Heritability. Family studies indicate that the closer a person’s genetic relatedness to a person with schizophrenia, the greater the likelihood of developing the disorder. The paternal age is a factor in schizophrenia because of the increased likelihood of mutations in the chromosomes of cells that produce sperms.
What are the genetic factors of schizophrenia?
The genetic variations associated with schizophrenia include duplications, deletions, and microdeletions. One of the most-studied deletions with a high rate of schizophrenia is the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. It's estimated that about 22% of people with this deletion have schizophrenia. 7
What is the inheritance pattern of schizophrenia?
The inheritance pattern for schizophrenia is usually unknown. The risk of developing schizophrenia is somewhat higher for family members of affected individuals as compared to the general public; however, most people with a close relative who has schizophrenia will not develop the disorder themselves.
How much of schizophrenia is hereditary?
What researchers have found is that schizophrenia does indeed run in families, but this does not completely account for the cause of schizophrenia. For example, parents and children share 50% of their genes but the risk of getting schizophrenia if one has a schizophrenic parent is only 6%.
How likely is schizophrenia hereditary?
You’re more likely to get schizophrenia if someone in your family has it. If it’s a parent, brother, or sister, your chances go up by 10%. If both your parents have it, you have a 40% chance of...

What is the approximate heritability of schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia and heredity A 2017 study from Denmark based on nationwide data on over 30,000 twins estimates the heritability of schizophrenia at 79 percent. The study concluded that, based on the risk of 33 percent for identical twins, the vulnerability for schizophrenia isn't solely based on genetic factors.
What is meant by the heritability of schizophrenia?
Heritability is the proportion of variance explained by genetic factors. The concordance rates of schizophrenia for monozygotic twins have been found to be about 40 to 50%, and heritability estimates are around 80% 46,47.
What is the inheritance pattern of schizophrenia?
Inheritance. The inheritance pattern for schizophrenia is usually unknown. The risk of developing schizophrenia is somewhat higher for family members of affected individuals as compared to the general public; however, most people with a close relative who has schizophrenia will not develop the disorder themselves.
Is schizophrenia 100% genetic?
The researchers conclude: "The estimated 79% heritability of schizophrenia is congruent with previous reports and indicates a substantial genetic risk. The high genetic risk also applies to a broader [range of] schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
Is schizophrenia dominant or recessive?
The familial nature of schizophrenia does not conform to simple dominant or recessive modes of inheritance. Schizophrenia is a common and severe mental illness of thought, emotion, and behavior that affects about 1% of the general population.
Which mental disorder has the highest rate of heritability?
Heritability and genetics Most psychiatric disorders are highly heritable; the estimated heritability for bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and autism (80% or higher) is much higher than that of diseases like breast cancer and Parkinson disease.
How does schizophrenia run in the family?
You're more likely to get schizophrenia if someone in your family has it. If it's a parent, brother, or sister, your chances go up by 10%. If both your parents have it, you have a 40% chance of getting it.
Is schizophrenia hereditary from grandparents?
The risk goes up significantly if a grandparent (or other close relatives) also has schizophrenia. (E.F. Torry, 1996). Genetic inheritance is only one of the many factors (both biological and environmental) that contribute to the cause of schizophrenia.
Is schizophrenia developed or are you born with it?
Schizophrenia is thought to be the result of a culmination of biological and environmental factors. While there is no known cause of schizophrenia, there are genetic, psychological, and social factors thought to play a role in the development of this chronic disorder.
Can schizophrenia be prevented?
Prevention. There's no sure way to prevent schizophrenia, but sticking with the treatment plan can help prevent relapses or worsening of symptoms. In addition, researchers hope that learning more about risk factors for schizophrenia may lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
What are 5 causes of schizophrenia?
It can also help you understand what — if anything — can be done to prevent this lifelong disorder.Genetics. One of the most significant risk factors for schizophrenia may be genes. ... Structural changes in the brain. ... Chemical changes in the brain. ... Pregnancy or birth complications. ... Childhood trauma. ... Previous drug use.
Does trauma cause schizophrenia?
Is childhood trauma linked to schizophrenia? Research suggests that, yes, childhood trauma can play an important role in whether someone might develop schizophrenia. A 2019 study suggests that childhood trauma can be so stressful that it could increase the likelihood of someone developing schizophrenia later in life.
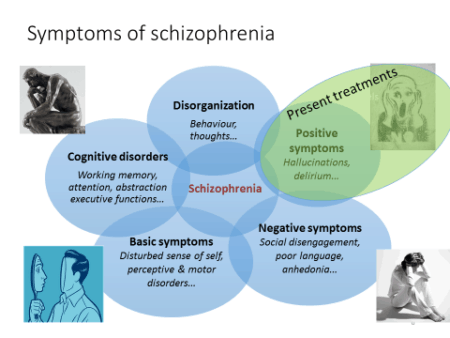
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia? Some people hear voices, or they may hallucinate visions, smells, or tactile sensations. They may also hold delusions. A person with schizophrenia might believe he is Jesus or that he’s being controlled by aliens.
What percentage of the population is affected by schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic disorder that affects about 1 percent of the population.
What is the chance of one twin being schizophrenic?
Over the years, researchers have found that the chance of one twin suffering from schizophrenia if the other did was anywhere from 44 to 87 percent. The most common figure cited was 81 percent. And a 2012 analysis of records for all people in Denmark found that the chance of suffering from schizophrenia if a parent did was 67 percent.
Can a child with schizophrenia become apathetic?
For example, a child with a family history of schizophrenia who is also neglected is more likely to become apathetic, losing interest in her usual activities and possibly end up in bed for much of the day. If she’s not neglected, she might hear voices and show other symptoms but not become apathetic.
Is schizophrenia a nuclear family?
A 2014 report from the Consortium on the Genetics of Schizophrenia Family Study in the United States with nearly 300 families concluded that the risk of schizophrenia was only 31 percent within a nuclear family. The group’s strategy is to identify endophenotypes—specific symptoms linked to genes. In 2014 the group announced that it had found 12 of these markers. In 2016, it reported on another 13.
Is family history of illness weaker?
In those patients, one study indicates, the family history of illness was weaker. The patients were more likely to be female and to have other illnesses and stresses like a history of unemployment. Most likely, several small variations in genes combine to increase the risk of symptoms.
Can schizophrenia cause movement problems?
People with schizophrenia sometimes become “flat”—with few facial expressions—or even completely unresponsive. They may develop movement problems, sometimes as a side-effect of medication. They may also have depression and bipolar disorder and be diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder.
What are the causes of schizophrenia?
These factors include genetics, brain and other body risk factors, environmental factors, societal factors, and lifestyle factors.
What happens if both parents are schizophrenic?
If both of the parents are suffering from schizophrenia, then the risk of an individual developing the disorder increases by 40%.
How many different types of schizophrenia are there?
The symptoms of schizophrenia are divided into 2 different categories – positive symptoms and negative symptoms.
What is the measure of the differences in people's genes accounting for the differences in their traits?
Heritability is a measure of the differences in people’s genes accounting for the differences in their traits. Traits, here, also include disorders such as schizophrenia.
How much does schizophrenia increase with one parent?
If only one parent suffers from schizophrenia, then the risk of an individual developing the disorder increases by 13%.
What is the C4A gene associated with schizophrenia?
These studies have implicated the C4A gene which increased the risk of schizophrenia, they have also been able to identify 108 genetic loci which are associated with schizophrenia, and also have implicated a strong association of 129 over 136 single-nucleotide polymorphism or SNP with the development of schizophrenia.
What are the negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
These symptoms include diminished emotional expressions and scarcity of initiation when it comes to activities that are goal-directed .
Is schizophrenia genetically heritable?
Schizophrenia is highly heritable as shown by MZ/DZ twin comparisons and is calculated to be at about 80%, although if familial transmission were Mendelian, it would be considered 100%. Since the field of genetics has produced the needed technology to examine DNA at the molecular level (beginning in the 1980’s), researchers have attempted to find a major gene for schizophrenia, without success. Once it was realized that the most likely underlying genetic mechanism is multiple gene variants of small individual effect, it was realized that large sample sizes would be needed to detect them. Thus, international collaborations were organized, the most important being the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (PGC), now over 900 investigators having accumulated over 100,000 individual DNA samples.
Is schizophrenia genetic or molecular?
In summary, the genetic basis for schizophrenia is heterogeneous, while some individuals inherit a large number of common risk genes, others inherit mutations that are of high risk within their individual families. This heterogeneity makes it unlikely that molecular genetics will be useful for prediction of who will develop schizophrenia, but on the other hand, classes of genes involved may lead to novel drug targets for developing future medications.
