What is the function of stratum lucidum?
Mar 25, 2020 · The sub-layer of skin called the stratum spinosum is believed to aid in flexibility, and it enables the epidermis, or outer layer of skin, to better withstand the effects of friction and abrasion. The stratum spinosum is thicker in those areas of the skin, such as the soles of the feet and palms of the hands, that experience a greater degree of abrasion from contact with …
What does the stratum granulosum do?
Apr 23, 2020 · What is the function of the stratum Spinosum layer? The main function of the stratum spinosum is to allow keratinocytes to mature. In this layer, they begin to produce their own keratin as well are Click to see full answer. Regarding this, …
What is the stratum functionalis?
Mar 07, 2022 · The stratum spinosum prevents foreign materials from passing through the epidermis. The main job of the prickle cell layer is to help the skin retain moisture and natural emollients that can keep the epidermis lubricated and resistant to cracking. The actual process through which this happens is somewhat complex.
Which stratum of the epidermis is the most superficial?
Stratum Spinosum. Cells of the stratum spinosum begin the process of keratinization and continue into the stratum granulosum, which is covered by the outermost and most keratinized layer, the stratum corneum. From: Cunningham's Textbook of Veterinary Physiology (Sixth Edition), 2020. Related terms: Esophagus; Keratinocyte; Lymph; Dermis; Stratum Corneum
What is the function of stratum spinosum?
The stratum spinosum helps make your skin flexible and strong. Between the stratum spinosum layer and the stratum lucidum layer. Keratinocytes have granules within them, and in this layer they're visible under a microscope.Oct 19, 2021
What does the stratum spinosum protect?
Melanin is transferred to keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum to protect cells from UV rays. The dermis connects the epidermis to the hypodermis, and provides strength and elasticity due to the presence of collagen and elastin fibers.
What is specific about stratum spinosum?
The prickle cell layer (stratum spinosum) is the next layer (8-10 layers of cells). The cells in these layers have lots of desmosomes, which anchor the cells to each other, and contain thick tufts of intermediate filaments (keratin).
What is the function of stratum?
The stratum corneum (SC), the skin's outermost layer and interface with the outside world is now well recognized as the barrier that prevents unwanted materials from entering, and excessive loss of water from exiting the body.Oct 1, 2012
What is the function of dendritic cells found within the stratum spinosum of the epidermis?
Langerhans cells, dendritic cells, are the skins first line defenders and play a significant role in antigen presentation. These cells need special stains to visualize, primarily found in the stratum spinosum.Nov 19, 2021
What is the function of dendritic cells found within the stratum spinosum of the epidermis quizlet?
Epidermal dendritic cells help activate the immune system within the body. Spiky hemispheres that in conjunction with sensory nerve endings form a sensitive touch receptor.
What happens to keratinocytes in stratum spinosum?
Stratum Spinosum and Granulosum This layer gets its name from the fact that the cells located here contain many granules. The keratinocytes produce a lot of keratin in this layer—they become filled with keratin. This process is known as keratinization.Jan 3, 2021
Why is it called stratum spinosum?
From the stratum basale, the keratinocytes move into the stratum spinosum, a layer so called because its cells are spiny-shaped cells. The stratum spinosum is partly responsible for the skin's strength and flexibility.
What is the purpose of the stratum corneum of the epidermis?
The stratum corneum is the outer layer of the skin (epidermis). It serves as the primary barrier between the body and the environment.
What are the functions of the 5 layers of the epidermis?
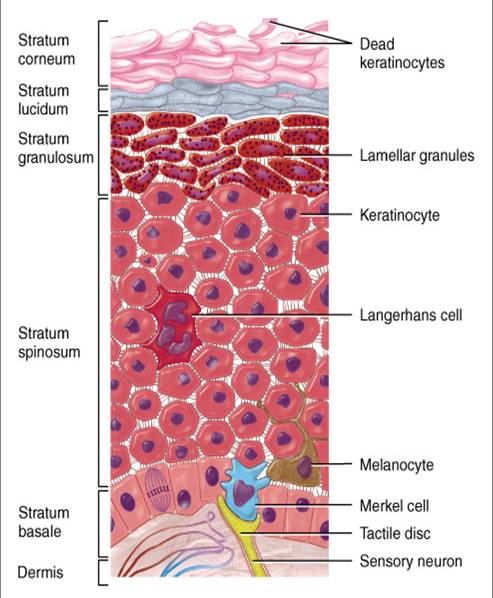
The epidermis provides a protective waterproof barrier that also keeps pathogens at bay and regulates body temperature. The main layers of the epidermis are: stratum corneum, stratum lucidium, stratum granulosm, stratum spinosum, stratum germinativum (also called stratum basale).Aug 13, 2020
Which of the following is a function of stratum corneum?
As such, the stratum corneum primarily functions as a barrier between the deeper layers of skin and the outside environment, preventing toxins and bacteria from entering the body. It also helps to keep moisture from evaporating into the atmosphere, which keeps the skin hydrated.Feb 18, 2022
What are the layers of the epidermis?
The 5 Layers of Your Skin. Stratum Basale or Basal Layer. The deepest layer of the epidermis is called the stratum basale, sometimes called the stratum germinativum. Stratum Spinosum or the Spiny layer. This layer gives the epidermis its strength. Stratum Granulosum or the Granular Layer. Stratum Lucidum.
What is the function of the stratum spinosum?
The main function of the stratum spinosum is to allow keratinocytes to mature. In this layer, they begin to produce their own keratin as well are. Click to see full answer.
Why are keratinocytes flat?
It's dead keratinocytes are flat sacs completely filled with keratin because their nuclei and organelles disintegrated upon cell death Primary function is to protect the skin against abrasion and penetration. The glycolipid layer of cells keeps the stratum corneum waterproof.
Which layer of the epidermis contains keratinocytes?
Stratum Spinosum and Granulosum Layers of the epidermis: The epidermis is made up of 95% keratinocytes but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans cells, Merkel cells, and inflammatory cells.
Which part of the skin contains melanocytes?
The stratum basale also contains melanocytes, cells that produce melanin, the pigment primarily responsible for giving skin its color. Melanin is transferred to keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum to protect cells from UV rays.
What is the koilocytosis of exophytic papillomas?
The term koilocytosis is used to describe cells with papillomavirus-induced cytopathic effects , which consist of extensive cytoplasmic vacuolation and nuclear pyknosis. Intranuclear inclusion bodies may also be present; these occur in the upper layers of the epidermis (see Figure 26-3, C). Endophytic papillomas are cup-shaped masses of epithelial hyperplasia that occur below the level of the surrounding normal skin. Koilocytosis and intranuclear inclusions are often prominent. Histopathology of pigmented plaques are characterized by locally extensive epidermal hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, hyperpigmentation, and clumped keratohyalin granules; koilocytes and viral inclusions are generally not observed.7 Feline sarcoids have dermal fibroplastic proliferations with overlying epithelial hyperplasia that includes long, thin rete ridges that extend into the tumor; they may be confused with sarcomas. 40 Feline plaques exhibit moderate to marked epidermal hyperplasia and koilocytosis. Intranuclear inclusions are sometimes present. In situ SCCs are characterized by epithelial hyperplasia, dysplasia, and increased numbers of mitotic figures, with an intact basement membrane. Loss of the basement membrane and invasion of the dermis indicates invasive SCC.
What is the physical barrier of the epidermis?
The physical barrier of the epidermis involves several different components, including the stratum corneum and the keratinocytes of the stratum granulosum and spinosum. Tight junctions between cells play a major role in the barrier function of the skin.
What is the layer above the stratum basalis?
The stratum spinosum is the layer above the stratum basalis and is typically five to ten cell layers thick. Keratinocytes adhere to each other by desmosomes. These desmosomes are composed of a number of key adhesion molecules, including the transmembrane proteins, desmogleins and desmocollins, which are linked to intracytoplasmic intermediate ...
What is the stratum of a rat?
Stratum Spinosum. The stratum spinos um is a characteristic of human skin but is not seen in the thin skin of the rat, although it is present in the thick skin of the paw pads. A stratum spinosum is also seen in the keratinised epithelium of the oesophagus and fore-stomach. The cells of the stratum spinos um are linked by desmosomes, ...
Where are viral inclusions found?
Viral inclusions have been noted in nuclei of cells in the stratum granulosum of warts, with scattered viral particles in stratum spinosum nuclei and extracellular aggregates in surface keratin debris.1 Toluidine blue-positive intracytoplasmic inclusions noted histologically in the stratum granulosum and spinosum were electron-dense inclusions not limited by a membrane and were proposed to be an aberrant form of keratohyalin. 1 Melanocytes have been shown to contain degenerate melanogenic organelles, with reductions in number and size of melanosomes and some giant melanosomes; this correlates with the hypopigmentation seen histologically.25
Where are LCs located?
LCs are the dendritic cells of the epidermis, they reside in the stratum spinosum in very close contact with keratinocytes and extend their dendritic processes to the stratum corneum. They arise mainly from fetal liver-derived monocytes and, to a minor extent, from yolk sac-derived myeloid precursors seeding the skin before birth ( Chorro et al., 2009; Hoeffel et al., 2012 ). After birth, LCs maintain a short term and low rate of in situ proliferation that suffices to maintain their numbers in adulthood. LC's close interaction with keratinocytes begins before they seed the skin, as keratinocyte-derived IL-34 ensures they seed to the epidermis during development ( Wang et al., 2012 ), and chemokines such as CCL2, CCL8, and CCL20 produced by murine hair follicle keratinocytes regulate their recruitment in adulthood in response to stress and inflammation ( Nagao et al., 2012 ).
What are the layers of the epidermis?
The top layer of the skin is the epidermis which is divided into four layers: the stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale. The last three layers have a thickness of around 20–100 μm [14, 15], and these are often collectively referred to as the viable epidermis.
Content
The thorny stratum It is a layer of the epidermis whose name is due to the fact that it has a large number of tonofilaments that radiate from the cytoplasm towards the desmosomes, which are proteins that connect adjacent cells.
General characteristics
The epidermis is made up of cells called keratinocytes, named for their keratin biosynthesis capacity. The stratum spinosum, in addition to having keratinocytes, has scattered melanin granules and Lanhergans cells.
Histology
The skin consists of two main layers: dermis and epidermis. The latter is a stratified squamous epithelium composed of keratinocytes, which are cells with the ability to synthesize keratin.
Features
In the stratum spinosum, the lamellar bodies participate in the formation of the intercellular water barrier of the epidermis. This barrier is established during the differentiation of keratinocytes.
Langerhans cells
Langerhans cells, present in the stratum spinosum, are derived from CD34 stem cells in the bone marrow. These cells are responsible for finding and presenting antigens that enter through the skin.
Melanocytes
Melanocytes are dendritic cells found in the basal layer. They spread the tonofilaments between the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum. Their function is the biosynthesis of melanin, which protects against the actions of UV light and sunlight. The ratio of melanocytes to keratinocytes varies between 1: 4 and 1:10.
What is the deepest layer of the epidermis?
The deepest/innermost layer of the epidermis is the stratum basale. Histologically, the stratum basale is a single layer of cuboidal keratinocytes that directly abut and attach to the dermis. The two primary functions of the stratum basale are 1) proliferation and 2) attachment of the epidermis to the dermis. Click to see full answer.
What is the stratum germinatum?
The stratum germinatum (SG) provides the germinal cells necessary for the regeneration of the layers of the epidermis. These germinal cells are separated from the dermis by a thin layer of basement membrane.
What is the function of the stratum spinosum?
Answer and Explanation: The main function of the stratum spinosum is to allow keratinocytes to mature. In this layer, they begin to produce their own keratin as well are.
Where are the most important cells in the skin?
Stratum Basale This is where the skin's most important cells, called keratinocytes, are formed before moving up to the surface of the epidermis and being shed into the environment as dead skin cells.

Content
General Characteristics
- The epidermis is made up of cells called keratinocytes, named for their keratin biosynthesis capacity. The stratum spinosum, in addition to having keratinocytes, has scattered melanin granules and Lanhergans cells. When the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum migrate towards the outermost part of the epidermis, they begin to produce keratohyalin granules and lamellar bo…
Histology
- The skin consists of two main layers: dermis and epidermis. The latter is a stratified squamous epithelium composed of keratinocytes, which are cells with the ability to synthesize keratin. From the deepest to the most superficial, the layers that make up the epidermis are: basal or germinative stratum, spinous stratum, granular stratum, lucid stratum and corneal stratum. Kera…
Features
- In the stratum spinosum, the lamellar bodies participate in the formation of the intercellular water barrier of the epidermis. This barrier is established during the differentiation of keratinocytes. The elements of the water barrier of the epidermis are the cell envelope (EC) and the lipid envelope. The cell envelope is formed by the deposition of...
Langerhans Cells
- Langerhans cells, present in the stratum spinosum, are derived from CD34 stem cells in the bone marrow. These cells are responsible for finding and presenting antigens that enter through the skin. Langerhans cells, similar to macrophages, express the major histocompatibility complexes I and II, as well as immunoglobulin G (IgG) receptors and complement C3b receptors. Analysis of …
Melanocytes
- Melanocytes are dendritic cells found in the basal layer. They spread the tonofilaments between the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum. Their function is the biosynthesis of melanin, which protects against the actions of UV light and sunlight. The ratio of melanocytes to keratinocytes varies between 1: 4 and 1:10. Throughout their lives, melanocytes maintain their ability to replica…
References
- Bereiter-Hahn, J., Matoltsy, A. G., Richards, K. S. 1986. Biology of the Integument 2, vertebrates. Springer, Berlin.
- Bloom, W., Fawcett, D. W. 1994. A textbook of Histology. Chapman & Hall, New York.
- Burns, T., Breathnach, S., Cox, N., Griffiths, C. 2010. Rook’s textbook of dermatology. Wiley, Oxford.
- Bereiter-Hahn, J., Matoltsy, A. G., Richards, K. S. 1986. Biology of the Integument 2, vertebrates. Springer, Berlin.
- Bloom, W., Fawcett, D. W. 1994. A textbook of Histology. Chapman & Hall, New York.
- Burns, T., Breathnach, S., Cox, N., Griffiths, C. 2010. Rook’s textbook of dermatology. Wiley, Oxford.
- Eroschenko, V. P. 2017. Atlas of histology with functional correlations. Wolters Kluwer, Baltimore.