What is the function of the spinalis muscle?
Spinalis muscle. Written By: Spinalis muscle, any of the deep muscles of the back near the vertebral column that, as part of the erector spinae (sacrospinalis) muscle group, assist in extension (e.g., bending backward), lateral flexion (bending to the side), and rotation of the spine.
What are the types of spinalis muscles?
The spinalis muscles are the most medial erector spinae muscles. They are divided into three regional groups, from superior to inferior: Spinalis capitis muscle originates from the spinous processes of C7-T1 vertebrae and inserts into the midline of the occipital bone .
What is the spinalis cervicis muscle?
The Spinalis Cervicis muscle is variably present. The Spinalis Cervicis muscle originates from the spinous processes of the axis and sometimes the 3rd and 4th cervical spinous processes. The Spinalis Cervicis muscle is inserted on the lower part of ligamentum nuchae (C4 to C6) and the spinous process of C7 to T2.
Where does the blood supply to the spinalis muscles come from?
The blood supply to the spinalis muscles comes from the vertebral, deep cervical, occipital, intercostal and lumbar arteries. The function of the spinalis muscles is to extend and laterally flex the cervical and thoracic regions of the spine. Learn more about these erector spinae group by reading the following article:

What does spinalis mean in muscles?
The spinalis is a portion of the erector spinae, a bundle of muscles and tendons, located nearest to the spine. It is divided into three parts: Spinalis dorsi, spinalis cervicis, and spinalis capitis.
What are the 3 spinalis muscles?
Spinalis muscle. The spinalis, longissimus and iliocostalis muscles form the erector spinae group of the deep back muscles. Together they form a broad powerful muscle group responsible for major movement of the spine.
What action does the erector spinae perform?
The function of the spinal erectors is to move the vertebral column. Bilateral contraction of these muscles extends the spine, while unilateral contraction causes lateral flexion (ipsilateral). They also help to maintain posture by steadying the spine on the pelvis during walking.
What is the primary action of the longissimus spinalis and iliocostalis muscles?
Iliocostalis muscle acts in synergy with the two other erector spinae components (longissimus and spinalis) to produce movements of the vertebral column. When these muscles contract unilaterally, they produce ipsilateral lateral flexion of the spine, while when acting bilaterally, they extend the spine.
Is spinalis a deep muscle?
The deep back muscles are posterior to the erector spinae. They are short muscles associated with the spinous and transverse processes of the vertebrae. The three deep muscles of the back include the semispinalis, multifidus, and rotatores.
What holds the spine together?
Each vertebra is held to the others by groups of ligaments. Ligaments connect bones to bones; tendons connect muscles to bones. There are also tendons that fasten muscles to the vertebrae. The spinal column also has real joints (just like the knee or elbow or any other joints) called facet joints.
What are the 7 back muscles?
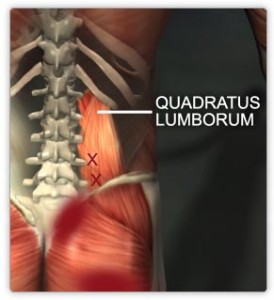
The muscles in the back are the trapezius, rhomboids, latissimus dorsi, erector spinae, multifidus, and quadratus lumborum. How can I prevent back pain? Keep your back muscles in good shape to prevent back pain.
What muscle straightens the back?
The erector spinae (/ɪˈrɛktər ˈspaɪni/ irr-EK-tər SPY-nee) or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back.
What happens when the erector spinae contract?
Erector spinae muscle group have 3 major functions. Unilateral contraction of erector spinae results in lateral flexion (ipsilateral) and rotation of the cervical, thoracic spine and lumbar spines. Bilateral contraction of erector spinae causes extension of the head, neck and cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae.
What causes pain in the erector spinae?
An Erector spinae injury occurs when the muscles and connective tissues of the lower back become overused or stretched beyond their normal range of movement. Erector spinae pain can occasionally occur at the time of the injury, whilst playing a sport, perhaps a slip or trip.
What is the function of the longissimus?
The erector spinae muscles, including longissimus, are the most powerful extensors of the vertebral column. Their main actions include spine extension and lateral flexion. Longissimus capitis also rotates the head.
What is the role of the iliocostalis muscle?
iliocostalis muscle, any of the deep muscles of the back that, as part of the erector spinae (sacrospinalis) muscle group, aid in extension (bending backward), lateral flexion (bending to the side), and rotation of the spinal column.
What is the function of the iliocostalis muscle?
Function. Laterally flexes and extends the lower cervical region. Maintains the erect posture and stabilizes the vertebral column during flexion in the upper portion of the torso. It also acts in contrast to abdominal muscles and in opposition to the action of gravity.
Which is the deepest muscle?
The levatores costarum, interspinales and intertransversarii muscles form the deepest layer of the deep back muscles and are sometimes referred to as the segmental muscles or the minor deep back muscles.
What muscle causes lower back pain?
The most common muscles that are responsible for Low Back Pain are the Iliopsoas, Quadratus Lumborum, the Gluteals and the Multifidus muscles. They are the muscles that attach in and around your spine. The Iliopsoas is actually two muscles that meet at the front of your hip.
How can I relax my spinal erections?
0:523:173 Exercises You Can Do To Prevent Erector Spinal Tightness - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipImagine pressing the curve of your neck into the wall your chin should tuck down. And you canMoreImagine pressing the curve of your neck into the wall your chin should tuck down. And you can imagine a string pulling your head towards the ceiling.
What are the muscles along the spine called?
Overview. The paraspinal muscles, sometimes called the erector spinae, are three muscle groups that support your back. You use them every time you lean to one side, arch your back, bend forward, or twist your torso.
What is the origin and insertion of the spinalis muscle?
Origin: Variable origin on the spinous processes of the axis and sometimes the 3rd and 4th cervical spinous process. Insertion: Lower part of ligamentum nuchae (C4 to C6) and spinous process of C7 to T2. Nerve Supply: Posterior rami of cervical and thoracic spinal nerves (C4 to T1).
What muscles are part of the erector spinae group?
Erector Spinae MusclesSpinal Nerve.Lumbar.Foramen.Fascia.Tubercle.Spinous Process.Iliocostalis.Longissimus.More items...
What is spinalis thoracis?
Spinalis Thoracis belongs to the medial column of the erector spinae, named the Spinalis muscles. It is the most prominent and well-organised portion of the spinalis muscle, with spinalis capitis and spinalis cervicis superiorly. Its muscle fibres running superiorly.
What is the function of the spinalis cervicus?
The function of the spinalis muscle is to extend and laterally (side to side) bend the neck and trunk. Last medically reviewed on January 20, 2018.
Where is the spinalis muscle located?
The spinalis muscle is a subsection of the erector spinae, which is a confluence of tendons and muscles that is located near the spine.
What are the three parts of the spinal nerve?
It innervates at the posterior (back) branches of spinal nerves C2 to L3. The spinalis is split into three parts: the spinalis dorsi, the spinalis cervicis, and the spinalis capitis.
Introduction
The spinalis muscle group are part of the the erector spinae (ES) group (the intermediate layer of the intrinsic back muscles ). The ES is made of three subgroups, with the group divisions occurring by location.
Anatomy
The spinalis thoracis is the major spinalis muscle, arising from the bones of the lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebral spine and inserted into the bones of the upper thoracic vertebral spine.
Function
Spinalis works synergistically with the other members of the erector spinae group. Erector spinae muscle group have 3 major functions.
Where is the spinalis thoracis muscle located?
The spinalis thoracis is the major spinalis muscle, arising from the bones of the lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebral spine and inserted into the bones of the upper thoracic vertebral spine. It may be prolonged into the neck (spinalis cervicis) and head (spinalis capitis).
Which muscle group is responsible for bending backwards?
Spinalis muscle, any of the deep muscles of the back near the vertebral column that, as part of the erector spinae (sacrospinalis) muscle group, assist in extension ( e.g., bending backward), lateral flexion (bending to the side), and rotation of the spine. The spinalis thoracis is the major spinalis muscle, arising from the bones ...
Why is it important to understand the physiology of the spinal cord?from byjus.com
Understanding the physiology of the spinal cord helps in detecting and determining the various methods to deal with diseases and damage related to the spinal cord. Also Read: Peripheral Nervous System.
What is the spinal cord?from byjus.com
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. It encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid.
What level does the spinal cord end?from en.wikipedia.org
The spinal cord ends at the level of vertebrae L1–L2, while the subarachnoid space —the compartment that contains cerebrospinal fluid — extends down to the lower border of S2. Lumbar punctures in adults are usually performed between L3–L5 ( cauda equina level) in order to avoid damage to the spinal cord. In the fetus, the spinal cord extends the full length of the spine and regresses as the body grows.
What are the two areas of the spinal cord that are most commonly injured?from en.wikipedia.org
The two areas of the spinal cord most commonly injured are the cervical spine (C1–C7) and the lumbar spine (L1–L5) . (The notation C1, C7, L1, L5 refer to the location of a specific vertebra in either the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar region of the spine.) Spinal cord injury can also be non-traumatic and caused by disease ( transverse myelitis, polio, spina bifida, Friedreich's ataxia, spinal cord tumor, spinal stenosis etc.)
What is the name of the nerve that connects the spinal cord to the coccyx?from en.wikipedia.org
The spinal cord proper terminates in a region called the conus medullaris, while the pia mater continues as an extension called the filum terminale , which anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx. The cauda equina ("horse's tail") is a collection of nerves inferior to the conus medullaris that continue to travel through the vertebral column to the coccyx. The cauda equina forms because the spinal cord stops growing in length at about age four, even though the vertebral column continues to lengthen until adulthood. This results in sacral spinal nerves originating in the upper lumbar region. For that reason, the spinal cord occupies only two-thirds of the vertebral canal. The inferior part of the vertebral canal is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and the space is called the lumbar cistern.
How does motor information travel down the spinal cord?from en.wikipedia.org
Motor information travels from the brain down the spinal cord via descending spinal cord tracts. Descending tracts involve two neurons: the upper motor neuron (UMN) and lower motor neuron (LMN). A nerve signal travels down the upper motor neuron until it synapses with the lower motor neuron in the spinal cord. Then, the lower motor neuron conducts the nerve signal to the spinal root where efferent nerve fibers carry the motor signal toward the target muscle. The descending tracts are composed of white matter. There are several descending tracts serving different functions. The corticospinal tracts (lateral and anterior) are responsible for coordinated limb movements.
What is the outermost layer of the spinal cord?from en.wikipedia.org
The spinal cord (and brain) are protected by three layers of tissue or membranes called meninges, that surround the canal. The dura mater is the outermost layer, and it forms a tough protective coating. Between the dura mater and the surrounding bone of the vertebrae is a space called the epidural space. The epidural space is filled with adipose tissue, and it contains a network of blood vessels. The arachnoid mater, the middle protective layer, is named for its open, spiderweb-like appearance. The space between the arachnoid and the underlying pia mater is called the subarachnoid space. The subarachnoid space contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which can be sampled with a lumbar puncture, or "spinal tap" procedure. The delicate pia mater, the innermost protective layer, is tightly associated with the surface of the spinal cord. The cord is stabilized within the dura mater by the connecting denticulate ligaments, which extend from the enveloping pia mater laterally between the dorsal and ventral roots. The dural sac ends at the vertebral level of the second sacral vertebra.
Introduction of the Spinalis Cervicis
The Spinalis group of the muscle is part of the erector spinae (ES) group (the intermediate layer of the intrinsic back muscles). Spinalis Cervicis muscle is the cervical portion of the spinalis muscle with spinalis capitis muscle superiorly and spinalis thoracis muscle inferiorly. The Spinalis Cervicis muscle is variably present.
The Common conditions that affect the neck muscles which include
Spinalis Cervicis Spasms: Spasms also known as muscle cramps, muscle spasms occur when a muscle contracts and can’t relax. Most spasms are short, lasting only for a few seconds. But you might have a sore or stiff neck afterward.
Exercise for the Spinalis Cervicis muscle
Chin tuck exercise Sit straight and look straight ahead with the ears directly over the shoulders. Place a finger on the chin. Without moving the finger, pull the chin and head straight backward until a good stretch is felt at the base of the head and top of the neck. Hold for 5 seconds if possible.
What is the function of the erector spinae?
The erector spinae are divided into three groups, from medial to lateral: The function of the spinal erectors is to move the vertebral column. Bilateral contraction of these muscles extends the spine, while unilateral contraction causes lateral flexion (ipsilateral).
Where does the spinal nerve supply blood?
The blood supply to the spinalis muscles comes from the vertebral, deep cervical, occipital, intercostal and lumbar arteries.
What is the erector spinae?
Erector spinae muscles. The erector spinae muscles comprise the intermediate layer of the deep (intrinsic) muscles of the back. They extend on either side of the vertebral column, between the base of the cranium superiorly and pelvis inferiorly. The erector spinae are divided into three groups, from medial to lateral:
What is the function of the longissimus?
The function of the longissimus muscles is to extend and laterally flex (ipsilateral) the spine. Longissimus capitis also helps to rotate the head ipsilaterally. Learn all the details about the longissimus muscles by taking a look at the article provided below: Longissimus muscle Read article.
Where is the Iliocostalis muscle innervated?
Similar to the other erector spinae groups, iliocostalis muscles are innervated by the lateral branches of the posterior rami of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves. Arterial supply is via branches of the occipital, deep cervical, vertebral, posterior intercostal, subcostal, lumbar and lateral sacral arteries.
Where does the Iliocostalis lumborum originate?
Iliocostalis lumborum muscle originates from three points; lateral crest of sacrum, medial end of iliac crest and thoracolumbar fascia. It attaches to the angle of ribs 5-12, transverse processes of vertebrae L1-L4 and adjacent thoracolumbar fascia. The erector spinae comprise of many muscles and a lot of attachments.
Which muscle is the most lateral erector spinae?
The iliocostalis muscles are the most lateral erector spinae muscles. According to their attachments and location, they are regionally divided into three groups, from superior to inferior: Iliocostalis colli muscle originates from the angle of ribs 3 to 6 and inserts into the transverse processes of vertebrae C4-C6.
What is the function of the Spinae muscle?
Its function is similar to that of the other erector spinae muscles, i.e., extension of the vertebral column. It also helps maintain erect posture. Also, it will help in bending and twisting to the same side.
Where is the Spinalis muscle located?
Spinalis muscle lies closest to the vertebral column. It begins as a thick tendon from the sacrum and travels up. The longest of these three muscles, longissimus inserts at the mastoid process, which is the temporal process that is located behind the ear, at the base of the skull. Iliocostalis lies furthest from the vertebral column, ...
What muscles help the spine to move?
The erector spinae is one of the three true or intrinsic back muscles. It is this muscle group that allows the spine to return to erect position after bending. We bend backwards when these muscles contract, and when only the muscles on one side of the vertebral column contract, we are able to bend sideways. So, these muscles allow us to bend sideways, and facilitate the rotation of the spine and movement of the head. These help in maintaining the alignment of the spine.
What muscles are involved in the erector spinae?
The erector spinae is a muscle group that consists of three muscles – iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis. These muscles help us to straighten our back.
What muscles help us straighten our back?
These muscles help us to straighten our back. Bodytomy focuses on the location and function of erector spinae muscles. The erector spinae is a muscle group that consists of three muscles – iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis. These muscles help us to straighten our back. Bodytomy focuses on the location and function of erector spinae muscles.
What is the insertion point of the Iliocostalis lumborum?
The insertion point of the iliocostalis lumborum are the inferior borders of the angles of the last pair of the true ribs (seventh rib), and the false and floating ribs, which means eighth to twelfth pair of ribs.
Where does the Iliocostalis thoracis muscle insert?
Arising from the upper borders of the angles of the inferior six ribs (seventh to the twelfth pair of ribs), Iliocostalis thoracis muscle inserts into the upper borders of the angles of first to the sixth pair of ribs, and into the posterior transverse process of the C7, which is the seventh cervical vertebra.
Anatomy of a Spinalis
A Spinalis is the deeper part of the back muscles, running along the spinal column. It is the main back muscles responsible for bending the spine. This is called flexion, and it is divided into two parts: spinalis, which is on the top and middle of the back, and transversa, which is on the bottom.
What is Spinalis?
Spinalis is a type of protein found in meat. It is classified as an undenatured (also called “natural”) protein. This means that it is not processed or treated in any way. This type of protein is also considered the best type of protein because it contains the highest concentration of protein without being processed.
Benefits of Spinalis
Spinalis is a vegetable also known as asparagus. Asparagus is most commonly known as a vegetable, but is in fact an edible plant in the lily family. Asparagus is one of the more bitter vegetables on the market today, but some people do enjoy it. Asparagus is known to be a powerful diuretic, which means that it increases the flow of urine.
Spinalis Steak Recipe
Spinalis is a pre-chewed, reduced bone-in beef steak. It is usually made from the psoas major muscle, which is located at the back of the body. Spinalis steak is part of the quadriceps muscle group and is one of the more tender cuts of beef. They are often ground and used in beef patties and burgers.
Symptoms of Spinalis
Spinalis is a painless condition that is typically associated with knee pain, back pain, and arthritis. It is also known as spinal scoliosis. Spinalis is caused by a growth of bone along the spine, and occurs when the spine is curved.
/images/library/1921/Screen_Shot_2016-07-18_at_19.12.05.png)