What is the function of the thymus quizlet?
the thymus aids in the production of lymphocytes, and it is the site of maturation for t cells.
What is the function of thymosin Class 11?
(c) Thymosins – Thymosin is secreted by the thymus gland. It plays a major role in protecting the body against infectious agents. It helps in the differentiation of T-lymphocytes and also promotes the reproduction of antibodies. Hence, it provides both cell-mediated and humoral immunity.
What is the function of thymosin and thymopoietin?
The thymus gland produces several hormones, including: Thymopoietin and thymulin: These hormones are involved in the process where T cells get turned into different types of disease fighters. Thymosin: This hormone boosts the immune system's response. Thymosin also stimulates hormones that control growth.3 days ago
What is the function of thyroxine?
Thyroxine plays a crucial role in heart and digestive function, metabolism, brain development, bone health, and muscle control. It affects almost all of the body's systems, which means proper thyroxine levels are vital for health.Jan 23, 2022
What is adrenal gland Class 10?
Adrenal glands, also known as suprarenal glands, are small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of both kidneys. Adrenal glands produce hormones that help regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress and other essential functions.
What is the meaning of thymosin?
Medical Definition of thymosin : a mixture of polypeptides isolated from the thymus also : any of these polypeptides.
What is thymosin required for quizlet?
- Thymosin is a hormone secreted by thymus for the stimulation of T-cells. Function: Aids with social bonding, sexual reproduction in both sexes, and during and after childbirth.
What is prolactin hormone function?
Prolactin is a hormone that's responsible for lactation, certain breast tissue development and milk production. Higher-than-normal levels of prolactin in your blood can cause certain symptoms, such as irregular periods, infertility and erectile dysfunction.Feb 15, 2022
What is the function of thymosin?
Of the thymosin peptide family, thymosin β4, is the most abundant member and is also expressed in many cell types. Thymosin β4 is the principal G-actin sequestering molecule in mammalian cells, playing an important role in the organization of the cytoskeleton. The structures of thymosins and the complex between thymosin β4 and actin are shown in Fig. 21.25.
What is the role of thymosins in cancer?
Thymosins may play a stronger future role in the diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of cancers. Tα1 plasma levels in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients are significantly lower than those observed in either benign patients or urothelial carcinoma (UC) patients, while ProTα levels were lower in UC patients relative to benign or RCC patients (Jou et al., 2013 ). Likewise, Tβ4 and Tβ10 expression levels correlate with cancers. Şahin et al. (2017) found that for gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors, Tβ4 overexpression correlated with high-risk groups. Theunissen et al. (2014) observed Tβ4 and Tβ10 reactivity in 30% and 96%, respectively, of hepatocellular carcinoma patients, and they noted that while cells undergoing stromal invasion had uniformly high levels of Tβ10, Tβ4 was completely absent.
What is thymosin 4?
Thymosin β4 (Tβ4) is a 43-amino acid signature motif peptide that defines the beta-thymosin (βT) family of proteins. βTs are intrinsically unstructured in their free states and undergo disorder-to-order transitions in carrying out their biological functions. This property poses challenges in determining their 3D structures, mainly favoring structural studies on the complexes formed between βTs and their interaction partners. One of the βTs’ primary binding partners is monomeric actin, a major component of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells. Tβ4’s role in this system is to maintain the highly concentrated pool of monomeric actin that can be accessed through profilin by actin filament nucleating machineries. Here, we give an account of the structures of βTs that have been illuminated by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and X-ray crystallography. NMR has been the method of choice for probing regions that have intrinsic conformational preference within the largely disordered βTs in their native states in solution. X-ray crystallography has demonstrated at atomic detail how βTs interact with actin. Detailed analysis of these structures highlights the disorder-to-order transition of Tβ4 in binding to actin and its isoform specificity.
Is thymosin a protein?
Thymosin, a protein hormone of the thymus gland, has been purified from bovine thymus tissue. Thymosin is an acidic protein, and is free of carbohydrate, lipid, and nucleotides. Based upon amino acid analyses, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and sedimentation equilibrium data, thymosin has a molecular weight of 12,000 ± 200.
Discovery
The discovery of thymosins in the mid 1960s emerged from investigations of the role of the thymus in development of the vertebrate immune system. Begun by Allan L.
Function and application
Thymosin produces GM-CSF (white blood cell stimulating factor) by stimulating keratinocytes in the epidermis.
Where is thymosin found?
It was originally found in thymus glands. Thymosin stimulates the development of disease fighting T- cells. Thymus gland does not function throughout the lifetime. White blood cells called lymphocytes which pass through the thymus are transformed into T cells.
Which gland produces thymosin?
Thymosin hormones are typically produced by the thymus gland and trigger the creation of T-cells, which are used by the immune system to fight disease.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
Hypothalamus releases ADH (also called as vasopressin) from neurohypophysis. It facilitates water reabsorption from the latter part of the tubule. It can also affect kidney function via its effects on blood vessels. This increases the blood pressure due to which GFR increases.
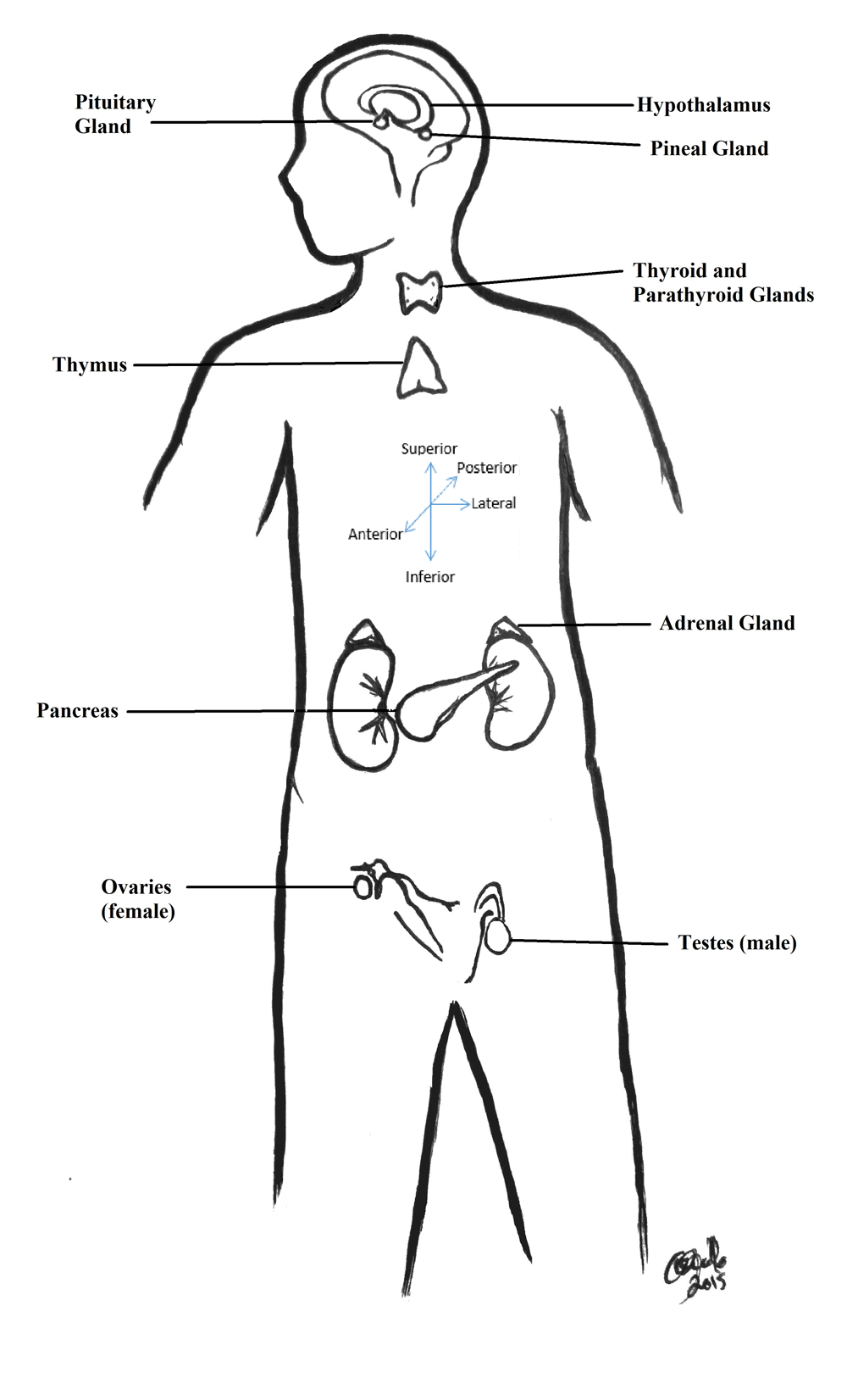
Where is the thymus gland located?
The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs , is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells. 484 views.
What is the purpose of the thymus gland?
The purpose of the thymus gland is to produce T-lymphocytes (or T-cells), the type of lymphocytes that fight against parasites, cancer cells and that help the immune system to recognize what is the body’s own cells and what is different.
What is the difference between B and T cells?
T cell - Wikipedia. Thymosin hormone was only necessary in the beginning of life to make a distinction between the T-cells and the B-cells. B-cells are lymphocytes that came from the bone marrow and were not further processed by thymosin into T-cells.
What is the thymus?
The thymus produces and secretes thymosin, a hormone necessary for T cell development and production. The thymus is special in that, unlike most organs, it is at its largest in children. Once you reach puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. 41 views · Answer requested by.