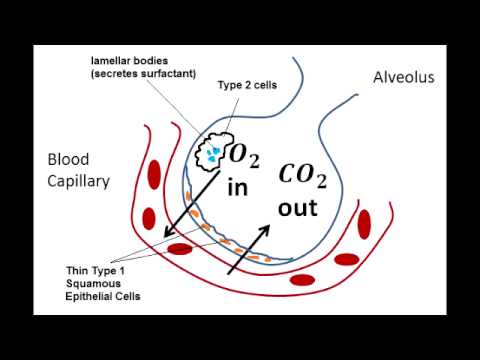
What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 pneumocytes?
Type 2 pneumocytes represent 60% of the alveolar cell population numerically, but occupy only 5–10% of the alveolar surface area. Unlike the thin, flat type 1 cells, type 2 pneumocytes are rounded cells which are commonly located in obtuse angles in the polygonal alveolus (Fig. 10.15a).
What is the function of pneumocytes in the lungs?
Outline the function of pneumocytes in the lungs type I pneumocytes carry out gas exchange type II pneumocytes create a moist surface inside the alveoli Outline the role of the parts of an alveolus in a human lung. a. the (spherical) wall of an alveolus maximizes/allows gas exchange
What is type 2 pneumocyte hyperplasia?
Type II pneumocyte hyperplasia (bronchoalveolar lavage [BAL]). In patients with acute lung injury, type II pneumocytes are markedly enlarged and may mimic adenocarcinoma, as seen here. This patient had diffuse infiltrates and marked respiratory distress resulting from diffuse alveolar damage.
How many types of pneumocytes are there in the lungs?
There are two types of pneumocytes as type 1 and type 2 pneumocytes. More than 95% of the alveoli surface is lined by type 1 pneumocytes.
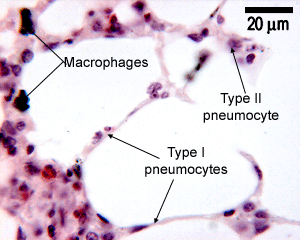
What is the function of the Pneumocyte?
Type I pneumocytes cover 95% of the internal surface of each alveolus. These cells are thin and squamous, ideal for gas exchange. They share a basement membrane with pulmonary capillary endothelium, forming the air-blood barrier where gas exchange occurs.
What are the functions of Pneumocyte 1 and Pneumocyte II?
Type 1 pneumocytes are thin flattened cells that are responsible for the gas exchange between alveoli and capillaries. Type 2 pneumocytes are smaller cells that are cuboidal in shape. They are responsible for the secretion of pulmonary surfactants in order to reduce the surface tension in the alveoli.
What is the function of the type I pneumocytes quizlet?
What is the role of type I pneumocytes? - The wall of each alveolus is made of a single layer of epithelial cells. - The epithelial cells are mainly type I pneumocytes. - Type I pneumocytes are very thin cells so they are adapted for gas exchange.
What do type II cells produce?
Type II cells produce and secrete pulmonary surfactant and for that purpose they need to synthesize the lipids of surfactant.
Where are type 2 pneumocytes found?
the alveoliType II pneumocytes were found to be preferentially located on thick elastic fibers which formed the main structural framework of the alveoli in humans.
Where are type 2 pneumocytes located?
the alveoliThe type II pneumocytes are located in the less movable portions of the alveoli. Alveolar movement may be most concerned with type II pneumocyte location. After alveolar damage, type II pneumocytes proliferate on the alveolar wall to replace sloughed type I pneumocytes for repair.
What is produced by type 2 pneumocytes?
The main function of type 2 pneumocytes is the production of pulmonary surfactant: Surfactant is a complex mixture of phospholipids (mainly dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine), carbohydrates (glycosaminoglycans) and proteins (including SP-A, SP-B, SP-C and SP-D)
What is produced by type II pneumocytes quizlet?
Type II pneumocytes secrete a liquid known as pulmonary surfactant which reduces the surface tension in alveoli. As an alveoli expands with gas intake, the surfactant becomes more spread out across the moist alveolar lining.
What is the purpose of the substance secreted by the type II Pneumocyte quizlet?
Outline the structure and function of type II pneumocytes. rounded cells that occupy 5% of the alveolar surface area. They secrete a fluid containing surfactant inside the alveoli to prevent the sides of the alveolus adhering to one another by reducing surface tension.
What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 pneumocytes?
Type 1 vs Type 2 Pneumocytes. Type 1 pneumocytes are alveolar cells that line the alveolar surface. Type 2 pneumocytes are alveolar cells that secrete surfactant proteins to reduce surface tension.
Are type 2 pneumocytes stem cells?
In the bronchiolar-alveolar compartment (site 3), type II pneumocytes and bronchoalveolar stem cells may function as stem cell.
Which cell produces surfactant?
Pulmonary surfactant is produced by alveolar type II cells and is required for lung function after birth. Pulmonary surfactant is composed of lipids and four lipid-associated proteins, SP-A, SPB, SP-C, and SP-D, that regulate surfactant function, structure, metabolism, and innate host defense.
How do type 1 and type 2 pneumocytes in the alveoli differ?
Type I and type II pneumocytes make up the alveolar epithelium. Type I cells are flat with cytoplasmic projections and a protuberant nucleus. They do not divide. Type II cells are cuboidal, metabolically active cells with abundant cytoplasmic organelles.
What are the two types of pneumocytes?
The type I pneumocytes form part of the barrier across which gas exchange occurs. They can be identified as thin, squamous cells whose most obvious feature is their nuclei. Type II pneumocytes are larger, cuboidal cells and occur more diffusely than type I cells.
What is produced by type II pneumocytes quizlet?
Type II pneumocytes secrete a liquid known as pulmonary surfactant which reduces the surface tension in alveoli. As an alveoli expands with gas intake, the surfactant becomes more spread out across the moist alveolar lining.
What is Type 1 alveolar cell?
The alveolar epithelium comprises two main cell types: the alveolar type I and alveolar type II cell. The type I cell is a complex branched cell with multiple cytoplasmic plates that are greatly attenuated and relatively devoid of organelles; these plates represent the gas exchange surface in the alveolus.
What are Type 2 Pneumocytes?
Type 2 pneumocytes are a type of alveolar cells that are cuboidal in shape. They cover a relatively less surface area (about 5%) of alveoli in comparison to type 1 cells. Type 2 pneumocytes are responsible for producing pulmonary surfactants in order to reduce the surface tension in the alveoli. Therefore, type 2 cells contain secretory organelles full of granules (lamellar bodies) to produce these surfactants.
What is the Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Pneumocytes?
Type 1 pneumocytes are extremely thin, flattened epithelial cells lining the alveoli, while type 2 pneumocytes are small cuboidal epithelial cells that contain secretory organelles. Moreover, functionally, type 1 pneumocytes are responsible for the process of gas exchange between alveoli and capillaries, while type 2 pneumocytes are responsible for the secretion of pulmonary surfactants in order to reduce surface tension. So, this is the key difference between type 1 and type 2 pneumocytes.
What type of cell is responsible for the gas exchange between the alveoli and the capillaries?
Type 1 pneumocytes are thin flattened cells that are responsible for the gas exchange between alveoli and capillaries. Type 2 pneumocytes are smaller cells that are cuboidal in shape. They are responsible for the secretion of pulmonary surfactants in order to reduce the surface tension in the alveoli. Type 2 cells are the most numerous cells in the ...
What type of cell is the alveoli?
More than 95% of the alveoli surface is lined by type 1 pneumocytes. They are flattened, thin and large cells. Type 2 pneumocytes are small cuboidal cells that do not cover much of the surface area of alveoli. They contain secretory organelles which secrete pulmonary surfactants to reduce surface tension in the alveoli.
What are the cells that line the alveoli?
These cells line the alveoli and are present in the majority of the inner surface of the lungs. There are two types of pneumocytes as type 1 and type 2 pneumocytes. More than 95% of the alveoli surface is lined by type 1 pneumocytes.
Why are pneumocytes connected by occluding junctions?
Hence, they minimize the diffusion distance for respiratory gases. In order to prevent the leakage of tissue fluid into the alveolar air space , type 1 pneumocytes are connected by occluding junctions.
What type of cell is found in the alveolar wall?
Type 1 pneumocytes are one of the two types of pneumocytes found in the alveolar wall. They are flattened alveolar cells that cover more than 95% of the surface area of alveoli. These cells participate in the process of gas exchange between alveoli and capillaries. In fact, they form part of the barrier across which gas exchange happens.
When do type II neutrocytes not develop?
In premature babies born earlier than the 30 week of pregnancy, type II#N#pneumocytes are usually not fully developed, so they do not carry out#N#their function normally. What is a possible consequence of this?
What is the exchange of gases between lungs and air?
a. ventilation is exchange of gases between lungs and air.
What are the functions of the valves in the heart?
Describe the functions of valves in the mammalian heart. a. prevents backflow/ensures one-way flow/controls direction of flow. open valves allow blood to flow through. closed «semilunar» valves allow ventricles/chambers to fill with blood. valves open when pressure is higher upstream/OWTTE/converse for closed valves.
What gas dissolves in water lining the alveolus?
b. O2 gas dissolves in water lining the alveolus ✔