What does the trigeminal nerve do?
- The trigeminal nerves begin within four nuclei — or collections of nerve cell bodies — in your brain. ...
- These three sensory nuclei merge to become one sensory root near the pons, which is the largest, central part of your brainstem.
- This sensory root becomes the trigeminal ganglion as it leaves the brainstem on each side. ...
Is trigeminal neuralgia a serious condition?
Trigeminal neuralgia pain is exceptionally severe. Although the condition is not life-threatening, the intensity of the pain can be debilitating. Trigeminal neuralgia relief is possible: Medical and surgical treatments can bring the pain under control, especially when managed by an expert physician and surgeon.
What are the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve?
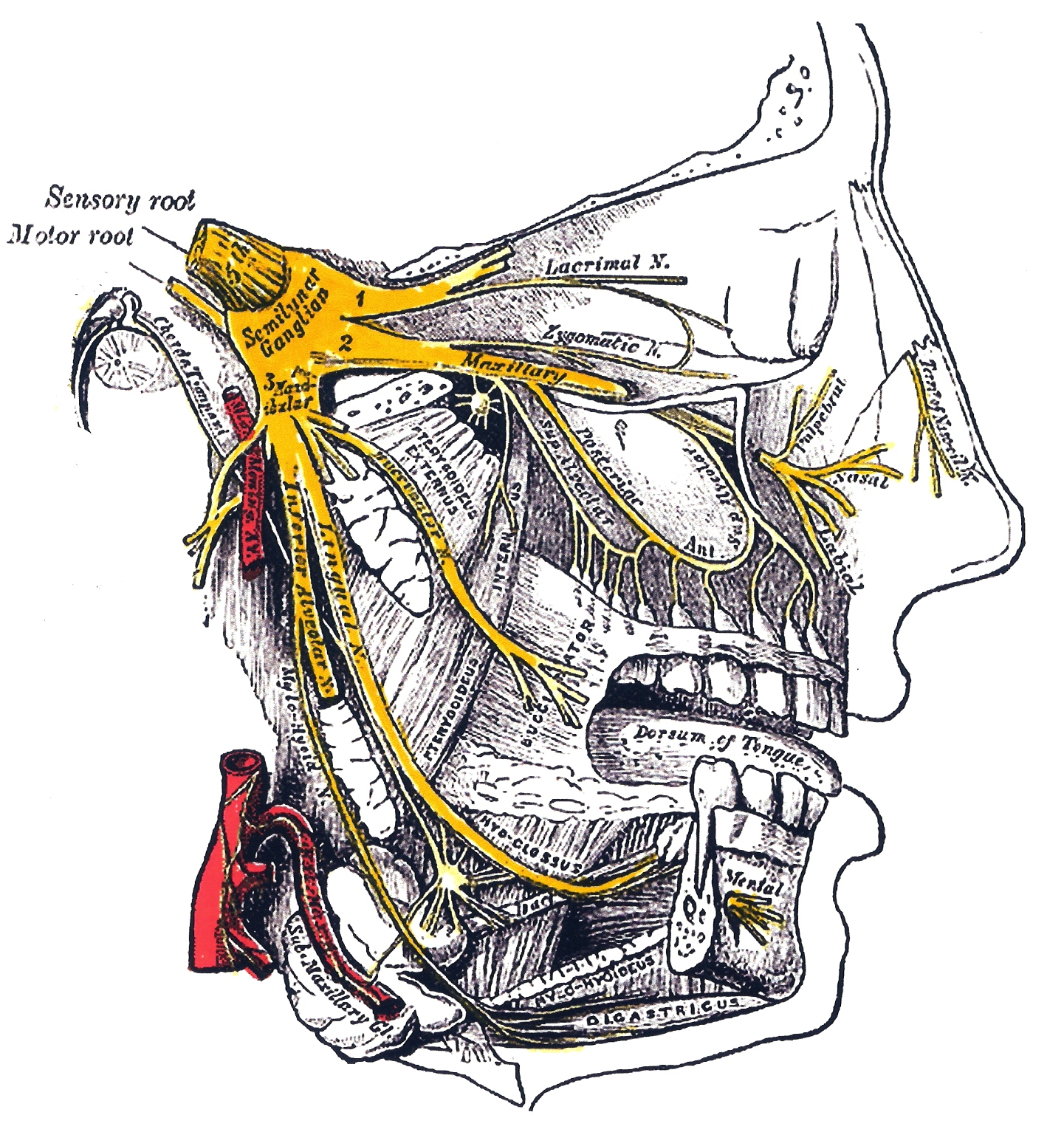
Trigeminal nerve branches
- Ophthalmic nerve. The ophthalmic nerve [V1] passes forward in the dura of the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, leaves the cranial cavity, and enters the orbit through the superior ...
- Maxillary nerve. ...
- Mandibular nerve. ...
What does trigeminal nerve mean?
The trigeminal nerve is one set of the cranial nerves in the head. It is the nerve responsible for providing sensation to the face. One trigeminal nerve runs to the right side of the head, while the other runs to the left. Each of these nerves has three distinct branches. "Trigeminal" derives from the Latin word "tria," which means three, and "geminus," which means twin.

What is the function of the trigeminal nerve quizlet?
trigeminal nerve, has both sensory and motor components. it is the main sensory nerve to the head, relaying sensation of touch, pain, and temperature. - alpha motor neurons innervate and control muscles required for mastication. THere are 3 main divisions of this nerve; ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular.
What does trigeminal nerve supply?
The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head. It is the motor nerve for the muscles of mastication and contains proprioceptive fibers.
Where does the trigeminal nerve affect?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that causes painful sensations similar to an electric shock on one side of the face. This chronic pain condition affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from your face to your brain.
What happens if you cut the trigeminal nerve?
The sensory root fibers, which transmit the pain signals to the brain, are severed (Fig. 5). Cutting the nerve causes permanent facial numbness and should only be considered for recurrent pain that has not responded to other treatments.
What activates trigeminal nerves?
This abnormal wave of electrochemical activity Is often stimulated by several different stimuli. These stimuli are irrational signals from other parts of the nervous system, such as stress, irregular sleep, a flashing light, a range of food ingredients, weather changes, and noise.
Who treats trigeminal nerve?
Make an appointment with your primary care provider if you have symptoms common to trigeminal neuralgia. After your initial appointment, you may see a doctor trained in the diagnosis and treatment of brain and nervous system conditions (neurologist).
What disease affects the trigeminal nerve?
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN), also called tic douloureux, is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal or 5th cranial nerve, one of the most widely distributed nerves in the head. TN is a form of neuropathic pain (pain associated with nerve injury or nerve lesion.)
What is the most common cause of trigeminal neuralgia?
Evidence suggests that in up to 95% of cases, trigeminal neuralgia is caused by pressure on the trigeminal nerve close to where it enters the brain stem, the lowest part of the brain that merges with the spinal cord. This type of trigeminal neuralgia is known as primary trigeminal neuralgia.
Does trigeminal nerve supply teeth?
The mandibular teeth are primarily supplied by the inferior alveolar nerve which is a branch of the mandibular nerve (third division of the trigeminal nerve).
Does trigeminal supply the tongue?
The mandibular part of the trigeminal nerve supplies sensation to the lower third of the face, the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, the oral mucosa of the mouth, and the lower teeth.
Does the trigeminal nerve supply the tongue?
[13] General sensation to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is by innervation from the lingual nerve, a branch of the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3).
What are the 3 main branches of the trigeminal nerve?
The different branches are namely the ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) nerves. The ophthalmic nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the face and skull above the palpebral fissure as well as the eye and portions of the nasal cavity.
How many nerves does the trigeminal ganglion have?
The trigeminal ganglion splits into three trigeminal nerve branches. These branches travel along each side of your head to different parts of your face.
What nerves help with pain?
The trigeminal nerves play essential roles in helping your face feel pain, touch, warmth or cold. The mandibular branches of the trigeminal nerves help you bite, chew and swallow. In some cases, people develop numbness or other signs of trigeminal neuropathy from an accident, dental procedure or facial surgery. Trigeminal neuralgia can cause stabbing, shock-like facial pain or a constant burning sensation. Talk to your provider about finding relief from these trigeminal nerve conditions.
What is the name of the condition that affects only one side of the face?
Trigeminal neuralgia tends to affect only one side of your face. Some people develop facial twitches (tics) after the pain subsides.
What is the name of the condition where an artery wraps around the trigeminal nerve and causes irritation?
Primary trigeminal neuralgia occurs when an artery or vein wraps around the trigeminal nerve and causes irritation.
What is the pain on one side of the face?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a type of trigeminal neuropathy brought on by nerve damage. The condition causes sudden, intense facial pain on one side of your face. The pain can feel like an electrical shock. Approximately 150,000 people develop trigeminal neuralgia every year. It's also called tic douloureux.
What is the fifth cranial nerve?
The trigeminal nerve, also called the cranial nerve V (that's the Roman numeral five), is the fifth of 12 cranial nerves.
How many nuclei are there in the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerves begin within four nuclei — or collections of nerve cell bodies — in your brain. Three of these nuclei control the functioning of your senses. The fourth controls motor function (or your movement).
How do axons form the mesencephalic tract?
As the myelinated axons leave the mesencephalic nucleus, they coalesce to form the mesencephalic tract. The individual axon s then split into central and peripheral branches. The central branches convey impulses from the neuromuscular spindles within the muscles of mastication, and from the bite force reflex arcs, to the motor neuron of the trigeminal nerve. Other central fibers also integrate with the reticular formation and the sensory trigeminal nerve. Others also gain access to the cerebellum by way of the superior cerebellar peduncle. This interplay between the proprioceptive and motor divisions of the trigeminal nerve helps to regulate the activity of the stretch muscles; and by extension, the process of mastication.
How many nuclei does the trigeminal nerve have?
Unlike the other cranial nerves, the trigeminal nerve is quite large. It has four nuclei that send fibers to form its tracts and is associated with three separate branches. Key facts about the trigeminal nerve (CN V) Type. Mixed (motor and sensory) Nuclei. Motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve.
What nerve is CN V?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V): want to learn more about it?
What is the trigeminal nerve?
As the name suggests, the trigeminal nerve is a tripartite entity made up of distinct terminal divisions. Each component of the nerve is responsible for a specific region of the face, and transmits specific impulses. The three divisions of the trigeminal nerve are:
What does MOM mean in medical terms?
The acronym MOM can be used to recall the three branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Where does the ophthalmic nerve receive its meningeal tributary?
Once formed, the ophthalmic nerve also receives its meningeal tributary from the dura of the anterior cranial fossa. Key facts about the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V1) Branches. Nasociliary nerve.
Which nerve is responsible for the motor, sensory, and autonomous functions of the head and neck?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V) The principal regulator of the sensory modalities of the head is the trigeminal nerve. This is the fifth of twelve pairs of cranial nerves that are responsible for transmitting numerous motor, sensory, and autonomous stimuli to structures of the head and neck . While the trigeminal nerve (CN V) is largely a sensory nerve, ...
What is the most common problem associated with the trigeminal nerve?
A condition called trigeminal neuralgia is the most common problem associated with the trigeminal nerve. There are also several other medical problems that can involve the trigeminal nerve or its branches.
What is the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerve is most commonly associated with trigeminal neuralgia, a condition characterized by severe facial pain. Since it is large and has several divisions, the trigeminal nerve or its branches can also be affected by a number of medical conditions including infections, trauma, and compression from tumors or blood vessels.
What causes nerve pain in the trigeminal nerve?
It can occur without any specific cause, and sometimes it can be triggered by an injury or inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. This condition often causes pain that is severe in intensity. Medications used for pain management include antidepressants and anticonvulsants, both of which are frequently used for nerve pain.
What can be done to prevent permanent deficits of the trigeminal nerve?
Treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medication, if started in a timely manner, can prevent permanent deficits of the trigeminal nerve in the setting of infection.
Where are the trigeminal nerve roots located?
Location. The trigeminal nerve roots and ganglion, like those of other cranial nerves, are located right outside the brainstem. The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that serves as the physical connection between the spinal cord and the cerebral cortex of the brain. All 12 cranial nerves (12 in each side) emerge from the brainstem.
Which nerve is smaller than the sensory nerve?
The motor nerve branch of the trigemin al nerve is smaller than the sensory branches ...
Which nerves are located in the head?
Ophthalmic. The frontal nerve, the lacrimal nerve, and the nasociliary nerves converge in the ophthalmic nerve. These nerves and their small branches are located in and around the eye, forehead, nose, and scalp. The ophthalmic nerve enters into the skull through a small opening called the superior orbital fissure before it converges in ...
What happens when the trigeminal nerve is damaged?
Surgery to correct trigeminal neuralgia sometimes involves moving the nerve away from another nerve or artery that is touching or compressing it, and leaving in a sort of pillow made of Teflon felt to keep the nerve protected from future contact. However, other procedures to cure this nerve pain disorder require doctors to cut the nerve surgically, destroy it with heated electrodes, or inject Botox into it in an attempt to halt nerve signals. This is done when the pain from the nerve impingement is worse than any side effects that may be caused by harming the trigeminal nerve. In other words: To get rid of the pain, get rid of the nerve that sends the pain signals.
What is the name of the nerve that touches a vein?
When the trigeminal nerve touches a vein or artery or is compressed by these vessels, it becomes irritated, sending out sizzles of pain zinging along its branches. Sometimes the pain hits so hard that aftershocks, in the form of twitches, remain. This nerve pain is called trigeminal nerve pain, trigeminal neuralgia, or tic douloureux (which means "painful tic" in French).
What nerve is involved in migraines?
The trigeminal nerve also is implicated in migraine. One type of migraine treatment, an FDA-approved device people wear on their heads called the Cefaly, sends electrical stimulation to the trigeminal nerve, which appears to create a sedative effect and reduce migraine attacks in some people.
What is the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerve is the largest nerve in your head, one of 12 pairs of cranial nerves. (It is the fifth pair.) Its primary job is to provide sensations from your face and head to your brain, telling it when you feel pain or heat or coldness, among others.
What happens if you cut the trigeminal nerve?
If the nerve is cut, "reflex tears" in your eyes could stop; these are tears automatically triggered when the eye encounters an irritant , such as the vapor of an onion or a foreign body. Emotional tears, though, continue to flow even if the trigeminal nerve, which reports sensations in the eye back to the brain, is impaired.
How long does it take for a facial nerve to grow back?
For some, this can last a lifetime. For others, the nerve grows back, usually within 1 to 6 years. If pain resumes as well, then the patient may need to have these surgeries performed again.
Where is the trigeminal nerve located?
The trigeminal nerve's location starts out at the base of your neck, in a root connected to your brainstem. This root then splits, like a plant or tree, into two branches that cover both sides of your face. That's the twin, or geminus, part.
What are the areas of cutaneous distribution of the trigeminal nerve?
The areas of cutaneous distribution (dermatomes) of the three sensory branches of the trigeminal nerve have sharp borders with relatively little overlap (unlike dermatomes in the rest of the body, which have considerable overlap). The injection of a local anesthetic, such as lidocaine, results in the complete loss of sensation from well-defined areas of the face and mouth. For example, teeth on one side of the jaw can be numbed by injecting the mandibular nerve. Occasionally, injury or disease processes may affect two (or all three) branches of the trigeminal nerve; in these cases, the involved branches may be termed:
What are the three branches of the trigeminal nerve?
The three major branches of the trigeminal nerve—the ophthalmic nerve (V 1 ), the maxillary nerve (V 2) and the mandibular nerve (V 3 ) —converge on the trigeminal ganglion (also called the semilunar ganglion or gasserian ganglion), located within Meckel's cave and containing the cell bodies of incoming sensory-nerve fibers.
What is the trigeminal nerve?
e. The trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve, or simply CN V) is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name ("trigeminal" = tri-, or three, and - geminus, or twin: thrice-twinned) derives from the fact that each of the two nerves ...
How is sensory information processed?
Sensory information is processed and modified at each level in the chain by interneurons and input from other areas of the nervous system. For example, cells in the main trigeminal nucleus (Main V in the diagram below) receive input from the reticular formation and cerebral cortex. This information contributes to the final output of the cells in Main V to the thalamus.
What nerve is involved in numbed teeth?
For example, teeth on one side of the jaw can be numbed by injecting the mandibular nerve. Occasionally, injury or disease processes may affect two (or all three) branches of the trigeminal nerve; in these cases, the involved branches may be termed: V1/V2 distribution – Referring to the ophthalmic and maxillary branches.
Which ganglia contains sensory fibers?
The trigeminal ganglion is analogous to the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord, which contain the cell bodies of incoming sensory fibers from the rest of the body. From the trigeminal ganglion, a single, large sensory root (portio major) enters the brainstem at the level of the pons.
Where are motor fibers located in the pons?
Motor fibers pass through the trigeminal ganglion without synapsing on their way to peripheral muscles, but their cell bodies are located in the nucleus of the fifth nerve, deep within the pons.
What is the ophthalmic nerve?
The ophthalmic nerve is primarily responsible for the sensory innervation of the face and scalp above the orbits. It also contains sympathetic nerve fibers responsible for pupil dilation and supplies the ciliary body, iris, lacrimal gland, conjunctiva, and cornea. In addition to these superficial sensory functions, the ophthalmic nerve also supplies the superior portion of the nasal cavity, the frontal sinus, and even deeper structures including the dura mater and portions of the anterior cranial fossa.
What is the function of the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Its primary function is to provide sensory and motor innervation to the face. The trigeminal nerve consists of three branches on either side that extend to different territories of the face. These branches join at the trigeminal ganglia which are located within the Meckel cave of the cranial cavity. The different branches are namely the ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) nerves. The ophthalmic nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the face and skull above the palpebral fissure as well as the eye and portions of the nasal cavity. The maxillary nerve is also a sensory branch and innervates portions of the nasal cavity, sinuses, maxillary teeth, palate, and the middle portion of the face and skull above the mouth and below the forehead. The mandibular nerve is unique in that it contains both sensory and motor fibers. It provides sensory innervation of the buccal mucosa, mandibular teeth, and the skin below the mouth. The motor portion of V3 innervates all the muscles of mastication. Additionally, V3 provides sensory information from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue; this is differentiated from taste which is produced by CN VII.[1][2]
What is the best treatment for trigeminal neuralgia?
One of the most common surgical procedures related to the trigeminal nerve is surgical therapy for trigeminal neuralgia (discussed later). Even though surgery can offer the patient significant pain relief, it also has a considerable risk of permanent damage to the trigeminal nerve which could result in facial numbness. For this reason, surgical intervention is often recommended only after several pharmaceutical therapies have been attempted. The surgical interventions that are done for trigeminal neuralgia are split into two categories: non-destructive and destructive. The goal of non-destructive surgery is to alleviate nerve compression by removing any structure that may be impinging on the nerve and maintaining the nerve intact. Destructive procedures aim to disrupt the trigeminal nerve completely so that pain is no longer transmitted by the nerve. The result of a destructive procedure is the irreversible loss of sensation of the affected side of the face. [7][8][9]
What is Wallenberg syndrome?
Wallenberg syndrome is a condition that occurs when the lateral portion of the medulla in the brainstem becomes damaged, typically due to stroke. A lesion in this region of the brain stem results in an ipsilateral sensory loss in the territory of the trigeminal nerve and contralateral sensory loss in the rest of the body. Wallenberg syndrome is often recognized in the clinical setting to localize brainstem lesions. [10]
What causes cluster headaches?
Cluster headaches have a very similar presentation as trigeminal neuralgia, and therefore the two are often considered on the same differential. Cluster headaches most often present as a severe headache on one side of the head that affects the territory of the trigeminal nerve. These headaches can be accompanied by other symptoms such as nasal congestion, swelling, and lacrimation on the affected side. While the cause of cluster headaches is currently unknown, there is often an external stimulus that serves as a trigger for the onset of symptoms. Prophylactic treatment usually includes a combination of trigger avoidance and pharmacotherapy. Acute attacks can be remediated with fast-acting triptans and oxygen.
Which nerve is responsible for innervation of the facial muscles?
The only branch of the trigeminal nerve that has a motor component in the mandibular nerv e (V3). This branch supplies motor innervation to the facial muscles involved in mastication which include the masseter, temporalis muscle, and the lateral and medial pterygoids. Additionally, V3 gives off branches that innervate the tensor veli palatini, the mylohyoid, the tensor tympani, and the anterior portion of the digastric muscle.
Which nerve innervates the muscles of mastication?
The mandibular nerve is the only branch of the trigeminal nerve that has both sensory and motor components. The motor component innervates all of the muscles of mastication (enumerated below). The sensory portion is responsible for pain and temperature information from the mandibular teeth, buccal mucosa, temporomandibular joint, the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and the face below the territory of the maxillary nerve.
How does trigeminal neuralgia feel?
Trigeminal neuralgia symptoms may include one or more of these patterns: Episodes of severe, shooting or jabbing pain that may feel like an electric shock. Spontaneous attacks of pain or attacks triggered by things such as touching the face, chewing, speaking or brushing teeth. Bouts of pain lasting from a few seconds to several minutes.
What is the pain in the face called?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from your face to your brain. If you have trigeminal neuralgia , even mild stimulation of your face — such as from brushing your teeth or putting on makeup — may trigger a jolt of excruciating pain.
What causes trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia can also be caused by a tumor compressing the trigeminal nerve. Some people may experience trigeminal neuralgia due to a brain lesion or other abnormalities. In other cases, surgical injuries, stroke or facial trauma may be responsible for trigeminal neuralgia.
What nerve causes pain in the cheek and jaw?
Constant aching, burning feeling that may occur before it evolves into the spasm-like pain of trigeminal neuralgia. Pain in areas supplied by the trigeminal nerve, including the cheek, jaw, teeth, gums, lips, or less often the eye and forehead.
What is the name of the nerve that is disrupted by blood pressure?
In trigeminal neuralgia, also called tic douloureux, the trigeminal nerve's function is disrupted. Usually, the problem is contact between a normal blood vessel — in this case, an artery or a vein — and the trigeminal nerve at the base of your brain. This contact puts pressure on the nerve and causes it to malfunction.
Can trigeminal neuralgia cause pain?
You may initially experience short, mild attacks. But trigeminal neuralgia can progress and cause longer, more-frequent bouts of searing pain. Trigeminal neuralgia affects women more often than men, and it's more likely to occur in people who are older than 50.
Can you have pain on both sides of your face?
Pain affecting one side of the face at a time, though may rarely affect both sides of the face. Pain focused in one spot or spread in a wider pattern. Attacks that become more frequent and intense over time.