What Are the Functions of The Golgi Apparatus/Golgi Complex?
- The Golgi apparatus is responsible for transporting molecules and sorting them. ...
- The Golgi complex also aids in synthesizing molecules, such as lipids and saccharides found in the cell.
- The Golgi apparatus makes up a system of transport for molecules within the structure. ...
Why is the Golgi aparatus the most important organelle?
Why the Golgi Apparatus is THE most important organelle. The Golgi Apparatus is important because it processes and packages protein and lipid. without the golgi apparatus you would lose your DNA, because DNA is composed of protein. Also, without lipids your cells would have misformed shpaes because the cell membrane is somposed of a bi lipid ...
What is the function of the Golgi?
Postural Stability and GTOs
- Each GTO is innervated by a single myelinated Ib afferent. ...
- Ib axons are fast conducting (72–120 m/s), bifurcate when entering the spinal cord, and send branches rostrally and caudally via the dorsal columns.
- Branches that enter the gray matter principally terminate in Rexed's laminae V–VII (Fig. ...
How does Golgi apparatus maintain homeostasis?
How do Golgi bodies maintain homeostasis? The Golgi apparatus helps maintain cellular homeostasis by secreting proteins. These proteins may be signalling peptides that help induce changes in gene expression in target cells. These changes in gene expression may be used to regulate levels of metabolites and promote homeostasis.
What does the Golgi aparatus do?
The Golgi apparatus, or Golgi complex, functions as a factory in which proteins received from the ER are further processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations: lysosomes, the plasma membrane, or secretion. In addition, as noted earlier, glycolipids and sphingomyelin are synthesized within the Golgi.

What is the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also called Golgi complex or Golgi body, is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells (cells with clearly defined n...
How was the Golgi apparatus discovered?
The Golgi apparatus was observed in 1897 by Italian cytologist Camillo Golgi. In Golgi’s early studies of nervous tissue, he established a staining...
How is the Golgi apparatus structured?
In general, the Golgi apparatus is made up of approximately four to eight cisternae, although in some single-celled organisms it may consist of as...
What is the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is a type of organelle (i.e., a structure located in the cell) that processes a...
Where is the Golgi apparatus located?
The Golgi apparatus is a series of stacked membranes that are located within the cytoplasm (i.e., gel-like fluid held in the cell membrane) in all...
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The function of the Golgi apparatus is processing and packaging proteins that have exited the rough endoplasmic reticulum to be further transported...
What are the most important facts to know about the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is an organelle that processes and packages proteins and lipid molecules (i.e.,...
What is the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is a type of organelle (i.e., a structure located in the cell) that processes and packages proteins and lipid molecules (i.e., fat molecules). These are later transported to other cell compartments (e.g., lysosomes or the plasma membrane) or secreted from the cell.
Where is the Golgi apparatus located?
The Golgi apparatus is a series of stacked membranes that are located within the cytoplasm (i.e., gel-like fluid held in the cell membrane) in all eukaryotic cells (i.e., complex cells). It can typically be found adjacent to the nucleus and rough endoplasmic reticulum (an organelle involved in protein synthesis).
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The function of the Golgi apparatus is processing and packaging proteins that have exited the rough endoplasmic reticulum to be further transported inside and/or outside the cell. In plant cells, the Golgi body also serves as the site for the synthesis of complex polysaccharides.
What are the most important facts to know about the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is an organelle that processes and packages proteins and lipid molecules (i.e., fat molecules) that are later exported to other cell compartments or secreted from the cell. The Golgi body has Golgi stacks, which are involved in modifying proteins and other complex polysaccharides.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle in eukaryotic organisms that moves molecules from the endoplasmic reticulum to their destination. The organelle also modifies products of the endoplasmic reticulum to their final form. The Golgi apparatus is comprised of a series of flattened sacs that extend from the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the function of the Golgi?
The Golgi also has important functions in tagging vesicles with proteins and sugar molecules, which serve as identifiers for the vesicles so they can be delivered to the proper target. The organelle is also called the Golgi complex or Golgi body.
What is the trans face of the Golgi apparatus?
The side furthest from the endoplasmic reticulum is known as the trans face of the Golgi apparatus, and this is where products are headed. After having any modifications or additions to their structure, the products are packaged in vesicles and tagged with markers that indicate where the vesicle needs to end up.
How does the Golgi apparatus form?
This model suggests that the sacs themselves tend to move from the cis face to the trans face of the Golgi apparatus over time. New sacs are formed closest to the endoplasmic reticulum. These sacs “age” as they move towards the trans face of the Golgi apparatus and their product becomes fully mature.
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum has a number of ribosomes, which assemble proteins from instructions contained in messenger RNA . Throughout the rest of the endoplasmic reticulum, these protein products are folded and modified. As they reach the Golgi apparatus, more modifications are made.
Where is the Golgi apparatus located?
Golgi Apparatus Location. The Golgi apparatus is situated in between the endoplasmic reticulum and the cell membrane. Most often, the Golgi appears to be an extension of the endoplasmic reticulum which is slightly smaller and smoother in appearance. However, the Golgi apparatus can be easily mistaken for smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
Which apparatus is responsible for the final presentation and assembly of products?
While the endoplasmic reticulum produces most of the products and bases used, it is the Golgi apparatus that is responsible for the final presentation and assembly of products. Often, the environment must be slightly different from that present in the endoplasmic reticulum to obtain certain end products. The many sacs of the Golgi apparatus ...
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
Another important function of the Golgi apparatus is in the formation of proteoglycans. Enzymes in the Golgi append proteins to glycosaminoglycans, thus creating proteoglycans. Glycosaminoglycans are long unbranched polysaccharide molecules present in the extracellular matrix of animals.
Where is the Golgi apparatus located?
In mammals, a single Golgi apparatus is usually located near the cell nucleus, close to the centrosome. Tubular connections are responsible for linking the stacks together.
What was the first organelle to be discovered?
Owing to its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system. After first observing it under his microscope, he termed the structure as apparato reticolare interno ("internal reticular apparatus"). Some doubted the discovery at first, arguing that the appearance of the structure was merely an optical illusion created by the observation technique used by Golgi. With the development of modern microscopes in the twentieth century, the discovery was confirmed. Early references to the Golgi apparatus referred to it by various names including the "Golgi–Holmgren apparatus", "Golgi–Holmgren ducts", and "Golgi–Kopsch apparatus". The term "Golgi apparatus" was used in 1910 and first appeared in the scientific literature in 1913, while "Golgi complex" was introduced in 1956.
What is the name of the structure that Golgi discovered?
After first observing it under his microscope, he termed the structure as apparato reticolare interno ("internal reticular apparatus"). Some doubted the discovery at first, arguing that the appearance of the structure was merely an optical illusion created by the observation technique used by Golgi.
Where do enzymatic reactions occur in Golgi stacks?
Enzymatic reactions within the Golgi stacks occur exclusively near its membrane surfaces , where enzymes are anchored. This feature is in contrast to the ER, which has soluble proteins and enzymes in its lumen. Much of the enzymatic processing is post-translational modification of proteins.
Is the Golgi apparatus dependent on microtubules?
Localization and tubular connections of the Golgi apparatus are dependent on microtubules. In experiments it is seen that as microtubules are depolymerized the Golgi apparatuses lose mutual connections and become individual stacks throughout the cytoplasm.
Is the Golgi stacking observed in yeast?
There are structural and organizational differences in the Golgi apparatus among eukaryotes. In some yeasts, Golgi stacking is not observed. Pichia pastoris does have stacked Golgi, while Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, or Golgi complex, functions as a factory in which proteins received from the ER are further processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations: lysosomes, the plasma membrane, or secretion. In addition, as noted earlier, glycolipids and sphingomyelin are synthesized within the Golgi.
How are proteins transported from the Golgi apparatus?
Transport from the Golgi apparatus. Proteins are sorted in the transGolgi network and transported in vesicles to their final destinations. In the absence of specific targeting signals, proteins are carried to the plasma membrane by constitutive secretion. (more...)
Which polysaccharides are synthesized in the Golgi apparatus?
The other cell wall polysaccharides (hemicelluloses and pectins), however, are complex, branched chain molecules that are synthesized in the Golgi apparatus and then transported in vesicles to the cell surface.
Which pathway is responsible for the incorporation of new proteins and lipids into the plasma membrane?
Some proteins are carried from the Golgi to the plasma membraneby a constitutive secretory pathway, which accounts for the incorporation of new proteins and lipids into the plasma membrane, as well as for the continuous secretion of proteins from the cell.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
Golgi apparatus is the site for the synthesis of various glycolipids, sphingomyelin, etc. In the plant cells, complex polysaccharides of the cell wall are synthesised in the Golgi apparatus. To learn more about Golgi Apparatus and other cells organelles, visit BYJU’S. Test your Knowledge on Golgi Apparatus. Q 5.
What is the function of Golgi bodies?
Golgi Bodies Functions. Its main function is the packaging and secretion of proteins. It receives proteins from Endoplasmic Reticulum. It packages it into membrane-bound vesicles, which are then transported to various destinations, such as lysosomes, plasma membrane or secretion.
How many cisternae are in a Golgi?
Cisternae is a flattened, disk-shaped, stacked pouches that make up the Golgi apparatus. A Golgi stack mostly contains 4 to 8 cisternae.
Where is the Golgi apparatus found?
The name is given on the name of the scientist, who discovered the organelle, i.e. Camillo Golgi. It is found in all the eukaryotic cells , plants as well as animals. They are membrane-bound organelle present in the cytosol of the cell.
How many Golgi stacks are there in an animal cell?
Animal cells generally contain around 10 to 20 Golgi stacks per cell, which are connected by tubular connections. Golgi complex is mostly found near the nucleus. Creation, or evolution, whichever one, you hold a belief in has worked in wondrous ways to evolve or design the various living beings in this world in the most optimum ways.
What is the function of the Golgi?
In fact, one of the functions of the Golgi is to make new vesicles out of the existing membrane of the Golgi and put into those vesicles the glycoproteins and other substances that are made in the Golgi network.
What is the Golgi body?
=. A Golgi body, also known as a Golgi apparatus, is a cell organelle that helps process and package proteins and lipid molecules, especially proteins destined to be exported from the cell. Named after its discoverer, Camillo Golgi, the Golgi body appears as a series of stacked membranes.
Where is the Golgi body located?
Some of them are tubules, and some of them are vesicles. The Golgi is located right near the nucleus.
Do carbohydrates move out of the Golgi?
For example, carbohydrates are put on some of the proteins, and then afterwards these glycoproteins--meaning they have carbohydrate as well as protein on them, these glycoproteins move out of the Golgi to the rest of the cell. And they do so inside other vesicles. Those vesicles are actually made from the Golgi network.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
In plant cells, the Golgi Apparatus is the site of synthesis for complex polysaccharides that form a part of the cell wall of plants. The Golgi Apparatus forms the transportation network for movement of molecules and proteins to and from other organelles of the cell.
What is the function of the Golgi complex?
Also known as the Golgi complex, its primary function is to receive, process and sort proteins coming from and to the ER. Functionally, The Golgi Apparatus has four distinct regions: The cis Golgi network, The Golgi Stack which is further divided into medial and trans sub-regions, and the trans-Golgi network.
What is the process of glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus?
Protein processing events for glycoproteins within the Golgi apparatus comprises of a series of events that terminates in modification or glycosylation of the carbohydrate moieties of the protein structures. In the ER, the proteins undergo post-translational modifications.
How are proteins transported to other organelles?
Proteins, lipids, and molecules are transported to other cellular compartments and organelles by the process of Exocytosis that occurs in the Golgi Apparatus. . Exocytosis is a transport and secretory pathway that makes use of vesicles to transport substances from the Golgi to other organelles.
When was the Golgi apparatus discovered?
The Golgi Apparatus was discovered by biologist Camillo Golgi in 1898 during an experiment that involved staining neuronal cells. It was described as an intracellular reticular compartment inside the cell.
Which pathway allows the Golgi apparatus to move materials into the cell?
In a similar fashion, the Golgi apparatus is also involved in a secretory pathway that allows movement of materials into the cell, from its Cis-face. . Endocytosis is a vesicular transport pathway that makes use of vesicles to transport materials into the Golgi apparatus for processing or modification.
When was the reticular structure of Golgi discovered?
Following this discovery, in 1900 , Golgi, Negri, and Cajal attempted to stain and visualize this compartment in many other different kinds of cells. This discovered structure has initially coined the term “ The reticular structure of Golgi “.
Introduction
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in most eukaryotes. This organelle is located near the nucleus and endoplasmic reticulum, but it does not directly contact these structures. The name “Golgi” comes from Camillo Golgi, who first discovered the structure in 1898.
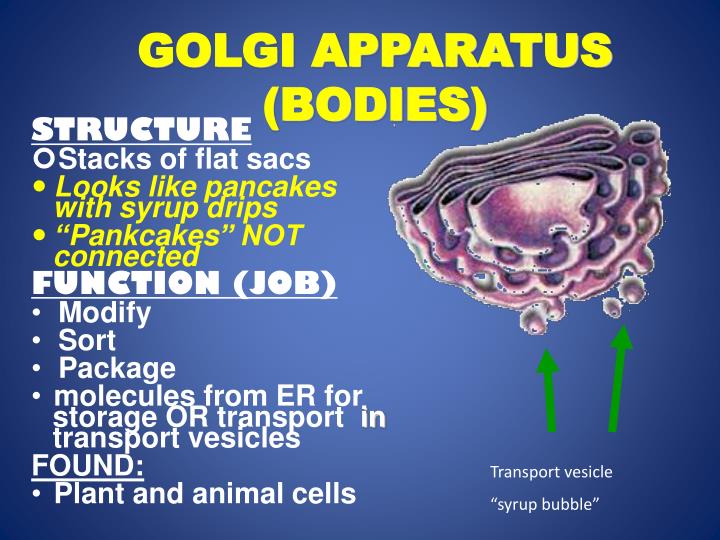
The Golgi Apparatus Structure
The Golgi apparatus is also called the Golgi complex or the Golgi body. It is a stack of membrane-bound sacs called cisternae. These are connected by tubules that form the Golgi complex.
The Molecule Modification Role of the Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying molecules that it takes from the ER. The two main ways in which this happens are through glycosylation and phosphorylation.
The Role of the Golgi Apparatus as a Transport Network for Molecules
The Golgi apparatus can be seen as a transport network for molecules. It can do this due to the tubules that connect the different parts of the Golgi.
How Do The Cis Golgi Network and Trans Golgi Network Co-function?
The cis Golgi network and trans-Golgi network work together in coordinating the functions of the organelle. As its name suggests, the cis Golgi network is found on the inside of a cell. It connects to different cells and helps transport material from one part of the organelle to the other.
Golgi Apparatus Disassembly and Reassembly
The Golgi apparatus can disassemble and reassemble during cytokinesis. The typical Golgi shape is a stack of vesicles, but the whole structure can disassemble and reassemble due to its dynamism.
Summary
The Golgi apparatus is a type of organelle that has many essential functions. It’s located near axons and dendrites, which means it can be found near cell bodies as well.

Definition
Operation
- Regardless of the product, the vesicles containing the product move from the endoplasmic reticulum and into the cis face of the Golgi apparatus. In laymans terms, this is the side facing the endoplasmic reticulum. The side furthest from the endoplasmic reticulum is known as the trans face of the Golgi apparatus, and this is where products are headed. After having any modificatio…
Products
- There are many products that are produced by eukaryotes, from proteins that can carry out chemical reactions to lipid molecules that can build new cell membranes. Some products are meant for the endoplasmic reticulum or the Golgi apparatus itself and travel in the opposite direction of most vesicles. While the endoplasmic reticulum produces most of the products and …
Causes
- In secretory cells, or cells which produce large amounts of a substance that your body needs, the Golgi apparatus will be very large. Consider the cells in your stomach that secrete acid. The acid is produced by reactions in the endoplasmic reticulum and is modified as is goes through the Golgi apparatus. Once to the trans side of the Golgi apparatus, the acid is packaged in a vesicle and s…
Structure
- The image below shows the structure of the Golgi apparatus. The cis face of the organelle is closest to the endoplasmic reticulum. The trans face is the side furthest from the nucleus, which secretes vesicles to various parts of the cell. Further, there are a number of lumens and cisternae through which products flow. These appear as a series of flattened sacs stack on each other, m…
Formation
- The most prevalent theory of how the Golgi apparatus forms is the cisternal maturation model. This model suggests that the sacs themselves tend to move from the cis face to the trans face of the Golgi apparatus over time. New sacs are formed closest to the endoplasmic reticulum. These sacs age as they move towards the trans face of the Golgi apparatus and their product become…
Development
- Although it may seem like there could never be enough lipids to produce the continual flow of cell membrane needed to continually make transport vesicles between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus, there are constantly segments of cell membrane being produced and recycled by the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and other organelles in the …
Function
- The Golgi also creates lysosomes. These sacs contain digestive materials. The sacs are pinched off from the Golgi apparatus, and they are used to process materials which have been phagocytized or to digest organelles which no longer function. The lysosome delivers raw ingredients to the endoplasmic reticulum. While this article primarily discusses the operation of …
Overview
The Golgi apparatus , also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. It is of partic…
Discovery
Owing to its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system. After first observing it under his microscope, he termed the structure as apparato reticolare interno ("internal reticular apparatus"). Some doubted the discovery at first, arguing that the appearance of the structure was merely an optica…
Subcellular localization
The subcellular localization of the Golgi apparatus varies among eukaryotes. In mammals, a single Golgi apparatus is usually located near the cell nucleus, close to the centrosome. Tubular connections are responsible for linking the stacks together. Localization and tubular connections of the Golgi apparatus are dependent on microtubules. In experiments it is seen that as microtubules are depolymerized the Golgi apparatuses lose mutual connections and become in…
Structure
In most eukaryotes, the Golgi apparatus is made up of a series of compartments and is a collection of fused, flattened membrane-enclosed disks known as cisternae (singular: cisterna, also called "dictyosomes"), originating from vesicular clusters that bud off the endoplasmic reticulum. A mammalian cell typically contains 40 to 100 stacks of cisternae. Between four and eight ci…
Function
The Golgi apparatus is a major collection and dispatch station of protein products received from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Proteins synthesized in the ER are packaged into vesicles, which then fuse with the Golgi apparatus. These cargo proteins are modified and destined for secretion via exocytosis or for use in the cell. In this respect, the Golgi can be thought of as similar to a po…
Vesicular transport
The vesicles that leave the rough endoplasmic reticulum are transported to the cis face of the Golgi apparatus, where they fuse with the Golgi membrane and empty their contents into the lumen. Once inside the lumen, the molecules are modified, then sorted for transport to their next destinations.
Those proteins destined for areas of the cell other than either the endoplasmic …
Current models of vesicular transport and trafficking
• In this model, the Golgi is viewed as a set of stable compartments that work together. Each compartment has a unique collection of enzymes that work to modify protein cargo. Proteins are delivered from the ER to the cis face using COPII-coated vesicles. Cargo then progress toward the trans face in COPI-coated vesicles. This model proposes that COPI vesicles move in two directions: anterograde vesicles carry secretory proteins, while retrograde vesicles recycle Golgi-sp…
Brefeldin A
Brefeldin A (BFA) is a fungal metabolite used experimentally to disrupt the secretion pathway as a method of testing Golgi function. BFA blocks the activation of some ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs). ARFs are small GTPases which regulate vesicular trafficking through the binding of COPs to endosomes and the Golgi. BFA inhibits the function of several guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) that mediate GTP-binding of ARFs. Treatment of cells with BFA thus disrupts th…