What is the gel used for in gel electrophoresis?
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory method used to separate mixtures of DNA, RNA, or proteins according to molecular size. In gel electrophoresis, the molecules to be separated are pushed by an electrical field through a gel that contains small pores.
What gel is used in DNA electrophoresis?
agarose gelsTraditional agarose gels are most effective at the separation of DNA fragments between 100 bp and 25 kb. To separate DNA fragments larger than 25 kb, one will need to use pulse field gel electrophoresis6, which involves the application of alternating current from two different directions.
Why is the gel in the electrophoresis buffer?
For electrophoresis that separates by charge, scientists use buffer to transmit that charge through the gel. Buffer also maintains the gel at a stable pH, minimizing changes that could occur in the protein or nucleic acid if subjected to unstable pH.
What does agarose gel mean?
Agarose gel is a three-dimensional matrix formed of helical agarose molecules in supercoiled bundles that are aggregated into three-dimensional structures with channels and pores through which biomolecules can pass.
How do you read gel?
0:426:48Electrophoresis: How to Read Results - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd as the electrophoresis reaction is occurring the negative current here is going to push. TheMoreAnd as the electrophoresis reaction is occurring the negative current here is going to push. The samples toward the positive end and so you may end up with something that looks a little like. This.
How is agarose gel made?
Agarose is a polysaccharide derivative of agar. Gels are made by heating up agarose in an appropriate buffer. The gel contains microscopic pores that act as a molecular sieve. Certain molecules can also interact with agarose to varying degrees affecting their mobility.
What purpose does the buffer serve?
The function of a buffer is to keep the pH of a solution within a narrow range.
What is the purpose of the running buffer?
The running buffer contains ions that conduct current through the gel. When proteins are loaded into wells at the top edge and current is applied, the proteins are drawn by the current through the matrix slab and separated by the sieving properties of the gel.
How is DNA separated in gel electrophoresis?
Key points: Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size. DNA samples are loaded into wells (indentations) at one end of a gel, and an electric current is applied to pull them through the gel. DNA fragments are negatively charged, so they move towards the positive electrode.
Why are there 2 bands in gel electrophoresis?
This is because after the enzyme has cut the DNA there will be two different sized DNA fragments. If the patient has a mutation on both of his genes, two bands will result because all of the fragments will be cut.
How does agarose gel work?
Agarose gel electrophoresis is used to resolve DNA fragments on the basis of their molecular weight. Smaller fragments migrate faster than larger ones; the distance migrated on the gel varies inversely with the logarithm of the molecular weight.
Why agarose is used instead of agar?
Agarose is a result of purification of polysaccharide agar. In other words, agar is purified from agar by removing agaropectin in agar. Agarose is very beneficial to bacteria culture since it does not contain protein, food of the bacteria. An agarose is generally extracted from seaweed of agar.
Why agarose gel is not used for proteins?
Proteins are separated by the charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too small to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresis can also be used for the separation of nanoparticles.
What does gel electrophoresis used to separate DNA fragments?
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size. DNA samples are loaded into wells (indentations) at one end of a gel, and an electric current is applied to pull them through the gel. DNA fragments are negatively charged, so they move towards the positive electrode.
Why does DNA move through an agarose gel?
Gel electrophoresis and DNA DNA is negatively charged, therefore, when an electric current is applied to the gel, DNA will migrate towards the positively charged electrode. Shorter strands of DNA move more quickly through the gel than longer strands resulting in the fragments being arranged in order of size.
What are the components of gel electrophoresis?
The gel electrophoresis apparatus consists of a gel, which is often made from agar or polyacrylamide, and an electrophoretic chamber (typically a hard plastic box or tank) with a cathode (negative terminal) at one end and an anode (positive terminal) at the opposite end.
What is gel electrophoresis?
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments (or other macromolecules, such as RNA and proteins) based on their size and charge. Electrophoresis involves running a current through a gel containing the molecules of interest. Based on their size and charge, the molecules will travel through ...
What is DNA gel made of?
Gels for DNA separation are often made out of a polysaccharide called agarose, which comes as dry, powdered flakes. When the agarose is heated in a buffer (water with some salts in it) and allowed to cool, it will form a solid, slightly squishy gel.
How to determine the absolute size of a DNA fragment?
Using electrophoresis, we can see how many different DNA fragments are present in a sample and how large they are relative to one another. We can also determine the absolute size of a piece of DNA by examining it next to a standard "yardstick" made up of DNA fragments of known sizes .
What is the term for separating DNA fragments and other macromolecules by size and charge?
Gel electrophoresis. A technique used to separate DNA fragments and other macromolecules by size and charge.
Why do DNA fragments move faster?
Because all DNA fragments have the same amount of charge per mass, small fragments move through the gel faster than large ones. When a gel is stained with a DNA-binding dye, the DNA fragments can be seen as bands, each representing a group of same-sized DNA fragments.
How does DNA travel through the pores of a gel?
As the gel runs, shorter pieces of DNA will travel through the pores of the gel matrix faster than longer ones. After the gel has run for awhile, the shortest pieces of DNA will be close to the positive end of the gel, while the longest pieces of DNA will remain near the wells.
What is the process of pulling DNA through a gel?
DNA samples are loaded into wells (indentations) at one end of a gel, and an electric current is applied to pull them through the gel.
What is Gel Electrophoreses Used For?
The purpose of gel electrophoresis is to visualize, identify and distinguish molecules that have been processed by a previous method such as PCR, enzymatic digestion or an experimental condition. Often, mixtures of nucleic acids or proteins that are collected from a previous experiment/method are run through gel electrophoresis to determine the identity or differentiate between molecules.
What are some examples of gel electrophoresis?
Examples of Gel Electrophoresis 1 TAE Agarose Gel Electrophoresis is most commonly used for DNA. 2 TBE and Denaturing PAGE (polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) are common for RNA separation. 3 SDS PAGE is a denaturing gel electrophoresis commonly used for protein identification and separation.
How does DNA affect gel electrophoresis?
However, the size of each molecule hinders its progress through the gel. Large molecules hit parts of the gel matrix, and are slowed down. Small DNA molecules can slip between the various components of the gel matrix, and quickly make their way to the other side of the gel. After a certain amount of time, the dyed DNA molecules can be seen aggregating in different areas of the gel, based on how far they moved during gel electrophoresis. This allows researchers to identify the segments, and compare the DNA of different organisms.
How is agarose TAE poured?
The agarose TAE solution is poured into a casting tray that, once the gel solution has cooled down and solidified, creates a gel slab with a row of wells at the top.
How does gel work?
The gel works in a similar manner to a sieve separating particles by size. The electrophoresis works to move the particles, using their inherent electric charge, through the sieve. When researchers are trying to distinguish between different segments of DNA, for example, the process is simple. The samples are loaded into channels at the start ...
Where is the TAE gel placed?
The solid gel is placed into a chamber filled with TAE buffer. The gel is positioned so that the chamber wells are closest to the negative electrode of the chamber.
What is the name of the compound that intercalates DNA?
Ethidium bromide intercalates between DNA and is visible in UV light. Sometimes ethidium bromide is added directly to the agarose gel solution in step 2. The ethidium bromide stained gel is then exposed to UV light and a picture is taken. DNA bands are visualized in from each lane corresponding to a chamber well.
What is the gel electrophoresis chamber made of?
The gel electrophoresis apparatus consists of a gel, which is often made from agar or polyacrylamide, and an electrophoretic chamber (typically a hard plastic box or tank) with a cathode (negative terminal) at one end and an anode (positive terminal) at the opposite end.
What is the name of the compound that replaces DNA?
RNA, complex compound of high molecular weight that functions in cellular protein synthesis and replaces DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a carrier of genetic codes in some viruses.
How does the density of pores affect the rate of molecule migration?
The density of pores and the type of substance used to make the gel further influence the rate of molecule migration.
Why do dyed samples have to be run alongside experimental samples?
Often a dyed “ladder,” or marker with multiple molecules of known and varying molecular weights, is run alongside experimental samples to serve as a reference for size . The dye enables the visualization of the marker as it moves through the gel; samples typically are also dyed for visualization.
What is Gel Electrophoresis?
Gel electrophoresis is a process where a sample, typically proteins or DNA, in solution is pulled apart or separated inside a mold using electrical charges.
How to use agarose in electrophoresis?
Which buffer to use is determined by whether DNA or Protein samples will be used. Simply boiling together agarose and electrophoresis buffer will dissolve the agarose. Then carefully pour the agarose solution into the casting tray like pouring a Jell-O mold. While the agarose is still steaming and liquid, slide the comb into the agarose where the casting tray is indented. The agarose will then need to cool and solidify. Once the gel is ready it will be solid with a firm Jell-O-like consistency. Very carefully remove the comb to reveal the wells then remove the tape or bumpers so both ends of the solid agarose material are exposed. A traditional electrophoresis chamber will have a negative and positive electrode with space between for the material to sit. The electrodes will connect to a removal top and will plug into a power supply.
How is DNA electrophoresis performed?
Both DNA and Protein electrophoresis can be performed with the same equipment and in the same manner. Horizontal gel electrophoresis uses an agarose gel, which under a microscope has a mesh-like structure. While vertical electrophoresis uses a polyacrylamide gel. Polyacrylamide gels are a thinner consistency, which can make the viewing the electrophoresis process easier. This technique is based on the movement of charged molecules when they are exposed to an electrical field. This movement occurs across the sheet of gel, or to put it another way, in a gel-medium. But what does electricity have to do with DNA or proteins?
Why is gel electrophoresis important?
Gel electrophoresis is simply identification. Due to its versatility, it has become one of the most important tools of crime scene investigation and protein analysis. Forensic investigators use this tool of genotyping DNA samples to distinguish one human being from another. Gel electrophoresis is commonly used around the world for not only for the investigation of crime scenes but also for identifying missing persons, attaching names to bodies in mass disasters, naming the victims in human rights violations, and in paternity testing.
What is the purpose of elution?
Elution can be used to then take the fragment of the sample from the material to be used for further future use. The elution process is very simply just cutting out the fragment from the gel and forcing it through a strainer in a centrifuge to remove the agarose but keep everything inside the pores. After this process, you’re left with a solution of DNA or Protein dissolved in electrophoresis buffer. Elution is done in such a way that the individual fragments of DNA can be used for further downstream processing, such as genome sequencing.
How to stain a gel?
To stain the gel, simply submerge it in the chosen stain for several minutes. Then rinse by submerging in water. Gels stained with Methylene Blue, Coomassie Blue or color development buffer can be placed directly on a light box and can be seen with the naked eye. The samples will be a blueish-purple color. Gels stained with Ethidium Bromide require an ultraviolet light and amber UV-blocking glasses to view.
Why is DNA negatively charged?
DNA is negatively charged. This is due to the presence of phosphate groups. The DNA helix does not consist just of the four bases adenosine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Its backbone contains billions of phosphate groups, each with a tiny negative electrical charge. The presence of phosphate groups gives DNA its helical shape.
Overview
- The process of gel electrophoresis works because negatively charged molecules move away from the negative pole of the electric current and smaller molecules will move faster than larger molecules. Thus, a size separation is achieved within the pool of molecules running through the gel. The gel works in a similar manner to a sieve separating particles by size. The electrophoresi…
Gel Conditions
- The types of gel most typically used are agarose and polyacrylamide gels. Each type of gel is well-suited to different types and sizes of analyte. Polyacrylamide gels are usually used for proteins, and have very high resolving power for small fragments of DNA. Agarose gels on the other hand have lower resolving power for DNA but have greater range of separation, and are therefore use…
Applications
- Gel electrophoresis is used in forensics, molecular biology, genetics, microbiology and biochemistry. The results can be analyzed quantitatively by visualizing the gel with UV light and a gel imaging device. The image is recorded with a computer operated camera, and the intensity of the band or spot of interest is measured and compared against standard or markers loaded on t…
- When the current is switched on, the samples tend to move towards the positively charged side of the apparatus since the phosphate backbones of the molecules confer a negative charge on them. After the samples have run a sufficient distance, the matrix is studied to view the bands that are formed by the separation of the molecules.
- The invention of gel electrophoresis has been vital for many fields as its application exists in a wide variety of areas. It is more often used with PCR – polymerase chain reaction to analyze the separated bands; also can be used in mass spectrometry; Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), DNA fingerprinting, Genomic library creation, electroblotting techniques f…
Use
- The first step to gel electrophoresis is to set the gel matrix. Agarose is used to separate DNA molecules, and acrylamide is used to separate proteins. The gel starts off as a liquid, which is poured into a molding tray. A comb is placed in the liquid matrix so that when the matrix solidifies, wells are formed to load samples in them. Once the gel has solidified, it is removed from the mo…
- Salt water solution is poured into the bottom of the electrophoresis chamber, and the gel matrix is submerged slightly within this solution. The salt water serves two purposes: aiding the flow of electricity and keeping the gel matrix moist. Since DNA is propelled by a negative charge, place your matrix so your samples will be located next to your negative electrical connection. DNA sa…
Introduction
- Gel electrophoresis is a process of separating bio molecules of different sizes by running them through a sievelike matrix using electricity. The larger molecules move more slowly, while smaller molecules slip through the matrix and move faster and farther, thus separating the different fragments based on size.
- Gel electrophoresis is a method used in laboratories to measure and sort strands of DNA. It is necessary because DNA under normal conditions is too small to manipulate, even when viewed using most microscopes. The gel electrophoresis lab uses a relatively straightforward procedure, and the same basic technique can be used to separate individual proteins, as well.
Example
- 1. TAE Agarose Gel Electrophoresis is most commonly used for DNA. 2. TBE and Denaturing PAGE (polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) are common for RNA separation. 3. SDS PAGE is a denaturing gel electrophoresis commonly used for protein identification and separation.
- Now, turn on your electrophoresis chamber. Under negative power, your DNA samples will be forced across the length of the chamber. Small strands of DNA will move more quickly through the gel matrix, and in a short amount of time they will separate themselves from longer, slower strands. The dye in the coloring agent lets you follow the track of the DNA. You will not be able t…
History
- A 1959 book on electrophoresis by Milan Bier cites references from the 1800s. However, Oliver Smithies made significant contributions. Bier states: "The method of Smithies... is finding wide application because of its unique separatory power." Taken in context, Bier clearly implies that Smithies' method is an improvement.
Definition
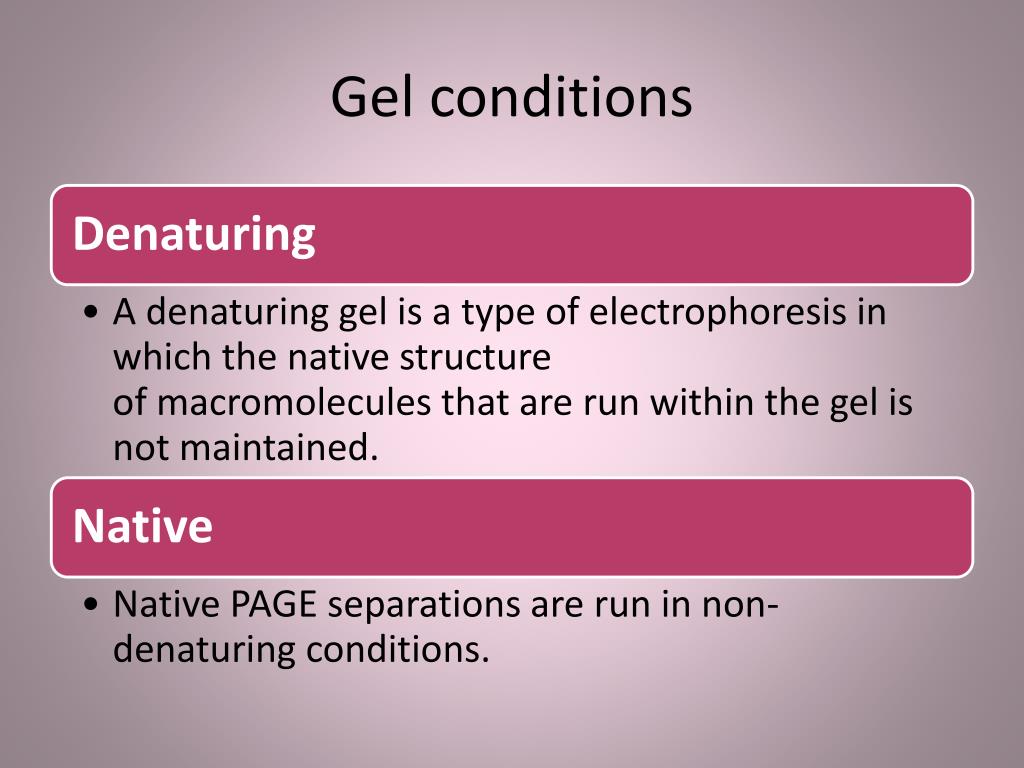
- There are two types of gel electrophoresis: native and denaturing. Native gel electrophoresis usually attempts to keep RNA or protein in its native structure while running it through the gel. Denaturing gel electrophoresis attempts to reduce the RNA or protein into its most linear structure before or during gel electrophoresis.The denaturation of the RNA or protein is accomplished by …
- “Electrophoresis” is an Anglo-Greek word, where “Electro” stands for electric field and “Phoresis” refers to movement. Thus, Gel Electrophoresis is a method where the biomolecules are separated under the influence of the electric field.Gel electrophoresis is used for separation of charged molecules such as nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and proteins. Let’s understand the basic principle t…
Visualization
- After the electrophoresis is complete, the molecules in the gel can be stained to make them visible. DNA may be visualized using ethidium bromide which, when intercalated into DNA, fluoresce under ultraviolet light, while protein may be visualised using silver stain or Coomassie Brilliant Blue dye. Other methods may also be used to visualize the separation of the mixture's c…
Construction
- Your next step is to create an electrophoresis chamber. This is a small rectangular box, wired with a positive and negative electrical connection at either end. Chambers are typically shallow, small enough to fit on a tabletop, and built from clear materials like Plexiglas.