
On the basis of their function, meristems have been classified into three types: It is the outermost layer of the young growing region which develops to form epidermal tissue system. It is composed of narrow, elongated, prosenchymatous, meristematic cells that gives rise to the vascular tissues system.
Full Answer
What kinds of tissue can a meristem cell become?
They can develop to become one of three primary meristems: the protoderm, ground meristem, or procambium. The protoderm will go on to form the epidermal tissues of the plant; the ground meristem will form the cortext and pith of the plant; and the procambium will become xylem and phloem, the vascular tissues of the plant.
Are undifferentiated cells found in meristematic tissue?
The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells ( meristematic cells) capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until a time when they get differentiated and then lose the ability to divide.
What happens to the cells formed by meristematic tissue?
The characteristics of meristematic tissue are as follows:
- The cells of these tissues are commonly called meristems.
- The meristematic tissue has the quality of self-renewal. ...
- They have very small and few vacuoles.
- The meristematic tissue is living and thin-walled.
- The protoplasm of the cells is very dense.
- The meristematic tissues heal the wounds of an injured plant.
What are the five types of connective tissue?
These are:
- Areolar Connective Tissue
- Adipose Tissue
- Dense Irregular Tissue
- Dense Regular Tissue
- Cartilages
- Bones
- Blood
What are the functions of different types of meristematic tissue?
The zone where these cells exist is known as meristem. The cells of the meristematic tissue divide actively to form specialized structures such as buds of leaves and flowers, tips of roots and shoots, etc. These cells help to increase the length and girth of the plant.
What are the three function of meristematic tissue?
Primary meristematic tissue helps the plant increase in length or vertical growth, meaning it helps the plant grow up toward the sun and down into the soil. Secondary meristematic tissue helps the plant increase the girth or lateral growth of its stems, branches, and roots.
What is the function of primary meristematic tissue?
A primary meristem is a type of meristematic tissue that is responsible for the primary growth. Primary growth is a growth in length. It is responsible for the increase in the height of a plant as opposed to the increase in diameter, which is the role of secondary growth.
What is the function of lateral meristem tissue?
Plants grow through the help of a tissue called a meristem. The meristem contains cells whose sole purpose is to divide so that the plant gets bigger. Apical meristems allow the plant to grow up and down, and lateral meristem allows the plant to grow out, or laterally.
What is primary meristem and secondary meristem?
Definition. Primary meristem refers to a type of meristem involved in the primary growth and thus gives rise to the primary tissues of the plant while secondary meristem refers to a type of meristem involved in the secondary growth and thus gives rise to the secondary tissues of the plant.
What are meristem 2 give the main function of meristem?
Meristematic tissue: Meristematic tissues are responsible for plant growth. They are present at the tips of roots,stem and branches. The cells present in these tissues constantly divide to produce new cells. The cells actively divide to produce new cells.
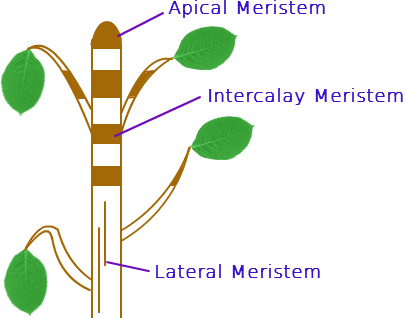
What is the difference between apical lateral and intercalary meristem?
The apical meristem is present in the apex of stem and roots. The lateral meristem is present in the sides of stem and roots and the intercalary meristem is present between the tip and the base of the stem and leaves. The intercalary meristem is involved in the increase of length between nodes.
What is secondary meristematic tissue?
A secondary meristem is a type of meristematic tissue that is responsible for the secondary growth in plants, i.e. growth in girth or thickness. It is opposed to the primary meristem that is involved in the primary growth, i.e. growth in height or length.
What is the major function of plant meristems quizlet?
What is the major function of plant meristems? To grow.
What is the function of apical meristem Class 9?
Apical meristem: These meristems are present at the tip regions of root, shoot, and leaves. They are the active regions in the cell division which helps in the growth and the elongation of root and shoot. It gives rise to new leaves and hence these are referred as primary tissues in the plant growth.
What is the function of parenchyma?
Parenchyma cells are essential for activities like photosynthesis, storage, secretion, assimilation, respiration, excretion and radial transport of water and solute.
What is secondary or lateral meristem?
Secondary, or lateral, meristems, which are found in all woody plants and in some herbaceous ones, consist of the vascular cambium and the cork cambium. They produce secondary tissues from a ring of vascular cambium in stems and roots.
What are the characteristics of meristematic tissues?
The main characteristics of cells of meristematic tissues are: (iii) The cells contain a dense protoplasm and conspicuous nuclei. (iv) The cells are spherical, oval or polygonal in shape. (v) They do not store reserve food material and are in an active state of metabolism.
What is a meristem?
A group of young meristematic cells of a growing organ. It is the early embryonic meristem from which other advanced meristems are derived. In a plant, it occupies a small area at the tip of stem and root. It further divides to form primary meristem.
What is the Tunica corpus theory?
Tunica-corpus theory: ADVERTISEMENTS: This theory was proposed by Schmidt (1924). According to this theory, mass of dividing cells are of two types: Tunica, the outer consisting of one position of different meristems or more peripheral layers of cells, forming the outer region and Corpus, the central undifferentiated multilayered mass of cell. ...
Which cell theory is based on the root and shoot apices?
Histogen cell theory: This theory was given by Hanstein (1868). According to this theory root and shoot apices consists of the central or inner mass called Plerome surrounded by the middle region composed of isodiametric cells called periblem and the outermost uniseriate layer of Dermatogen.
Introduction
Meristematic tissue is any plant tissue that consists of undifferentiated cells that can undergo rapid cell division. These rapidly growing tissues are found at the tips or apices of plant organs. They are responsible for producing new cells and tissues required by growing plants, such as buds, roots, leaves, and flowers.
Types of Meristematic Tissue
Meristematic tissues are characterized by localized regions of high cell division rates. In vascular plants, they include:
What are Induced Meristematic Tissues?
Induced meristematic tissues are plant organs that have meristematic cells. These tissues are formed through artificial treatment. The new tissues formed by this treatment are not genetically identical to the original tissue. Examples of Induced meristematic procedures are:
Apical Dominance Explained
Apical dominance is a form of plant control in which the shoot tip determines the growth of shoots and roots.
Summary
Meristematic tissues are the plant structures that have cells that can divide to produce more plant parts. They are found in the roots, stems, and leaves of plants. These tissues allow for growth and adaptation to respond to changes in an environment or other stimuli such as damage caused by pests.
What is secondary meristem?
Secondary meristem: Origin: from primary meristem. It is developed later on life. It give rises to secondary permanent tissue. 2. Types of Meristematic tissue on the basis of position: i. Apical meristem. ii.
What is the lateral meristem?
Lateral Meristem: Position: present on lateral side of stem and root. It helps in increases the diameter or thickness of plants. Example: vascular cambium (primary meristem) and cork cambium (secondary meristem) 3. Types of meristematic tissue on the basis of function: i. Protoderm.
What is a group of cells that has power of continuous division?
Meristematic tissue is a group of cells that has power of continuous division. Meristematic tissue is commonly called as meristems.
What is Meristem?
Meristems in plants are the center of active mitotic cell division where plant growth occurs. Mitotic cell division happens when a parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Meristematic tissues are groups of densely packed cells with thin cell walls.
Meristematic Function
Meristem comes from the Greek word meristos, which means divisible. The main function of meristematic tissue is to begin the process of new cell growth. Plant meristematic tissue is also responsible for the formation of post-embryonic organs (organogenesis). Meristematic cells are often compared to stem cells in animals.
Meristematic Tissue
The role and function of meristematic tissue are dependent on its location on the plant.
Where is the lateral meristem located?
Lateral Meristem. It is located in the stems and roots on the lateral side. It increases the thickness of the plant. Vascular cambium and cork cambium are the two lateral meristems. These divide preclinically or radially and give rise to secondary permanent tissues.
Which zone of the apical meristem contains active dividing cells?
Various cell divisions facilitate the growth of the cells in the roots and shoots and help in cellular enlargement. Apical meristem is divided into-promeristem zone, which contains actively dividing cells, and the meristematic zone, which contains protoderm, procambium and ground meristem.
What is the term for the building blocks of a plant structure?
Carl Wilhelm von Nägeli coined the term “meristem.”. Meristematic tissue contains undifferentiated cells, which are the building blocks of the specialized plant structures. Meristematic tissues contain living cells with varied shapes. They possess a large nucleus devoid of the vacuole. The cells have no intercellular space.
Which tissue has the quality of self-renewal?
The meristematic tissue has the quality of self-renewal. Every time the cell divides, one cell remains identical to the parent cell, and the others form specialized structures. They have very small and few vacuoles. The meristematic tissue is living and thin-walled. The protoplasm of the cells is very dense.
What is the zone of the cell that divides to form specialized structures?
The cells have no intercellular space. The zone where these cells exist is known as meristem. The cells of the meristematic tissue divide actively to form specialized structures such as buds of leaves and flowers, tips of roots and shoots, etc. These cells help to increase the length and girth of the plant. Let us have a detailed look ...
What is the protoplasm of a plant?
The protoplasm of the cells is very dense. The meristematic tissues heal the wounds of an injured plant. The cells of the meristematic tissue are young and immature. They do not store food. They exhibit a very high metabolic activity. They possess a single, large and prominent nucleus.

Meristematic Tissue Characteristics
Meristematic Tissue Classification
Classification Based on Origin
Classification Based on Position
Classification Based on Functions
- The meristematic tissue is classified into the following three types on the basis of their functions: i) Protoderm: It forms the outermost portion of the primary meristem found at the apex of the stem and root. It develops into the epidermis. ii) Procambium: It develops into primary vascular tissues. It forms the isolated strands of elongated cells...
Meristematic Tissue Functions
Summary
FAQs on Meristematic Tissues