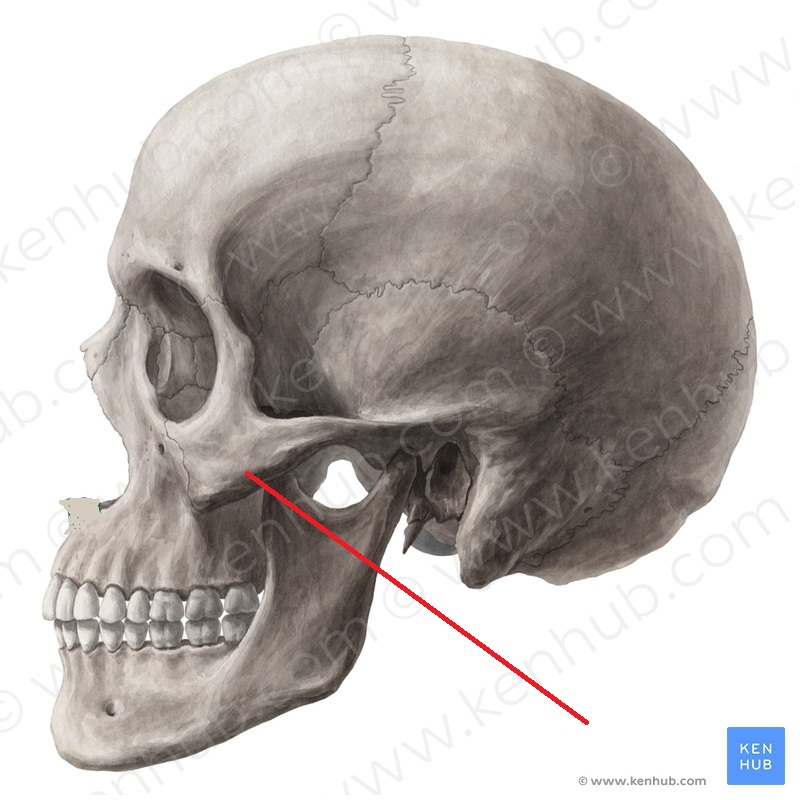
What does zygomatic bone mean?
The zygomatic bone is a paired facial bone. Both zygoma or cheek bones are irregular and articulate with other bones of the cranium and face. They are important contributors to mastication or chewing, providing an attachment point for the masseter muscle – a jaw adductor that closes the jaw.
What is the temporal process of zygomatic bone?
What is temporal process? : a process of the zygomatic bone that with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone with which it articulates laterally forms part of the zygomatic arch. What is temporal in science? temporal. (Science: anatomy) Of or pertaining to the temple or temples; as, the temporal bone; a temporal artery.
What is the function of zygomatic major?
Zygomaticus major
- Origin. The zygomaticus major muscle arises from the lateral surface of the zygomatic bone. ...
- Insertion. The zygomaticus major inserts into the skin at the angle of the mouth, blending with the fibers of the levator anguli oris, orbicularis oris and more deeply placed muscles.
- Action. ...
- Innervation. ...
- Blood supply. ...
- Cheek dimples. ...
Does zygomatic contain sinuses?
The temporal bone does not contain a sinus. Does the zygomatic bone have a sinus? It contains the largest of the paranasal sinuses, the maxillary sinus. The hollow space is the frontal sinus, one of the paranasal sinuses, which we’ll look at shortly. Next we’ll look at the zygomatic bone. The zygomatic bone forms the bony prominence of the cheek.
What's the zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone (or zygoma) is a paired, irregular bone that defines the anterior and lateral portions of the face. The zygomatic complex is involved in the protection of the contents of the orbit and the contour of the face and cheeks.[1]
What is the purpose of the zygomatic process of the temporal bone?
The zygomatic process is a place for muscle attachment, mainly muscles involved in chewing. In addition, this process of the temporal bone helps strengthen the entire cheekbone area.
Is the zygomatic bone a facial bone?
In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from Ancient Greek: ζῠγόν, romanized: zugón, lit. 'yoke'), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone....Zygomatic boneFMA52747Anatomical terms of bone8 more rows
Why is it called zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone is also known as the zygomatic arch, the zygoma, the malar bone, the cheek bone and the yoke bone. The word "zygomatic" comes from the Greek "zygon" meaning a yoke or crossbar by which two draft animals such as oxen could be hitched to a plow or wagon.
What happens if the zygomatic bone is damaged?
Fractures of the ZMC or zygomatic arch can often lead to unsightly malar depression, which should be corrected to restore a normal facial contour. ZMC fractures can also cause significant functional issues, including trismus, enophthalmos and/or diplopia, and paresthesias of the infraorbital nerve.
Where is the zygomatic bone?
zygomatic bone, also called cheekbone, or malar bone, diamond-shaped bone below and lateral to the orbit, or eye socket, at the widest part of the cheek. It adjoins the frontal bone at the outer edge of the orbit and the sphenoid and maxilla within the orbit.
How do you remember the zygomatic bone?
Here's a quick facial bones mnemonic to help you remember them: My Mouth's Palate Never Liked Zucchini in Vinegar.My = Mandible.Mouth's = Maxilla.Palate = Palatine.Never = Nasal.Liked = Lacrimal.Zucchini = Zygomatic.In = Inferior Nasal Conchae.Vinegar = Vomer.
Which bones protect the brain?
The skull protects the brain and forms the shape of the face. The spinal cord, a pathway for messages between the brain and the body, is protected by the backbone, or spinal column.
What are the two processes of zygomatic bone?
The three processes are: Zygomatic process of frontal bone from the frontal bone. Zygomatic process of maxilla from the maxilla (malar process) Zygomatic process of temporal bone from the temporal bone.
What causes zygomatic pain?
Zygomatic arch pain is commonly reported by patients visiting the orofacial pain clinic and is majorly accepted to be caused by masseter muscle pain. But a variety of conditions may present as orofacial pain in the zygomatic arch region, including life-threatening diseases such as salivary gland tumors.
What is the temporal process?
Medical Definition of temporal process : a process of the zygomatic bone that with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone with which it articulates laterally forms part of the zygomatic arch.
What makes up the zygomatic process?
The zygomatic process of the temporal arises by two roots: an anterior, directed inward in front of the mandibular fossa, where it expands to form the articular tubercle. a posterior, which runs backward above the external acoustic meatus and is continuous with the supramastoid crest.
What is the purpose of the Maxillae?
Your maxilla is a crucial bone in your skull's structure and enables many basic functions, such as chewing and smiling. If it's fractured, it can affect many other important bones around it and keep you from accomplishing even simple daily tasks.
What is the difference between the zygomatic process and the zygomatic arch?
Zygomatic Arch Definition The zygomatic arch is formed from parts of both the zygomatic bone and the temporal bone. The extension of the temporal bone is known specifically as the zygomatic process, and attaches directly to the similarly shaped process on the zygomatic bone.
What is the zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone (zygoma) is an irregularly shaped bone of the skull. It is often referred to as the cheekbone, and it comprises the prominence just below the lateral side of the orbit. The zygomatic bone is nearly quadrangular in shape and it features three surfaces, five borders and two processes. Besides forming the prominence of the cheek, ...
What bone forms the zygomatic arch?
Besides forming the prominence of the cheek, the zygomatic bone also contributes to the formation of the zygomatic arch, the walls of the temporal and infratemporal fossae, and the floor and lateral wall of the bony orbit. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the zygomatic bone. Key facts about the zygomatic bone.
What are the three surfaces of the zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone has three surfaces: lateral, posteromedial and orbital. The lateral (facial) surface faces towards the outside. It is smooth and convex, and it features a small opening called the zygomaticofacial foramen. This foramen transmits the zygomaticofacial nerve, artery and vein between the orbit and the face.
What is the border between the lateral and orbital surfaces of the zygomatic bone?
It is the border between the lateral and orbital surfaces of the zygomatic bone. The anteroinferior (maxillary) border is the articular surface for the zygomaticomaxillary suture. It also serves as an attachment site for the levator labii superioris muscle.
Which surface faces the temporal and infratemporal fossae?
The posteromedial (temporal) surface faces towards the temporal and infratemporal fossae. Its anteriormost portion is rough and serves for the articulation with the zygomatic (malar) process of maxilla via the zygomaticomaxillary suture. The posteromedial surface spreads over the medial side of the temporal process, comprising a part of the lateral wall of the infratemporal fossa. Near the base of the frontal process, the posteromedial surface features the zygomaticotemporal foramen which transmits the zygomaticotemporal nerve from the orbit to the temporal fossa.
Which border is serrated and articulates with the greater wing of sphenoid bone superiorly via?
The posteroinferior border is rough and serves as the attachment site for the masseter muscle. The posteromedial border is serrated and articulates with the greater wing of sphenoid bone superiorly via the sphenozygomatic suture, and with the orbital surface of maxilla inferiorly.
Where does the maxillary process occur?
The maxillary process arises from the anterosuperior angle of the zygomatic bone. It extends anteriorly, comprising the inferolateral margin of the orbit. The inferior margin of this process participates in the joint with the maxilla. Posteriorly, it is continuous with the orbital surface of the bone.
What is the function of zygomatic bone?
Zygomatic bone anatomy is not over-complex; its main function is to provide structure and strength to the mid-face. The cheekbones have three surfaces, four processes, three foramina, and three articulations. Processes are projecting pieces of bone that insert into other bones.
What is the zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone is a paired facial bone. Both zygoma or cheek bones are irregular and articulate with other bones of the cranium and face. They are important contributors to mastication or chewing, providing an attachment point for the masseter muscle – a jaw adductor that closes the jaw.
Where is the Zygomatic Bone Located?
Zygomatic bone location can easily be felt as it forms the ridge above the fleshy area of the cheeks, along the outer rim of the eyes .
What is the lateral surface of the zygoma?
From a lateral view, the zygoma are rectangular in form. The lateral surface provides a point of attachment for the zygomaticus major and minor muscles.
How many processes are there in the zygomatic bone?
There are four processes of the zygomatic bone, but these are not zygomatic processes! A process is named after the bone it meets with. In the zygoma, these four processes are the: Orbital process of the zygomatic bone. Maxillary process of the zygomatic bone. Temporal process of the zygomatic bone.
Which process of the cheekbone forms the zygomatic arch?
Together with the temporal process of the cheekbone, the zygomatic process of the temporal bone forms the zygomatic arch. This arch surrounds a large hollow that allows the temporal and masseter muscles to pass through to the lower jaw. It is this arch that gives the mid-face its shape.
Where are zygomatic processes found?
Zygomatic processes, however, are found on other bones that extend into the zygoma. There are three zygomatic processes: Zygomatic process of the frontal bone. Zygomatic process of the temporal bone. Zygomatic process of the maxilla bone (or malar process of the maxilla bone) Zygomatic process of the maxilla bone.
What is the zygomatic muscle?
The zygomaticus major muscle is also known as musculus zygomaticus major and the greater zygomatic muscle, as well as musculus zygomaticus.
What is the zygomaticus major?
The zygomaticus major muscle is a muscle that controls facial expression, drawing the mouth’s angle upward and outward. The zygomaticus major muscle starts at the cheekbone and extends to the corner of the mouth. ...
Which muscle is responsible for the rise of the corners of the mouth?
The zygomaticus major muscle starts at the cheekbone and extends to the corner of the mouth. This muscle causes the corners of a person’s mouth to rise when they smile.