
How is blood typing done?
How blood typing is performed. In order to determine your blood type, a lab technician will mix your blood sample with antibodies that attack types A and B blood to see how it reacts. If your blood cells clump together when mixed with antibodies against type A blood, for example, you have type B blood.
What is the principle of blood grouping?
Principle Of Blood Grouping. When the antigen A is present on the red blood cells, then the person is said to have Type A Blood. A person having antigen B on the red blood cells is considered to have Type B Blood. When both antigens, A and B are present on the red blood cells, then the person’s blood type is classified as AB.
Why is it important to know your blood type?
The test is essential if you need a blood transfusion or are planning to donate blood. Not all blood types are compatible, so it’s important to know your blood group. Receiving blood that’s incompatible with your blood type could trigger a dangerous immune response.
What is the principle of Rh D typing?
Rh (D) typing is based on the principle of agglutination. Normal human red blood cells, possessing antigens, will clump in the presence of antibody directed toward the antigens. Why is O-Negative blood so important?
How many principle blood types are there?
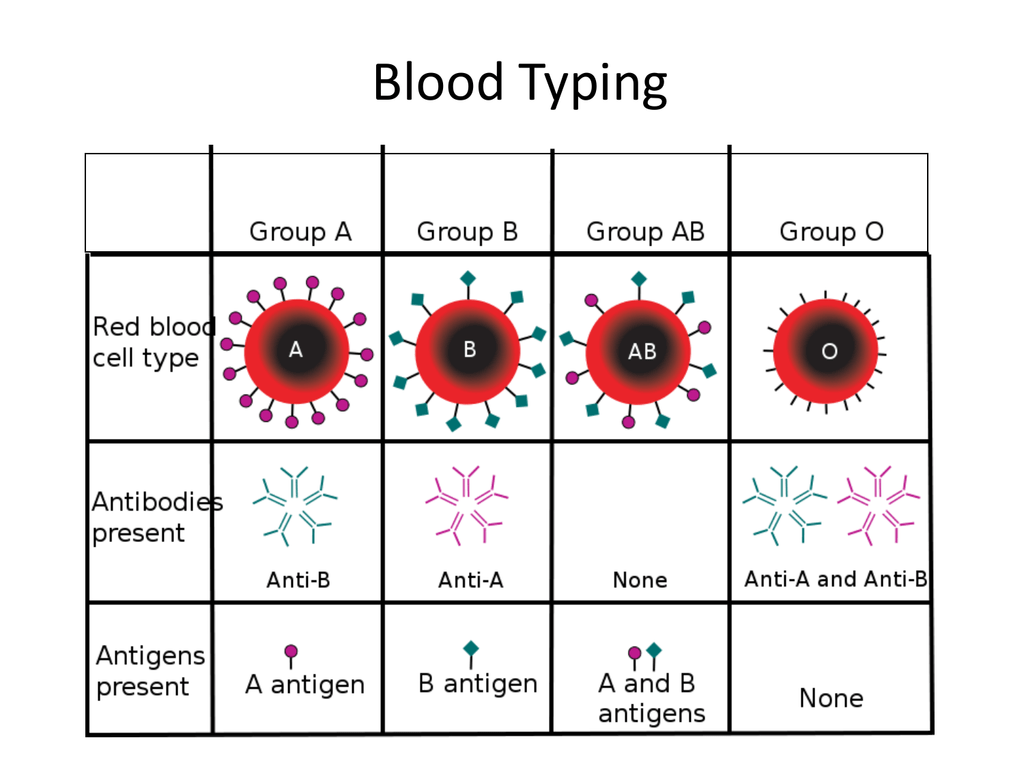
four principal typesThere are four principal types: A, B, AB, and O. There are two antigens and two antibodies that are mostly responsible for the ABO types. The specific combination of these four components determines an individual's type in most cases.
What is the purpose of blood typing in forensics?
Forensic scientists often use techniques to identify blood types (blood typing) because an individual's blood type isn't affected by disease, drugs, climate, occupation, living conditions, or any other physical circumstances. Additionally, scientists use blood-typing to determine paternity.
What determines blood type?
Blood types are determined by the presence or absence of certain antigens – substances that can trigger an immune response if they are foreign to the body. Since some antigens can trigger a patient's immune system to attack the transfused blood, safe blood transfusions depend on careful blood typing and cross-matching.
What are the 4 main components of blood?
It has four main components: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Blood has many different functions, including: transporting oxygen and nutrients to the lungs and tissues. forming blood clots to prevent excess blood loss.
When was blood typing first used in forensics?
In 1900 human blood groups were identified, and in 1915 a method for determining blood types was discovered - and was used immediately in criminal investigations.
What are the advantages of using blood as an evidence at the crime scene?
Properly collected and preserved blood evidence can establish a strong link between an individual and a criminal act. Blood evidence or the lack of blood evidence can also be used to bolster or contradict a witness statement or any statements that the suspect may make.
Do you think blood typing is a strong evidence in crime cases?
For example, if a suspect's ABO blood type matches the type O blood found at the crime scene, the evidence is not very convincing because 45% of the population has type O blood....Evidence And Tools Used In Forensic Science.Antibody added to sampleResults of test indicates blood type to beanti-Aanti-B+—A—+B++AB1 more row
Why might blood typing be done prior to a DNA test?
In cases of questioned paternity, ABO blood-typing can be used to exclude a man from being a child's father. For example, a man who has type AB blood could not father a child with type O blood, because he would pass on either the A or the B allele to all of his offspring.
Introduction
Blood Grouping and Rh Typing is used to determine the blood group and Rh factor of a sample of blood. ABO blood grouping and Rh typing are the most common blood group systems. There are nearly 300 blood group systems so far discovered. Other common remaining systems are MNS, Lutheran, Kell, Duffy, etc.
Principle
ABO blood grouping and Rh typing are based on the principle of agglutination. The normal red blood cells (RBCs) possessing antigens will clump in the presence of corresponding antibodies.
Procedure
Label the two different clean slides with the unique ID of the patient.
Keynotes
In the case of doubtful agglutination reactions, further microscopic examination should be done to confirm the result.
What are the components of blood grouping?
Principle Of Blood Grouping. The human blood consists of 4 main components, the red blood cells, the white blood cells, the plasma and the platelets. The red blood cells are the components that help in determining a person’s blood type. The ABO system is the main blood grouping system behind the principle that helps classify people into one ...
Why is it important to know your blood group?
There are many occasions on which knowing your blood group or blood group check can come in handy such as an accident in which you or your family member requires blood transfusion due to heavy loss of blood during an accident.
What is the ABO blood group?
The ABO blood group of a person depends on whether his red blood cells contain one, both, or neither of the 2 blood group antigens A and B, and therefore the human blood groups are differentiated as type A, type B, type AB, or O as mentioned earlier. Antibodies for the antigens A and B exist naturally in the plasma and these are referred ...
What is the blood type of a person with antigen B?
A person having antigen B on the red blood cells is considered to have Type B Blood. When both antigens, A and B are present on the red blood cells, then the person’s blood type is classified as AB. When neither antigens, A nor B are present, the person is said to have Type O Blood. This is called the basic grouping system ...
Why is a blood grouping test important?
Thus, a blood grouping test is very important for every individual to help know his blood group and Rh-type as it will be convenient for healthcare providers to provide medical care immediately in case of an emergency. It is also useful to know your blood type if you wish to donate blood to a dear one in case of emergency.
Why do you need a blood group card?
Knowing your blood group in advance would save the hospital valuable time because they do not have to wait for your blood grouping test reports. If you’re traveling overseas, carrying a blood group card could help in emergency situations, and help in getting medical help faster.
How to know if blood is Rh positive?
Similarly, Rh typing is done by mixing the blood sample with an anti-Rh serum. If the blood cells clump together in response to the anti-Rh serum, it indicates that the blood is Rh-positive. If no clumping occurs, the blood is determined to be Rh-negative. Thus, a blood grouping test is very important for every individual to help know his blood ...
What is blood banking?
Blood banking is the process that takes place in the lab to make sure that donated blood, or blood products, are safe before they are used in blood transfusions and other medical procedures. Blood banking includes typing the blood for transfusion and testing for infectious diseases.
What are the blood types?
According to the American Association of Blood Banks, distribution of blood types in the U.S. includes the following:
Who are the blood donors?
Most blood donors are volunteers. However, sometimes, a patient may want to donate blood a couple of weeks before undergoing surgery, so that his or her blood is available in case of a blood transfusion. Donating blood for yourself is called an autologous donation. Volunteer blood donors must pass certain criteria, including the following:
What tests are done in blood banking?
A certain set of standard tests are done in the lab once blood is donated, including, but not limited to, the following:
Why is leukocyte reduced blood filtered?
Leukocyte-reduced blood has been filtered to remove the white blood cells that contain antibodies that can cause fevers in the recipient of the transfusion . (These antibodies, with repeated transfusions, may also increase a recipient's risk of reactions to subsequent transfusions.)
What are the components of blood?
Each unit of blood is broken down into components, such as red blood cells, plasma, cryoprecipitated AHF, and platelets. One unit of whole blood, once it's separated, may be transfused to several patients, each with different needs.
What cells help fight infection?
White blood cells. These cells help to fight infection, and aid in the immune process.
What is the most common blood group system?
ABO blood grouping and Rh typing are the most common blood group systems. There are nearly 300 blood group systems so far discovered. Other than ABO and Rh are MNS, Lutheran, Kell, Duffy, etc. Karl Landsteiner discovered ABO ( A, B and O) in 1900. Two years later, Decastello and Sturli added AB and finally ABO system gets completed. In 1940, Karl Landsteiner and Winner discovered Rh factor in red blood cells (RBCs) of Rhesus monkey ( Macca rhesus ).
How to prepare 10% RBCs?
Preparation of 10% RBCs suspension in normal saline-Mix 5 drops ( 50µl each) of sedimented RBCs with 2 ml of normal saline. Centrifuge at 1500 RPM for 1 minute and discard the supernatant. Put 2 ml of normal saline into the sedimented RBCs and mix it well. This preparation gives a 10% suspension of RBCs.
How does ABO work?
ABO blood grouping and Rh typing work on the principle of agglutination. The normal red blood cells possessing antigens will clump in the presence of corresponding antibodies.
What is the blood group percentage in the US?
Blood group % in US population are A-41%, B-9%, AB-4% and 0-46%.
Can you test blood with finger prick?
Blood obtained from finger-prick may be tested directly by the slide method quickly without making 10% RBCs suspension to avoid clotting and drying. A test that shows no agglutination within 2 minutes is considered negative. Never interpret peripheral drying as fibrin stands as clumping.

Introduction
Principle
- ABO blood grouping and Rh typing are based on the principle of agglutination. The normal red blood cells (RBCs) possessing antigens will clump in the presence of corresponding antibodies.
Test Requirements
- Antisera A,B and Rhesus (Rh)
- Clean and grase free galss slides
- Clean sticks for mixing (optional since slide can be used for this purpose)
- EDTA blood or clotted blood/ skin puncture using lancet at spot test
Procedure
- Label the two different clean slides with the unique ID of the patient.
- Pipette 50/50 µL (one-one drop) of the blood and deliver it to the first slide in two corners and a drop in remaining slide at centre.
- Put the 1 drop of A, B and Rh antisera onto each slide respectively and mix it thoroughly with the help of the clean sticks or using a clean glass slide.
- Label the two different clean slides with the unique ID of the patient.
- Pipette 50/50 µL (one-one drop) of the blood and deliver it to the first slide in two corners and a drop in remaining slide at centre.
- Put the 1 drop of A, B and Rh antisera onto each slide respectively and mix it thoroughly with the help of the clean sticks or using a clean glass slide.
- Tilt the glass slide back and forth for up to 2 minutes.
Result Interpretation
- Applications of ABO Blood Grouping and Rh Typing
It is applicable for the following streams- 1. Prior to blood transfusion and cross-matich. 2. In case of haemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) 3. Determination of paternity in medico-legal cases 4. Relationship of blood groups, susceptibility to variety of diseases e.g. blood group A is more p…
Keynotes
- In the case of doubtful agglutination reactions, further microscopic examination should be done to confirm the result.
- Each negative Rh result should be confirmed by the Du Test.
- For clarification of the aggltination, add a drop of normal saline/physiological saline. Tilt the glass slide back and forth and observe for agglutination/clumping.
- In the case of doubtful agglutination reactions, further microscopic examination should be done to confirm the result.
- Each negative Rh result should be confirmed by the Du Test.
- For clarification of the aggltination, add a drop of normal saline/physiological saline. Tilt the glass slide back and forth and observe for agglutination/clumping.
- To omit prozone and postzone phenomenon, use 10% suspension of RBCs in the palce of using whole blood.