What does the thalamus do in our body?
While the thalamus is classically known for its roles as a sensory relay in visual, auditory, somatosensory, and gustatory systems, it also has significant roles in motor activity, emotion, memory, arousal, and other sensorimotor association functions. Anatomically, the thalamus lies deep within the brain, adjacent to the midline third ventricle.
What causes damage to the thalamus?
The following is an extensive list of potential thalamic stroke risk factors:
- Extremely high blood pressure
- Restricted blood flow to the brain
- Restricted oxygen levels in the brain
- High quantities of protein buildup in the brain
- Head injuries causing an abundance of bleeding in the brain tissues, which can lead to embolism
- Aneurysms
What senses does the thalamus control?
The function of the thalamus is to regulate the body's voluntary motor control, consciousness and its sleep/wake cycle. It also regulates the senses of sight, sound, taste, touch and the sense of where the person's body is in space. The thalamus decides which signals from the ears, eyes, mouth and skin to relay to its area in the cerebral cortex. The thalamus doesn't relay information about ...
What happens if the thalamus is damaged?
Treating Thalamic Brain Injury
- Physical Therapy. If your brain injury damaged your thalamus, you might experience problems coordinating movements — a condition called apraxia.
- Sensory Reeducation Exercises. You can also treat sensory issues by rewiring the brain. ...
- Speech and Cognitive Therapy. ...
- Deep Brain Stimulation. ...
See more
What does thalamus do in the brain?
The thalamus is a mostly gray matter structure of the diencephalon that has many essential roles in human physiology. The thalamus is composed of different nuclei that each serve a unique role, ranging from relaying sensory and motor signals, as well as regulation of consciousness and alertness.
What is the function of the thalamus in the brain quizlet?
Functions: The thalamus receives sensory information from other areas of the nervous system and sends this information to the cerebral cortex. The thalamus is also important for processing information related to movement.
What are the major functions of the thalamus and hypothalamus quizlet?
The thalamus, as part of the reticular activating system, will arouse you from sleep. The hypothalamus regulates many body functions including, hunger, thirst, satiety, circadian rhythms, body temperature, and sexual responses.
Does the thalamus secrete melatonin?
The thalamus has a strong nonphotic influence on sleep, circadian rhythmicity, pineal melatonin production, and secretion. The opening of the sleep gate for nonrapid eye movement sleep is a thalamic function but it is assisted by melatonin which acts by promoting spindle formation.
What is the thalamus quizlet?
Thalamus. the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla.
What is the function of hypothalamus quizlet?
Hypothalamus uses a set-point to regulate the body's systems including: electrolyte and fluid balance, blood pressure, body temperature, body weight.
What is the function of the thalamus The hypothalamus the cerebellum?
A major role of the thalamus is to support the motor and language system. Damage to the thalamus can lead to permanent coma. The important function of hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. It also secretes neurohormones.
Which part of the brain controls the five senses?
Parietal lobe It figures out the messages you receive from the five senses of sight, touch, smell, hearing and taste. This part of the brain tells you what is part of the body and what is part of the outside world.
What is Thalamus?
The thalamus may be a small structure within the brain located just above the brainstem between the cerebral mantle and therefore the midbrain has extensive nerve connections to both. The main and primary function of the thalamus is to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral mantle. It also aids in the regulation of sleep, alertness, and wakefulness.
Where is the thalamus located?
The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter that is located in the forebrain and is superior to the midbrain. It is also near the center of the brain, where the nerve fibers project out to the cerebral cortex in all directions. The medial surface of the thalamus constitutes the upper part of the lateral wall of the third ventricle ...
What is the function of the diencephalon?
Thalamus function is to act as a relay centre in between the subcortical areas and the cerebral cortex.
What is the medial surface of the thalamus?
The medial surface of the thalamus constitutes the upper part of the lateral wall of the third ventricle and is connected to the surface that is corresponding to the opposite thalamus by a flattened gray band, the interthalamic adhesion. The lateral part of the thalamus consists of the pulvinar, the lateral nuclei, ...
What is the lateral part of the thalamus?
The lateral part of the thalamus consists of the pulvinar, the lateral nuclei, and the medial and lateral geniculate nuclei. These are the newest part of the thalamus phylogenetically. There are areas of substantia alba within the thalamus including the stratum zonale that covers the dorsal surface, and therefore the external and internal medullary lamina. The external lamina covers the lateral surface and the internal lamina helps to divide the nuclei into anterior, medial, and lateral groups.
What is the brain's function?
It also aids in the regulation of sleep, alertness, and wakefulness. The brain consists of the ventricles or fluid-filled spaces. The thalamus surrounds the third ventricle. It is a subdivision of a part of the brain called the diencephalon and is one of the most important structures derived from the diencephalon during embryonic development.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the sensory information relay?
The thalamus is believed to process both the sensory information as well as a relay of each of the primary sensory relay areas that receive strong feedback connections from the cerebral cortex. Similarly, the medial geniculate nucleus acts as a key auditory relay between the center of the midbrain and therefore the primary auditory area.
What is the function of the thalamus?
The thalamus is involved in several cognitive functions, such as serving as a central hub to relay sensory information to the brain, regulating sleep and consciousness, and the regulation of anger and aggression.
How does the thalamus stimulate the brain?
In sense, stimulating the thalamus “supercharges” the connections between the thalamus and other parts of the brain , making them work faster and more efficiently. ADVERTISEMENT.
What is the role of the thalamus in sleep?
When asleep, the thalamus suppresses the relay of information to the sensory-motor cortex through a process known as GABA-mediated inhibition.
Why was the thalamos named after Galen?
Galen named the organ thalamos after the Greek word for “storeroom” as he believed that the thalamus contained the vital spirits that traveled down the optic nerve to the eye and allowed for sight. The connection between the thalamus and the sense of sight remained for centuries, as is evident in the French name for the region “couche optique” ...
What is the thalamus?
“The thalamus is thus a critical interface between information traveling from the cortex to the motor centers, and from the senses back to the cortex, and is therefore involved in many aspects of the initiation and control of movement.”. — Mark Plumb. The thalamus is also thought to play an important role in the regulation ...
Which part of the brain relays information from the retina to the right area?
Although he got specific details wrong, it is true that the thalamus plays a role in relaying the contents of vision to the right area. Information from the retina is sent to the thalamus, specifically the lateral geniculate nucleus, which then relays that information to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe.
Which part of the brain relays sensory information?
Information from sensory systems is sent to the thalamus, then the specific thalamic nuclei relay that signal to the appropriate area of the brain. For example, the medial geniculate nucleus plays a role in relaying auditory information to the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe, while the ventral posterior nucleus relays somatosensory information ...
What is the function of the thalamus?
The primary function of the thalamus is to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex.
Where is the thalamus located?
The thalamus lies at the top of the brain stem near the center of the brain, from where nerve fibers project out towards the cerebral cortex. The thalamus is divided into two prominent bulb-shaped masses of around 5.7 cm in length and positioned symmetrically on each side of the third ventricle. The thalamus is supplied with blood by four branches ...
What are the two regions of the brain?
Brain regions. Also located in the diencephalon are the epithalamus and the perithalamus, which contain regions called the zona incerta and the reticulate nucleus. These are distinct from the thalamus proper.
Which artery supplies the thalamus with blood?
The thalamus is supplied with blood by four branches of the posterior cerebral artery, namely the polar artery, paramedian thalamic-subthalamic arteries, thalamogeniculate arteries and the posterior choroidal arteries. Within the thalamus lie myelinated nerve fibers called lamellae that separate the structure into individual parts.
What are the two parts of the thalamus?
Distinct groups of neurons make up other parts such as the periventricular, the nucleus limitans, and the intralaminar elements collectively called the allothalamus.
Which part of the brain surrounds the third ventricle?
The thalamus surrounds the third ventricle. It is a subdivision of part of the brain called the diencephalon and is one of the largest structures derived from the diencephalon during embryonic development.
What is the function of the thalamus?
The thalamus is composed of different nuclei that each serve a unique role, ranging from relaying sensory and motor signals, as well as regulation of consciousness and alertness. Clinically, there are only a few conditions related to thalamic damage and dysfunction. Most of these conditions are rare, but some of the more common conditions have significant anatomical changes that are visible with neuroimaging. Surgical interventions of the thalamus in the past have had limitations, but currently, this field is evolving due to increased accessibility through the advancement of microsurgical techniques and improved neuroimaging.
What is the role of the thalamus in the sensory system?
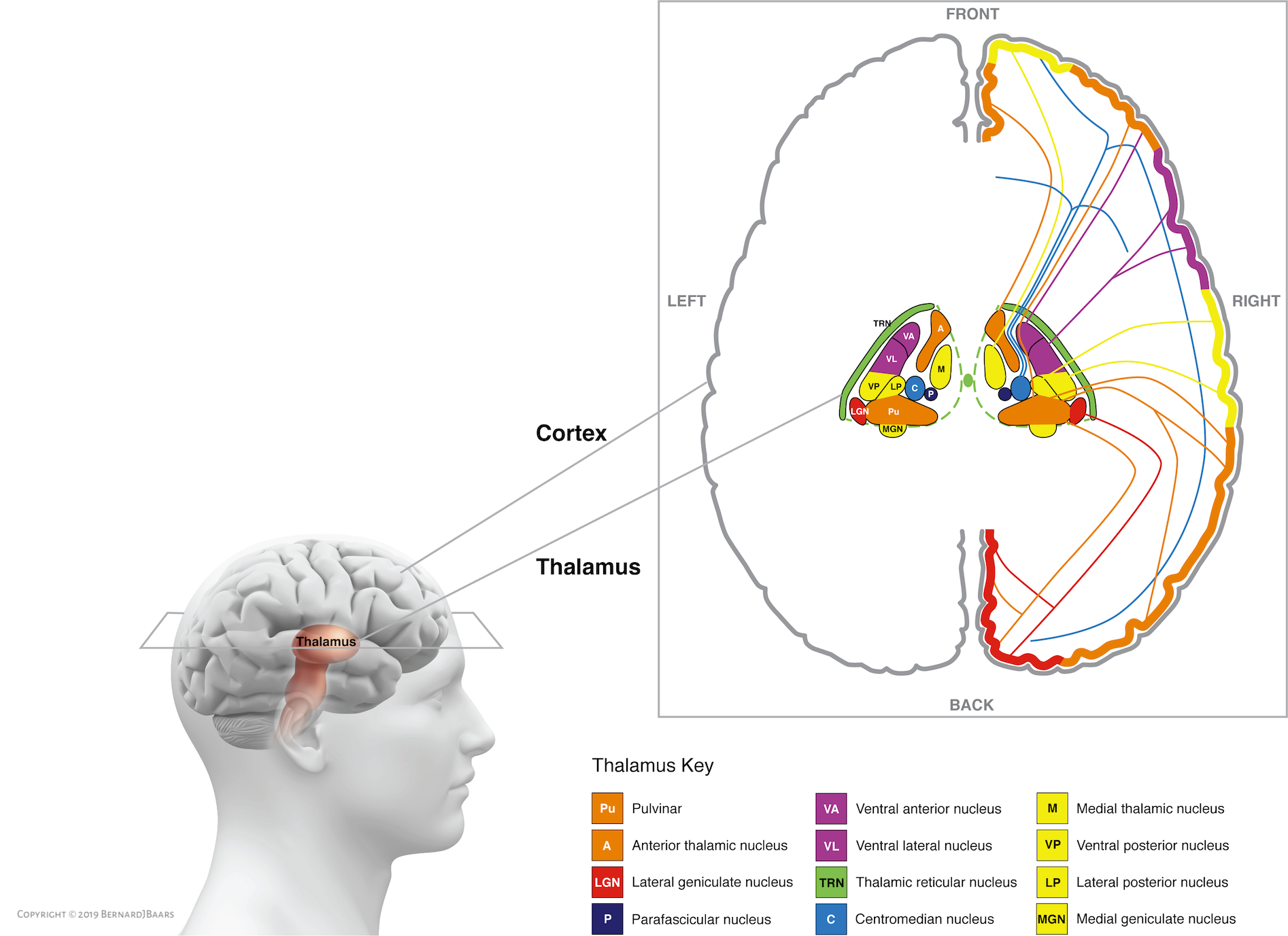
Generally, the thalamus acts as a relay station filtering information between the brain and body. Except for olfaction, every sensory system has a thalamic nucleus that receives, processes, and sends information to an associated cortical area. The lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus receives visual sensory information from the retina to route to the visual cortex of the occipital lobe. The medial geniculate nucleus receives auditory sensory information from inferior colliculus and projects it to the primary auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. The ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus is subdivided further by three. The spinothalamic tract is the sensory pathway for pain, temperature and crude touch that originates in the spinal cord and feeds into the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus for further processing, while the ventral posteromedial nucleus receives sensory information from the trigeminal nerve about the face. Lastly, the ventral intermediate nucleus has correlations with pathological tremors. [5]
Why are thalamic tumors so challenging?
Due to the deep location of the thalamus, thalamic tumors have historically been challenging to manage. Recently contemporary microsurgical techniques and advances in neuroimaging have resulted in some improvement in outcomes of resections involving the thalamus. [9]
What is the ictus of epilepsy?
The reticular thalamic nucleus, a pacemaker zone for rhythmic cortical activity, might be the ictus for generalized spike-wave, as seen in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. [14]
How many functional components does the thalamus have?
Functionally, the thalamus divides into five major functional components as[6]:
What is the thalamus made of?
The thalamus is made up of a series of nuclei which are responsible for the relay of the different sensory signals. These nuclei are formed mainly by neurons of excitatory and inhibitory nature. The thalamocortical neurons receive sensory or motor information from the rest of the body and present selected information via nerve fibers (thalamocortical radiations) to the cerebral cortex. The thalamus also has connections with the hippocampus, mammillary bodies, and fornix via the mammillothalamic tract.[2] The connection of limbic system structures to the anterior nuclei of the thalamus allows the thalamus to be involved in learning and episodic memory.[3] The thalamus is also involved in the regulation of sleep and wakefulness. [4]
Where is the thalamus located?
The thalamus is a paired gray matter structure of the diencephalon located near the center of the brain. It is above the midbrain or mesencephalon, allowing for nerve fiber connections to the cerebral cortex in all directions — each thalamus connects to the other via the interthalamic adhesion. The thalamus forms the upper and lateral walls of the third ventricle while the dorsal surface is part of the floor of the body of the lateral ventricle. Laterally, the thalamus limits with the posterior arm of the internal capsule. Anterolaterally, it limits with the head of the caudate and ventral nucleus with the subthalamus and hypothalamus.
What is the purpose of the thalamus?
The thalamus is made up of different types of nuclei, each of which serve a unique purpose, from relaying sensory and motor signals to the regulation of consciousness and alertness.
Why is the thalamus important for sleep?
Due to the thalamus being important for generating normal sleep thalamocortical rhythms, sleep disorders may result from damage such as insomnia. Language deficits because of thalamic damage, known as thalamic aphasia, can result in difficulties with lexical semantics.
What is the difference between the thalamus and the cerebral cortex?
Whereas the connections between the thalamus and the cerebral cortex are ipsilateral, meaning they communicate on the same side of the brain.
Why does my thalamus feel tingly after a stroke?
Thalamic pain syndrome can occur when there are disturbances in one of the pathways of the thalamus which affects the sensation of temperature following a stroke. This can result in tingling or burning pain, as well as discomfort with temperature changes.
What is the outer covering of the thalamus?
Reticular nucleus. The reticular nucleus forms a sheet that makes the outer covering of the thalamus and can influence the activity of other nuclei within the thalamus. The reticular nucleus receives input from the cerebral cortex as well as the dorsal thalamic nuclei.
What is the thalamus made of?
The thalamus is mostly comprised of grey matter but is also surrounded by two layers of white matter. They are oval shaped in appearance, almost looking like eggs, with two protuberances on the surface. One of these is known as the medial geniculate bodies, which are important for the processing of auditory information.
What are the functions of the brain?
Below are a list of some of the associated functions: 1 Contributions to perception 2 Relaying motor information 3 Relaying sensory information 4 Role in memory 5 Alertness and attention 6 Consciousness and awareness 7 Role in cognition
What is the function of the thalamus?
The thalamus relays and integrates a myriad of motor and sensory impulses between the higher centres of the brain and the peripheries. The gross structure, anatomical relationships, nuclear composition, some neuronal tracts that terminate at the thalamus and its blood supply will be discussed in this article.
How does the left thalamus communicate with the right thalamus?
The left thalamus communicates with the right thalamus by way of the interthalamic adhesion. Thalamus and related structures (superior view) The overall appearance of the thalamus may seem unremarkable with the exception of two protuberances on the posteroventral surface.
What is the central hub of the nervous system?
The thalamus is ideally situated at the core of the diencephalon, deep to the cerebral cortices and conveniently acts as the central hub. The thalamus relays and integrates ...
What are the three parts of the thalamus?
As a result of the location of the internal medullary lamina, each thalamus is divided into roughly three main parts: the anterior, medial and lateral thalamus . The anterior part lies between the short limbs of the internal medullary lamina, while the medial and lateral parts lie on the respective side of the main stem of the “Y”. The left thalamus communicates with the right thalamus by way of the interthalamic adhesion.
Where are the lateral dorsal nuclei located?
The lateral dorsal nucleus, lateral posterior nucleus and the pulvinar are found on the upper level of the bus (dorsal surface of the thalamus); whereas the ventral anterior, ventral lateral and the subdivisions of the ventral posterior nuclei are found on the lower level of the bus (ventral surface of the thalamus).
How many nuclei are there in the thalamus?
In the medial segment of the thalamus, there are three nuclei. The median nucleus is the most medial of the three structures. The medial dorsal nucleus is superior to the medial nucleus, but both are lateral to the median nucleus and medial to the internal medullary lamina.
Which part of the thalamus is narrowest?
It is narrowest at the anterior end and widest at the posterior part. The thalami are made up of grey matter that is partitioned by a “Y” shaped white matter structure known as the internal medullary lamina.
Where is the thalamus located?
The thalamus is located in the forebrain near the junction with the midbrain , the brainstem, and the hypothalamus. It exhibits midline symmetry, and its left and right sectors correspond with left and right hemispheres of the brain. On its medial surface, the thalamus forms the upper part of the lateral wall of the third ventricle.
What are the sensory nuclei in the thalamus?
Sensory relay nuclei: The thalamus's sensory relay nuclei include the medial geniculate nucleus, the ventral posterior nucleus, the lateral geniculate body, and the medial geniculate body. These nuclei relay signals from areas such as the inferior colliculus of the midbrain and send them to processing centers such as the primary visual cortex ...
What are the different types of thalamic nuclei?
3 Types of Thalamic Nuclei 1 Sensory relay nuclei: The thalamus's sensory relay nuclei include the medial geniculate nucleus, the ventral posterior nucleus, the lateral geniculate body, and the medial geniculate body. These nuclei relay signals from areas such as the inferior colliculus of the midbrain and send them to processing centers such as the primary visual cortex or the primary auditory cortex. 2 Association nuclei: Unlike sensory relay nuclei, which process signals from the midbrain and spinal column, association nuclei received their signals from specific regions of the cerebral cortex. They redirect these signals back to a more generalized area of the cerebral cortex, where they may be processed in a more general, abstract sense. 3 Non-specific nuclei: Some thalamic nuclei, such as the midline thalamic nuclei and the intralaminar nuclei, seem to regulate consciousness and alertness. Thalamic lesions or thalamic strokes can greatly impair alertness. Severe damage to the thalamus can ultimately send the body into a permanent coma.
What are the subregions of the thalamus?
Subregions of the thalamus include the eptithalamus, the ventral thalamus, and the subthalamic thalamus. Much like the cerebral cortex to which it connects, the thalamus consists primarily of gray matter. However, layers of white matter can be found on the external medullary laminae, the internal medullary laminae, ...
Which part of the brain is responsible for sensory processing?
The thalamus relays sensory signals from the spinal cord and brainstem to the cerebral cortex, where they undergo higher-order mental processing. From vision to hearing to touch to taste, nearly all sensory impulses pass through the thalamus. Subregions of the thalamus include the eptithalamus, the ventral thalamus, and the subthalamic thalamus.
What part of the brain is responsible for processing stimuli?
When stimuli reach a part of the brain called the diencephalon, they are processed by the thalamus. Mindfulness expert Jon Kabat-Zinn teaches you how to incorporate meditation into your everyday life to improve your health and happiness.
Where does blood come from in the thalamus?
Blood supply to the thalamus comes from various branches of the posterior cerebral artery. These include the posterior communicating artery, along with paramedian thalamic-subthalamic arteries, inferolateral (thalamogeniculate) arteries, posterior lateral choroidal arteries, and posterior medial choroidal arteries.
What is the role of the thalamus in the body?
The thalamus also plays a significant role in sensory perception and movement. Certain areas of the thalamus are dedicated to specific parts of the body and where the sensations are meant to travel toward the cerebral cortex.
Why is it important to understand the anatomy of the thalamus?
Understanding the anatomy of the thalamus will help you in comprehending the specific regulatory mechanisms of this structure.
What are the parts of the thalamus?
The anterior, mediodorsal, and centromedian nuclei of the thalamus are the primary parts that play a role in this emotional regulation: 1 Anterior: involved in the storage of memory and emotion. 2 Mediodorsal: responsible for motivation, enthusiasm, and emotions related to inspiration. 3 Centromedian: governs the emotional component of pain.
Why is the thalamus important?
The thalamus is extremely important to the regulation of the human nervous system. It is the center of information processing, and is what maintains consciousness, organizes subconscious information and regulates the very survival of the human being. There is still much to be learned about this structure and it poses quite the challenge due to its countless neuronal connections to structures within the central nervous system, limbic system, and more.
How many ends does the thalamus have?
The thalamus has two ends, the anterior and posterior poles, and four surfaces: medial, lateral, superior, and inferior. Nuclei in a given pole or surface regulate specific functions or processing of sensory information and maintain particular connections with parts of the nervous and limbic system. Understanding the anatomy of the thalamus will ...
What is the limbic system?
Limbic System. Miscellaneous Functions of the Thalamus. The thalamus, or the dorsal and ventral thalamus collectively, are two oval structures made up of gray matter at the base of the cerebrum. This structure’s primary function is as a relay center through which sensory nerves transmit signals from the spinal cord and brainstem on the way to ...
What is the lateral surface of the thalamus?
The lateral surface of the thalamus is covered by a layer of myelinated fibers called the external medullary lamina which separates the lateral surface from the reticular nuclei.

What Is Thalamus?
- The thalamus may be a small structure within the brain located just above the brainstem between the cerebral mantle and therefore the midbrain has extensive nerve connections to both. The main and primary function of the thalamus is to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral mantle. It also aids in the regulation of sleep, alertness, and wa...
Thalamus Structure
- The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter that is located in the forebrain and is superior to the midbrain. It is also near the center of the brain, where the nerve fibers project out to the cerebral cortex in all directions. The medial surface of the thalamus constitutes the upper part of the lateral wall of the third ventricle and is connected to the surface that is corresponding to the …
Anatomy
- The topography or position of the thalamus, as well as its structure and nucleus, input and output fibres, and blood supply.
Location
- The diencephalon includes the thalamus. It is found immediately above the midbrain, deep in the forebrain. On each side of the third ventricle, there is the thalamus. Its anterior section creates the interventricular foramen's posterior boundary. The pulvinar structure is formed when the posterior end of the brain is extended. The superior colliculus is overshadowed by the thalamic pulvinar. T…
What Is The Function of The Thalamus?
- The thalamus performs multiple functions, generally, they are believed to act as a relay station, or hub, and act as relaying information between different subcortical areas and the cerebral cortex. Every sensory system particularly includes a thalamic nucleus that receives sensory signals and sends them to the associated primary cortical area. For example, in the sensory system, the inp…
Thalamus and Injury
- The thalamus is involved in a wide range of important tasks. The consequences of thalamus injury differ from one person to the next. 1. The following are some of the most common thalamic injuries adverse effects: 2. Tingling, numbness, hypersensitivity, and pain are examples of sensory disorders. 3. Light sensitivity or vision loss 4. Impaired motor skills 5. Tremors 6. Attention deficit…
Physiology
- Between the cortex and the spinal cord, as well as other parts of the lower brain, the thalamus occupies a key location. As a result, it serves as a crucial relay point for messages travelling from the brain's lower to higher levels. Before reaching the brain's higher regions, almost all sensory information passes through the thalamus. Thalamus not only relays or passes sensory informati…