What is the function of trachea in insects?
In insects, a few land arachnids, and myriapods, the trachea is an elaborate system of small, branching tubes that carry oxygen to individual body cells; in most land vertebrates, the trachea is the windpipe, which conveys air from the larynx to the two main bronchi, with the lungs and their air sacs as the ultimate ...
Where is the trachea on a grasshopper?
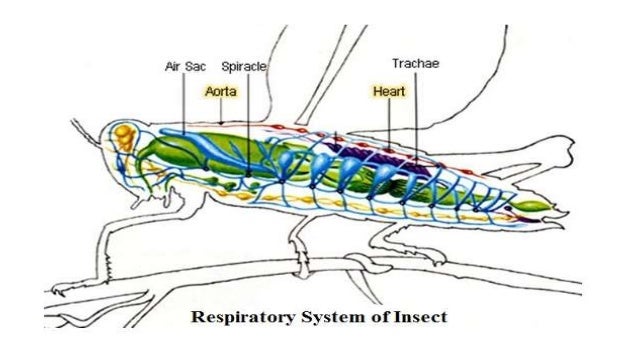
The grasshopper abdomen has longitudinal tracheae that run along the midgut, heart, nerve cord, and lateral body wall. Transverse tracheae run from each spiracle to the longitudinal tracheae. Dorsal air sacs attach near each spiracle.
What is the function of the spiracles in a grasshopper and where are they located?
Air enters the insect's body through valve-like openings in the exoskeleton. These openings (called spiracles) are located laterally along the thorax and abdomen of most insects — usually one pair of spiracles per body segment.
What is the function of trachea in arthropods?
Air enters the insect's body through the spiracle and enters the trachea. The trachea are tubes that are strengthened by rings of cuticle. From the trachea the air moves into smaller tubes called tracheoles that spread throughout the body of the insect and allow oxygen to be delivered to the various parts of the body.
What helps grasshopper to breathe?
Instead of nostrils, insects breathe through openings in the thorax and abdomen called spiracles.
What can the trachea also be called and its function?
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi.
What are the five 5 parts of a grasshopper and its function?
The grasshopper body is divided into 3 basic components: the head, which bears the sen- sory structures such as eyes, antennae, and mouthparts; the thorax, which bears the structures associated with movement, namely the legs and wings; and the abdomen, which bears the digestive and reproductive structures.
What are spiracles and trachea?
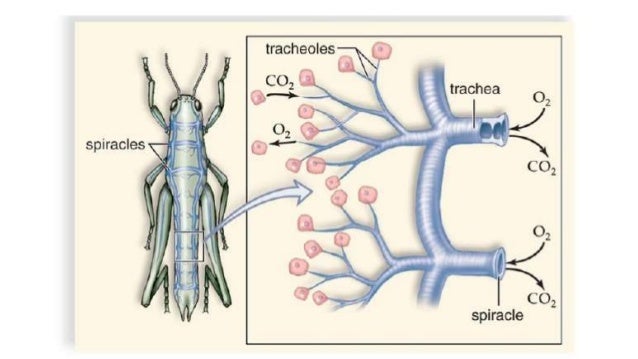
Air enters the respiratory systems of insects through a series of external openings called spiracles. These external openings, which act as muscular valves in some insects, lead to the internal respiratory system, a densely networked array of tubes called tracheae.
Which animals breathe through trachea?
What Animals Use a Tracheal System to Breathe? Insects, centipedes and arachnids use their tracheal system to breathe.
Do grasshoppers have tracheae?
Grasshoppers have eighteen spiracles, nine to a side. On each side, a longitudinal trunk (the primary trachea) connects all ipsilateral spiracles.
What is a trachea?
(TRAY-kee-uh) The airway that leads from the larynx (voice box) to the bronchi (large airways that lead to the lungs). Also called windpipe. Enlarge.
What is the function of trachea quizlet?
The tracheal is an armored tube that allows air to pass from the pharynx to the lungs. The bronchi are tubes that take air from the trachea into the lungs.
Where is the trachea located?
Where is the trachea located? Your trachea sits in your lower neck and upper chest, below your larynx. It is behind the notch at your lower throat, between the inside edges of your collarbones. In a diagram of your trachea and other respiratory organs, you can see the trachea between the top lobes of the lungs.
Where is the trachea located in insects?
Most insects respire through a system of tubes called tracheae that connect to the air via spiracles that can be actively opened or closed (1). Tracheal tubes form a complex network of gas-filled vessels that divide throughout the body segments, legs, and wings.
What is a trachea?
(TRAY-kee-uh) The airway that leads from the larynx (voice box) to the bronchi (large airways that lead to the lungs). Also called windpipe. Enlarge.
What are the five 5 parts of a grasshopper and its function?
The grasshopper body is divided into 3 basic components: the head, which bears the sen- sory structures such as eyes, antennae, and mouthparts; the thorax, which bears the structures associated with movement, namely the legs and wings; and the abdomen, which bears the digestive and reproductive structures.
What is grasshopper anatomy?
Grasshopper Anatomy. Grasshoppers are complex insects that have many similarities and differences in comparison to humans. Introduction to Grasshoppers: Grasshoppers are complex insects and have many specifics when it comes to their body systems and functions. Grasshoppers, like all insects, have a three part body of a head, thorax, and abdomen.
What are grasshoppers?
Introduction to Grasshoppers: Grasshoppers are complex insects and have many specifics when it comes to their body systems and functions. Grasshoppers, like all insects, have a three part body of a head, thorax, and abdomen. They also have compound eyes like other insects.
How do grasshoppers digest food?
The digestive system of a grasshopper starts off with the mandibles and maxillae for chewing their food much like our mouth and teeth that breaks down our food into little particles. After the chewing it goes to the salivary glands, to the esophagus, to the crop, to the gizzard, to the mid gut, to the gastric ceca, to the hind gut and then finally out the anus!#N#In the salivary glands food is mixed with saliva and transported from the esophagus to the crop where the food starts to grind. Then the chemical digestion takes place in the stomach and the gastric ceca digests bacteria. The mid gut and hind gut work to absorb the useful productes and solidify and abort the others. Humans have teeth to chew food and an esophagus where it travels down from. Food is absorbed and nutrients are taken out of the food and then aborted just like the process that grasshoppers undergo.
How many parts does a grasshopper have?
Grasshoppers have a three part body and a hard shell exoskeleton of chitin. Their three part body contains of a head, a thorax, and an abdomen. The exoskeleton is divided into section with flexible joints that allows movement more easily. The joints that the grasshoppers have can be compared to humans because they allow movement but our connect our bones while the grasshoppers needs connection of its three tagmata. That is because humans have an endoskeleton and outer covering is there to protect the organs we have inside.
Why are grasshoppers compared to humans?
The joints that the grasshoppers have can be compared to humans because they allow movement but our connect our bones while the grasshoppers needs connection of its three tagmata. That is because humans have an endoskeleton and outer covering is there to protect the organs we have inside.
Do grasshoppers have brains?
Grasshoppers are invertebrates without a backbone but they do have a brain, while humans are vertebrates with a backbone but also have a brain. Grasshopper eyes are compound and are more effective than the ones of humans. However, on their head they have antennae that feel and sense things.
How does air flow through grasshoppers?
The liquid seals in the tubing move to the right as air enters the spiracles in the thorax and is discharged through the spiracles in the abdomen. The rubber diaphragm seals the thorax from the abdomen.
What insects ventilate the trachea?
Large, active insects like grasshoppers, forcibly ventilate their tracheae. Contraction of muscles in the abdomen compresses the internal organs and forces air out of the tracheae. As the muscles relax, the abdomen springs back to its normal volume and air is drawn in. Large air sacs attached to portions of the main tracheal tubes increase the effectiveness of this bellowslike action.
What seals the thorax from the abdomen?
The rubber diaphragm seals the thorax from the abdomen. The one-way flow of air increases the efficiency of gas exchange as CO2-enriched air can be expelled without mingling with the incoming flow of fresh air. Gas Exchange in Aquatic Insects. Even aquatic insects use a tracheal system for gas exchange. Some, like mosquito larvae ("wigglers"), get ...
What controls the valves that enables the grasshopper to open and close them?
valves controlled by muscles that enables the grasshopper to open and close them;
How do aquatic insects get air?
Even aquatic insects use a tracheal system for gas exchange. Some, like mosquito larvae ("wigglers"), get their air by poking a breathing tube — connected to their tracheal system — through the water surface.
What is the system of air-filled tubes that exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between tissues called?
Insects, and some other invertebrates, exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between their tissues and the air by a system of air-filled tubes called tracheae. Tra cheae open to the outside through small holes called spiracles.
How big are tracheoles?
The branches penetrate to every part of the body. At their extreme ends, called tracheoles, they may be less than 1 µm in diameter. Every cell in the insect's body is adjacent to, or very close to, the end of a tracheole.
What is the lining of the trachea?
Lining the trachea are mucosal membranes comprised of epithelial cells, mucus-secreting goblet cells, and hair-like projections called cilia that move foreign particles up and out of the airway.
How big is the trachea?
The trachea is roughly 4 to 5 inches long and 1 inch in diameter. It starts just under the larynx (voice box) and runs down the center of the chest behind the sternum (breast bone) and in front of the esophagus. 1 . The trachea is connected to the larynx via a ring of cartilage known as the cricoid cartilage.
What is the trachea vulnerable to?
The trachea is vulnerable to infections, inflammation, and other stresses that can damage cells. This can lead to conditions like tracheal stenosis, in which the trachea narrows and restricts breathing, and tracheal cancer, an extremely rare form of cancer.
What is the function of lymphatic vessels in the trachea?
The lymphatic vessels help remove microbes on the surface of the wall of the trachea so they can be isolated and neutralized by the immune system. 3
How is the trachea connected to the larynx?
The trachea is connected to the larynx via a ring of cartilage known as the cricoid cartilage . As the trachea descends the chest, it is surrounded by 16 to 22 U-shaped rings of cartilage that hold the windpipe open like scaffolding, allowing the flow of air.
What is the posterior wall of the trachea?
The posterior wall of the trachea not covered by cartilage is composed of connective tissue and smooth muscle. The muscle will flex and expand when needed to change the diameter of the trachea. The trachea ends at the carina, a ridge of cartilage that separates and forms the junction into the bronchi.
Where are particles trapped in the airway?
Most particles that enter the airway are trapped in the thin layer of mucus on the trachea walls. These are then moved upwards toward the mouth by cilia, where they can be swallowed.
What are the features of a grasshopper?
The major features of an adult grasshopper's external structure are illustrated in Figure 37-3. The body of a grasshopper clearly shows three tagmata. The most anterior tagma, the head, bears the mouthparts. It also has a pair of unbranched antennae as well as simple and compound eyes.
What is the structure of the grasshopper's abdomen?
The segments in the most posterior tagma, the abdomen, are composed of upper and lower plates that are joined by a tough but flexible sheet of exoskeleton. The same flexible sheet also connects the segments to one another. The exoskeleton is covered by a waxy cuticle that is secreted by the cells of the epidermis. The rigid exoskeleton supports the grasshopper's body, and the cuticle retards the loss of body water. Both structures are adaptations for a terrestrial life.
How do grasshoppers get nutrients?
Nutrients and other materials are transported through the body of a grasshopper by an open circulatory system that is similar to that of the crayfish. Hemolymph flows through a large dorsal vessel called the aorta (ay-OHR-tuh), which is shown in Figure 37-5. The muscular heart, which is located in the abdomen and thorax, pumps the hemolymph forward through the aorta and into the part of the coelom nearest the head. The hemolymph then percolates through the coelom toward the abdomen and reenters the heart through small pores along its length.
What are grasshopper wings made of?
The wings are powered by muscles attached to the inside of the exoskeleton in the thorax. Note that insect wings develop as outgrowths of the thorax and are composed of exoskeleton material. Thus, they are not homologous to bird and bat wings, which develop from limb buds.
What are insect mouthparts used for?
Mouthparts are used for biting and chewing in grasshoppers (a), piercing and sucking in mosquitoes (b), and sponging and lapping in houseflies (c).
How do insects exchange oxygen?
However, insects exchange these gases with the environment through a complex network of air tubes called trachea. Trachea also serve this purpose in some spiders. In grasshoppers, air enters the tracheae through spiracles on the sides of the thorax and abdomen, as seen in Figures 37-3 and 37-5. The ends of the tracheae branch near the cells of the body and are filled with fluid. Oxygen diffuses into the cells from this fluid while carbon dioxide diffuses in the reverse direction. Air can be pumped in and out of the tracheae by the movements of the abdomen and wings.
What is the sound-sensing organ of the thorax?
Other nerves extend from the ganglia to the muscles and sensory structures in the thorax and abdomen. One such structure is a sound-sensing organ called the tympanum (TIM-puh-nuhm). The tympanum is a large, oval membrane that covers an air-filled cavity on each side of the first abdominal segment. Sounds cause the tympanum to vibrate, and the vibrations are detected by nerve cells that line the cavity. Tympana are also found in many other insects that use sound in communication, such as crickets and cicadas. In addition, sensory hairs that are similar to those of a crayfish are distributed over an insect's body. At the base of each hair is a nerve cell that is activated if the hair is touched or moved by vibration.