What are the different genotypes of peas?
1. The possible genotypes are PpYY, PpYy, ppYY, and ppYy. The former two genotypes would result in plants with purple flowers and yellow peas, while the latter two genotypes would result in plants with white flowers with yellow peas, for a 1:1 ratio of each phenotype.
What is the dominant gene for pea color?
And that the genes can come in different versions. So the pea color gene comes in two versions or alleles, yellow and green. To make things simpler, geneticists usually label a dominant trait with a capital letter and the recessive trait with a lowercase letter. In this case we will use Y for the yellow version and y for the green one.
What is the difference between s and C alleles in peas?
In pea plants the S allele produces round peas and the s allele produces wrinkled peas when in the homozygous state. The C allele produces yellow peas and the c allele produces green peas when in the homozygous state. A test cross is set up between two pea plants: SsCc x sscc which resulted in the progeny below.
Why are green peas YY and yellow peas y?
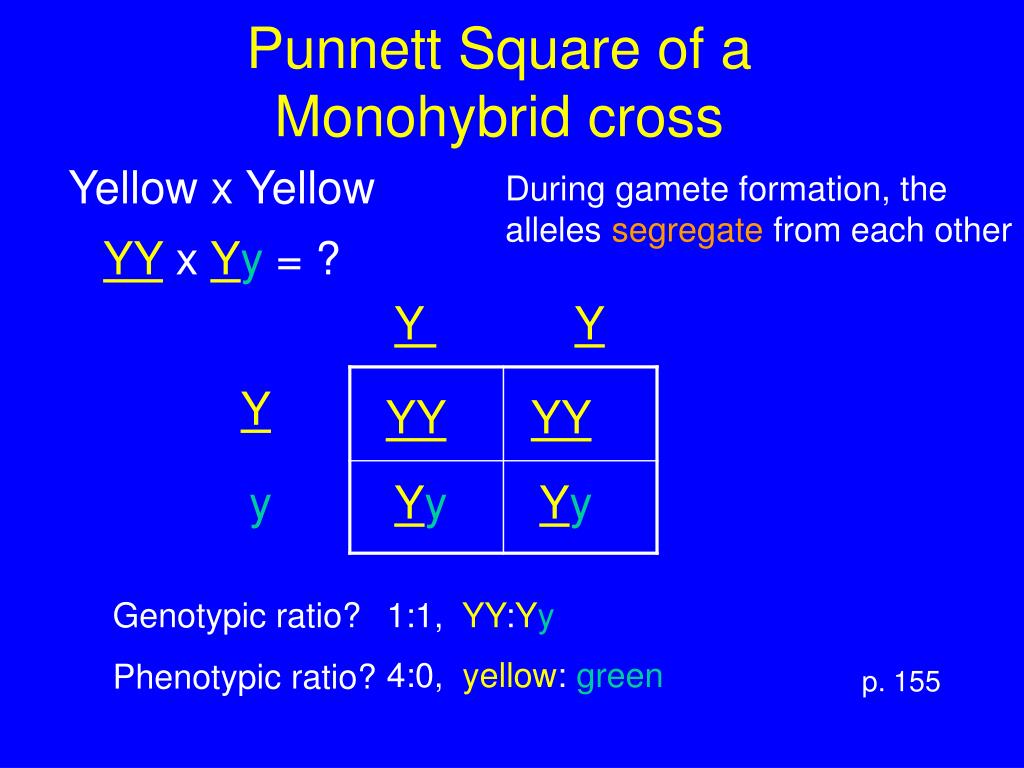
Since Mendel’s plants were purebred, the yellow peas had two yellow alleles and so were YY and the green peas had two green alleles and were yy. Each parent can pass one copy of their gene to the next generation.

Which genotype will produce a green pea?
The pea “color” gene comes in a yellow version (Y) and a green version (y). Just like us, pea plants have two copies of most of their genes. This means that there are three possible combinations for this color gene: YY.
What is the genotype of a pea plant?
A purple-flowered pea plant may have the genotype PP or Pp. A white-flowered pea plant would have the genotype pp.
What is the genotype for round peas?
RGiven an inheritance pattern of dominant–recessive, the genotypic and phenotypic ratios can then be determined. In pea plants, round peas (R) are dominant to wrinkled peas (r). You do a test cross between a pea plant with wrinkled peas (genotype rr) and a plant of unknown genotype that has round peas.
What is phenotype and genotype of pea plant?
An organism's genotype is its specific combination of alleles for a given gene. So, for example, in the pea plants above, the possible genotypes for the flower-color gene were red-red, red-white, and white-white. The phenotype is the physical manifestation of an organism's allellic combination (genotype).
What is genotype BB?
An organism with two dominant alleles for a trait is said to have a homozygous dominant genotype. Using the eye color example, this genotype is written BB.
What is the genotype of the phenotype wrinkled green peas?
Pure-bred round -yellow pea seeds have genotype RRYY and the pure-bred wrinkled-green pea seeds have genotype rryy. Keeping this in mind, write the phenotypes of the following genotypes of hybrid pea seeds.
What is RR genotype?
The (RR) genotype is homozygous dominant and the (rr) genotype is homozygous recessive for seed shape. In the image above, a monohybrid cross is performed between plants that are heterozygous for round seed shape. The predicted inheritance pattern of the offspring results in a 1:2:1 ratio of the genotype.
What is the genotype for a pea plant heterozygous for round seeds?
RrSince this pea plant is heterozygous for round shape, its genotype would be Rr.
Is PP genotype or phenotype?
A simple example to illustrate genotype as distinct from phenotype is the flower colour in pea plants (see Gregor Mendel). There are three available genotypes, PP (homozygous dominant ), Pp (heterozygous), and pp (homozygous recessive).
Is TT purebred or hybrid?
The result of this cross was all tall hybrid pea plants (Tt). When these second-generation plants were crossed, the result was one tall (TT) purebred; two tall (Tt) hybrids; and one short (tt) purebred. Mendel concluded that tallness in pea plants was dominant, and became the expressed trait, (uppercaseT).
What are the heterozygous genotypes?
The presence of two different alleles at a particular gene locus. A heterozygous genotype may include one normal allele and one mutated allele or two different mutated alleles (compound heterozygote).
Which is a phenotype?
Phenotype refers to an individual's observable traits, such as height, eye color and blood type. A person's phenotype is determined by both their genomic makeup (genotype) and environmental factors.
What are the possible genotypes of peas?
Answers: 1. The possible genotypes are PpYY, PpYy, ppYY, and ppYy. The former two genotypes would result in plants with purple flowers and yellow peas, while the latter two genotypes would result in plants with white flowers with yellow peas, for a 1:1 ratio of each phenotype. 2.
What are the two alleles of a diploid?
Phenotypes and Genotypes. Two alleles for a given gene in a diploid organism are expressed and interact to produce physical characteristics. The observable traits expressed by an organism are referred to as its phenotype.
How many types of monohybrid crosses did Mendel perform?
Mendel performed seven types of monohybrid crosses, each involving contrasting traits for different characteristics. Out of these crosses, all of the F 1 offspring had the phenotype of one parent, and the F 2 offspring had a 3:1 phenotypic ratio.
How is recessive trait expressed?
The recessive trait will only be expressed by offspring that have two copies of this allele (Figure 2), and these offspring will breed true when self-crossed.
How many copies of the characteristic are passed to offspring?
The seven characteristics that Mendel evaluated in his pea plants were each expressed as one of two versions, or traits. Mendel deduced from his results that each individual had two discrete copies of the characteristic that are passed individually to offspring. We now call those two copies genes, which are carried on chromosomes.
Why do we have two copies of each gene?
The reason we have two copies of each gene is that we inherit one from each parent. In fact, it is the chromosomes we inherit and the two copies of each gene are located on paired chromosomes. Recall that in meiosis these chromosomes are separated out into haploid gametes.
Can genotypic ratios be determined from a Punnett square?
Because each possibility is equally likely, genotypic ratios can be determined from a Punnett square. If the pattern of inheritance (dominant and recessive) is known, the phenotypic ratios can be inferred as well. For a monohybrid cross of two true-breeding parents, each parent contributes one type of allele.
