke’s language comprehension center in the temporal association cortex.
Where is the limbic association area located?
This area is found in the anterior pole of the tem-poral lobe, in the ventral portion of the frontal lobe, and in the cingulate gyrus lying deep in the longitu-dinal fissure on the midsurface of each cerebral hemisphere. It is concerned primarily with behavior,emotions, and motivation. We will learn that the limbic cortex is part of a much more extensive system, the limbic system, that includes a complex set of neuronal structures in the midbasal regions of the brain. This limbic system provides most of the emo-tional drives for activating other areas of the brain and even provides motivational drive for the process of learning itself.
What is the area of language comprehension?
2.Area for Language Comprehension. The major areafor language comprehension, called Wernicke’s area , lies behind the primary auditory cortex in the posteriorpart of the superior gyrus of the temporal lobe. Wediscuss this area much more fully later; it is the most important region of the entire brain for higher intel-lectual function because almost all such intellectual functions are language based.
What is the brain abnormality that causes the inability to recognize faces?
An interesting type of brain abnormality called prosophenosia is inability to recognize faces. Thisoccurs in people who have extensive damage on the medial undersides of both occipital lobes and along the medioventral surfaces of the temporal lobes, as shown in Figure 57–6. Loss of these face recognition areas, strangely enough, results in little other abnor-mality of brain function.
What is sensory integration?
Integrates sensory information, forms comprehensive understanding of stimulus, determines size, texture, and relationship of parts
Where does the smell receptor receive signals?
Receives signals from smell receptors in the superior nasal cavities
Which lobe is close to the limbic system?
Anterior portion of the frontal lobe (Closely linked to the limbic system)